- Tìm kiếm thành viên Tìm kiếm thành viên và những người bạn đang theo dõi
- Tìm kiếm câu trả lời Tìm kiếm câu trả lời cho câu hỏi của bạn
- Giáo dục công dân
- Tiếng anh thí điểm
- Tự nhiên và xã hội
- Lịch sử và Địa lý
- Khoa học tự nhiên
- Hoạt động trải nghiệm
- Hoạt động trải nghiệm, hướng nghiệp
- Giáo dục kinh tế và pháp luật
Chủ đề / Chương

Luyện tập tổng hợp
- Trắc nghiệm
- Giải bài tập SGK
- Đóng góp lý thuyết

- Nguyễn Hoàng Ân
1/"Do your homework, son", said the mother.
=>The mother told
2/No other members in the class are as tall as Lucie is.
=>Lucie is the
3/When was the last time you watched an action movie?
=>When did

1 The mother told her son to do his homework
2 Lucie is the tallest member in the class
3 When did you last watch an action movie?

=>The mother told her son if he did his homwork.
=>Lucie is the tallest in the class.
=>When did you last watch an action movie?

- Yến Chi Nguyễn
1. The weather is fine , but Thu is still bringing a raincoat with her.
=> Although__________________
2. "Do your homework , son", said the mother.
=> The mother told___________
3. No other members in thr class are as tall as Lucie is.
=> Lucie is the_______________
4. When was the last time you watched an action movie?
=> When did________________
4. "What time does your class start?" she asked her son.
-> She asked__________________
II. Imagine that you have recently visited a place of interest . In about 80 - 100 words, write a paragraph about your trip. Your paragraph may include:
When and where you went
How you got there
Who you went with
What the place was like
What you did there
Your impression of the place

- nguyễn khôi nguyên
1. We should teach young children to care for the environment.
" I suggest young children ...................................................................................
2. We are eager to make a trip to the countryside this July.
" We are looking .................................................................................................
3. City life is not as peaceful as country life.
" Country life is ....................................................................................................
4. Drivers and passengers must fasten the seat belt when travelling in cars.
" It is compulsory for .........................................................................................
5. The boy hasn't visited his grandparents for two months.
" The boy last .......................................................................................................
6. He can’t drive because he’s very young. ( S + to be + tính từ + enough + To V )
" He’s not ............................................................................................................
7. The Prime Minister will open three more new schools in the town next autumn.
" Three more new schools will ...........................................................................
8. Why don’t you make posters on energy saving?
" I suggest that you ............................................................................................
9. “We are keen on setting out to sea again," said the fishermen.
" The fishermen said that ...................................................................................
10. No other members in the class are as tall as Lucie is.
" Lucie is the ......................................................................................................

- Nguyen Huynh
1)When was the last time you watched an action movie?
When____________________________________________________________
2)They keep a large collection of books in the school library.
A large collection of books ____________________________________________
3)They’ll take you to the English Lake District.
You’ll ____________________________________________________________
4) His friend found the most fashionable shops in Bond Street.
The most fashionable shops __________________________________________
5) The working people have considered May Day a great holiday.
May Day _________________________________________________________
6) They could see smoke rising up from cottages.
Smoke____________________________________________________________7) The farmer was feeding the ducks and hens when we came.
The ducks and hens_________________________________________________
8) Now my sister is reading picture books
Picture books______________________________________________________
9) They don’t use cars and trucks to carry food to market.
Cars and trucks_____________________________________________________ 10) It's impossible to solve this problem.
This problem______________________________________________________

1. This is the first time I _______ the experiment on plants. (have done, do, would do, did)
2. I am delighted (that, to, in order to, so that) you passed your exam.
3. I am very pleased ( when, that, for, how) my students are very intelligent.
4. My mother asked me where I had gone ( yesterday, the day before, today, that day )
5. Remember to write english as.................as possible ( many, much, more, most )

- Trần Gia Hân
question1:read.then answer the question below
the second sunday in may is mother's day . It is a public h dayoliday in both britain and America. on that day children send cards to their mother's.they give their mother flowers or can sweets as presents. father and children do the cooking so that mother'scan have a rest.
In the USA. Mother's day started in 1860s there was a smail town called prunty town in the middle of the USA.people to make friends whit each other again. so the started
"Mother's friend ship day".on that day,she visited all the other mother in the town and said "let us bes friend with each orther again''
1)when is mother's day?
2)what do children send on mother''s day?
3)which town was mother's day born?

Test 1.VI 1. The beauty of Dalat made an impression on the musicianm so he composed a lot of songs there. -> The musician _____________________________,so a lot __________________ 2. The last time we paid a visit to this school was when we left for the United States. -> We last visited____________________ 3. Stop playing ! It's high time you started the revision to the first English test. -> I wish that you __________________ 4. No other city in Malaysia is as busy as Kuala Lumpur, the capital city. -> Kuala Lumpur, the capital city, ___________________________

Peported speech:
1. ‘I’ve no idea what the time is but I’ll dial 1080 and find out’ said his daughter. 2. he said, ‘ my wife has just been made a judge.’ 3. ‘I’ll come with you as soon as I am ready,’ she replied.. 4. ‘I have a German lesson this afternoon and I haven’t done my homework yet,’ said the boy. 5. ‘If you let the iron get too hot you will scorch your clothes.’ I warned her. 6. ‘You haven’t given me quite enough. The bill is for $16 and you have paid me only $10’ he pointed out. 7. ‘ Do you play the guitar?’ said Peter. 8. ‘Will you have time to play regularly?’ he said . 9. ‘Did you play for your school team?’ said Bill. 10. “Put your pistol on the table,’ said the director. 11. ‘ Please book me a seat in a non- smoker,’ said the traveller. 12. ‘Don’t forget your sandwiches,’ said his mother. 13. ‘ Don’t go near the water, children,’ she said. 14. ‘Search the house,’ said the police. 15. ‘ Don’t make mountains out of molehills,’ he said. 16. ‘ Put down that gun. It is loaded,’ she ordered. 17. ‘ Can the children get dinner at school, John?’ said Janes. 18. ‘ Is there a bus- stop in your town, James ?’ I wanted to know. 19. ‘ How often does it meet?’ George said to her. 20. ‘ Were your own boys happy here?’ Linda said to Maria. 21. ‘ Open the safe!’ The raiders order the clerk. 22. ‘ Please do as I say’ he begged me. 23. ‘ Don’t make too much noise, children,’ said the mother. 24. ‘ You’d better slow down. There’s a speed limit here,’ she said to me. ( advise) 25. ‘ I could not get into the house because I had lost my keys, so I had to break the door,’ said he. 26. ‘ The mirror is there so that you can see your self when you are dancing,’ she told him. 27. ‘ I wrote to him the day before yesterday. I wonder why he hasn’t rung up,’ she said. 28. ‘ My horse might win,’ said the owner. 29. ‘ You needn’t speak to my sister,’ David said to Janes. 30. ‘ If I were taller, I would climb the door,’ he said. 31. ‘ What happened to you, Linda ?’ I asked. 32. ‘ How long has your son learnt English?,’ I said to Mrs. Kent. 33. ‘ When will you go back?,’ said Susan. 34. ‘ Who have you seen at the meeting?’ We asked the workers. 35. ‘ Where were you last night ?’ she said to Janes 36. ‘ What will you buy the day after tomorrow, Helen?’ said the mother.

