- +91-9556432150
- [email protected]

Business Area in SAP – A Detailed Overview & Set of Questions
Published by pradeep on october 22, 2022 october 22, 2022, business area in sap.
The Business Area in SAP is the highest organizational cost structure unit. You can specify it either as per Functional lines, Product lines or as per responsibilities assigned region-wise.
Below are some quick questions that may help you understand this term better. you can also read them to prepare for your SAP FICO job interviews .
A Business Area in SAP corresponds to specific business segments of a company and may cut across different Company Codes (Product Lines). They can further represent various responsibility areas, such as Branch Units, plant engineering, automotive, etc. Also, its configuration is optional (not mandatory).
‘0001- Plant engineering
‘0002- Automotive
Use of Business Area in SAP
Business areas we primarily use to facilitate external segment reporting across company codes , covering the company’s main areas of operation (product lines, subsidiaries).
Assign Balance Sheet Items
You can assign all balance sheet items, such as fixed assets, receivables , payables, material stock, and the entire P/L statement directly to business areas. You should assign banks’ capital and taxes only manually (indirectly) to business areas, not directly for this reason. Although, it is impossible to create legally-required financial statements, tax, and tax reports at the business areas level. Balance sheets and P/L statements at the business area level only are suitable for use in internal reporting.
Create a Balance sheet and P & L
To be able to create a balance sheet and P/L statement, we need to update the data for each business area in the transaction figures in the general ledger. Therefore, we have two different procedures to do this.
Procedure 1
When posting the original document, the system supplies the business area with the proper information.
You create a customer invoice. The system can allocate the sales revenue to exactly one business area. The receivables inherit this business area.
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Customer/receivable | UN1 | 200 |
| Revenues | UN1 | 200 |
When we make an adjustment posting in the general ledger in a second step, the system changes the business area used in the original posting to the correct value. Particularly when we didn’t enter the initial value. This may sometimes distribute the posting to several business areas.
Procedure 2
You create a customer invoice. The system must allocate the sales revenue to several business areas. We post the receivables without a business area and make a transfer posting for the receivable in a second step.
| Customer/Receivable | 700 | |
| Revenues | UN1 | -300 |
| Revenues | UN2 | -400 |
After splitting
| Receivable | -700 | |
| Receivable | UN1 | 300 |
| Receivable | UN2 | 400 |
Business Area in SAP General ledger Accounting
Automatic/manual assignment.
You cannot directly assign G/L account master data to a business area. You must enter the business area either manually or derive from that entered in the CO account assignment object.
Though we have certain business transactions for which automatic procedures exist. These analyze documents/ transaction figures in the system and use them to create new documents (Foreign Currency valuation). Subsequently, they assign the line items generated to the business areas entered in the documents/transaction figures that were read.
Business Area in SAP Asset Accounting
This section describes the role played by the “business area” organizational unit within Asset Accounting .
Automatic/Manual Account Assignment
The system allocates Assets to a single business area in its master record. Further, it automatically posts every posting to an asset balances sheet account in that business area. Consequently, the business area for an asset is passed on to all line items connected with the asset. Therefore, you do not need to make a manual assignment to a business area at any point.
Asset Dr -UN1- 5000
Vendor Cr- UN1-5000
Depreciation
The asset balance is reduced by the depreciation amount in the value adjustment (accumulated depreciation) account with the business area of the asset. Also, the expense line items receive the business area of that asset.
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Depreciation | UN1 | 100 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | UN1 | -100 |
Asset Retirement (Scrapping)
Here the system clears the asset amount and any existing depreciation with the business area of the asset. It assigns the asset’s business area to the expenses line item.
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| APC | UN1 | -5000 |
| Depreciation | UN1 | 100 |
| Loss in Scrapping | UN1 | 4900 |
Business Area in Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable
This segment describes the role played by the “Business area “organizational unit within the Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable systems.
You cannot allocate customer or vendor master records to a business area. Thus, you usually determine the business area from the business area allocated to the related G/L account posting and do not need to enter it manually.
The business area for G/L account items has to be either manually entered or derived from the SAP CO allocation object that you enter.
How Business Area in SAP works for an invoice?
In an invoice, the customer/vendor item takes the business area of the expenses or revenue postings. If the business area has been entered in the document, it is copied into the line item automatically.
However, if there is more than one business area in the document, the customer/vendor items remain unallocated. Also, a transfer posting is made at a later date to the receivables or payable account.
Furthermore, the system checks that any business area entered in the customer/vendor item is the same as that in the offsetting G/L account item and issues an error message if this is not the case.
In customizing, you can set the status of this message or even suppress it from display entirely.
Noteworthy, the taxes are always posted without a business area. Subsequently, at a later date, the system makes a transfer posting from the tax account to the business areas allocated to the revenue or expenses account.
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Customer/Receivable | UN1 | 230 |
| Revenue | UN1 | -200 |
| Output Tax | -30 |
Business Area in SAP for Payment
For customer/vendor items in payment documents, the procedure is the same as it is for the items in the invoice that they clear. Therefore, these items take the business area from the invoice.
Cash discount and exchange rate difference postings take their business area from the customer/vendor item they originated from. If this item was posted without a business area and then later has one specified via a transfer posting in the general ledger. You must make this allocation yourself retroactively for both the cash discount and exchange rate difference posting.
Bank items are currently posted without a business area (unless one is entered manually). There is also no standard function that allocates the bank items to the business area of the cleared customer/vendor items.
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Bank | 224 | |
| Customer/Receivable | UN1 | -230 |
| Cash Discount paid | UN1 | 6 |
Business Area for Down payment
The system cannot automatically derive the business area of the underlying item with down payments since the invoice that belongs to the down payment is not entered until later.
The business area in the customer/vendor item from the invoice is therefore not entered automatically and has to be entered manually.
The bank item is currently posted without a business area. There is no standard function that allocates the bank item to the business areas of the customer/vendor items.
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Bank | 100 | |
| Customer/Receivable | -100 |
Business Area in SAP Cost Accounting
Automatic/ manual account assignment.
Account assignment objects in Cost Accounting are allocated to a single business area in the master record. When you post to an account assignment object in Cost Accounting, the system automatically determines the business area. You do not have to assign the posting to the business area manually.
Assessment, Distribution, Activity Allocation
Costs that have initially been allocated to an allocation object in Cost Accounting (default cost center) and therefore also to a default business area are later broken down by certain distribution keys to final recipients (such as cost centers). The allocation object is then relieved of the costs.
