

Data Analysis in Research
Ai generator.

Data analysis in research involves systematically applying statistical and logical techniques to describe, illustrate, condense, and evaluate data. It is a crucial step that enables researchers to identify patterns, relationships, and trends within the data, transforming raw information into valuable insights. Through methods such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and qualitative analysis, researchers can interpret their findings, draw conclusions, and support decision-making processes. An effective data analysis plan and robust methodology ensure the accuracy and reliability of research outcomes, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge across various fields.
What is Data Analysis in Research?
Data analysis in research involves using statistical and logical techniques to describe, summarize, and compare collected data. This includes inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to find useful information and support decision-making. Quantitative data provides measurable insights, and a solid research design ensures accuracy and reliability. This process helps validate hypotheses, identify patterns, and make informed conclusions, making it a crucial step in the scientific method.
Examples of Data analysis in Research
- Survey Analysis : Researchers collect survey responses from a sample population to gauge opinions, behaviors, or characteristics. Using descriptive statistics, they summarize the data through means, medians, and modes, and then inferential statistics to generalize findings to a larger population.
- Experimental Analysis : In scientific experiments, researchers manipulate one or more variables to observe the effect on a dependent variable. Data is analyzed using methods such as ANOVA or regression analysis to determine if changes in the independent variable(s) significantly affect the dependent variable.
- Content Analysis : Qualitative research often involves analyzing textual data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses. Researchers code the data to identify recurring themes, patterns, and categories, providing a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Correlation Studies : Researchers explore the relationship between two or more variables using correlation coefficients. For example, a study might examine the correlation between hours of study and academic performance to identify if there is a significant positive relationship.
- Longitudinal Analysis : This type of analysis involves collecting data from the same subjects over a period of time. Researchers analyze this data to observe changes and developments, such as studying the long-term effects of a specific educational intervention on student achievement.
- Meta-Analysis : By combining data from multiple studies, researchers perform a meta-analysis to increase the overall sample size and enhance the reliability of findings. This method helps in synthesizing research results to draw broader conclusions about a particular topic or intervention.
Data analysis in Qualitative Research
Data analysis in qualitative research involves systematically examining non-numeric data, such as interviews, observations, and textual materials, to identify patterns, themes, and meanings. Here are some key steps and methods used in qualitative data analysis:
- Coding : Researchers categorize the data by assigning labels or codes to specific segments of the text. These codes represent themes or concepts relevant to the research question.
- Thematic Analysis : This method involves identifying and analyzing patterns or themes within the data. Researchers review coded data to find recurring topics and construct a coherent narrative around these themes.
- Content Analysis : A systematic approach to categorize verbal or behavioral data to classify, summarize, and tabulate the data. This method often involves counting the frequency of specific words or phrases.
- Narrative Analysis : Researchers focus on the stories and experiences shared by participants, analyzing the structure, content, and context of the narratives to understand how individuals make sense of their experiences.
- Grounded Theory : This method involves generating a theory based on the data collected. Researchers collect and analyze data simultaneously, continually refining and adjusting their theoretical framework as new data emerges.
- Discourse Analysis : Examining language use and communication patterns within the data, researchers analyze how language constructs social realities and power relationships.
- Case Study Analysis : An in-depth analysis of a single case or multiple cases, exploring the complexities and unique aspects of each case to gain a deeper understanding of the phenomenon under study.
Data analysis in Quantitative Research
Data analysis in quantitative research involves the systematic application of statistical techniques to numerical data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends. Here are some common methods used in quantitative data analysis:
- Descriptive Statistics : This includes measures such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range, which summarize and describe the main features of a data set.
- Inferential Statistics : Techniques like t-tests, chi-square tests, and ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) are used to make inferences or generalizations about a population based on a sample.
- Regression Analysis : This method examines the relationship between dependent and independent variables. Simple linear regression analyzes the relationship between two variables, while multiple regression examines the relationship between one dependent variable and several independent variables.
- Correlation Analysis : Researchers use correlation coefficients to measure the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
- Factor Analysis : This technique is used to identify underlying relationships between variables by grouping them into factors based on their correlations.
- Cluster Analysis : A method used to group a set of objects or cases into clusters, where objects in the same cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters.
- Hypothesis Testing : This involves testing an assumption or hypothesis about a population parameter. Common tests include z-tests, t-tests, and chi-square tests, which help determine if there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
- Time Series Analysis : This method analyzes data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals to identify trends, cycles, and seasonal variations.
- Multivariate Analysis : Techniques like MANOVA (Multivariate Analysis of Variance) and PCA (Principal Component Analysis) are used to analyze data that involves multiple variables to understand their effect and relationships.
- Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) : A multivariate statistical analysis technique that is used to analyze structural relationships. This method is a combination of factor analysis and multiple regression analysis and is used to analyze the structural relationship between measured variables and latent constructs.
Data analysis in Research Methodology
Data analysis in research methodology involves the process of systematically applying statistical and logical techniques to describe, condense, recap, and evaluate data. Here are the key components and methods involved:
- Data Preparation : This step includes collecting, cleaning, and organizing raw data. Researchers ensure data quality by handling missing values, removing duplicates, and correcting errors.