- zZz Nguyễn zZz
1, “ How did you know the results “
2, “ When can I see the director?”
3, “ Could I have a cup of coffee?”
=> She asked me ....
4, “My friend said “Are you going to leave tomorrow?”
=> My friend asked me ......
5, Have you done your homework?” said my mother
=> My mother asked me ....
6, “ There is an accident “ said the policeman
=> The policeman .....

- Đoàn Quỳnh Trang
True or False
Today,when English is one of the major languages in the world, it requires an effort of the imagination to realize that this is relatively recent thing-that in Shakespeare's time,for example,only a few million people spoke,and the language was not thought to be very important by the other nations of Europe,and was unknown to the rest of the world.
English has become a world language because of its establishment as a mother tongue outside England,in all the continents of the world. This exporting of English began in the seventeenth century,with the first settlements in the United States,assisted by massive immigration in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries,that has given the English language its present standing in the world.
1. English was spoken by a few million people in Shakespeare's time.......
2. It is considered as a mother language outside England.......
3. English was spoken in North America in the seventeenth century.........
4. Most of the immigration in the USA do not speak English.............
Khoá học trên OLM (olm.vn)
- Ngữ văn lớp 9
- Tiếng Anh lớp 9
- Vật lý lớp 9
- Hoá học lớp 9
- Sinh học lớp 9
- Lịch sử lớp 9
- Địa lý lớp 9
English Grammar – Direct and Indirect Speech exercises Exercises with Answers
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises – Writing and communicating effectively require an understanding of direct and indirect speech . Indirect speech expresses the meaning of what was said without utilizing the speaker’s precise words, whereas direct speech quotes someone verbatim. Both forms are important to spoken and written language because they fulfill different purposes and adhere to different standards. We’ll look at the guidelines, purposes, and practice of direct and indirect speech exercises in this post to help you improve your understanding and application of these language tools.
What is Direct and Indirect Speech?
Functions of direct and indirect speech, rules for direct and indirect speech.
- Exercise 1- Identify Direct or Indirect Speech
- Exercise 2- Change the Sentences
- Common Challenges and Pitfalls
- Exercise 3 – Multiple Choice Questions
Direct speech, often enclosed within quotation marks, is a verbatim repetition of someone else’s words. It allows for the exact words spoken by a person to be conveyed. If someone were to directly state, “I love chocolate,” for example, it would be quoted as “She said, ‘I love chocolate.'”
On the other hand, indirect speech—also referred to as reported speech—transmits the idea or content of what was said rather than paraphrasing the speaker’s precise words. Pronouns, tenses, and other aspects typically need to be changed to make the sentence make sense within the reporting speaker’s context. For example, “She said that she loved chocolate” is an indirect report of the same statement. Without having to use exact quotations from the speaker, indirect speech summaries or paraphrases what has been stated.
Direct Speech Functions:
Quoting Verbatim : Direct speech allows for the exact words of the speaker to be quoted, preserving their original expression and tone.
Emphasis : Direct speech can emphasize specific words or phrases, as it directly presents the speaker’s words without any alteration.
Clarity: It provides clarity about who said what, especially in dialogue-heavy texts or when attributing specific statements to individuals.
Indirect Speech Functions:
Summarizing: Indirect speech summaries what someone said without quoting them verbatim, condensing the information while maintaining its meaning.
Integration: Indirect speech integrates the reported information into the speaker’s own sentence, making it flow more smoothly within the context.
Narrative Distance: It can create narrative distance, allowing the reporting speaker to distance themselves from the reported speech, which can be useful for maintaining a consistent narrative voice or perspective.
Rule 1: Reporting Verb
It is implied that the reported speech also occurred in the past when the reporting verb—the verb that begins the reported speech—is in the past tense. As a result, in indirect speech, all present tenses are converted to their corresponding past tenses from direct speech.
For example:
Direct: She said, “I am happy.”
Indirect: She said (that) she was happy.
However, the tenses do not alter in indirect speech if the quotes’ contents convey universal truths or routine behaviors.
The tenses of the direct speech in the indirect speech stay the same whether the reporting verb is in the present tense or the future tense.
Rule 2: Tense Changes
Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect.
Direct: “I have been to Boston,” she told me.
Indirect: She told me that she had been to Boston.
Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous.
Direct: “I am playing the guitar,” she explained.
Indirect: She explained that she was playing the guitar.
Direct: He said, “She has finished her homework.”
Indirect: He said that she had finished her homework.
Simple Present changes to Simple Past.
Direct: “I am unwell,” she said.
Indirect: She said that she was unwell.
Rule 3: Past and Future Tenses
Simple Past changes to Past Perfect.
Direct: She said, “Irvin arrived on Sunday.”
Indirect: She said that Irvin had arrived on Sunday.
Past Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous.
Direct: “We were playing basketball,” they told me.
Indirect: They told me that they had been playing basketball.
Future changes to Present Conditional.
Direct: She said, “I will be in Scotland tomorrow.”
Indirect: She said that she would be in Scotland the next day.
Future Continuous changes to Conditional Continuous.
Direct: He said, “I’ll be disposing of the old computer next Tuesday.”
Indirect: He said that he would be disposing of the old computer the following Tuesday.
Rule 4: Interrogative Sentences
When an interrogative word (what, where, or when) opens a sentence in direct speech, there is no need for a conjunction in indirect speech because the question word functions as a joining clause on its own.
Direct: “Where do you live?” asked the boy.
Indirect: The boy enquired where I lived.
“If” or “whether” should be used as the connecting clause in a direct speech sentence that starts with an auxiliary verb or helpful verb.
Direct: She said, “Will you come for the party?”
Indirect: She asked whether we would come for the party.
Reporting verbs such as “said/said to” change to “enquired”, “asked”, or “demanded”.
Direct: He said to me, “What are you wearing?”
Indirect: He asked me what I was wearing.
Rule 5: Changes in Modals
Modals change while converting direct speech to indirect speech:
“Can” becomes “could”.
“May” becomes “might”.
“Must” becomes “had to” or “would have to”.
For example:Direct: She said, “She can dance.”
Indirect: She said that she could dance.
However, modals such as “could”, “would”, “should”, “might”, and “ought to” remain unchanged in indirect speech.
Rule 6: Pronouns
The first person in direct speech changes according to the subject of the speech.
The second person in direct speech changes according to the object of the reporting speech. The third person in direct speech remains unchanged.
Direct: He said, “I am in class Twelfth.”
Indirect: He says that he was in class Twelfth.
Rule 7: Requests, Commands, Wishes, Exclamations
Indirect Speech is supported by some verbs like requested, ordered, suggested, and advised. Forbid-forbade is used for negative sentences. Therefore, the imperative mood in the direct speech changes into the Infinitive in indirect speech. For example,
Direct: She said to her, “Please complete it.”
Indirect: She requested her to complete it.
In exclamatory sentences that express grief, sorrow, happiness, applause, interjections are removed and the sentence is changed to an assertive sentence.For example,
Direct: She said, “Alas! I am undone.”
Indirect: She exclaimed sadly that she was broke.
Rule 8: Punctuations
In direct speech, the words actually spoken should be in (‘’) quotes and always begin with a capital letter.Example: She said, “I am the best.”
Full stop, comma, exclamation or question mark, are placed inside the closing inverted commas. Example: They asked, “Can we sing with you?”
If direct speech comes after the information about who is speaking, a comma is used to introduce the speech, placed before the first inverted comma. For example: He shouted, “Shut up!”
Rule 9: Change of Time
Words expressing nearness in time or place change to express distance.
Time expressions remain unchanged if the reporting verb is in the present or future tense.For example:
Direct: He said, “His girlfriend came yesterday.”