Business Area in SAP Material Management
Materials are assigned to a business area based on the combination of division and plant. Every time a material is posted, the relevant material stock account is automatically assigned to the business area belonging to that account.
The business area from the other line items is either (depending on the business transaction in question) derived from the account assignment object posted in Cost Accounting or from the material involved. You do not need to manually assign a business area.
Initial Entry of Stock Balances Goods/Invoices Received
The notable thing about the business transactions being examined here is that they generate a posting record that makes a posting to the material stock account (or the account representing this account) and whose offsetting posting has no business area in it. In this case, the offsetting item takes the business area from the material.
Additional, automatically-generated items that are directly linked to a certain material (price differences, exchange rate differences, freight charges) are also assigned to the same business area as the material.
The payable (vendor) is only allocated to a business area if there is one specified for the material. If more than one is specified in the invoice, the payable is posted without a business area.
Goods Receipt
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Material Stock | UN1 | 1250 |
| Price Difference | UN1 | 50 |
| UN1 | -1300 |
Invoice receipt
| Account | Business Area | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor/Payable | UN1 | -1300 |
| GR/IR | UN1 | 1300 |
Some Important Questions related to Business Area in SAP
How to draw financial statements in a business area in sap.
We draw Financial statements per business area for internal reporting purposes. It will help if you put a “tick mark in the check box in the configuration against the company for which you want to enable business area financial statements.
When we post transactions in SAP FI we can assign the same to a Business Area so that the system captures the values per business area for internal financial statements.
Can we attach “Business Area” to a Transaction by not assigning the same in a posting?
Yes, you can derive the business area from other account assignments, for example, cost center and Asset Master. We need to define the business area in the master record of Cost Center & Asset Master.
How to post Cross-Company Code Business Area posting?
Using a Cross Company code transaction, one should be able to post to different Business Areas cutting across various Company Codes. Also, any number of Business Area-Company code combinations are possible.
Why do you need to know this?
Though the Business Area in SAP is an optional setting in FICO or S/4HANA Finance , it is essential for a consultant to have good knowledge. This is because a company may demand it in their plant or business to configure. Secondly, it is part of the Cost Structure which is a must-have skill for SAP Functional-consultants. Hence, this is when you must possess relevant skills to work on it.
Additionally, you may have questions on business areas in SAP Finance Interviews . You should have a good configuration knowledge of the business area in SAP in order to perform the task that your client delegated.
Visit Course Page: SAP S4 HANA FICO Training
Related Posts
SAP MRP – Material Requirement Planning in Material Management
What is SAP MRP? SAP MRP (Material requirements planning) is a planning tool to help production and procurement planners create feasible and realistic plans so they can quickly initiate procurement or production processes. Planners need Read more…

SAP Career for Freshers- What is the right process?
How is SAP Career for Freshers? SAP Career for Freshers seems challenging initially. If you’ve recently completed SAP training, specifically in SAP finance, and you find yourself applying for various jobs without success. Or perhaps Read more…
Tax on Sale Purchase in SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4 HANA covers the business processes like Procure-to-Pay, Order-to-Cash and record-to-report. To understand the functioning of tax on sale purchase in SAP we need to know all tax-relevant steps within the end-to-end scenarios. Additionally, Read more…

Blog about all things SAP
ERProof » SAP CO » SAP CO Training » SAP Business Area
SAP Business Area
In some cases, organizations opt for using profit centers for the type of reporting satisfied by Business Areas. However, profit center use is more for analyzing the profitability of specific products, whereas Business Areas are more intended to report on the type of Business.
SAP Business Area Configuration
Configuration of SAP Business area is straightforward and generally requires just two steps – creation of the SAP business area and activating it for use across financial statements.
To create a new business area, use transaction code OX03 or follow menu path:
SPRO > Reference IMG > Enterprise Structure > Definition > Financial Accounting > Define Business Area
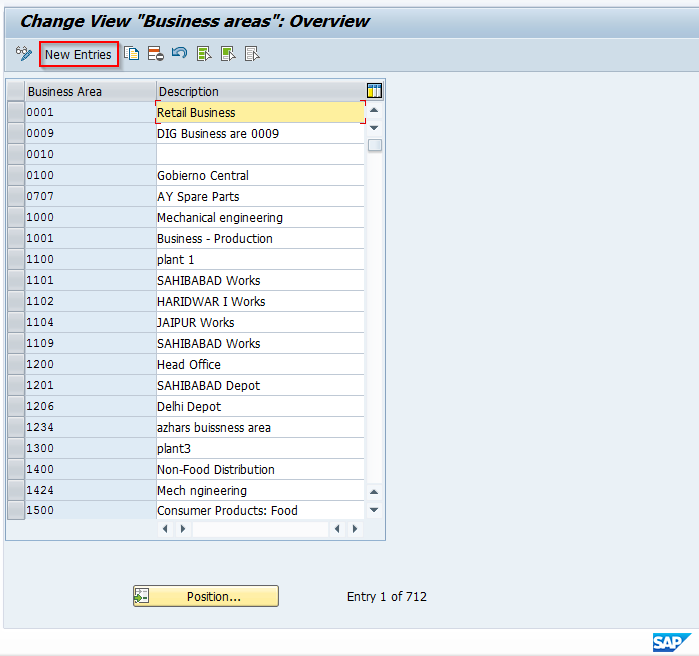
You will be taken to a screen that appears as follows. Click on the New entries button on the menu.
