
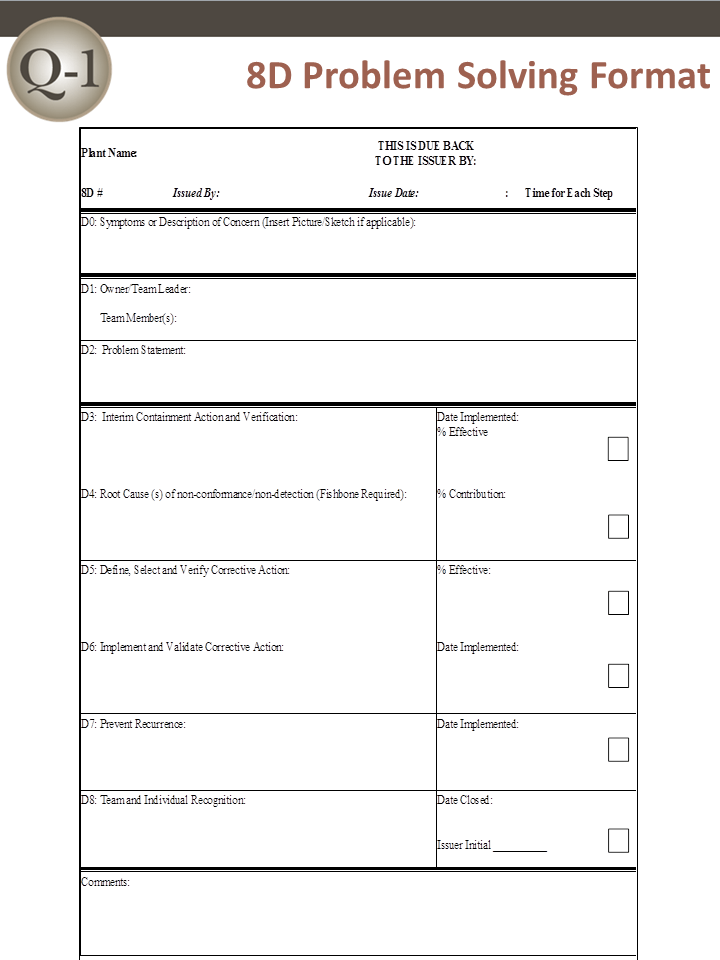
8D report preparation in Downloadable PPT, Excel and PDF templates| with Example |

This article is written by Tiago A. Rodrigues Rita . He is experienced in the Automotive Sector.
8D report communicates how 8D methodology is used to solve a recurring problem or customer complaints . Most of the customers ask 8D report as a proof of the implementation of solution to their complaints. Hence lets learn how to prepare a 8D report through an easy example. You will also get downloadable and editable 8D report templates with example. You will be able to find 8D templates in Excel, PPT and PDF formats.
Before continuing with this its recommended to learn our article on 8D problem solving in which we have clearly explained the 8 steps in 8D and when to use 8D. In this article we are doing its practical side.
Let’s do it.
An Example for the preparation of 8D report
Let’s imagine that you are a chef at a diner restaurant, and suddenly an order has returned. The customer is complaining that the snack was carried out scorched.

You quickly need to carry out an analysis to understand what actually happened at the time of snack production, take the appropriate actions and prevent this from happening more often in the future.
Then, you decide to use the 8D in order to solve the problem.
let’s see how the resolution of this analogy would be using the 8D methodology .
Get our Membership
You are using a non-member version of Know Industrial Engineering platform, for manufacturing industry professionals. Get our membership now and access the benefits below:
- Earn a side income - Contribute to the articles on this platform and start earning. Around $6 USD for first article, $12 USD for each successful referral and subsequent bonuses.
- Global audience - Showcase your expertise to global audience and get hired or get clients faster.
- Get trained on article writing.
- Access premium content - Online tools, exclusive articles, etc.
- Get discounts - Our members are eligible for special reduction on trainings, exams, and certification fees.
- Ad free experience
- Network with our members globally
Check below in 9 steps how to apply it easy with a simple practical example.
Before we begin, download the templates in excel, PPT and PDF to support you in you daily routine. Excel and PPT template are editable, which you can use for other projects.
8D report templates with example (Download)
8d problem solving step 1 – customer complaint.
We need to describe the problem related by the customer , according to customer´s language. Tip: In this step it is very important to faithfully describe what the customer complained about, how the information was passed on.