Indirect: He said that his girlfriend had come the day before.
Exercise Set 1: Identity Direct or Indirect Speech
a. Identify whether the following sentences are in direct or indirect speech:-
- “We have been waiting here for hours,” they complained.
- She said that she was going to Paris the following month.
- “She plays the piano beautifully,” he remarked.
- “I want to be a doctor when I grow up,” she said.
- “I have lived here for ten years,” he stated.
- He stated that he had finished reading that book the previous week.
- “He can speak three languages fluently,” they informed us.
- He mentioned that he had a busy schedule that week.
- She suggested that they should have dinner together.
- “I can’t attend the meeting tomorrow,” he explained.
- They explained that they had finished the project the previous night.
- I said to her, “When do you do your homework.”
- “I might visit Spain next summer,” he mentioned.
- We asked him if he was ill.
- “I lost my keys yesterday,” he admitted.
- She mentioned that she would buy some groceries on her way home.
- She assured that she would be ready in five minutes.
- He said, “May you live long.”
- “I don’t like horror movies,” she confessed.
- She requested to pass her the salt.
- He reminded me that the train left at 8 AM.
- She declared that she was attending the conference the following month.
- “Please pass the message to Sarah,” Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech are requested.
- “We should submit the report by Friday,” she suggested.
- She informed us that the movie started at 7 PM.
- Direct Speech
- Indirect Speech
- Direct Speech
- Indirect Speech
b. In the following exercise, the given sentences are either in direct or indirect speech. Convert them into the opposite form of speech:
- Sita said that she shall come to see the pictures.
- I said to the teacher, “I am working hard.”
- The traveler said to me, “Can you tell me the way to the nearest inn?”
- The teacher told me that I had not done my homework
- Hari asked his father if he could go to the pictures that night
- He said, “What a great misery!”
- I said to the teacher, “I am sorry”.
- The merchant exclaimed with sorrow that he was ruined.
- Ram will say that he saw his teacher in the park.
- He said to me, “Trust in God and do the right.”
- He said that the man should come
- He said to me, “You played very well yesterday.”
- He requested him to let him study.
- She exclaimed that she loved chocolate ice cream.
- I said that I had been ill since Monday.
- He reminded us that the concert started at 7 PM.
- I asked her if she wanted my help
18.The boy requested his papa to forgive him that time.
19.“She is writing a novel,” he mentioned.
- He said, “She lives in Amritsar.”
- Mohan requested Rajan to go to the station with him.
- Prem said to Pran, “Were you present at the meeting?”
- The teacher said to the boy, “Shut the door.”
- The spectators said, “Bravo well played, Mohan!”
- He said, “The train will be late.”
- Sita said, “I shall come to see the picture.”
- I told the teacher I was working hard.
- The traveler asked me if I could tell him the way to the nearest inn.
- The teacher said to me, “You have not done your homework.
- Hari said to the father, “May I go to the pictures tonight?”
- He exclaimed that it was a great misery.
- I told the teacher I was sorry
- The merchant said, “Alas, I am ruined?”
- Ram will say, “I saw my teacher in the park.”
- He advised me to trust in God and do the right.
- He said, “The man shall come.”
- He told me that I had played very well the previous day.
- He said to me, “Let me study.”
- “I love chocolate ice cream,” she exclaimed.
- I said, “I have been ill since Monday.”
- “The concert starts at 7 PM,” he reminded us.
- I said to her, “Do you want my help?”
- The boy said, “Papa! Forgive me this time.”
- He mentioned that she was writing a novel.
- He said that she lives in Amritsar.
- Mohan said to Rajan, “Please go to the station with me.”
- Prem asked Pran if he had been present at the meeting.
- The teacher asked the boy to shut the door.
- The spectators applauded Mohan saying that he had played well.
- He said that the train will be late.
Exercise Set 2: Change the Sentences
a. Change the following Direct speech sentences to Indirect speech:
- Sahil said to me, “When are you returning? “
- “What is the time?” the stranger asked Ashna.
- The professor said to Shipra, “Why are you quiet? “
- Dhronacharya said to Arjun, “Aim at the fish’s eye. “
- “Bring the witness,” said the judge.
- “Ring the Fire-brigade,” said the woman.
- Bobby said to me, “I must do the homework.”
- My brother told me, “You were right.”
- Sharma told me, “Please sit here till I come back.”
- The coach said, “Bravo! You have performed excellently.”
- Raju said, “Alas! My kitty got injured.”
- Romi said, “I may come to the seminar”
- Bunny said to Sunny, “Do you see me?”
- The little kid said, “Let me sit here.”
- Grandpa said, “May God bless you.”
- “Call the first convict,” said the jury.
- “Call the ambulance,” said the man.
- Bruce said to me, “I shall do the work.”
- My mother said to me, “You were wrong.”
- Mr Richard said to me, “Please wait here till I return.”
- The captain said to me, “Bravo! You have played well.”
- Raj said, “Alas! My pet died.”
- Ruchi said, “I may go there.”
- Bucky said to Steve, “Do you hear me?”
- The boy said, “Let me come in.”
- Sahil asked me when I was returning.
- The stranger asked Ashna what the time was.
- The professor asked Shipra Why she was quiet.
- Dhronacharya ordered Arjuna to aim at the fish’s eye.
- The judge ordered to bring the witness.
- The woman urged to ring the fire brigade.
- Bobby said to me he had to do the homework.
- My brother told me that I was right.
- Sharma requested me to sit here till she comes back.
- The coach applauded me by saying that I had performed excellently.
- Raju told sadly that his kitty got injured.
- Romi said that she might come to the seminar.
- Bunny asked Sunny if he saw him.
- The little kid requested to let him sit here.
- Grandpa blessed me that God might bless me.
- The jury ordered to call the first convict.
- The man urged to call the ambulance.
- Bruce said to me he would do the work.
- My mother told me that I was wrong.
- Mr Richard requested me to wait there till he returned.
- The captain applauded me, saying that I had played well.
- Raj exclaimed sadly that his pet died.
- Ruchi said that she might go there.
- Bucky asked Steve if he heard him.
- The boy asked to let him come in.
b. Change the following Indirect speech sentences to Direct speech:
- Sarah said that she loved pizza.
- David told me that he was going to the movies that night.
- Emily asked me to pass her the salt.
- Tom said that he had a big test the next day.
- Jessica said that she was so tired.
- Mary exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- John said that he didn’t understand.
- The teacher asked the students to be quiet.
- Peter said that he wasn’t feeling well.
- Rachel told me that she was so happy to see me.
- Amy asked me to help her with her homework.
- Ben said that he was hungry.
- Charlie couldn’t believe that he had won the lottery.
- Diana apologized for being late.
- Emily said that she thought it was going to rain.
- Fred said that he was exhausted.
- Harry hoped that I had had a nice birthday.
- Isabella said that she was so excited to go on vacation.
- Jack said that he was really proud of me.
- She said that she was studying for her exam.
- He said that they would go to the beach.
- She exclaimed that she didn’t like seafood.
- He told me that they were coming to visit us the next day.
- She mentioned that she had finished her homework.
- He observed that it was raining heavily.
- Sarah said, “I love pizza.”
- David said, “I’m going to the movies tonight.”
- Emily said, “Can you pass me the salt?”
- Tom said, “I have a big test tomorrow.”
- Jessica said, “I’m so tired.”
- Mary exclaimed, “What a beautiful day!”
- John said, “I don’t understand.”
- The teacher said, “Please be quiet.”
- Peter said, “I’m not feeling well.”
- Rachel said, “I’m so happy to see you!”
- Amy said, “Please help me with my homework.”
- Ben said, “I’m hungry.”
- Charlie said, “I can’t believe I won the lottery!”
- Diana said, “I’m so sorry for being late.”
- Emily said, “I think it’s going to rain.”
- Fred said, “I’m exhausted.”
- Harry said, “I hope you had a nice birthday.”
- Isabella said, “I’m really excited to go on vacation!”
- Jack said, “I’m really proud of you.”
- She said, “I am studying for my exam.”
- He said, “We will go to the beach.”
- She exclaimed, “I don’t like seafood.”
- He said, “They are coming to visit us tomorrow.”
- She mentioned, “I have finished my homework.”
- He observed, “It’s raining heavily.”
Common Challenges and Pitfalls:
a. Maintaining Accuracy in Reporting:
Making sure the words or intentions of the original speaker are accurately reported is one challenge. There is a chance that the speaker’s message will be misunderstood or misrepresented when direct speech is converted to indirect speech, particularly if the original remark was unclear or complex. If not managed appropriately, this could result in miscommunications or misunderstandings.