- Descriptive Analysis : Researchers use descriptive statistics to summarize the basic features of the data. This includes measures such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and graphical representations like histograms and pie charts.
- Inferential Analysis : This involves using statistical tests to make inferences about the population from which the sample was drawn. Common techniques include t-tests, chi-square tests, ANOVA, and regression analysis.
- Qualitative Data Analysis : For non-numeric data, researchers employ methods like coding, thematic analysis, content analysis, narrative analysis, and discourse analysis to identify patterns and themes.
- Quantitative Data Analysis : For numeric data, researchers apply statistical methods such as correlation, regression, factor analysis, cluster analysis, and time series analysis to identify relationships and trends.
- Hypothesis Testing : Researchers test hypotheses using statistical methods to determine whether there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. This involves calculating p-values and confidence intervals.
- Data Interpretation : This step involves interpreting the results of the data analysis. Researchers draw conclusions based on the statistical findings and relate them back to the research questions and objectives.
- Validation and Reliability : Ensuring the validity and reliability of the analysis is crucial. Researchers check for consistency in the results and use methods like cross-validation and reliability testing to confirm their findings.
- Visualization : Effective data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and plots, are used to present the data in a clear and understandable manner, aiding in the interpretation and communication of results.
- Reporting : The final step involves reporting the results in a structured format, often including an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. This report should clearly convey the findings and their implications for the research question.
Types of Data analysis in Research
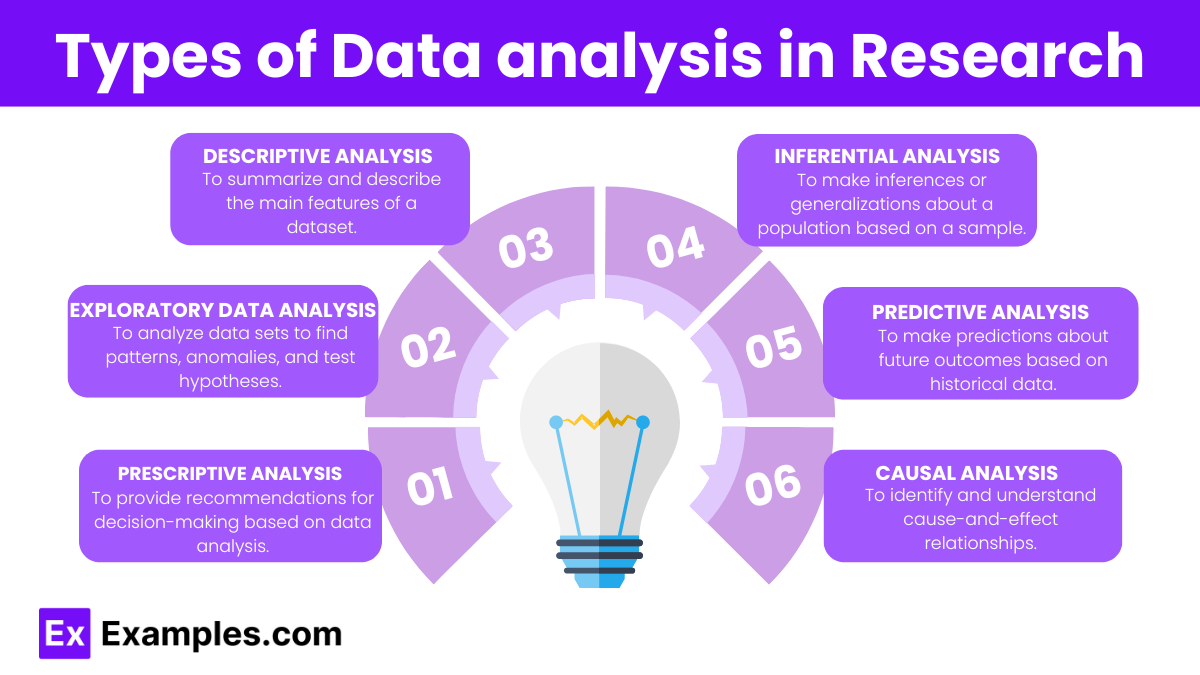
- Purpose : To summarize and describe the main features of a dataset.
- Methods : Mean, median, mode, standard deviation, frequency distributions, and graphical representations like histograms and pie charts.
- Example : Calculating the average test scores of students in a class.
- Purpose : To make inferences or generalizations about a population based on a sample.
- Methods : T-tests, chi-square tests, ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), regression analysis, and confidence intervals.
- Example : Testing whether a new teaching method significantly affects student performance compared to a traditional method.
- Purpose : To analyze data sets to find patterns, anomalies, and test hypotheses.
- Methods : Visualization techniques like box plots, scatter plots, and heat maps; summary statistics.
- Example : Visualizing the relationship between hours of study and exam scores using a scatter plot.
- Purpose : To make predictions about future outcomes based on historical data.
- Methods : Regression analysis, machine learning algorithms (e.g., decision trees, neural networks), and time series analysis.
- Example : Predicting student graduation rates based on their academic performance and demographic data.