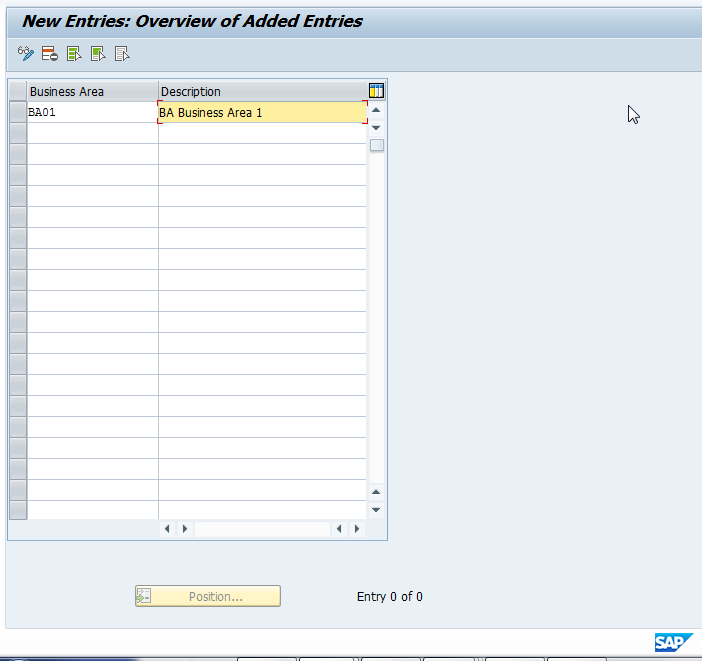
Add a four-characters value for the name of your new business area entry and give it a meaningful description. An example may look as follows:
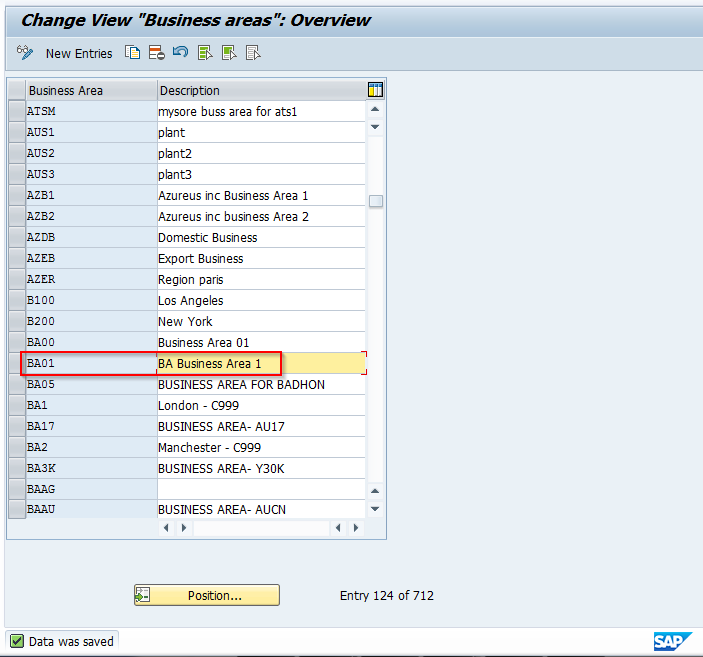
Save your entry and create a new transport request if required by your system. SAP Business Area has now been created and is available in the list of values.
Activation of SAP Business Area
The next step is to activate the business area functionality within company codes you will using them. If you have several company codes that will be using business area functionality for financial statements, make the setting here so that the field is always ready for input when you post documents, regardless of other field controls.
To activate, use transaction code OB65 , or follow menu path:
SPRO > SAP Reference IMG > Financial Accounting > Financial Accounting Global Settings > Business Area > Enable Business Area Balance Sheet
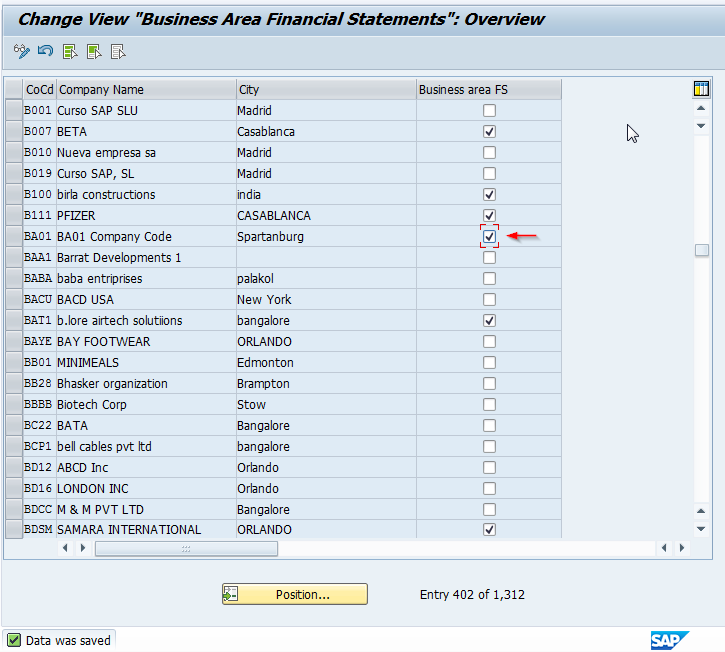
The screen will look as follows. Scroll to the company codes that will be using the business area functionality and select the Business Area FS check box for each.
A business area has now been created and company codes that will be using it have been activated to ensure field input is always available.
Assignment in Master Data
SAP Business Areas are most often populated from master data records in which they are assigned. An example would be the assignment of SAP business area within a cost center master record. Let’s take a look at where on a cost center this would be done.
To create a cost center, use transaction KS01 or follow the menu path:
SAP Easy Access Menu > Accounting > Controlling > Cost Center Accounting > Master Data > Cost Center > Individual Processing > Create
Create a cost center with a unique ID, assign a validity date range, and hit the enter key. You will come to the basic data tab for the cost center creation. Enter all required fields as well as the business area. Note that the business area is time dependent and can be changed at each new fiscal year, if required.
The screen will appear as follows:
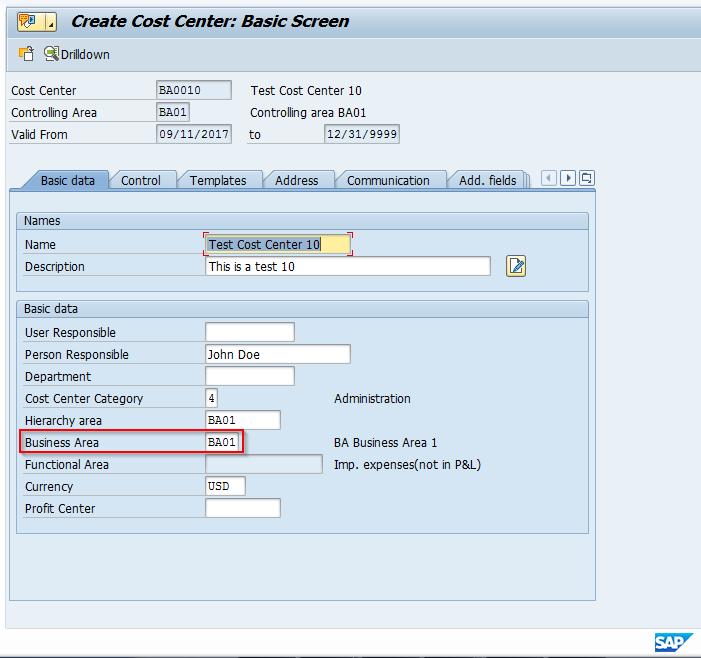
Enter any of the other required information on other tabs and save your master record. The cost center has now been created with the business area field populated.