b. Maintaining Clarity and Coherence:
Keeping the reported speech coherent and clear presents another difficulty, particularly when handling complicated phrases or concepts. It’s imperative to make sure the indirect speech both effortlessly integrates into the surrounding context and appropriately communicates the original statement’s intended meaning. A reported speech’s ambiguity or odd wording might mislead readers or listeners and lessen the communication’s overall impact.
Exercise Set 3: Multiple Choice Questions
a. Given below are questions sentences in Direct/Indirect Speech along with four options. You are required to read the Direct and Indirect Speech questions carefully and select the option that expresses the same sentence in the reverse speech i.e., Indirect/Direct Speech:
1. His father says “Honesty is the best policy” (a) His father called honesty is the best policy (b) His father asked if honesty is the best policy (c) His father exclaimed that honesty is the best policy (d) His father says that honesty is the best policy
2. Rama said, ‘I am very busy now.’ (a) Rama said that he was very busy then (b) Rama said that he would be very busy now, (c) Rama said that he is very busy then. (d) Rama said that he is very busy now.
3. He said to him,’ Isn’t your name Khalid?’ (a) He said that his name was Khalid (b) He inquired whether his name was not Khalid (c) He asked is his name was not Khalid (d) He asked why his name was Khalid
4. All said to the beggar, ‘I know you very well’. (a) Ali recognized the beggar (b) Ali told the beggar that he knew him very well (c) Beggar knew Ali too (d) Beggar was recognized by Ali
5. He said, “Yes, I’ll come and see you.” (a) He accepted that he will come and see me (b) He said that he will come and see me (c) He agreed that he will come and see me (d) He said that he would come and see me
6. Ram remarked “What a wonderful day!” (a) Ram exclaimed that it was a wonderful day (b) Ram asked if it was a wonderful day (c) Ram said what a wonderful day (d) Ram asked what a wonderful day
7. The monk said to the followers “Anger kills Intellect” (a) The monk said to the followers anger kills intellect (b) The monk told the followers that anger kills intellect (c) The monk asked followers if anger kills intellect (d) The monk told the followers that anger has killed intellect
8. The poor beggar said, “O God, have mercy on my soul”. (a) The poor beggar prayed to God to have mercy on his soul. (b) The poor beggar, invoking God, implored him to have mercy on his soul. (c) The poor beggar exclaimed that God, have mercy on his soul. (d) The poor beggar told God to have mercy on his soul.
9. John’s father reminded him to take his umbrella. (a) John’s father said, “Remember your umbrella John ?” (b) “Here, is your umbrella John,” said his father. (c) “Are you going to take your umbrella or not ?” said John to his father. (d) “Don’t forget to take your umbrella, John,” said his father.
10. He swore in the name of God that he was ignorant of the matter. (a) He said, “I’m ignorant by God (b) He declared, “God knows I was ignorant of the matter.” (c) He said, “By God ! I’m ignorant of the matter.” (d) He said he was ignorant of God
11. Raj said, “I’m teaching English online” (a) Raj told I am teaching English online (b) Raj asked me if I was teaching English online (c) Raj said he was teaching English online (d) Raj ordered that I am teaching English online
12. The father warned his son that he should be beware of him. (a) The father warned his son, “Beware of me!” (b) The father warned his son, “Watch that chap!” (c) The father warned his son, “Be careful about him.” (d) The father warned his son, “Don’t fall into the trap.”
13. He said to me, “I expect you to attend the function.” (a) He told me that he had expected me to attend the function (b) He told me that he expected me to attended the function (c) He told me that he expected me to have attended the function (d) He told me that he expected me to attend the function
14. John asked, “How long will it take to travel from Germany to South Africa?” (a) John asked how long it will take to travel from Germany to South Africa (b) John asked how long would it take to travel from Germany to South Africa (c) John asked how long it should take to travel from Germany to South Africa (d) John asking how long must it take to travel from Germany to South Africa
15. The designer said to her, “Will you have the dress ready by tomorrow evening?” (a) The designer asked her if she would have the dress ready by next evening. (b) The designer asked her that she would have the dress ready by next evening. (c) The designer asked her that if she will like to have the dress by next evening. (d) The designer asked her that she will have the suit ready by next evening.
16. They said, “Let us come in”. (a) They told that let them be allowed to come in. (b) They requested that they might be allowed to come in. (c) They said that if they are allowed to come in. (d) They requested me to let them come in.
17. Reshma said to Priya, “Why are you sketching on the wall?” (a) Reshma asked Priya why was she sketching on the wall. (b) Reshma asked Priya why had she been sketching on the wall. (c) Reshma asked Priya that why is she sketching on the wall. (d) Reshma asked Priya why she was sketching on the wall.
18.Jacob fell as he’d have wished’, the father said. (a) The father said that Jacob has fallen as he would have wished. (b) The father said that Jacob had fallen as he would have wished. (c) The father said that Jacob had fallen as he had wished. (d) The father said that Jacob had been fallen as he would have been wished.
19. Arya said to Tara, “David will leave for his mother’s place tomorrow.” (a) Arya told Tara that David will leave for his mother’s place tomorrow. (b) Arya told Tara that David will leave for his mother’s place the next day. (c) Arya told Tara that David would leave for his mother’s place the next day. (d) Arya informed Tara that David would be leaving for his mother’s place the next day.
20. The Professor said that nobody could solve the problem. (a) The Professor said, ‘Nobody can solve the problem’. (b) The Professor said, ’Nobody could solve the problem’. (c) The Professor exclaimed, ‘Nobody could solve the problem’. (d) The Professor exclaimed, ‘Nobody can solve the problem?’.
21. She said, “Why didn’t you send a friend request to me?” (a) She asked me why had I not sent a friend request to her. (b) She enquired why I had not sent a friend request to her. (c) She enquired why I did not send a friend request to her. (d) She questioned why I had not sent a friend request to her.
22. The judge commanded them to call the accused in the court. (a) The Judge said, ‘Call the accused in the court’. (b) The Judge ordered, ‘Call the accused in the court’. (c) The Judge command, ‘Call the accused in the court’. (d) The Judge said to them, ‘Call the accused in the court’.
23. The instructor asked Ronny if he was ready for the race. (a) ‘Ronny, are you ready for the race?’, the instructor asked. (b) ‘Are you ready for the race Ronny?’, the instructor asked. (c) ‘Ronny, ready for race?’ the instructor said. (d) ‘Ronny, are you ready for the race?’, said the instructor.
24. Manager said to Shekher, “Why didn’t you attend the meeting yesterday?” (a) The manager enquired Shekhar why did not he attend the meeting the day before. (b) The manager asked Shekhar why he did not attend the meeting the previous day. (c) The manager asked Shekhar why he had not attended the meeting the day before. (d) The manager enquired Shekhar that why didn’t he attend the meeting yesterday.
25. Kiara said that she had been planning for that for a while. (a) Kiara said, “I had a plan for this for a while.” (b) Kiara said, “I have planned for this for a while.” (c) Kiara said, “I have been planning for this for a while.” (d) Kiara said, “I planned this for a while.”
- (d) His father says that honesty is the best policy
- (a) Rama said that he was very busy then
- (b) He inquired whether his name was not Khalid
- (b) Ali told the beggar that he knew him very well
- (d) He said that he would come and see me
- (a) Ram exclaimed that it was a wonderful day
- (b) The monk told the followers that anger kills intellect
- (a) The poor beggar prayed to God to have mercy on his soul.
- (d) “Don’t forget to take your umbrella, John,” said his father.
- (c) He said, “By God ! I’m ignorant of the matter.”
- (c) Raj said he was teaching English online
- (a) The father warned his son, “Beware of me!”
- (a) He told me that he had expected me to attend the function
- (b) John asked how long would it take to travel from Germany to South Africa
- (a) The designer asked her if she would have the dress ready by next evening.
- (b) They requested that they might be allowed to come in.
- (d) Reshma asked Priya why she was sketching on the wall.
- (b) The father said that Jacob had fallen as he would have wished.