8D Problem solving STEP 2 – Team Building
We need to build the multifunctional team that will work in the investigation, this can be performed by the responsible persons for the area affected. Tip: Create a strong team that has knowledge on the related subject, if possible, extend participation to everyone who, at some point, has any contact related to the problem

8D Problem solving STEP 3 – Problem Description
Problem description with details, characterize and transform from the customer language to our language. Tip: Be as detailed in the description of the problem as possible, include images, videos if possible to help the understanding the problem.

8D Problem solving STEP 4 – Containment action
In this step we need to develop or propose / containment action in order or Take action so that the customer does not continue to receive products with the same problem. ***Give a destiny to the snack returned. Tip: Try to develop a containment action where the customer is satisfied and safe for that moment, unfortunately the failure has already occurred now we need to restore the image with the customer.

8D Problem solving STEP 5 – Finding the root cause and corrective action
Now we need to find the root cause, using auxiliary tools, if you read our article about 8D , you can find some kind of tools to support the analysis to find and confirm the root cause. Tip: During the analysis you can use the following tools to support the team to solve the problem:
- Tendency Chart
- Brainstorming
- Affinity Diagram
- Cause and Effect Diagram
- Why Why Analysis
- FTA – Fault Tree Analysis
- SIPOC / Flowchart
- Capability Studies
To support us, we´ll use fish bone diagram and the why why analysis:

In conjunction with the multifunctional team, we need to raise the possibilities that may have contributed to the problem having occurred, taking into account the 6M’s After that we score according to the potential using Highly likely / low probability or Improbable. This score will support us on focus just the high potential causes.
After we find the most potential root causes, we use the Why Most analysis in order to confirm if in fact this happened because of the potential cause raised by the team.
The more common way to use the Why-Why analysis, it´s just asking 5 times the “Why” to the potential root causing, until we no longer have an answer to the 5 Why´s. Normally after that, we´ll find the root cause inside the potential cause. But, to support us on this analysis we´ll use the Why-Why to find 3 kind of root cause:
Occurrence Root Cause
Why did the problem occur?
Detection Root Cause
Why did not detect the problem?
Systematic Root Cause
Why did not prevent the problem?

8D Problem solving STEP 6 – Validation of the proposed root cause and corrective action
The team need to create plan in order to confirm / validate the proposed solutions in step 5º . Depend on the problem you are facing, you can use tests in low scale to get a feedback quickly. Tip: Use short scale tests / use auxiliary tools tools to proof the effectiveness of corrective actions. This step is very important to avoid gap and in the future the problem appear again.
Tools to support the validation of root cause
- Correlation
- Simulations

8D Problem solving STEP 7 – Implementation of Corrective action
According to the results in the step 6º, you can make official what was has been proven during the validations of solutions, this step is very important because is from this topic will you systematize the actions to the future.

8D Problem solving STEP 8 – Preventive action
Now we need implement the actions on the system, and make a plan in order to avoid the re-incidence of the fail. In this step it´s very important that all documentation be update, to ensure that all analysis was implemented to all internal process. Tip: Use preventive actions to avoid recidivism / transform the actions in best practices and update all documentations related with the process.

8D Problem solving STEP 9 – Closure
In the last step we need to present all results, recognition about all participants, lessons learned to Others areas, and 8D Finalization

Bellow you can find the template filled with the example:

We hope you have enjoyed the article on 8D report templates with example.
Thank you. Hope you have noticed downloadable and editable 8D PPT template. Go and download it, present before your team and solve your customer complaints.
You may refer more 8D report preparation example from here .
Tiago is a Professional with more than 15 years of experience in Process Engineering, project management, and team leadership, with a strong focus on continuous improvement projects and process development in the automotive sector.
Share this:
I wanted to learn this since long, thanks👍

To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- my-task icon Admin and security
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all use cases arrow-right icon