This tutorial explained the concept of SAP Business Area within the FI – CO organizational structure. A brief explanation of the functionality was given, the configuration steps required were reviewed including creation and activation of SAP Business Area on a company code, and finally assignment to a master data record was completed.
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP CO tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP Operating Concern
Go to previous lesson: SAP Controlling Area
Go to overview of the course: Free SAP CO Training
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Do you have a question and want it to be answered ASAP? Post it on our FORUM here --> SAP FORUM !
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
SAP Business Area Tutorial, Tables, Tcodes and PDF training guides
The term Business in area in SAP refers to a section or an operational area/wing of a company. This separation is used for financial accounting purpose and it is useful for large companies. For an example Sales, Marketing & production can be considered as three different business areas of a company.
Business Area Transaction codes
Bapi functions for business area, sap business area tables, table fields storing data related to business area, table data elements available for business area.
- Business Area PDF Tutorials
- Business Area related Fiori Apps

Here is a list of transaction codes used to deal with Business Area in SAP
- FF$D : Convert business areas
- MC.H : INVCO: Business Area Anal.Sel. Stock
- MCBI : INVCO: Business Area Anal. Selection
- OCCG : Business area for MM
- OMBD : Business Area from MM View
- OVF0 : C SD Table T134G Business Areas
- OVF1 : C SD Table TVTA Business Areas
- OVF2 : C SD Table TVTA Business Areas
- OVX2 : Business area->Plant/Division
- OX03 : Customizing: Business Area Setup
- S_ALR_87009633 : CM: Region/Business Area/Product Grp
- S_ALR_87011834 : CM: Region/Business Area/Product Grp
- S_ALR_87013608 : CElem.: Business Area Allocations
- S_ALR_87013652 : CM: Region/Business Area/Product Grp
- CXN5 : Assign Company Codes/Business Areas
- CXNB : Download Business Areas/Companies
Here is a list of SAP BAPI function modules available for Business Area
- BAPI_BUSINESSAREA_GETLIST : List of Business Areas
- BAPI_BUSINESSAREA_GETDETAIL : Business Area Details
- BAPI_BUSINESSAREA_EXISTENCECHK : Check if business area exists
- BAPI_COST_ELEM_FIXACCOUNT_GET : Read Fixed Account Assignment for Company Code/Business Area/Cost Element
Here is a list of important tables storing Business Area related data in SAP
- A039 : Overhead Type/Business Area
- A060 : Controlling Area/Business Area
- A063 : Controlling Area/Business Area/Cost Center
- A105 : Controlling Area/Company Code/Business Area
- A138 : Price per Company Code/Business Area
- AGS_BUSAREACUSTT : Text Table for Business Area
- AGS_BUSAREA_CUST : Business Area
- FLQGSBER_SUBST : Liquidity Calculation: Replacement of Business Area
- FPCR_ACC_GSBER : Assignment Business Area to Accountant
- GSBLCA : Business area consolidation: deviating records
- J_3GGBBKVB : Sales Area per Company Code/Business Area/Plant
- KOT4002 : Debited Company Code/Debited Business Area
- KOT4003 : Debited Company Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient
- KOT4004 : Debited Co. Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient/Equi. Type
- KOT4005 : Debited Co. Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient/Equipment
- KOTJ002 : Debited Company Code/Debited Business Area
- KOTJ003 : Debited Company Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient
- KOTJ004 : Debited Co. Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient/Equi. Type
- KOTJ005 : Debited Co. Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient/Equipment
- KOTJ007 : Debited Co. Code/Debited Business Area/Recipient Category
- OFIC_BUSAREA_SLS : Customizing Orgfinder: Business Area (for Sales)
- OFIC_BUSAREA_SRV : Customizing Orgfinder: Business Area (for Service)
- POC_I_BUS_AREA : Business Area
- POC_I_BUS_AREA_T : Business Area
- SABA01 : SAP Solution Manager: Business Area
- SABA01T : SAP Solution Manager: Business Area Descriptions
- SMOT134G : Organization Unit: Business Area Determination
- SMOTGSB : Business Areas
- SMOTGSBT : Business area names
- T030G : Standard Accounts Table – Business Area Breakdown
- T134G : Organization Unit: Business Area Determination
- T134H : Organiz. Unit: Business Area Determ. – MM View
- T243D : Convert Sender Business Areas
- T5F5N : ‘Bilan Social’ business areas
- T5F5O : Description of ‘Bilan Social’ business areas
- T5V2J : NACE codes (Business area codes; Næringskoder)
- TBKKCBUSAREACLR : Clearing accounts for business area change
- TFIN020 : Assignment of Business Areas to Company Codes
- TGSB : Business Areas
- TGSBG : Cross-system business areas
- TGSBK : Consolidation business areas
- TGSBT : Business Area Names
- TGSB_CUS : Additional Settings for Business Area Financial Statements
- TGSB_CUST : Additional Settings for Business Area Financial Statements
- TICL114 : Assignment of Organizational Unit to Business Area
- TJGI2 : IS-M/SD: Business Area Conversion ERP-Non-ERP System
- TJJPRDH_TGFELD : IS-M/AM: Product Hierarchy (S&P): Business Area Check Table
- TJJPRDH_TGFELDT : IS-M/AM: Product Hierarchy S&P): Business Areas Text Table
- TJL09 : IS-M/SD: Business Area Determination