- (c) Arya told Tara that David would leave for his mother’s place the next day.
- (a) The Professor said, ‘Nobody can solve the problem’.
- (b) She enquired why I had not sent a friend request to her.
- (d) The Judge said to them, ‘Call the accused in the court’.
- (a) ‘Ronny, are you ready for the race?’, the instructor asked.
- (c) The manager asked Shekhar why he had not attended the meeting the day before.
25.(c) Kiara said, “I have been planning for this for a while.”
b. Change the following dialogues in indirect speech of narration:
1. Mother: Where were you? Daughter: I was on the terrace playing. Mother: Please do not go without prior permission. Daughter: This was the first time ever that I went on the terrace. Mother: Remember, do not go there alone.
Answer: Mother asked her daughter where she had been. The daughter replied that she had been on the terrace playing. The mother then requested her not to go without prior permission. The daughter apologized saying that that had been the first time ever that she had gone on the terrace. The mother warned her not to go there alone.
2. Master: How are you feeling now? Worker: I am feeling better but I am not completely fine. Master: Do you need more rest? Worker: It is okay. I will report tomorrow
Answer: Master asked his worker how he was feeling then. The worker replied that he was feeling better but was not completely fine. The master further asked him if he needed more rest. The worker replied that that was okay and that he would report the next day
3. Rajesh: Where are you going, Rohan? Rohan: I am going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh: Do you worship everyday and go to the temple? Rohan: Yes, I go to the temple everyday to worship Lord Shiva.
Answer: Rajesh asked Rohan where he was going. Rohan replied that he was going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh then asked him if he worshiped every day and went to the temple. Rohan replied in the affirmative and said that he went to the temple every day to worship Lord Shiva.
4. Teacher: I want all students to quietly do the work. Students: Will you allow us to go for games after this? Teacher: First, all of you have to finish your work. Students: We promise that we will finish our work first
Answer. Teacher instructed the students that she wanted them to quietly do the work. The students asked if she would allow them to go for games after that. The teacher insisted that first, all of them had to finish their work. The students then promised her that they would finish their work first
5. Father. Why did you go to the market today? Son: I had to buy some material to do my project. Father: Who gave you the project? Son: My science teacher gave the project. Father: Do you need any money for it?
Answer: Father asked his son why he had gone to the market that day. Son replied that he had to buy some material to do his project. Father then asked him who had given the project. Son replied that his science teacher had given the project. Father then asked his son if he needed any money for that.
Conclusion:
In summary, the ability to comprehend and employ direct and indirect speech effectively is essential for both written and spoken communication. While indirect speech summarizes or paraphrases what was said in order to convey the content without utilizing the speaker’s exact words, direct speech permits the quotation of a speaker’s exact words while maintaining the speaker’s original expression and tone.
These abilities can be strengthened by practicing tasks like differentiating between direct and indirect communication, recognizing phrases that use each type of speech, and responding to multiple-choice questions. But it’s important to be aware of typical difficulties like reporting with accuracy, making sure that information is clear and coherent, and following grammar rules.
Exercises of Tenses
Exercises on Prepositions
Exercises of Articles
Exercises of Simple Present Tense
Exercise of Adjectives
Exercise of Conjunctions
Exercise of Clauses
Exercises of Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Exercises of Determiners
Exercises of Gerunds
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
English Grammar
All English Grammar Topics, Exercises, examples, MCQ Tests
English Grammar Examples
Active and Passive Voice Definition, Rules, Exercise, and Example Sentences
Countable and Uncountable Nouns Meaning, Definition, Difference and Examples
Direct and Indirect Speech, Format, Rules, Exercise, and Examples
Determiners Definition, Types, Exercise and Examples
All About Tenses | Tenses Examples, Types of Tenses in English Grammar
English Vocabulary for Bank PO Exams – Synonyms MCQ Videos
Noun Definition, Types, Exercise with Examples in Hindi and English
What is a Verb? Definition, Types of Verbs, Exercise and Verbs Examples in Hindi and English
What is a Preposition? Definition, Types, Exercise, and Examples in Hindi and English
Subject Verb Agreement Rules and Examples
Modals Definition | Modals Exercise, List of Modals with Examples
Master Tenses in English Grammar – The Easy Way
English Writing Skills
Analytical Paragraph Writing | Format, Examples, Samples
Report Writing Format | How to Report Writing Examples, Topics, Samples and Types
Letter to Editor Class 10 to 12, Topics, Sample and Example
Informal Letter Format, Topics, Examples
Article Writing Format, Topics and Examples
Classified advertisement writing examples
Letter to the Principal, Format, Samples
Story Writing , Format, Topics, Examples
Job Application with Biodata, Format, Topics, Examples
Leave Application Format for Office, School and Sample
Leave Application for Marriage, Format, Sample, and Examples
Speech Writing format, examples for Class 11, 12
Invitation writing tips for class 12
Report writing tips for class 12
10 Important Things to DO to score more in Debate writing question
Let us revise Reported Speech in 9 Quick Steps
Job Application Writing Tips for Class 12 English
Tips to ace the question on Analytical Paragraph writing in Class 10
- Diwali Wishes in Hindi
- Friendship Day Wishes in Hindi
- Dussehra wishes in Hindi
- Navratri Wishes in Hindi
- Hindi Diwas Quotes in Hindi
- Congratulations Message in Hindi
- Teacher’s Day Wishes in Hindi
- Ganesh Chaturthi Wishes in Hindi
- Janmashtami Messages in Hindi
- Raksha Bandhan Wishes in Hindi
- Birthday Wishes in Hindi
- Anniversary Wishes in Hindi
- Father’s Day Quotes and Messages
- Father’s Day quotes in Hindi
- International Yoga Day Slogans, Quotes and Sayings
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय योग दिवस Slogans, Quotes and Sayings
- Good Morning Messages in Hindi
- Good Night Messages in Hindi | शुभ रात्रि संदेश
- Wedding Wishes in Hindi
Important Days
- National Space Day Quiz| National Space Day MCQs
- World Soil Day – Date, History, Significance
- International Yoga Day Slogans, Quotes and Sayings by Famous people 2024
- Calendar MCQ Quiz for Various Competitive Exams
- CUET 2024 MCQ Quiz on Important Dates
The More Is always Less.
English With A Difference
For 2025 Board Exam CBSE Competency Based Questions :
Reading and grammar worksheet (pdf), personal mentorship, reported speech worksheet |.
Updated: Oct 29, 2023
Do the following exercises on Reported Speech. 4 Marks allotted for Board Exam
For Rules of Reported Speech, Click here
Q1. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follow :
Son : Mummy, Where have I put my wallet ?
Mother : I don’t know. Ask your father.
Son : He will say the same thing.
Mother : Why don’t you put things in their proper place ?
A son asked his mother (a) _________ ? The mother replied that (b) _________and advised him to ask his father. The son retorted saying that he would say the same 3 Page 7 of 7 thing. The mother asked him irritatingly (c) _________ The mother (c) ________
Q2. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follows.
Mother to me : Are you unwell today?
I to mother : No, Mummy, not at all.
Mother : Have you done any work today?
I replied : “Nothing”.
My mother asked me (a) __________. I replied to my mummy (b) __________. My mother again asked me (c) ___________.
Q3. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follows.
PATENT : I want to see the doctor. I am very sick.
RECEPTIONIST : I am sorry. The doctor is very busy. You'll have to wait for at least one hour.
A patient went to his doctor's clinic and told the receptionist (a) __________ The receptionist (b) __________ She further added that (c) __________
Q4. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follows.
Biju : Bina why don't you fold your umbrella?
Bina : It looks beautiful when it is kept open.
Biju : You should keep it folded otherwise it comes in the way.
Bina seldom folded her umbrella. Biju did not like it. He asked her (a) __________. Bina replied that (b) __________ Biju advised her to keep it folded otherwise (c) __________
Q5. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follows :
Ram : I want to meet the Principal.
Peon : Sir, he is not in his office.
Ram : When will he come back to the office ?
