Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts


Sparse, reliable biomarker discovery
Current issue, ai meets real-world patients, tcr cell therapies vanquish solid tumors — finally.
- Charlotte Harrison
Bispecific upstages Keytruda
Encapsulated stem cell–derived β cells exert glucose control in patients with type 1 diabetes.
- Bart Keymeulen
- Kaat De Groot
- Daniel Pipeleers
Combined small-molecule treatment accelerates maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons
- Emiliano Hergenreder
- Andrew P. Minotti
- Lorenz Studer
Engineered virus-like particles for transient delivery of prime editor ribonucleoprotein complexes in vivo
- Aditya Raguram
- David R. Liu

Announcements

Foundation models build on ChatGPT technology
Scientists are using ever more sophisticated AI algorithms trained on vast, unlabeled datasets to develop models that can ‘interpret’ biological data to help guide biomolecule design.

From Bench to Podcast: Stories from Biotech Labs
On this episode, Associate Editor Cláudia Vilhena interviews Nicoletta Cieri, first author of an article showing how a devised analytic framework can aid the prevention of post-transplant disease recurrence. Nicoletta and Cláudia explore the highlights of the story, discuss the future of individualized medicine and touch base on future career opportunites for postdocs.

Generative AI platforms drive drug discovery dealmaking
From Biopharma Dealmakers: Companies developing artificial intelligence-based platforms that enable the design of small-molecule and biologic drug candidates have been a focus of biopharma dealmaking in the past year.

Read the September issue of Biopharma Dealmakers
Our latest issue includes company profiles and editorial pieces covering innovations in oncology, CNS and artificial intelligence.
Nature Biotechnology is a Transformative Journal ; authors can publish using the traditional publishing route OR via immediate gold Open Access.
Our Open Access option complies with funder and institutional requirements .
Advertisement
Latest Research articles
Development of compact transcriptional effectors using high-throughput measurements in diverse contexts
Improved effectors for CRISPRi/CRISPRa are developed following high-throughput screening of transcriptional domains.
- Mike V. Van
- Michael C. Bassik
A resurrected ancestor of Cas12a expands target access and substrate recognition for nucleic acid editing and detection
ReChb is a Cas12a nuclease with expanded target access and substrate recognition.
- Ylenia Jabalera
- Igor Tascón
- Raul Perez-Jimenez

Comprehensive genome analysis and variant detection at scale using DRAGEN
DRAGEN rapidly identifies diverse types of genetic variants.
- Sairam Behera
- Severine Catreux
- Fritz J. Sedlazeck

A structurally informed human protein–protein interactome reveals proteome-wide perturbations caused by disease mutations
Protein–protein interactomes incorporating structural data predict the functional consequences of disease mutations.
- Dapeng Xiong
- Yunguang Qiu
Gold-siRNA supraclusters enhance the anti-tumor immune response of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy at primary and metastatic tumors
Gold-siRNA clusters boost the immune response of radiotherapy against primary and distant tumors.
- Yuyan Jiang
- Hongbin Cao
- Quynh-Thu Le
Droplet Hi-C enables scalable, single-cell profiling of chromatin architecture in heterogeneous tissues
Chromatin organization is measured in single cells using droplet microfluidics.
Latest Reviews & Analysis

An antigen discovery pipeline integrates multi-omics data and informs immunotherapy
We developed NeoDisc, a computational antigen discovery pipeline that integrates multi-omics data, including genomics, transcriptomics and mass spectrometry-based immunopeptidomics. NeoDisc accurately identifies and prioritizes tumor-specific antigens and designs personalized cancer vaccines. The pipeline reveals tumor heterogeneity and emphasizes defects in antigen presentation that might affect the success of cancer immunotherapy.
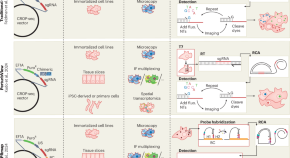
Advances in optical pooled screening to map spatial complexity
Two major advances in optical pooled screening improve substantially on sensitivity and robustness, expanding its applicability to a broader range of biological contexts.
- Maurice Kahnwald
- Marius Mählen
- Prisca Liberali
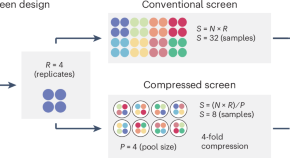