- Purpose : To provide recommendations for decision-making based on data analysis.
- Methods : Optimization algorithms, simulation, and decision analysis.
- Example : Suggesting the best course of action for improving student retention rates based on various predictive factors.
- Purpose : To identify and understand cause-and-effect relationships.
- Methods : Controlled experiments, regression analysis, path analysis, and structural equation modeling (SEM).
- Example : Determining the impact of a specific intervention, like a new curriculum, on student learning outcomes.
- Purpose : To understand the specific mechanisms through which variables affect one another.
- Methods : Detailed modeling and simulation, often used in scientific research to understand biological or physical processes.
- Example : Studying how a specific drug interacts with biological pathways to affect patient health.
How to write Data analysis in Research
Data analysis is crucial for interpreting collected data and drawing meaningful conclusions. Follow these steps to write an effective data analysis section in your research.
1. Prepare Your Data
Ensure your data is clean and organized:
- Remove duplicates and irrelevant data.
- Check for errors and correct them.
- Categorize data if necessary.
2. Choose the Right Analysis Method
Select a method that fits your data type and research question:
- Quantitative Data : Use statistical analysis such as t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis.
- Qualitative Data : Use thematic analysis, content analysis, or narrative analysis.
3. Describe Your Analytical Techniques
Clearly explain the methods you used:
- Software and Tools : Mention any software (e.g., SPSS, NVivo) used.
- Statistical Tests : Detail the statistical tests applied, such as chi-square tests or correlation analysis.
- Qualitative Techniques : Describe coding and theme identification processes.
4. Present Your Findings
Organize your findings logically:
- Use Tables and Figures : Display data in tables, graphs, and charts for clarity.
- Summarize Key Results : Highlight the most significant findings.
- Include Relevant Statistics : Report p-values, confidence intervals, means, and standard deviations.
5. Interpret the Results
Explain what your findings mean in the context of your research:
- Compare with Hypotheses : State whether the results support your hypotheses.
- Relate to Literature : Compare your results with previous studies.
- Discuss Implications : Explain the significance of your findings.
6. Discuss Limitations
Acknowledge any limitations in your data or analysis:
- Sample Size : Note if the sample size was small.
- Biases : Mention any potential biases in data collection.
- External Factors : Discuss any factors that might have influenced the results.
7. Conclude with a Summary
Wrap up your data analysis section:
- Restate Key Findings : Briefly summarize the main results.
- Future Research : Suggest areas for further investigation.
Importance of Data analysis in Research
Data analysis is a fundamental component of the research process. Here are five key points highlighting its importance:
- Enhances Accuracy and Reliability Data analysis ensures that research findings are accurate and reliable. By using statistical techniques, researchers can minimize errors and biases, ensuring that the results are dependable.
- Facilitates Informed Decision-Making Through data analysis, researchers can make informed decisions based on empirical evidence. This is crucial in fields like healthcare, business, and social sciences, where decisions impact policies, strategies, and outcomes.
- Identifies Trends and Patterns Analyzing data helps researchers uncover trends and patterns that might not be immediately visible. These insights can lead to new hypotheses and areas of study, advancing knowledge in the field.
- Supports Hypothesis Testing Data analysis is vital for testing hypotheses. Researchers can use statistical methods to determine whether their hypotheses are supported or refuted, which is essential for validating theories and advancing scientific understanding.
- Provides a Basis for Predictions By analyzing current and historical data, researchers can develop models that predict future outcomes. This predictive capability is valuable in numerous fields, including economics, climate science, and public health.
FAQ’s
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data analysis.
Qualitative analysis focuses on non-numerical data to understand concepts, while quantitative analysis deals with numerical data to identify patterns and relationships.
What is descriptive statistics?
Descriptive statistics summarize and describe the features of a data set, including measures like mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
What is inferential statistics?
Inferential statistics use sample data to make generalizations about a larger population, often through hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
What is regression analysis?
Regression analysis examines the relationship between dependent and independent variables, helping to predict outcomes and understand variable impacts.
What is the role of software in data analysis?
Software like SPSS, R, and Excel facilitate data analysis by providing tools for statistical calculations, visualization, and data management.
What are data visualization techniques?
Data visualization techniques include charts, graphs, and maps, which help in presenting data insights clearly and effectively.
What is data cleaning?
Data cleaning involves removing errors, inconsistencies, and missing values from a data set to ensure accuracy and reliability in analysis.
What is the significance of sample size in data analysis?
Sample size affects the accuracy and generalizability of results; larger samples generally provide more reliable insights.
How does correlation differ from causation?
Correlation indicates a relationship between variables, while causation implies one variable directly affects the other.
What are the ethical considerations in data analysis?
Ethical considerations include ensuring data privacy, obtaining informed consent, and avoiding data manipulation or misrepresentation.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Privacy Policy

Home » Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types
Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types
Table of Contents

Data Analysis
Definition:
Data analysis refers to the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, drawing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to interpret and derive insights from large datasets. The ultimate aim of data analysis is to convert raw data into actionable insights that can inform business decisions, scientific research, and other endeavors.