Peon : I think in another ten minutes.
Ram went to K.V.Jaipur for the admission of his daughter to that school. He went to the Principal's office and told the peon (a) -----------.Respectfully the peon told him that (b) -------------------.So Ram asked him (c)------------ .The peon replied that in his opinion the Principal would be back in another ten minutes.
Q6. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that below.
Receptionist : Good morning. This is Hotel Oberoi, Bangalore.
Mr. Deepak : Good morning. I would like to make a booking in your hotel. Kindly book a suite with attached bathroom and lobby for Monday, September 20, 2012.
Receptionist wished good morning to Mr. Deepak and told him that (a) __________ , Bangalore. Mr. Deepak also (b) __________ and said that (c) ___________ make a booking in their hotel. He requested her to book a suite with attached bathroom and lobby for Monday, September 20, 2012.
Q7. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follows :
Kokila : Maitryee ! My new dress is very pretty.
Maitryee : Will you show it to me?
Kokila : I will show it to you tomorrow when you come to my house.
Kokila told her friend Maitryee that (a) __________. Maitryee asked her if (b) __________. She replied, that she would love to show it to her (c) ___________.
Q8. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follows :
Customer : Waiter, come here.
Waiter : Yes Sir.
Customer : Look, there are flies in my soup.
Waiter : But sir, they are fresh flies.
Customer : What do you mean ?
Waiter : They arrived only this morning Sir.
A customer in a restaurant complained that there were flies in his soup. The waiter told the customer (a) __________ . When the customer asked (b) __________ , the waiter replied that they (c) __________ .
Q9. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph.
Mother : What are you doing?
Rani : Just watching TV.
Mother : Turn off the TV and help me in cleaning your room.
Rani : Ma, I will do it later.
Mother asked Rani what she was doing. Rani replied that (a) __________ TV. The mother asked her to turn it off and (b) __________ . Rani replied that (c) __________ .
Q10. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph.
Berry : Daddy! I am the happiest girl in the world.
Daddy : Have you won a million dollar lottery?
Berry : No! I have got something much better.
Berry screamed with joy that (a) ______. Her father asked (b) ______ a million dollar lottery. She replied that (c) ______ something much better.
Download Answer Key
Q11. Read the following conversation and complete the given paragraph. Write the correct answer against the correct blank number. Do not copy the whole sentence.
Miss Grundy : Mohit, you spent time on this homework assignment and it really shows.
Mohit : Thanks, Miss grundy. You mean it's that good?
Miss Grundy : No, I mean it's covered with stains from an evening's worth of snacks.
Mohit's teacher, Miss Grundy told him that (a) ______ and it really showed. Mohit thanked his teacher and asked her (b) ________. To that the angry teacher replied that (c)_________.
Q12. Read the following conversation and complete the given paragraph. Write the correct answer against the correct blank number. Do not copy the whole sentence.
Child : I want to buy a birthay card for my little sister.
Salesman : Do you want a small card or a big card?
Child : I want any cad that will show that I love my litle sister a lot.
Salesman : Then it would be better if you make one yourself.
A child told the salesman that (a)______________ his little sister. The sales man asked him (b)_________________ a big card. The child said that he wanted any card which would show his love for his sister a lot. The sales man then advised him (c)_____________.
Q13. Read the conversation given below and then complete the report by transforming sentences into reported speech.
Daughter : Will you allow me to go for trekking with my classmates?
Father : Dear, we are going to Singapore for a family holiday.
Daughter : The trekking camp will be in Chail and I may not get another chance to visit this place.
Nandika asked her father (a)________________ to go for trekking with her classmates. Her father replied that (b)_____________________ for a family holiday. Nandika told her father that (c)____________________ might not get another chance to visit that place.
Q14. Read the dialogue given below and complete the paragraph that follows :
Amit: Can you lend me your Physics book?
Sunil : Yes, but only for one day. Will you be able to return it to me tomorrow?
Amit : Definitely, Thanks.
Amit asked Sunil (a) __________ . Sunil replied in the affirmative but told him (b) __________ . He then asked him (c) __________ . Amit replied that he would definitely return it to him. He also thanked him.
Q15. Read the following dialogue given below and then complete the paragraph transforming the sentences into reported speech. Write your answer in your answer sheet with correct blank number. Do not copy the whole passage. Babita : where do you want to go?
Pragati : I want to to to the drop point near the zoo.
Babita : In that case you will have to get down at the Laxmi Nagar bus stop and take an auto.
Pragati : How long will I take to reach there?
Babita asked Pragati where she wanted to go. Pragati told her that (a) __________. Babita told her that in that case (b) __________ and take an auto. Pragati asked Babita (c) _____________.
Q16. Read the dialogue given below and complete the report by transforming the sentences into reported speech. Write your answer in your answer sheet with correct blank number. Do not copy the whole passage.
Seema : Do you know how to prepare custard?
Roma : I do not enjoy working in the kitchen.
Seema : But it is so easy.
Roma : I will ask my mother to teach me.
Seema asked Roma if (a) __________ prepare custard. Roma replied that (b) __________ in the kitchen. Seema commented that it was so easy. Roma said that (c) __________ teach her.
Q17. Read the following dialogue and then complete the paragraph by transforming the sentences into reported speech. Write your answer in your answer sheet with correct blank number. Do not copy the whole passage.
The Man scolded the servant (a) __________ . He questioned him if he had not asked him to get his breakfast ready by 8 O‟ clock. The servant apologized to him and explained that (b) __________ . The man asked him if he had not set the alarm before going to sleep. The servant answered politely that he had done so. His master further enquired the reason for the delay. The servant answered humbly that (c) __________ .
Q18. Read the following dialogue and then complete the paragraph by transforming the sentences into reported speech. Write your answer in your answer sheet with correct blank number. Do copy the whole passage.
Riya: When are you leaving for Kolkata?
Sandhya : I will leave right after the examination.
Riya : would you like me to drop you at the station?
Sandhya : Thanks, it would really help me.
Rita met Sandhya and asked her (a) __________. Sandhya replied (b) _________ . Rita then asked her (c) _________. Sandhy a thanked her and told her that it would really help her.
Q19. Read the following dialogue and then complete the paragraph by transforming the sentences into reported speech. Write your answer in your answer sheet with correct blank number. Do not copy the whole passage.
Father : When is the fancy dress competition in your school?
Son : It is next week.
Father : Are you taking part in it?
Son : Yes, I am taking part as an engine driver.
Father : Why have you chosen that role?
Son : So that I can reach late.
Father asked his son when the Fancy Dress competition in his school was. Son replied that (a) __________.Father enquired (b) _________.Son replied that he would be an engine driver. Father asked why he had chosen that role. He answered so that (c) __________.
Q20. Read the following dialogue and complete the report that follows. Write your answers in your answer sheet against the correct blank numbers. Do not copy the dialogue and report.
Shopkeeper : What can I do for you?
Mohan : I want to purchase the sugar.
Shopkeeper : Do you have the money?
Mohan : No, I have the credit card.
At the shop, the shopkeeper asked Mohan (a) __________. Mohan replied (b) __________. At this shopkeeper asked again (c) __________. Mohan replied in negative and told that he had the credit card.
Answer key from Q11 to Q20 is available for download below:
Recommended Reading: Competency-Based Grammar Worksheet
Recommended reading: listening skill worksheet | class xi-xii | board exam 2024| english core (englishwithadifference.com).
- Grammar Worksheet
Related Posts
Reported Speech | Narration | English Grammar | CBSE | ICSE | State Boards
English Competency-Based Questions | Class X
21 Important Competency-Board English Grammar Questions | Class IX-X
.png)
Hi, thanks for stopping by!
We have insatiable passion for Literature & Language and to empower English learners to build up a rock solid foundation.
Let the lessons come to you.
Thanks for subscribing!