- TKMGB : Business area consolidation: SD assignments
- TLMGB : Business area consolidation: MM assignments
- A039->GSBER : Business Area
- A060->GSBER : Business Area
- A063->GSBER : Business Area
- A105->GSBER : Business Area
- A138->GSBER : Business Area
- ACCRFI->GSBER : Business Area
- ACCTIT->GSBER : Business Area
- ACCTIT->PARGB : Trading partner’s business area
- ACCTIT->GSBER_GP : Business area reported to the partner
- ACEDSASSGMT->BUS_AREA : Business Area
- AD01DLI->GSBER : Business Area
- AD01DLI->PARGB : Trading partner’s business area
- ADRCITYCCS->GSBER : Business Area
- ADRSTRTCCS->GSBER : Business Area
- AFPO->GSBER : Business Area
- AFRV->GSBER : Business Area
- AFRV->SGSBR : Business Area
- AFRV_DEL->GSBER : Business Area
- AFRV_DEL->SGSBR : Business Area
- AFVC->GSBER : Business Area
- AGS_BUSAREACUSTT->BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- AGS_BUSAREACUSTT->NAME : Business Area
- AGS_BUSAREA_CUST->BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- AGS_BUSNSS_CONT->BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- AGS_ORGMODEL->BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- GSBER : Business Area
- PARGB : Trading partner’s business area
- GSBER_GP : Business area reported to the partner
- AGS_EJR_BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- IM_GSBER : Business area for dep. simulation
- GSBERO : Business Area in Original Document
- PARGBO : Trading Partner Business Area in Original Document
- BKK_GSBER_OLD : Old Business Area
- BKK_GSBER_NEW : New Business Area
- BKK_GLBUSA_LST_1 : Business Area Transfer BCA->FI Single Posting
- BKK_GLBUSA_LST_D : Business Area Debit Transfer BCA->FI Trans. Posting
- BKK_GLBUSA_LST_C : Business Area Credit Transfer BCA->FI Trans. Posting
- BKK_CGSBER : Business Area Offsetting Account Transfer BCA->FI
- CFGSBER : Business area
- CFPGSBR : Business area
- CKML_FLG_GSBER : Business Area Is Name-Forming
- CRMT_BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- GSBER_PAY : Business area in payment document
- ICPSG : Receiving Business Area in Local System
- GSBER_GLOB : Globally unique business area
- ICPPG : Receiving Business Area of Customer/Vendor
- PARGB_GP : assumed business area of the business partner
- DIVISION : Business area/division code
- FCML_GSBERP : Business Area (Process)
- TPM_BUSAREA : Business Area
- GSBER_EB : Business area
- RECV_BUSA : Receiving business area
- SEND_BUSA : Sending business area
- FLQXGSBER : Liquidity Calculation: Business Area Update
- FLQXFREEGSBER : Liquidity Calculation: Free Usage of Business Area
- FLQCHECKGSBER : Liquidity Calculation: Check Free Business Area
- FLQF4HELPGSBER : Liquidity Calculation: F4 Help for Free Business Area
- FLQGSBER : Liquidity Calculation: Replacement for Business Area
- FM_FLG_BUS_AREA : flg clear business area for collection
- XFMPP_GSBER : Partial Payment by Fund: Business Area Active
- PPARGB : Trading Partner Business Area of the Business Partner
- UGSBER : Original business area
- GRAC_BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- GSBER_KONS : Consolidation business area
- INH_GSBERI : Data origin for business area field
- IMA_VGSBER : Responsible business area
- IMA_AGSBER : Requesting business area
- GSKST : Business area from cost center
- ISM_PRDH_GFELD : IS-M/AM: Product Hierarchy: Business Area
- J_3GLGSBER : Providing Business Area
- J_3GEGSBER : Debited Business Area
- J_3RKGSBERD : Debet side business area
- J_3RKGSBERK : Credit side business area
- J_7LKZGSBER : Indicator: Differentiation Quantity Flow for Business Area
- OFIT_GSBER : Orgfinder: Business Area
- P06_SECACT : Section according to business area (labor court elections)
- DEBT_BUSA : Debited business area
- PRQ_ZGSBR : Business Area: Offsetting Posting
- POC_BUSINESS_AREA : Business Area
- POC_BUSINESS_AREA_NAME : Business Area Name
- PGSBER : Partner Business Area
- BUS_AREA_SUB : Indicator: Business Area Replaced
- PS_VGSBR : Business area for the project
- PS_PGSBR : Business area for WBS element
- PGBVW : Partner Business Area Default Value
- XGSBER : Indicator: Transfer business area
- XPARGB : Indicator: Transfer trading partner business area
- SMO3GSBER : Business area
- SMO3PARGB : Trading partner’s business area
- SMO3XGSBE : Indicator: Business area financial statements required?
- SMO3GSBER2 : Consolidation business area
- SMO3GSBER1 : Globally unique business area
- SMO3GTEXT : Business area description
- SMO3REGGB : Rule for determining the business area
- SMSY_AC_SRV_BROLE : Adaptive Computing: Business Area
- XAUGS : Activate display authorization for business area?
- GSBK : Business area consolidation active
- GBSNO : Activate: online zero balnce for business areas
- RLDNR_BC : Ledger for business area consolidation
- FC_GBCOBL : Check if company code/business area is active in doc.
- FC_ROLLUP2 : Rollup for Business Area Consolidation
- FC_RLDNR2 : Sender Ledger for Rollup to Business Area Consolidation
- FC_INDRU2 : Transfer Method for Business Area Cons is Rollup
- FC_INDPE2 : Transfer Method for Business Area Cons is Periodic Extract
- FC_INDLS2 : Ledger Selection is Active for Business Area Consolidation
- XGSBE : Indicator: Business area financial statements required?
- NGSBE : Ext.Receiving Comp.Code Configuration: Business Area Check
- XGBTR : Separate Payments for each Business Area?