Data Analysis Process
The following are step-by-step guides to the data analysis process:
Define the Problem
The first step in data analysis is to clearly define the problem or question that needs to be answered. This involves identifying the purpose of the analysis, the data required, and the intended outcome.
Collect the Data
The next step is to collect the relevant data from various sources. This may involve collecting data from surveys, databases, or other sources. It is important to ensure that the data collected is accurate, complete, and relevant to the problem being analyzed.
Clean and Organize the Data
Once the data has been collected, it needs to be cleaned and organized. This involves removing any errors or inconsistencies in the data, filling in missing values, and ensuring that the data is in a format that can be easily analyzed.
Analyze the Data
The next step is to analyze the data using various statistical and analytical techniques. This may involve identifying patterns in the data, conducting statistical tests, or using machine learning algorithms to identify trends and insights.
Interpret the Results
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions based on the analysis and identifying any significant findings or trends.
Communicate the Findings
Once the results have been interpreted, they need to be communicated to stakeholders. This may involve creating reports, visualizations, or presentations to effectively communicate the findings and recommendations.
Take Action
The final step in the data analysis process is to take action based on the findings. This may involve implementing new policies or procedures, making strategic decisions, or taking other actions based on the insights gained from the analysis.
Types of Data Analysis
Types of Data Analysis are as follows:
Descriptive Analysis
This type of analysis involves summarizing and describing the main characteristics of a dataset, such as the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range.
Inferential Analysis
This type of analysis involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. Inferential analysis can help determine whether a certain relationship or pattern observed in a sample is likely to be present in the entire population.
Diagnostic Analysis
This type of analysis involves identifying and diagnosing problems or issues within a dataset. Diagnostic analysis can help identify outliers, errors, missing data, or other anomalies in the dataset.
Predictive Analysis
This type of analysis involves using statistical models and algorithms to predict future outcomes or trends based on historical data. Predictive analysis can help businesses and organizations make informed decisions about the future.
Prescriptive Analysis
This type of analysis involves recommending a course of action based on the results of previous analyses. Prescriptive analysis can help organizations make data-driven decisions about how to optimize their operations, products, or services.
Exploratory Analysis
This type of analysis involves exploring the relationships and patterns within a dataset to identify new insights and trends. Exploratory analysis is often used in the early stages of research or data analysis to generate hypotheses and identify areas for further investigation.
Data Analysis Methods
Data Analysis Methods are as follows:
Statistical Analysis
This method involves the use of mathematical models and statistical tools to analyze and interpret data. It includes measures of central tendency, correlation analysis, regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and more.

Machine Learning
This method involves the use of algorithms to identify patterns and relationships in data. It includes supervised and unsupervised learning, classification, clustering, and predictive modeling.
Data Mining
This method involves using statistical and machine learning techniques to extract information and insights from large and complex datasets.
Text Analysis
This method involves using natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze and interpret text data. It includes sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and entity recognition.
Network Analysis
This method involves analyzing the relationships and connections between entities in a network, such as social networks or computer networks. It includes social network analysis and graph theory.
Time Series Analysis
This method involves analyzing data collected over time to identify patterns and trends. It includes forecasting, decomposition, and smoothing techniques.
Spatial Analysis
This method involves analyzing geographic data to identify spatial patterns and relationships. It includes spatial statistics, spatial regression, and geospatial data visualization.
Data Visualization
This method involves using graphs, charts, and other visual representations to help communicate the findings of the analysis. It includes scatter plots, bar charts, heat maps, and interactive dashboards.
Qualitative Analysis
This method involves analyzing non-numeric data such as interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses. It includes thematic analysis, content analysis, and grounded theory.
Multi-criteria Decision Analysis
This method involves analyzing multiple criteria and objectives to support decision-making. It includes techniques such as the analytical hierarchy process, TOPSIS, and ELECTRE.
Data Analysis Tools
There are various data analysis tools available that can help with different aspects of data analysis. Below is a list of some commonly used data analysis tools:
- Microsoft Excel: A widely used spreadsheet program that allows for data organization, analysis, and visualization.
- SQL : A programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases.
- R : An open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics.
- Python : A general-purpose programming language that is widely used in data analysis and machine learning.
- Tableau : A data visualization software that allows for interactive and dynamic visualizations of data.
- SAS : A statistical analysis software used for data management, analysis, and reporting.
- SPSS : A statistical analysis software used for data analysis, reporting, and modeling.
- Matlab : A numerical computing software that is widely used in scientific research and engineering.
- RapidMiner : A data science platform that offers a wide range of data analysis and machine learning tools.
Applications of Data Analysis
Data analysis has numerous applications across various fields. Below are some examples of how data analysis is used in different fields:
- Business : Data analysis is used to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and financial performance. This includes customer segmentation, sales forecasting, and market research.
- Healthcare : Data analysis is used to identify patterns and trends in patient data, improve patient outcomes, and optimize healthcare operations. This includes clinical decision support, disease surveillance, and healthcare cost analysis.
- Education : Data analysis is used to measure student performance, evaluate teaching effectiveness, and improve educational programs. This includes assessment analytics, learning analytics, and program evaluation.