- Help Center
- Asana Academy
- Certifications
- Work management hub
- Customer stories
- Get support
- Developer support
- Customer Success
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Project management |
- What is 8D? A template for efficient pr ...
What is 8D? A template for efficient problem-solving
How you respond when problems arise is one of the most defining qualities of a manager. Luckily, there are tools you can use to master problem-solving. The 8D method of problem-solving combines teamwork and basic statistics to help you reach a logical solution and prevent new issues from arising.
You’ve spent months overseeing the development of your company's newest project. From initiation, planning, and execution, you’re confident this may be your best work yet.
Until the feedback starts rolling in.
There’s no sugar-coating it—things don’t always go as planned. But production or process issues are hardly a signal to throw in the towel. Instead, focus on honing your problem-solving skills to find a solution that keeps it from happening again.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team. Plus, get an 8D template to make solving your issue easier.
3 ways to transform your enterprise project management
Watch a live demo and Q&A session to help you streamline goal-setting, accelerate annual planning, and automate how teams intake strategic work.
What is 8D?
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues.
How do you use the 8D method?
The 8D method is a proven strategy for avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems. If you’re noticing issues in your workflow or processes, then it’s a good time to give this problem-solving method a try.
To complete an 8D analysis, follow “the eight disciplines” to construct a statistical analysis of the problem and determine the best solution.
The eight disciplines of problem-solving
8D stands for the eight disciplines you will use to establish an 8D report. As you may notice, this outline starts with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. The “zero stage” was developed later as an initial planning stage.
To illustrate these steps, imagine your organization experienced a decline in team innovation and productivity this past year. Your stakeholders have noticed and want to see changes implemented within the next six months. Below, we’ll use the 8D process to uncover a morale-boosting solution.
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D8 problem solving approach (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6ab7c188-3258-4d2e-afe6-9a4a084cc09f/inline-productivity-8d-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the problem-solving process, evaluate the problem you want to solve. Understanding the background of the problem will help you identify the root cause in later steps.
Collect information about how the problem has affected a process or product and what the most severe consequences may be. Planning can include:
Gathering data
Determining the prerequisites for solving the problem
Collecting feedback from others involved
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D0 Planning (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/abc3621d-e1ae-47ff-b731-0ee38cff99e9/inline-productivity-8d-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If we look back at our example, you may want to figure out whether this decline in morale is organization-wide or only applies to a few departments. Consider interviewing a few employees from different departments and levels of management to gain some perspective. Next, determine what knowledge and skills you will need to solve this lapse in productivity.
D1: Form your team
Create a cross-functional team made up of people who have knowledge of the various products and workflows involved. These team members should have the skills needed to solve the problem and put corrective actions in place.
Steps in this discipline may include:
Appointing a team leader
Developing and implementing team guidelines
Determining team goals and priorities
Assigning individual roles
Arranging team-building activities
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D1 Team members (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/51986017-5150-4dd4-940c-252cd0eb8ba5/inline-productivity-8d-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
From our example, a solid team would consist of people with first-hand experience with the issues—like representatives from all departments and key people close to workshop-level work. You may also want to pull someone in from your HR department to help design and implement a solution. Most importantly, make sure the people you choose want to be involved and contribute to the solution.
D2: Identify the problem
You may have a good understanding of your problem by now, but this phase aims to break it down into clear and quantifiable terms by identifying the five W’s a and two H’s (5W2H):
Who first reported the problem?
What is the problem about?
When did it occur and how often?
Where did it occur (relating to the sector, supplier, machine, or production line involved)?
Why is solving the problem important?
How was the problem first detected?
How many parts/units/customers are affected?
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D2 Problem statement & description (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9825ecd6-2bd3-4559-a68c-b1ae8aca2e52/inline-productivity-8d-template-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Use your team’s insights to answer these questions. From our example, your team may conclude that:
Employees feel overwhelmed with their current workload.
There is no real structure or opportunity to share new ideas.
Managers have had no training for meetings or innovation settings.
Disgruntled employees know they can achieve more—and want to achieve more—even if they seem disengaged.
Once you answer these questions, record an official problem statement to describe the issue. If possible, include photos, videos, and diagrams to ensure all parties have a clear understanding of the problem. It may also help to create a flowchart of the process that includes various steps related to the problem description.
D3: Develop an interim containment plan
Much like we can expect speedy first aid after an accident, your team should take immediate actions to ensure you contain the problem—especially if the problem is related to customer safety.
An interim containment plan will provide a temporary solution to isolate the problem from customers and clients while your team works to develop a permanent corrective action. This band-aid will help keep your customers informed and safe—and your reputation intact.