English The Easy Way
Everybody can learn english, english dialogue.
- Do Your Homework - Family Dialogue
- Speaking English
- English Speaking Dialogues
Mother: How was school today?
Son: Yes, I have a lot of homework.
Mother: Ok, in what subjects do you have homework?
Son: I have homework in English, math, and socal studies.
Mother: Ok, that is a lot of homework. When are you going to start your homework?
Son: After dinner, I will do my homework.
Mother: No, I want you homework now. When you finish your homework you can watch T.V.
Son: Ok, I will do my homework.
Mother: Do you need help with your homework?
Son: No, it is Ok. I can do my homework myself.
Mother: Very good. I am going to make dinner. If you need help, just let me know.
Son: Thanks, I will start my homework now.
Mother: Good.
- Do Your Homework - Family_Dialogue
I Need A RIde Mom - Mother And Son Dialogue
What is your favorite sport?
Do You Have Enough Money? - Mother & Son Dialogue
Taking A Message
Do Your Homework
Buying Train Tickets
Cold Outside - Everyday Talk
Talking About Food - Small Talk
Going Out For Beakfast - Everyday Life Dialoguegue
Calling To Reserive A Hotel Room
Lunch Break Small Talk
Where are you going? Mother and Son Dialog
Office Work Project Small Talk
Coffee Break Small Talk
Ordering Pizza On The Phone
Morning Small Talk
Asking For Money Dialogue
Inviting Someone To A Party - Dialogue
Ordering Coffee - Dialogue
Small Talk At The Supermarket
Making An Appointment
Sending An E-Email Dialog
Dealing With Rude Questions
Asking Directions
Going To The Store
Are you a student? - With Voice/Audio
Where are you from?
How are you feeling?
What are you doing? - With Voice/Audio
What do you live? - With Voice/Audio
Where do you work? With Voice/Audio
Waiting For The Bus
Where To Meet - With Voice/Audio
I am Ill Today - With Voice/Audio
Telephone Dialog
Leaving A Message
Telephone Difficulties
Meeting New People