- Finance : Data analysis is used to monitor and evaluate financial performance, identify risks, and make investment decisions. This includes risk management, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection.
- Government : Data analysis is used to inform policy-making, improve public services, and enhance public safety. This includes crime analysis, disaster response planning, and social welfare program evaluation.
- Sports : Data analysis is used to gain insights into athlete performance, improve team strategy, and enhance fan engagement. This includes player evaluation, scouting analysis, and game strategy optimization.
- Marketing : Data analysis is used to measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, understand customer behavior, and develop targeted marketing strategies. This includes customer segmentation, marketing attribution analysis, and social media analytics.
- Environmental science : Data analysis is used to monitor and evaluate environmental conditions, assess the impact of human activities on the environment, and develop environmental policies. This includes climate modeling, ecological forecasting, and pollution monitoring.
When to Use Data Analysis
Data analysis is useful when you need to extract meaningful insights and information from large and complex datasets. It is a crucial step in the decision-making process, as it helps you understand the underlying patterns and relationships within the data, and identify potential areas for improvement or opportunities for growth.
Here are some specific scenarios where data analysis can be particularly helpful:
- Problem-solving : When you encounter a problem or challenge, data analysis can help you identify the root cause and develop effective solutions.
- Optimization : Data analysis can help you optimize processes, products, or services to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
- Prediction: Data analysis can help you make predictions about future trends or outcomes, which can inform strategic planning and decision-making.
- Performance evaluation : Data analysis can help you evaluate the performance of a process, product, or service to identify areas for improvement and potential opportunities for growth.
- Risk assessment : Data analysis can help you assess and mitigate risks, whether it is financial, operational, or related to safety.
- Market research : Data analysis can help you understand customer behavior and preferences, identify market trends, and develop effective marketing strategies.
- Quality control: Data analysis can help you ensure product quality and customer satisfaction by identifying and addressing quality issues.
Purpose of Data Analysis
The primary purposes of data analysis can be summarized as follows:
- To gain insights: Data analysis allows you to identify patterns and trends in data, which can provide valuable insights into the underlying factors that influence a particular phenomenon or process.
- To inform decision-making: Data analysis can help you make informed decisions based on the information that is available. By analyzing data, you can identify potential risks, opportunities, and solutions to problems.
- To improve performance: Data analysis can help you optimize processes, products, or services by identifying areas for improvement and potential opportunities for growth.
- To measure progress: Data analysis can help you measure progress towards a specific goal or objective, allowing you to track performance over time and adjust your strategies accordingly.
- To identify new opportunities: Data analysis can help you identify new opportunities for growth and innovation by identifying patterns and trends that may not have been visible before.
Examples of Data Analysis
Some Examples of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Social Media Monitoring: Companies use data analysis to monitor social media activity in real-time to understand their brand reputation, identify potential customer issues, and track competitors. By analyzing social media data, businesses can make informed decisions on product development, marketing strategies, and customer service.
- Financial Trading: Financial traders use data analysis to make real-time decisions about buying and selling stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. By analyzing real-time market data, traders can identify trends and patterns that help them make informed investment decisions.
- Traffic Monitoring : Cities use data analysis to monitor traffic patterns and make real-time decisions about traffic management. By analyzing data from traffic cameras, sensors, and other sources, cities can identify congestion hotspots and make changes to improve traffic flow.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Healthcare providers use data analysis to monitor patient health in real-time. By analyzing data from wearable devices, electronic health records, and other sources, healthcare providers can identify potential health issues and provide timely interventions.
- Online Advertising: Online advertisers use data analysis to make real-time decisions about advertising campaigns. By analyzing data on user behavior and ad performance, advertisers can make adjustments to their campaigns to improve their effectiveness.
- Sports Analysis : Sports teams use data analysis to make real-time decisions about strategy and player performance. By analyzing data on player movement, ball position, and other variables, coaches can make informed decisions about substitutions, game strategy, and training regimens.
- Energy Management : Energy companies use data analysis to monitor energy consumption in real-time. By analyzing data on energy usage patterns, companies can identify opportunities to reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
Characteristics of Data Analysis
Characteristics of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Objective : Data analysis should be objective and based on empirical evidence, rather than subjective assumptions or opinions.
- Systematic : Data analysis should follow a systematic approach, using established methods and procedures for collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data.
- Accurate : Data analysis should produce accurate results, free from errors and bias. Data should be validated and verified to ensure its quality.
- Relevant : Data analysis should be relevant to the research question or problem being addressed. It should focus on the data that is most useful for answering the research question or solving the problem.
- Comprehensive : Data analysis should be comprehensive and consider all relevant factors that may affect the research question or problem.
- Timely : Data analysis should be conducted in a timely manner, so that the results are available when they are needed.
- Reproducible : Data analysis should be reproducible, meaning that other researchers should be able to replicate the analysis using the same data and methods.
- Communicable : Data analysis should be communicated clearly and effectively to stakeholders and other interested parties. The results should be presented in a way that is understandable and useful for decision-making.