A framework for expanding discovery efforts with compressed phenotypic screens
Sample, financial and labor requirements are key barriers to scaling up high-content phenotypic discovery efforts. A broadly applicable method overcomes these challenges through experimental compression (by pooling various perturbations) and computational deconvolution (of their individual effects), empowering the use of phenotypic screening to advance therapeutic discovery.
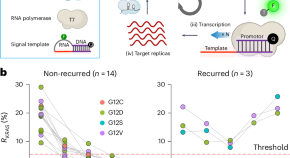
A CRISPR-based method for detecting mRNA in extracellular vesicles
A CRISPR-based assay both recognizes and amplifies target mRNA, achieving sub-attomolar sensitivity with single-nucleotide resolution. This method enables the detection of low-abundance mRNA in extracellular vesicles, providing clinically relevant information for precision oncology.
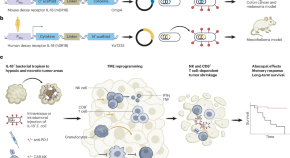
Bacteria displaying cytokines heat up the tumor microenvironment
Escherichia coli engineered to display cytokines destroy hard-to-treat tumors by boosting the activity of local native and adoptive immune effector cells.
- Marine Fidelle
- Laurence Zitvogel
Building better mRNA for therapeutics
Targeting double-stranded nucleic acids using the λexo–pdna system, a developmental route to hematopoietic stem cells.
- Adam C. Wilkinson
- Marella F. T. R. de Bruijn
Recoded gene circuits for multiplexed genetic code expansion
News & comment.

Pest control gets the CRISPR treatment
Precision genetic methods are enabling more efficient, environmentally friendly pest control methods for agricultural use as well as stopping the spread of disease.
- Caroline Seydel
A strategy to load, rethread and read protein sequences through a nanopore
- Iris Marchal
Niemann–Pick double win
Recent patents relating to the manufacture, preparation and use of T cells in treating cancer.
Cellular shuttles put mislocalized proteins in their right place
Collections.

Navigating the vaccines landscape
Trending - Altmetric
Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring
First self-amplifying mRNA vaccine approved
Science jobs
Call for global talents 2024 siat-ibt forum announcement.
We are seeking leading academic talents and young leading talents.
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT), Chinese Academy of Sciences(CAS)
Instructional Faculty Positions
The Biological and Environmental Science and Engineering (BESE) Division at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), a globally ...
Saudi Arabia (SA)
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Career Opportunities at the Yazhouwan National Laboratory, Hainan, China
YNL recruits leading scientists in agriculture: crop/animal genetics, biotech, photosynthesis, disease resistance, data analysis, and more.
Sanya, Hainan, China
Yazhouwan National Laboratory
Faculty Positions at the Mechano-X Institute (THUM), Tsinghua University
Interdisciplinary faculty positions at the Mechano-X Institute (THUM), Tsinghua University, all levels from Assistant, Associate to Full Professors.
Beijing (CN)
Tsinghua University - Mechano-X Institute
Scientist / Postdoc (m/f/d)
The Leibniz-Institut für Analytische Wissenschaften - ISAS - e. V. develops efficient analytical methods for health research. Thus, it contributes ...
Germany (DE)
Leibniz-Institut für Analytische Wissenschaften – ISAS – e.V.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Loading metrics
Open Access
The future is bright, the future is biotechnology
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Public Library of Science, San Francisco, California, United States of America and Cambridge, United Kingdom
- Richard Hodge,
- on behalf of the PLOS Biology staff editors