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D3 Interim containment action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d6279c36-ccc6-4de3-89d2-f221632a1059/inline-productivity-8d-template-5-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Because your findings revealed workers were overworked and managers lacked training, your team suggests scheduling a few mandatory training sessions for leaders of each department covering time and stress management and combating burnout . You may also want to have a presentation outlining the topics of this training to get key managers and stakeholders interested and primed for positive upcoming changes.
D4: Verify root causes and escape points
Refer back to your findings and consult with your team about how the problem may have occurred. The root cause analysis involves mapping each potential root cause against the problem statement and its related test data. Make sure to test all potential causes—fuzzy brainstorming and sloppy analyses may cause you to overlook vital information.
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D4 Root cause & escape points (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/301717c6-0434-4c88-addf-d500dc23ae87/inline-productivity-8d-template-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
In our example, focus on the “why” portion of the 5W2H. You and your team identify six root causes:
Managers have never had any training
There is a lack of trust and psychological safety
Employees don’t understand the objectives and goals
Communication is poor
Time management is poor
Employees lack confidence
In addition to identifying the root causes, try to pinpoint where you first detected the problem in the process, and why it went unnoticed. This is called the escape point, and there may be more than one.
D5: Choose permanent corrective actions
Work with your team to determine the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem and address the issues with the escape points. Quantitatively confirm that the selected permanent corrective action(s) (PCA) will resolve the problem for the customer.
Steps to choosing a PCA may include:
Determining if you require further expertise
Ensuring the 5W2Hs are defined correctly
Carrying out a decision analysis and risk assessment
Considering alternative measures
Collecting evidence to prove the PCA will be effective
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D5 Permanent corrective action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/53509966-18dd-4bb4-88a1-c7ca940fde3f/inline-productivity-8d-template-7-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your team decides to roll out the training used in the interim plan to all employees, with monthly company-wide workshops on improving well-being. You also plan to implement meetings, innovation sessions, and team-coaching training for managers. Lastly, you suggest adopting software to improve communication and collaboration.
D6: Implement your corrective actions
Once all parties have agreed on a solution, the next step is to create an action plan to remove the root causes and escape points. Once the solution is in effect, you can remove your interim containment actions.
After seeing success with the training in the interim phase, your stakeholders approve all of your team’s proposed PCAs. Your representative from HR also plans to implement periodic employee wellness checks to track employee morale .
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D6 PCA implementation plan (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ca68af4a-afa7-4be4-93cb-8a8321eb5172/inline-productivity-8d-template-8-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
To ensure your corrective action was a success, monitor the results, customer, or employee feedback over a long period of time and take note of any negative effects. Setting up “controls” like employee wellness checks will help you validate whether your solution is working or more needs to be done.
D7: Take preventive measures
One of the main benefits of using the 8D method is the improved ability to identify necessary systematic changes to prevent future issues from occurring. Look for ways to improve your management systems, operating methods, and procedures to not only eliminate your current problem, but stop similar problems from developing later on.
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] D7 Preventive measure (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cdd7b133-fb80-4db7-8935-1285a6b62b69/inline-productivity-8d-template-9-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Based on our example, the training your team suggested is now adopted in the new manager onboarding curriculum. Every manager now has a “meeting system” that all meetings must be guided by, and workloads and projects are managed as a team within your new collaboration software . Innovation is improving, and morale is at an all-time high!
D8: Celebrate with your team
The 8D method of problem-solving is impossible to accomplish without dedicated team members and first-class collaboration. Once notes, lessons, research, and test data are documented and saved, congratulate your teammates on a job well done! Make an effort to recognize each individual for their contribution to uncovering a successful solution.
![8d problem solving presentation [inline illustration] 8D Team congratulations & reward (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d2055965-bf3d-4bf4-a1ea-a0a7c4bf8a32/inline-productivity-8d-template-10-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
8D report template and example
Check out our 8D report template below to help you record your findings as you navigate through the eight disciplines of problem solving. This is a formal report that can be used as a means of communication within companies, which makes for transparent problem-solving that you can apply to the entire production or process chain.
Benefits of using the 8D method
The 8D method is one of the most popular problem-solving strategies for good reason. Its strength lies in teamwork and fact-based analyses to create a culture of continuous improvement —making it one of the most effective tools for quality managers. The benefits of using the 8D method include:
Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills rather than relying on an individual to provide a solution
Increased familiarity with a problem-solving structure
A better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools for problem-solving
Open and honest communication in problem-solving discussions
Prevent future problems from occurring by identifying system weaknesses and solutions
Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem-solving