Advantages of Data Analysis
Advantages of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Better decision-making: Data analysis helps in making informed decisions based on facts and evidence, rather than intuition or guesswork.
- Improved efficiency: Data analysis can identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in business processes, allowing organizations to optimize their operations and reduce costs.
- Increased accuracy: Data analysis helps to reduce errors and bias, providing more accurate and reliable information.
- Better customer service: Data analysis can help organizations understand their customers better, allowing them to provide better customer service and improve customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: Data analysis can provide organizations with insights into their competitors, allowing them to identify areas where they can gain a competitive advantage.
- Identification of trends and patterns : Data analysis can identify trends and patterns in data that may not be immediately apparent, helping organizations to make predictions and plan for the future.
- Improved risk management : Data analysis can help organizations identify potential risks and take proactive steps to mitigate them.
- Innovation: Data analysis can inspire innovation and new ideas by revealing new opportunities or previously unknown correlations in data.
Limitations of Data Analysis
- Data quality: The quality of data can impact the accuracy and reliability of analysis results. If data is incomplete, inconsistent, or outdated, the analysis may not provide meaningful insights.
- Limited scope: Data analysis is limited by the scope of the data available. If data is incomplete or does not capture all relevant factors, the analysis may not provide a complete picture.
- Human error : Data analysis is often conducted by humans, and errors can occur in data collection, cleaning, and analysis.
- Cost : Data analysis can be expensive, requiring specialized tools, software, and expertise.
- Time-consuming : Data analysis can be time-consuming, especially when working with large datasets or conducting complex analyses.
- Overreliance on data: Data analysis should be complemented with human intuition and expertise. Overreliance on data can lead to a lack of creativity and innovation.
- Privacy concerns: Data analysis can raise privacy concerns if personal or sensitive information is used without proper consent or security measures.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Uniform Histogram – Purpose, Examples and Guide

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...

Purpose of Research – Objectives and Applications

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...
A Step-by-Step Guide to the Data Analysis Process
Like any scientific discipline, data analysis follows a rigorous step-by-step process. Each stage requires different skills and know-how. To get meaningful insights, though, it’s important to understand the process as a whole. An underlying framework is invaluable for producing results that stand up to scrutiny.
In this post, we’ll explore the main steps in the data analysis process. This will cover how to define your goal, collect data, and carry out an analysis. Where applicable, we’ll also use examples and highlight a few tools to make the journey easier. When you’re done, you’ll have a much better understanding of the basics. This will help you tweak the process to fit your own needs.
Here are the steps we’ll take you through:
- Defining the question
- Collecting the data
- Cleaning the data
- Analyzing the data
- Sharing your results
- Embracing failure
On popular request, we’ve also developed a video based on this article. Scroll further along this article to watch that.
Ready? Let’s get started with step one.
1. Step one: Defining the question
The first step in any data analysis process is to define your objective. In data analytics jargon, this is sometimes called the ‘problem statement’.
Defining your objective means coming up with a hypothesis and figuring how to test it. Start by asking: What business problem am I trying to solve? While this might sound straightforward, it can be trickier than it seems. For instance, your organization’s senior management might pose an issue, such as: “Why are we losing customers?” It’s possible, though, that this doesn’t get to the core of the problem. A data analyst’s job is to understand the business and its goals in enough depth that they can frame the problem the right way.
Let’s say you work for a fictional company called TopNotch Learning. TopNotch creates custom training software for its clients. While it is excellent at securing new clients, it has much lower repeat business. As such, your question might not be, “Why are we losing customers?” but, “Which factors are negatively impacting the customer experience?” or better yet: “How can we boost customer retention while minimizing costs?”
Now you’ve defined a problem, you need to determine which sources of data will best help you solve it. This is where your business acumen comes in again. For instance, perhaps you’ve noticed that the sales process for new clients is very slick, but that the production team is inefficient. Knowing this, you could hypothesize that the sales process wins lots of new clients, but the subsequent customer experience is lacking. Could this be why customers don’t come back? Which sources of data will help you answer this question?
Tools to help define your objective
Defining your objective is mostly about soft skills, business knowledge, and lateral thinking. But you’ll also need to keep track of business metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). Monthly reports can allow you to track problem points in the business. Some KPI dashboards come with a fee, like Databox and DashThis . However, you’ll also find open-source software like Grafana , Freeboard , and Dashbuilder . These are great for producing simple dashboards, both at the beginning and the end of the data analysis process.
2. Step two: Collecting the data
Once you’ve established your objective, you’ll need to create a strategy for collecting and aggregating the appropriate data. A key part of this is determining which data you need. This might be quantitative (numeric) data, e.g. sales figures, or qualitative (descriptive) data, such as customer reviews. All data fit into one of three categories: first-party, second-party, and third-party data. Let’s explore each one.
What is first-party data?
First-party data are data that you, or your company, have directly collected from customers. It might come in the form of transactional tracking data or information from your company’s customer relationship management (CRM) system. Whatever its source, first-party data is usually structured and organized in a clear, defined way. Other sources of first-party data might include customer satisfaction surveys, focus groups, interviews, or direct observation.
What is second-party data?