Published: April 28, 2023
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002135
- Reader Comments
As PLOS Biology celebrates its 20 th anniversary, our April issue focuses on biotechnology with articles covering different aspects of the field, from genome editing to synthetic biology. With them, we emphasize our interest in expanding our presence in biotechnology research.
Citation: Hodge R, on behalf of the PLOS Biology staff editors (2023) The future is bright, the future is biotechnology. PLoS Biol 21(4): e3002135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002135
Copyright: © 2023 Hodge, on behalf of the PLOS Biology staff editors. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
The PLOS Biology Staff Editors are Ines Alvarez-Garcia, Joanna Clarke, RichardHodge, Paula Jauregui, Nonia Pariente, Roland Roberts, and Lucas Smith.
This article is part of the PLOS Biology 20th Anniversary Collection.
Biotechnology is a revolutionary branch of science at the forefront of research and innovation that has advanced rapidly in recent years. It is a broad discipline, in which organisms or biological processes are exploited to develop new technologies that have the potential to transform the way we live and work, as well as to boost sustainability and industrial productivity. The new tools and products being generated have a wide range of applications across various sectors, including medicine, agriculture, energy, manufacturing and food.
PLOS Biology has traditionally published research reporting significant advances across a wide range of biological disciplines. However, our scope must continue to evolve as biology increasingly becomes more and more applied, generating technologies with potentially game-changing therapeutic and environmental impact. To that end, we recently published a collection of magazine articles focused on ideas for green biotechnologies that could have an important role in a sustainable future [ 1 ], including how to harness microbial photosynthesis to directly generate electricity [ 2 ] and using microbes to develop carbon “sinks” in the mining industry [ 3 ]. Moreover, throughout this anniversary year we are publishing Perspective articles that take stock of the past 20 years of biological research in a specific field and look forward to what is to come in the next 20 years [ 4 ]; in this issue, these Perspectives focus on different aspects of the broad biotechnology field—synthetic biology [ 5 ] and the use of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of therapeutics [ 6 ].
One fast moving area within biotechnology is gene editing therapy, which involves the alteration of DNA to treat or prevent disease using techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 and base editors that enable precise genetic modifications to be made. This approach shows great promise for treating a variety of genetic diseases. Excitingly, promising phase I results of the first in vivo genome editing clinical trial to treat several liver-related diseases were reported at the recent Keystone Symposium on Precision Genome Engineering. This issue of PLOS Biology includes an Essay from Porto and Komor that focuses on the clinical applications of base editor technology [ 7 ], which could enable chronic diseases to be treated with a ‘one-and-done’ therapy, and a Perspective from Hamilton and colleagues that outlines the advances in the development of LNPs for the delivery of nucleic acid-based therapeutics [ 6 ]. LNPs are commonly used as vehicles for the delivery of such therapeutics because they have a low immunogenicity and can be manufactured at scale. However, expanding the toolbox of delivery platforms for these novel therapeutics will be critical to realise their full clinical potential.
Synthetic biology is also a rapidly growing area, whereby artificial or existing biological systems are designed to produce products or enhance cellular function. By using CRISPR to edit genes involved in metabolic pathways, researchers can create organisms that produce valuable compounds such as biofuels, drugs, and industrial chemicals. In their Perspective, Kitano and colleagues take stock of the technological advances that have propelled the “design-build-test-learn” cycle methodology forward in synthetic biology, as well as focusing on how machine-learning approaches can remove the bottlenecks in these pipelines [ 5 ].
While the potential of these technologies is vast, there are also concerns about their safety and ethical implications. Gene editing, in particular, raises ethical concerns, as it could be used to create so-called “designer babies” with specific traits or to enhance physical or mental capabilities. There are also concerns about the unintended consequences of gene editing, such as off-target effects that could cause unintended harm. These technologies can be improved by better understanding the interplay between editing tools and DNA repair pathways, and it will be essential for scientists and policymakers to be cautious and work together to establish guidelines and regulations for their use, as outlined at the recent International Summit on Human Genome Editing .
Basic research has also benefitted from biotechnological developments. For instance, methodological developments in super-resolution microscopy offer researchers the ability to image cells at exquisite detail and answer previously inaccessible research questions. Sequencing technologies such as Nanopore sequencers are revolutionising the ability to sequence long DNA/RNA reads in real time and in the field. Great strides have also been made in the development of analysis software for structural biology purposes, such as sub-tomogram averaging for cryo-EM [ 8 ]. The rate of scientific discovery is now at an unprecedented level in this age of big data as a result of these huge technological leaps.
The past few years has also seen the launch of AI tools such as ChatGPT. While these tools are increasingly being used to help write students homework or to improve the text of scientific papers, generative AI tools hold the potential to transform research and development in the biotechnology industry. The recently developed language model ProGen can generate and then predict function in protein sequences [ 9 ], and these models can also be used to find therapeutically relevant compounds for drug discovery. Protein structure prediction programs, such as AlphaFold [ 10 ] and RosettaFold, have revolutionized structural biology and can be used for a myriad of purposes. We have recently published several papers that have utilized AlphaFold models to develop methods that determine the structural context of post-translational modifications [ 11 ] and predict autophagy-related motifs in proteins [ 12 ].
The future of biotechnology is clearly very promising and we look forward to being part of the dissemination of these important new developments. Open access science sits at the core of our mission and the publication of these novel technologies in PLOS Biology can help their widespread adoption and ensure global access. As we look forward during this year of celebration, we are excited that biotechnology research will continue to grow and become a central part of the journal. The future is bright and the future is very much biotechnology.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A structurally informed human protein–protein interactome reveals proteome-wide perturbations caused by disease mutations. Protein–protein interactomes incorporating structural data predict ...
Biotechnology is a broad discipline in which biological processes, organisms, cells or cellular components are exploited to develop new technologies. New tools and products developed by ...
A monthly journal covering the science and business of biotechnology. It publishes new concepts and enabling technology of relevance to the biological, biomedical, agricultural and environmental...
Biotechnology is a revolutionary branch of science at the forefront of research and innovation that has advanced rapidly in recent years. It is a broad discipline, in which organisms or biological processes are exploited to develop new technologies that have the potential to transform the way we live and work, as well as to boost sustainability ...
It briefly introduces cyanobacteria as primary producers in natural structured microbial communities; describes various applications in biotechnology and bioremediation; and discusses innovations, challenges, and future trends in this exciting research field.
With the cost of sequencing a complete genome having dropped from $3 billion during the Human Genome Project to $600 today, there are growing efforts to create large-scale biobanks of complete...