Better collaboration = better problem solving
No matter how good a manager you are, production and process issues are inevitable. It’s how you solve them that separates the good from the great. The 8D method of problem solving allows you to not only solve the problem at hand but improve team collaboration, improve processes, and prevent future issues from arising.
Try Asana’s project management tool to break communication barriers and keep your team on track.
Related resources
How to use benchmarking to set your standards for success

How to scale retail management operations with Asana

How Asana’s digital team used work management to refresh our brand

Your guide to RACI charts, with examples

Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
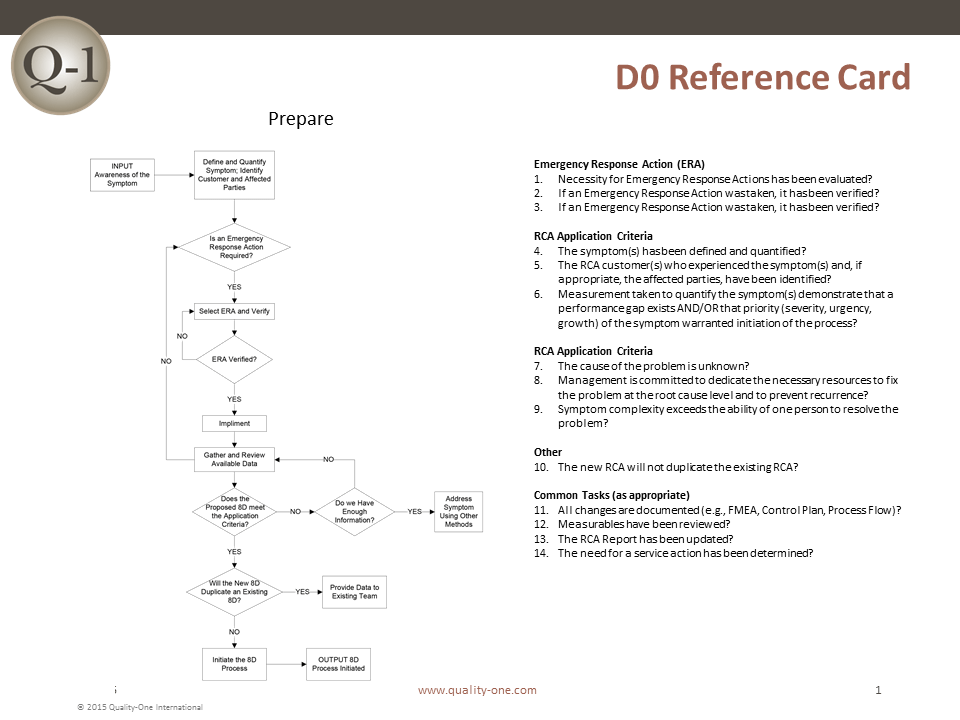
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
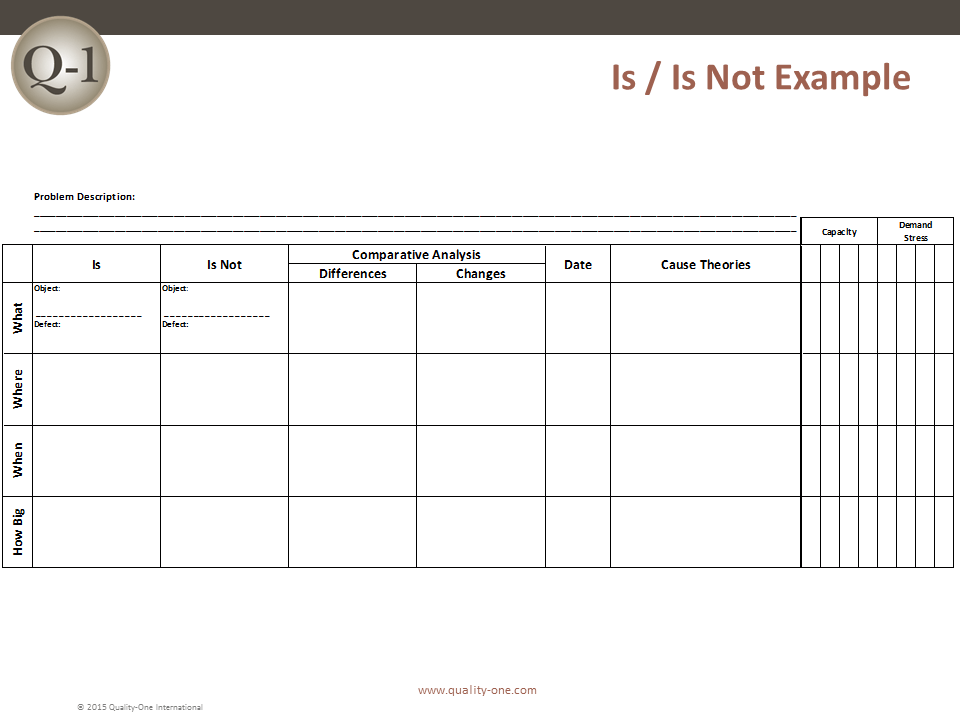
D2: Describe the Problem
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes
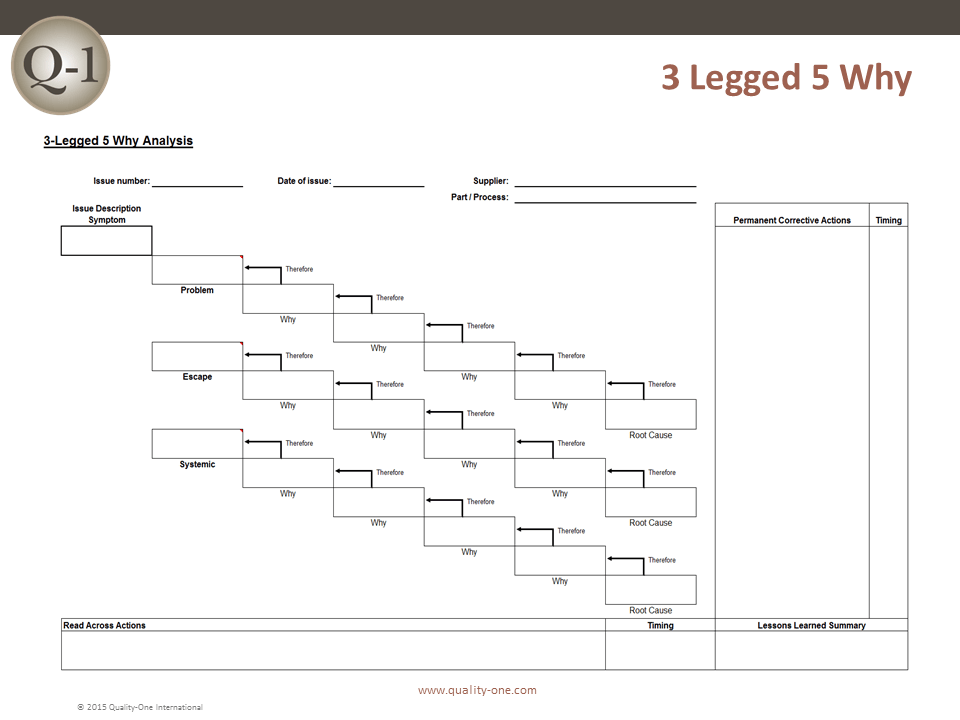
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me