- GSBER_BANK : Business Area for Bank Posting
- SGSBER : Sender business area
- P06_ACTIV : HR-F: Business area of company
- P06_TYPACT : Business area for ‘Bilan Social’
- P06_LIBACT : Name of ‘Bilan Social’ business area
- P20_BNAME : Business area name (“Bransje-navn”)
- ROLLUPN_GC : Rollup for business area consolidation
- GLFLEX_ECCS_GSBER : Standard scenario business area consolidation
- BKK_GLACCT_CLR_GSBER : General ledger clearing account for business area change
- CK_GESCHBE : Partner Business Area
- CK_DIR_PART_GESCHBER : Direct Partner Business Area
- FC_SIGNCFI : Delimiter for Companies & Business Areas
- FC_IGSGBFI : Sequence for converting companies/business areas
- GSBE1_FBWE : Business area
- FC_FLG_DEF : Use the assigned business area as the default
- GSBER_KUKON_KK : Business Area
- GTEXT : Business area description
- RERAFILLBUSAREA : Fill Business Area During Posting
- REXCSKXGSBER : Flag for expense posting to business area
- JKZGB : IS-M: Enter Business Area in Clearing Account
- ISM_PRDH_SPGFELD : IS-M/AM: ProdHie: Business Area for the Ext.Business Partner
- CO_XGSBER : Indicator: Account assignment business area has priority
- PMAIPP_GSBER : Business area is relevant for proposal for IM allocation
- TTET_USDIVISION_COM : Business Area/Division Code
- REGGB : Rule for determining the business area
- VVGSBERPRT : Business area of contract partner
- WLF_GSBER_CUSTOMER : Customer Business Area
- /CEERE/X48 : Business area
- /CEERE/XGSBER : Flag for expense posting to business area
- /ISDFPS/AC_BUS_AREA : Transfer Business Area
- /SAPSLL/SPLAMLO : Separation into Business Areas: Logistics
- /SAPSLL/SPLAMFI : Separation into Business Areas: Financial Accounting
- /SAPSLL/SPLAM : Separation into Business Areas: SPL Screening
SAP Business Area PDF Tutorials
- Consolidation (EC-CS) – PDF Tutorial
- Payments – PDF manual
- General Ledger Accounting (FI-GL) – PDF study material
- Preparations for Consolidation (FI) – PDF reference
- Financial Accounting – General Topics – PDF study material
- Payment Program for Payment Requests (FI-BL) – PDF Tutorial
- Funds Management-Basic Settings – PDF Training material
- Knowledge Base
SAP Business Area
- Created 2021-09-05
- Author SAP Online Tutorials
- Category SAP CO
Within SAP Financial Accounting, data is organized first at the company and then company code level for legal business entities to meet external financial statement requirements. But in some cases, financial statements may be required for internal purposes that are viewed across company codes. This could be based on a need for reporting broken down by geographical area, line of business, area of responsibility, etc. To meet this requirement, SAP provides an organizational unit called SAP Business Area . Because they are used to report across company codes, SAP Business Area is an independent entity that is not linked to a company code within the configuration of the organizational structure. We will see how the use of SAP business area is activated for a company code, but this is not a link. SAP business area functionality may not be required for all organizations and thus is considered to be optional functionality.
In some cases, organizations opt for using profit centers for the type of reporting satisfied by Business Areas. However, profit center use is more for analyzing the profitability of specific products, whereas Business Areas are more intended to report on the type of Business.
SAP Business Area Configuration
Configuration of SAP Business area is straightforward and generally requires just two steps – creation of the SAP business area and activating it for use across financial statements.
To create a new business area, use transaction code OX03 or follow menu path:
SPRO > Reference IMG > Enterprise Structure > Definition > Financial Accounting > Define Business Area
You will be taken to a screen that appears as follows. Click on the New entries button on the menu.
Add a four-characters value for the name of your new business area entry and give it a meaningful description. An example may look as follows:
Save your entry and create a new transport request if required by your system. SAP Business Area has now been created and is available in the list of values.
Activation of SAP Business Area
The next step is to activate the business area functionality within company codes you will using them. If you have several company codes that will be using business area functionality for financial statements, make the setting here so that the field is always ready for input when you post documents, regardless of other field controls.
To activate, use transaction code OB65 , or follow menu path:
SPRO > SAP Reference IMG > Financial Accounting > Financial Accounting Global Settings > Business Area > Enable Business Area Balance Sheet
The screen will look as follows. Scroll to the company codes that will be using the business area functionality and select the Business Area FS check box for each.
A business area has now been created and company codes that will be using it have been activated to ensure field input is always available.
Assignment in Master Data
SAP Business Areas are most often populated from master data records in which they are assigned. An example would be the assignment of SAP business area within a cost center master record. Let’s take a look at where on a cost center this would be done.
To create a cost center, use transaction KS01 or follow the menu path:
SAP Easy Access Menu > Accounting > Controlling > Cost Center Accounting > Master Data > Cost Center > Individual Processing > Create
Create a cost center with a unique ID, assign a validity date range, and hit the enter key. You will come to the basic data tab for the cost center creation. Enter all required fields as well as the business area. Note that the business area is time dependent and can be changed at each new fiscal year, if required.
The screen will appear as follows:
Enter any of the other required information on other tabs and save your master record. The cost center has now been created with the business area field populated.
This tutorial explained the concept of SAP Business Area within the FI–CO organizational structure. A brief explanation of the functionality was given, the configuration steps required were reviewed including creation and activation of SAP Business Area on a company code, and finally assignment to a master data record was completed.
Was this article helpful?
Related articles, leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
SAP Business Areas – Providing Another Dimension To Business Analysis
April 26, 2012 by Pete Comments are off
Concept Of An SAP Business Area
Basic financial statements are created in SAP on the basis of the company code. For traditional statements, all the transactions are grouped according to the company code and financial statements like balance sheet and Profit & Loss statements are drawn separately for every company code. But at times there is a need to carry out analysis across company codes according to some criteria other than the company code.
As an example, if there is a need to generate a financial report on the basis of a product line, geographical location or divisional sales, then this can be done using Business Areas . The purpose of business areas is to report on similar activities that occur across company multiple codes resulting is cross company reporting.
However the financial statements generated on the basis of business areas cannot be used for legal reporting purposes. For this reason, it is not possible to create the legally required financial statements and tax reports at business area level. Financial statements at business area level are therefore only suitable for internal reporting.
Concept Of A Business Area: Cross Company Code Analysis
Consider a situation where there are four companies in all, ABC Apparel, ABC Sports, ABC Shoes and ABC Services. The first three companies are involved in producing different product lines, whereas ABC Services provides sales and logistic services to the other three companies internally as well as its external customers. If the high level management team wants to know the performance of ABC services, then they can produce the financial statements for the company according to the company code for ABC Services.
But these financial statements will not be able to provide a picture about how much of the business of ABC Services was due to its own sister companies. In such a case a “services” business area can be created. Any transactions for the company codes ABC Apparel, ABC Sports or ABC Shoes dealing with services can be entered with the newly created services business area.
At the year end the management can draw financial statements for the services business area which will give them a clear picture of the performance of the services division.
It is to be noted that business areas are not directly assigned to company codes but are assigned only to the accounting transactions that are entered. Good SAP business practice allows the use of business areas ss optional and this is usually decided at a very early stage in the project. Business areas can be used standalone by entering them manually at the time of preparing accounting documents or they may be automatically determined by any one the methods described in the next section.
Determination Of Business Area
Business areas are to be entered while entering accounting transactions or they can be determined automatically. Substitutions can also be used to automatically provide the business areas while entering accounting documents according to some well defined criteria. Most commonly the business area to be determined is linked to various organizational elements and determined in the following ways:
- PLANT : Business areas can be assigned at plant level. This is because a plant usually produces a single line of products which are related to the same business. For example, if a plant produces shirts, then it makes sense to assign it to the Apparel business area. This is because any transaction related to a plant producing shirts will be assigned to the Apparel business area.