To enrich your analysis, you might want to secure a secondary data source. Second-party data is the first-party data of other organizations. This might be available directly from the company or through a private marketplace. The main benefit of second-party data is that they are usually structured, and although they will be less relevant than first-party data, they also tend to be quite reliable. Examples of second-party data include website, app or social media activity, like online purchase histories, or shipping data.
What is third-party data?
Third-party data is data that has been collected and aggregated from numerous sources by a third-party organization. Often (though not always) third-party data contains a vast amount of unstructured data points (big data). Many organizations collect big data to create industry reports or to conduct market research. The research and advisory firm Gartner is a good real-world example of an organization that collects big data and sells it on to other companies. Open data repositories and government portals are also sources of third-party data .
Tools to help you collect data
Once you’ve devised a data strategy (i.e. you’ve identified which data you need, and how best to go about collecting them) there are many tools you can use to help you. One thing you’ll need, regardless of industry or area of expertise, is a data management platform (DMP). A DMP is a piece of software that allows you to identify and aggregate data from numerous sources, before manipulating them, segmenting them, and so on. There are many DMPs available. Some well-known enterprise DMPs include Salesforce DMP , SAS , and the data integration platform, Xplenty . If you want to play around, you can also try some open-source platforms like Pimcore or D:Swarm .
Want to learn more about what data analytics is and the process a data analyst follows? We cover this topic (and more) in our free introductory short course for beginners. Check out tutorial one: An introduction to data analytics .
3. Step three: Cleaning the data
Once you’ve collected your data, the next step is to get it ready for analysis. This means cleaning, or ‘scrubbing’ it, and is crucial in making sure that you’re working with high-quality data . Key data cleaning tasks include:
- Removing major errors, duplicates, and outliers —all of which are inevitable problems when aggregating data from numerous sources.
- Removing unwanted data points —extracting irrelevant observations that have no bearing on your intended analysis.
- Bringing structure to your data —general ‘housekeeping’, i.e. fixing typos or layout issues, which will help you map and manipulate your data more easily.
- Filling in major gaps —as you’re tidying up, you might notice that important data are missing. Once you’ve identified gaps, you can go about filling them.
A good data analyst will spend around 70-90% of their time cleaning their data. This might sound excessive. But focusing on the wrong data points (or analyzing erroneous data) will severely impact your results. It might even send you back to square one…so don’t rush it! You’ll find a step-by-step guide to data cleaning here . You may be interested in this introductory tutorial to data cleaning, hosted by Dr. Humera Noor Minhas.
Carrying out an exploratory analysis
Another thing many data analysts do (alongside cleaning data) is to carry out an exploratory analysis. This helps identify initial trends and characteristics, and can even refine your hypothesis. Let’s use our fictional learning company as an example again. Carrying out an exploratory analysis, perhaps you notice a correlation between how much TopNotch Learning’s clients pay and how quickly they move on to new suppliers. This might suggest that a low-quality customer experience (the assumption in your initial hypothesis) is actually less of an issue than cost. You might, therefore, take this into account.
Tools to help you clean your data
Cleaning datasets manually—especially large ones—can be daunting. Luckily, there are many tools available to streamline the process. Open-source tools, such as OpenRefine , are excellent for basic data cleaning, as well as high-level exploration. However, free tools offer limited functionality for very large datasets. Python libraries (e.g. Pandas) and some R packages are better suited for heavy data scrubbing. You will, of course, need to be familiar with the languages. Alternatively, enterprise tools are also available. For example, Data Ladder , which is one of the highest-rated data-matching tools in the industry. There are many more. Why not see which free data cleaning tools you can find to play around with?
4. Step four: Analyzing the data
Finally, you’ve cleaned your data. Now comes the fun bit—analyzing it! The type of data analysis you carry out largely depends on what your goal is. But there are many techniques available. Univariate or bivariate analysis, time-series analysis, and regression analysis are just a few you might have heard of. More important than the different types, though, is how you apply them. This depends on what insights you’re hoping to gain. Broadly speaking, all types of data analysis fit into one of the following four categories.
Descriptive analysis
Descriptive analysis identifies what has already happened . It is a common first step that companies carry out before proceeding with deeper explorations. As an example, let’s refer back to our fictional learning provider once more. TopNotch Learning might use descriptive analytics to analyze course completion rates for their customers. Or they might identify how many users access their products during a particular period. Perhaps they’ll use it to measure sales figures over the last five years. While the company might not draw firm conclusions from any of these insights, summarizing and describing the data will help them to determine how to proceed.
Learn more: What is descriptive analytics?
Diagnostic analysis
Diagnostic analytics focuses on understanding why something has happened . It is literally the diagnosis of a problem, just as a doctor uses a patient’s symptoms to diagnose a disease. Remember TopNotch Learning’s business problem? ‘Which factors are negatively impacting the customer experience?’ A diagnostic analysis would help answer this. For instance, it could help the company draw correlations between the issue (struggling to gain repeat business) and factors that might be causing it (e.g. project costs, speed of delivery, customer sector, etc.) Let’s imagine that, using diagnostic analytics, TopNotch realizes its clients in the retail sector are departing at a faster rate than other clients. This might suggest that they’re losing customers because they lack expertise in this sector. And that’s a useful insight!