Aspect Ratio:
File Size: 39.8 MB
Number of Slides: 256
Terms of Usage
Training Presentation/Powerpoint:
8D Problem Solving Process & Tools
Description
The 8D (Eight Disciplines) approach is a systematic problem solving process. Popularized by Ford, the 8D process integrates best practices from various problem-solving methods and is now a standard in the automotive industry. The 8D problem solving process has proven to be highly effective in product and process improvement.
Following the logic of the PDCA cycle, the 8D process enables problem solving teams to identify root causes, develop proper actions to eliminate root causes, and implement permanent corrective action to prevent recurrence. It includes key analytical tools such as Is/Is Not Analysis and Root Cause Analysis using 5 Whys and the Fishbone Diagram.
This highly detailed training presentation will help you to teach employees in your company or organization to better understand team dynamics and solve problems using a disciplined approach.
Note: This training package includes:
8D Problem Solving PPT training presentation (PowerPoint format)
8D Problem Solving Report Template (PowerPoint format)
8D Report Worksheet (Word format)
8D Is/Is Not Worksheet (Excel format)
FMEA Form (Excel format)
8D Problem Solving poster (PDF format, in color and monochrome, printable in A3/A4 size paper)
Learning Objectives
Acquire knowledge of key concepts and principles in 8D problem solving.
Understand team-based problem solving dynamics and define roles within the 8D problem-solving team.
Familiarize yourself with the step-by-step 8D problem-solving process and the use of analytical tools.
Gain practical insights for achieving success in 8D problem solving.
Contents
1. Key C on cept s and Principles
• The Blind Men and the Elephant • The Mindset of a Traditional Problem Solver • Common Pitfalls in Problem Solving • What is a Problem? • What is Problem Solving? • What Problem Solving is Not • Impact of Problem Solving • Problem Solving Funnel • Problem Solving Philosophy • Benefits of Problem Solving • What is 8D problem solving? • Applying 8D Met hodology to Problem Solving • Why Use 8D? • 8D Problem Solving Process
2. Team Approach and Roles
• What is a Team? • Types of Teams • Importance of Team-based Approach to Problem-solving • Qualities of an Effective Team • Team Member Ground Rules • Tuckman's Model of Team Development Stages • Why is Teamwork Important? • Problem Solving Team's Maxims • Ingredients for Problem Solving Team Success • Keys to Team Success • What is a Problem Solving Team? • Key Roles in 8D Problem Solving
3. 8D Problem Solving Process
• Popular Problem Solving Methods • 8D Problem Solving Process • 8D Problem Solving Process vs 8D Report • The Importance of an 8D Report • D0: Plan • D1: Initiate Project Team • D2: Define the Problem • D3: Implement Containment Actions • D4: Identify Root Causes • D5: Develop and Verify Solution • D6: Implement Corrective Actions • D7: Prevent Recurrence • D8: Recognize Project Team • The 8D report: Capturing Solutions and Progress • Sample 8D Report / Template • Key Sections of the 8D Report • The Role of the 8D Report • 8D Report Templates Included (as part of this training presentation package)
4. Analytical Tools in 8D
• Brainstorming • Affinity Diagram • 5W2H • Is / Is Not • Control Chart • 5 Whys • Cause and Effect Diagram • Pareto Chart • Histogram • Scatter Diagram • FMEA
5. Practical Tips for Success
• Best Practices for 8D Problem Solving
Yo u may also be interested in the following training presentations (sold separately):
A3 Problem Solving Process & Tools
PDCA Problem Solving Process & Tools
Root Cause Analysis
5 Whys Analysis Toolkit
5 Steps of Problem Solving
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
Problem Solving & Visualization Tools
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Mistake-Proofing
Total Quality Management
Reducing the Cost of Quality

What do you think of this template?