- DIVISION : Business areas can be used to implement divisional financial statements or SEC segment level reporting. A business area can be used to categorize transactions on any criteria and divisional financial statements are one of the most common reasons of using business areas.
- SALES AREA : In many cases a sales area is involved in the sale of only one product, then all the transactions related to that sales area will be for the same business. In such a situation business areas may be linked to sales areas.
- DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL : Business areas allow preparation of financial statements according to the different distribution channels like direct sales, online sales, etc. This allows the top management to gauge the effectiveness of the various distribution channels and accordingly adjust the sales strategy.
- COST CENTER : Business areas cannot be directly linked to General ledger accounts. But in order to associate a general ledger account with a certain business area, cost centers can be used. A cost center can be linked to a general ledger account and whenever a transaction is recorded related to that cost center, the business area is automatically substituted in the accounting document.
- SUBSTITUTION RULES : Substitution rules can be set up to automatically determine and assign business areas to transactions on the basis of more complex rules. Substitutions work behind the scenes to determine the business areas.Whenever an accounting document is being generated, the substitution rule checks for some pre-requisite condition and if the condition is satisfied it substitutes the required business area while posting the accounting document.
Procedure To Define Business Areas
The step by step procedure to define business areas is as follows:
STEP 1: Navigate to the path as shown below in the implementation guide or execute the transaction OX03 from the SAP Easy Access menu. Use the transaction code SPRO to get to the Implementation guide from the SAP Easy Access menu.
Navigation Path To Define Business Areas
STEP 2: The screen shown below is displayed. All the existing business areas in the client are listed here. Click the ‘new entries’ button on the screen shown below to create new business areas.
List Of All Business Areas
STEP 3 : A blank table is displayed to enter the data. Enter the new business area and the description for the same. The business area can be up to four characters in length. Enter the data as shown below and click the save button on the screen as shown below.
NEW BUSINESS AREAS HAVE BEEN ENTERED
STEP 4: The message ‘Data was saved’ is displayed at the bottom of the screen as shown below. This confirms that the new business areas have been created.
Success Message Confirming Business Areas Have Been Created
- Everything SAP
- business area
About the Author: Pete
Pete has been working with SAP technologies for over 10 years. He started out as an ABAP consultant and then moved on to BW where he has worked many different clients covering a wide variety of industries. "I love introducing SAP technology (especially BI) to new clients and showing them how they can go from zero to hero within their business in super fast time". Contact me on twitter @PeterMoxon
- TutorialKart
- SAP Tutorials
- Salesforce Admin
- Salesforce Developer
- Visualforce
- Informatica
- Kafka Tutorial
- Spark Tutorial
- Tomcat Tutorial
- Python Tkinter
Programming
- Bash Script
- Julia Tutorial
- CouchDB Tutorial
- MongoDB Tutorial
- PostgreSQL Tutorial
- Android Compose
- Flutter Tutorial
- Kotlin Android
Web & Server
- Selenium Java
- SAP FICO Training
- SAP FICO Tutorials
- SAP FICO - Introduction
- SAP Financial Accounting
- What is SAP FICO
- What is client in SAP
- SAP FICO - Enterprise Structure
- Define Company in SAP
- Define Company Code in SAP
- Assign company code to company in SAP
- Define business area and consolidation business area in SAP
- Assign business area to consolidated business area in SAP
- Define credit control area in SAP
- Assign company code to credit control area in SAP
- ADVERTISEMENT
- Define functional area in SAP
- Maintain Financial Management Area in SAP
- Assign financial management area to company code in SAP
- How to create segments in SAP
- SAP FICO - Global Parameters
- What is Chart of accounts and how to create COA in SAP?
- Assign company code to chart of accounts
- What is Fiscal year in SAP?
- How to maintain fiscal year variant
- Assign company code to fiscal year variant
- Define account group in SAP
- Define retained earnings account
- Define posting period variant (PPV)
- Assign variants to company code in SAP
- Open and closing posting period variants
- Define field status variant and field status groups in FICO
- Assign company code to field status variant
- Define Tolerance group for G/L accounts
- Define Tolerance group for employees
- Check company code global parameters
- SAP FICO - Foreign Currency Transactions
- Check exchange rate types
- Define translation ratios for currency translation
- How to maintain exchange rates in SAP
- Define accounts for exchange rate differences
- Define foreign currency valuation methods
- Define accounting principles and assign to ledger group
- Define valuation areas and assign to accounting principles
- SAP FICO - New G/L Accounting
- How to activate new G/L accounting?
- Define ledgers for general ledger accounting
- Define currencies for leading currency
- Define & Activate Non-Leading Ledgers
- Define Zero-balance clearing account
- Define interest calculation types
- Define interest indicator
- SAP FICO - Accounts Receivable
- Define account group for customers
- Maintain number ranges for customer account groups
- Assign number ranges to customer account groups
- Define risk categories
- Define tolerance group for Customers
- Create sundry debtors accounts
- Define Customer Master Record
- SAP FICO - Accounts Payable
- What is Accounts Payable in SAP?
- Define vendor account groups
- Maintain number range intervals for vendor accounts
- Assign number ranges to vendor account groups
- Create payment terms
- Define accounts for cash discount taken
- Define Vendor reconciliation account
- Create vendor code
- SAP FICO - Tax on Sales and Purchases
- What is Sales tax and Purchase tax in SAP?
- Define tax calculation procedures
- Assign country to calculation procedure
- Assign tax codes for non taxable transactions
- Maintain tax codes for sales and purchases
- Define tax accounts in SAP
- SAP FICO - Bank Accounting
- What is Bank Accounting in SAP?
- Define bank key
- Define house bank in SAP
- Create check lots
- Automatic payment program
- SAP FICO - Asset Accounting
- What is Asset Accounting in SAP?
- Define Chart of Depreciation
- Assign chart of depreciation to company code
- Specify Account Determination
- Number range intervals for Assets
- Maintain Asset Classes
- SAP Controlling Training
- SAP CO Tutorials
- SAP FI TCodes
- ❯ SAP FICO Tutorials
- ❯ Define business area and consolidation business area in SAP
Define Business Area in SAP | Create Consolidation Business Area
How to define business area in sap.
Business area in SAP is an organizational unit within accounting that can be classified as geographical wise or product wise as per the requirements of an organization.. Under business area, you generate financial statements of balance sheet and profit & loss account for internal reporting.
- The definition of business area in SAP is optional.
- You can maintain number of business areas in SAP as per company needs.