Predictive analysis
Predictive analysis allows you to identify future trends based on historical data . In business, predictive analysis is commonly used to forecast future growth, for example. But it doesn’t stop there. Predictive analysis has grown increasingly sophisticated in recent years. The speedy evolution of machine learning allows organizations to make surprisingly accurate forecasts. Take the insurance industry. Insurance providers commonly use past data to predict which customer groups are more likely to get into accidents. As a result, they’ll hike up customer insurance premiums for those groups. Likewise, the retail industry often uses transaction data to predict where future trends lie, or to determine seasonal buying habits to inform their strategies. These are just a few simple examples, but the untapped potential of predictive analysis is pretty compelling.
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis allows you to make recommendations for the future. This is the final step in the analytics part of the process. It’s also the most complex. This is because it incorporates aspects of all the other analyses we’ve described. A great example of prescriptive analytics is the algorithms that guide Google’s self-driving cars. Every second, these algorithms make countless decisions based on past and present data, ensuring a smooth, safe ride. Prescriptive analytics also helps companies decide on new products or areas of business to invest in.
Learn more: What are the different types of data analysis?
5. Step five: Sharing your results
You’ve finished carrying out your analyses. You have your insights. The final step of the data analytics process is to share these insights with the wider world (or at least with your organization’s stakeholders!) This is more complex than simply sharing the raw results of your work—it involves interpreting the outcomes, and presenting them in a manner that’s digestible for all types of audiences. Since you’ll often present information to decision-makers, it’s very important that the insights you present are 100% clear and unambiguous. For this reason, data analysts commonly use reports, dashboards, and interactive visualizations to support their findings.
How you interpret and present results will often influence the direction of a business. Depending on what you share, your organization might decide to restructure, to launch a high-risk product, or even to close an entire division. That’s why it’s very important to provide all the evidence that you’ve gathered, and not to cherry-pick data. Ensuring that you cover everything in a clear, concise way will prove that your conclusions are scientifically sound and based on the facts. On the flip side, it’s important to highlight any gaps in the data or to flag any insights that might be open to interpretation. Honest communication is the most important part of the process. It will help the business, while also helping you to excel at your job!
Tools for interpreting and sharing your findings
There are tons of data visualization tools available, suited to different experience levels. Popular tools requiring little or no coding skills include Google Charts , Tableau , Datawrapper , and Infogram . If you’re familiar with Python and R, there are also many data visualization libraries and packages available. For instance, check out the Python libraries Plotly , Seaborn , and Matplotlib . Whichever data visualization tools you use, make sure you polish up your presentation skills, too. Remember: Visualization is great, but communication is key!
You can learn more about storytelling with data in this free, hands-on tutorial . We show you how to craft a compelling narrative for a real dataset, resulting in a presentation to share with key stakeholders. This is an excellent insight into what it’s really like to work as a data analyst!
6. Step six: Embrace your failures
The last ‘step’ in the data analytics process is to embrace your failures. The path we’ve described above is more of an iterative process than a one-way street. Data analytics is inherently messy, and the process you follow will be different for every project. For instance, while cleaning data, you might spot patterns that spark a whole new set of questions. This could send you back to step one (to redefine your objective). Equally, an exploratory analysis might highlight a set of data points you’d never considered using before. Or maybe you find that the results of your core analyses are misleading or erroneous. This might be caused by mistakes in the data, or human error earlier in the process.
While these pitfalls can feel like failures, don’t be disheartened if they happen. Data analysis is inherently chaotic, and mistakes occur. What’s important is to hone your ability to spot and rectify errors. If data analytics was straightforward, it might be easier, but it certainly wouldn’t be as interesting. Use the steps we’ve outlined as a framework, stay open-minded, and be creative. If you lose your way, you can refer back to the process to keep yourself on track.
In this post, we’ve covered the main steps of the data analytics process. These core steps can be amended, re-ordered and re-used as you deem fit, but they underpin every data analyst’s work:
- Define the question —What business problem are you trying to solve? Frame it as a question to help you focus on finding a clear answer.
- Collect data —Create a strategy for collecting data. Which data sources are most likely to help you solve your business problem?
- Clean the data —Explore, scrub, tidy, de-dupe, and structure your data as needed. Do whatever you have to! But don’t rush…take your time!
- Analyze the data —Carry out various analyses to obtain insights. Focus on the four types of data analysis: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive.
- Share your results —How best can you share your insights and recommendations? A combination of visualization tools and communication is key.
- Embrace your mistakes —Mistakes happen. Learn from them. This is what transforms a good data analyst into a great one.
What next? From here, we strongly encourage you to explore the topic on your own. Get creative with the steps in the data analysis process, and see what tools you can find. As long as you stick to the core principles we’ve described, you can create a tailored technique that works for you.
To learn more, check out our free, 5-day data analytics short course . You might also be interested in the following:
- These are the top 9 data analytics tools
- 10 great places to find free datasets for your next project
- How to build a data analytics portfolio

IMAGES
VIDEO