Product details
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability. The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team-oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future. 8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem-solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. The 8D methodology offers engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process.
The main stages of the 8D process are: Establish a team, Define problem, Develop Containment Actions, Identify Root Cause, Establish Corrective Action, Implement Corrective Actions, Prevent Recurrence, Recognize Team Effort.
This template contains all the necessary tools to prepare for solving a problem using the 8D process. The first slide is presented in the form of honeycombs, each of which describes one of the stages of the process. You can also provide a short explanation for each step. The slide can be used by engineers when building a model for solving an equipment failure problem. For example, you can specify the sequence of actions in the event of a turbine breakdown and indicate an action plan for each of the participants in the process. The second and third slide of the template are made in the form of a horizontal time line. This slide can be used when building sequential models. Also, these slides will be useful for crisis managers when building a model for a company’s exit from a crisis situation. The third slide is designed as sequential blocks with 8D process. A special feature of this slide is the arrangement of blocks at different levels. This slide will be useful for marketing specialists when building a plan for an advertising campaign for a new product or a plan to solve the problem of a competitor’s launch of a product similar to yours. Team leaders can use this slide in weekly meetings with the development team. The structure of this slide is ideal for testing bugs and discussing new client requirements for a software product.
This template follows the latest design trends with a neutral color scheme. You can also change the color and font sizes so that this template can be used in your other presentations. The 8D process template will be primarily useful for software developers when testing programs. Also, this template can be used by service managers, production workers, specialists of construction organizations.
Related Products
Petal Diagram

Challenges and Solutions
Swim Lane Flowcharts

Career Summary

Project Management Process
Positioning Statement

Business Assessment
Prioritization Matrix

Transformation Map
Theory of Change
You dont have access, please change your membership plan., great you're all signed up..., verify your account.
PowerSlides.com will email you template files that you've chosen to dowload.
Please make sure you've provided a valid email address! Sometimes, our emails can end up in your Promotions/Spam folder.
Simply, verify your account by clicking on the link in your email.
- Collections
Strategy / Business Plan
- Problem Solving
- 8D Problem Solving PPT
8D Problem Solving PPT Presentation Template & Google Slides

Eight-Noded Problem Solving Presentation Slide
Features of the template:.
- Critical Thinking
- Problem Solving Stages
- Problem Solving Process
- Problem Solving Techniques
- Root Cause Analysis
- Problem Solving Infographics
- 4 Options Problem Solving
- 8D Problem Solving
- Google Slides

296+ Templates

1105+ Templates

Team / Teamwork
352+ Templates

6695+ Templates

55+ Templates

492+ Templates

413+ Templates

72+ Templates

686+ Templates

13+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates


COMMENTS
This document outlines the 8D problem solving process used by Ford Motor Company to continuously improve quality and prevent issues from reoccurring. The 8D process involves 8 disciplines: 1) Define the problem/failure, 2) Establish an interim containment action, 3) Determine the root cause (s), 4) Choose a permanent corrective action, 5 ...
The Eight Disciplines (8D) are a problem solving tool used to correct, identify and remove recurring issues halting the production process. Learn more about 8D analysis at ASQ.org.
The 8D problem solving process has proven to be highly effective in product and process improvement. Following the logic of the PDCA cycle, the 8D process enables problem solving teams to identify root causes, develop proper actions to eliminate root causes, and implement permanent corrective action to prevent recurrence.
8D report communicates how 8D methodology is used to solve a recurring problem or customer complaints. Most of the customers ask 8D report as a proof of the implementation of solution to their complaints. Hence lets learn how to prepare a 8D report through an easy example.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team.
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems.
The document discusses the 8D problem solving process which consists of 8 steps (the D's) for product and process improvement. The 8 steps are: 1) use a team approach, 2) describe the problem, 3) implement short-term corrective actions, 4) define and verify root causes, 5) verify corrective actions, 6) implement permanent corrective actions, 7 ...
Understand team-based problem solving dynamics and define roles within the 8D problem-solving team. Familiarize yourself with the step-by-step 8D problem-solving process and the use of analytical tools. Gain practical insights for achieving success in 8D problem solving.
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems.
Eight-Noded Problem Solving Presentation Slide. The 8D problem-solving process is a methodology used by organizations to solve complex problems and improve processes. It involves eight steps, including defining the problem, establishing a team, identifying the root cause, developing and implementing a corrective action plan, verifying the ...