- To post items in business area, you need to enter business area when you enter the business transactions.
- Examples of business areas are product lines, branches, etc.
You can define business area in SAP through navigation method or transaction code.
- Navigation: – SPRO – Enterprise Structure – Definition – Financial Accounting – Define business area
- Transaction code: – OX03
Step 1) Enter transaction code “ OX03 ” in the SAP command field and enter to continue.
Step 2) On change view “Business areas”: Overview screen, Click on “New Entries” button to create new business areas as per the requirements of company.
Step 3) On new entries of business areas screen, update the following details.
- Business Area: – Give the four digits key that identifies that business area in SAP.
- Description: – Update the descriptive text of business area.

Scenario: We have defined four business areas as per geographical wise.
| TK10 | Bangalore Business Area |
| TK20 | Hyderabad Business Area |
| TK30 | Mumbai Business Area |
| TK40 | Vijayawada Business Area |
Step 4) After updating the details, click on save button to save the configured business areas data.

Now you are prompted for customizing request number, choose request and save the details.

Successfully we have created new business areas in SAP.
Maintain consolidation business area in SAP
Consolidation business area specifies the central business segments within a company. If you maintain consolidated business area in SAP, it is mandatory to assign business areas to consolidated business areas.
- Navigation: – SPRO – Enterprise Structure – Definition – Financial Accounting – Maintain consolidation business area.
Click on “New Entries” button.

Enter consolidation business area key and its description.

Click on save button and save the details.
Popular Courses by TutorialKart
App developement, web development, online tools.
Define Business Area in SAP FICO | How to Create Business Area in SAP
Define business area in sap.
Definition of Business area :- Business area is a separate area of operations or responsibilities of organizational units of financial accounting that is used for internal and external reporting. Different divisions of each business within a legal entity are created as Business areas for reporting of each operational area. So Financial statements can be created for each business area and these financial statements can be used for internal reporting purposes.
Business Area in SAP – Important Points
- This is an optional organizational unit, so it is not mandatory to define the business area in SAP systems
- Business areas are not assigned to any company codes.
- Using business area organizational units, the statements of Profit and Loss, Balance sheets
- You can define the business area with 4 characters and the same company code be used for the business area key.
Transaction Code for Creation of Business Area in SAP :- OX03
Steps for the Creation of New Business Areas in SAP:-
Step 1 :- Enter transaction code SPRO in the commend field
Step 2 :- Select SAP Reference IMG ( Shortcut key F5 )
Step 3 :- After selecting SAP Reference IMG, follow the below structure to configure the B usiness areas
Step 4 :- After Selecting Define Business Area , Select new entries to configure new B usiness areas
Step 5 :- Enter the 4 digit code in the business area field enter the name of business areas in the description field and save the settings.
Thus Business Areas ADKA, ADHY, ADMU are configured in SAP FICO.
Learn : How to create business areas in SAP S4 Hana .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Purpose. Business areas are primarily used to facilitate external segment reporting across company codes, covering the company's main areas of operation (product lines, branches). You can assign all balance sheet items, such as fixed assets, receivables, payables, and material stock, as well as the entire P&L statement directly to business areas.
However, the business area can also be derived from other account assignments, such as the cost center. To enable the system to do this, you must define the business area in the cost center master record. For more information, see the SAP Library under Financials Controlling Organization in Controlling Business Area.
What is Business Area in SAP; its use and role in SAP's various segments? Read important for SAP FICO Interviews questions on Business Area. +91-9556432150; [email protected]; ... Therefore, you do not need to make a manual assignment to a business area at any point. Asset Dr -UN1- 5000.
Assignment in Master Data. SAP Business Areas are most often populated from master data records in which they are assigned. An example would be the assignment of SAP business area within a cost center master record. Let's take a look at where on a cost center this would be done. To create a cost center, use transaction KS01 or follow the menu ...
Here is a list of important tables storing Business Area related data in SAP. A039 : Overhead Type/Business Area. A060 : Controlling Area/Business Area. A063 : Controlling Area/Business Area/Cost Center. A105 : Controlling Area/Company Code/Business Area. A138 : Price per Company Code/Business Area.
CO objects (such as, cost centers and internal orders) aid account assignment, as the business area can be derived from the master data records. When you post primary costs to a cost center, the system determines the business area automatically from the cost center master data. This enables the costs to be assigned to the correct business area.
Assignment in Master Data. SAP Business Areas are most often populated from master data records in which they are assigned. An example would be the assignment of SAP business area within a cost center master record. Let's take a look at where on a cost center this would be done. To create a cost center, use transaction KS01 or follow the menu ...
The step by step procedure to define business areas is as follows: STEP 1: Navigate to the path as shown below in the implementation guide or execute the transaction OX03 from the SAP Easy Access menu. Use the transaction code SPRO to get to the Implementation guide from the SAP Easy Access menu.
Step 1) Enter transaction code " OX03 " in the SAP command field and enter to continue. Step 2) On change view "Business areas": Overview screen, Click on "New Entries" button to create new business areas as per the requirements of company. Step 3) On new entries of business areas screen, update the following details.
Step 1: From SAP Easy Access S/4Hana screen, enter tcode "OX03" and enter to continue. Step 2: In next S/4Hana change view business area overview screen, it displays lit of business areas that are defined in SAP S/4 Hana System. To define the new business area in SAP S/4 Hana system, click on new entries option.
Let's define business areas in the SAP system. Step 1: - Enter transaction code "OX03" in the SAP command field and enter. Step 2: - On the change view business area overview screen, click on new entries to maintain new business areas as per company requirements. Step 3: - On the new entries screen, Update the following details.
Business Area (FI) Business areas are primarily used to facilitate external segment reporting across company codes, covering the company's main areas of operation (product lines, branches). You can assign all balance sheet items, such as fixed assets, receivables, payables, and material stock, as well as the entire P&L statement directly to ...
Step 2:- Select SAP Reference IMG ( Shortcut key F5 ). Step 3:- After selecting SAP Reference IMG, follow the below structure to configure the Business areas. Step 4:- After Selecting Define Business Area, Select new entries to configure new Business areas. Step 5:- Enter the 4 digit code in the business area field enter the name of business areas in the description field and save the settings.
The business area (BA) is also used to classify the master data and organizational unit substructures. It comprises a specific business task area. The task fields are processes. Examples of business areas are Purchasing, Sales and Marketing, Accounts. Business Area in SAP - Everything you need to know about Business Area; definition ...