Home / English Grammar / Direct and Indirect Speech / Direct and Indirect Speech Rules with Examples (Updated)
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules with Examples (Updated)

Understanding Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for conversion is crucial for effective communication. This updated guide explains the key rules, including how to choose the right reporting verbs, handle tense changes, and accurately convert speech. With clear examples and practical tips, it’s an ideal resource for students, ESL learners, and exam preparation.
Direct Speech
Direct speech is a form of reporting that presents someone’s exact words without any alterations. It is commonly enclosed in quotation marks.
Direct Speech Rules
Direct speech consists of the following elements.
- The speaker (subject)
- reporting verb
- object( to whom the speaker says something)
- reported speech
- Quotation marks
- Punctuation placement ( Commas , periods , question marks , and exclamation points )

Explanation: “I shall not go to school,” are the exact words of Riya, enclosed in quotation marks/inverted commas (“….”). This format, which uses commas and quotation marks/inverted commas, is called direct speech . In this sentence, ‘Riya’ is the subject or speaker, ‘says’ is the reporting verb, and ‘I shall not go to school’ is the reported speech.
For examples,
- Direct: “We can’t be quite happy in life,” he said .
- Direct: He said , “The Muslims bury their dead.”
- Direct: “ You’ve overcooked the steak again, Mary” , he said.
- Direct: Ramen said to Bina, “I’m going to your house this, week.”
- Direct: Ritu said, “I am going to the store.”
- Direct: “I can’t believe it,” she whispered, “but I saw a unicorn in the garden.”
People also ask
Indirect Speech
Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves paraphrasing someone’s words and reporting them indirectly, without using quotation marks. It requires a few changes in structure, such as tense and pronoun.
Indirect speech rules
- removing quotation marks
- changing pronouns
- adjusting tenses
- modifying time expressions
- making it into a statement
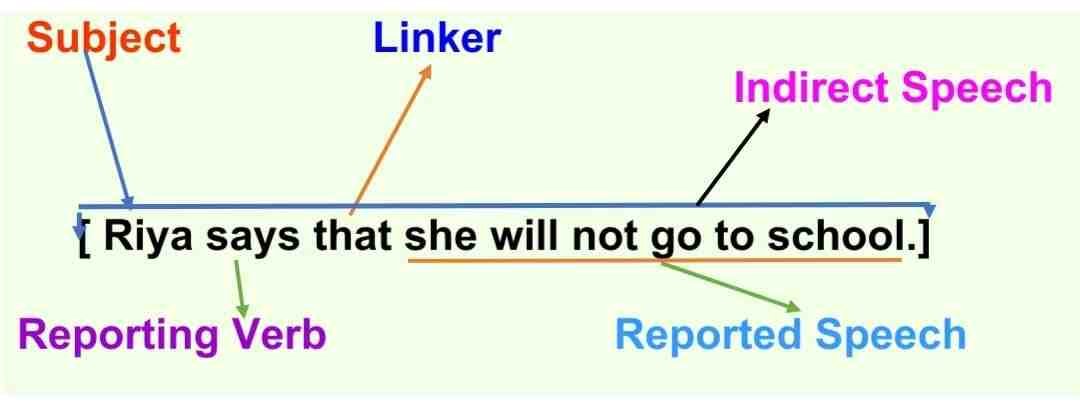
Similarly, we can report the above sentence without quoting Riya’s exact words while keeping the meaning the same. This format is called indirect speech. In this format, no commas or quotation marks/inverted commas are used; only a full stop (.) is used at the end of the sentence.
Direct Speech: “We can’t be quite happy in life,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that they couldn’t be quite happy in life.
Direct Speech: He said, “The Muslims bury their dead.” Indirect Speech: He said that the Muslims bury their dead.
Direct Speech: “You’ve overcooked the steak again, Mary”, he said. Indirect Speech: He told Mary that she had overcooked the steak again.
Direct Speech: Ramen said to Bina, “I’m going to your house this, week.” Indirect Speech: Ramen told Bina that he was going to her house that week.
Direct Speech: John said, “I am going to the store.” Indirect Speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Direct Speech: “I can’t believe it,” she whispered, “but I saw a unicorn in the garden.” Indirect Speech: She whispered that she couldn’t believe it but that she had seen a unicorn in the garden.
Rules between direct and indirect speech
The following comparison highlights the key differences between direct and indirect speech rules, including punctuation, tense changes, and adjustments to pronouns and time references.
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Conversion in General
Discover the essential rules of direct and indirect speech with a variety of examples to improve your language skills. Effortlessly understand the intricacies of converting statements, questions, and commands from one form to another.
Rule 1: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Reporting verbs ‘ Say ‘ and ‘ Tell ‘.
“Say” and “tell” are two frequently used reporting verbs. “Say” is generally followed by the reported speech, while “tell” is followed by the indirect object (the person being addressed).
Direct: He says , “I am your friend.” Indirect: He says that he is your friend.
Direct: He said to me, “I’m going to the store.” Indirect: She told me that he was going to the store.
Reporting verbs ‘Say’ and ‘Tell’ Chart
Rule 2: direct and indirect speech rules for reporting verb, ‘ ask ‘ and ‘ inquire’.
When reporting questions , “ ask “ and “ inquire “ are commonly employed reporting verbs.
Direct: He said to me, “Where are you going?” Indirect: He asked where I was going.
Direct: She said , “When will the concert start?” Indirect: She inquired, “When will the concert start?”
Direct: Sarah said , “What time does the movie start?” Indirect: Sarah asked what time the movie started.
Direct: “Could you please provide more details?” she said to me. Indirect: She inquired politely if I could provide more details.
Direct: The customer said , “Do you have this item in stock?” Indirect: The customer i nquired if that item had in stock.
Rule 3: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for reporting verb, “ Request “, “ Advise “, “ Order “, “ Beg “.
To report imperative sentences, “Request”, “Advise”, “Order”, and “beg” are often used.
Direct: “Please close the door,” she said . Indirect: She requested that the door be closed.
Direct: “You should study regularly,” he said. Indirect: He advised that regular studying should be done.
Direct: “Stand up straight,” the sergeant said . Indirect: The sergeant ordered that they stand up straight.
Direct: He said to me, “Go home at once” Indirect: He ordered me to go home at once.
Direct: She said , “Do not run in the sun” Indirect: She advised not to run in the sun.”
Direct: “Please forgive me,” she said. Indirect: She begged for forgiveness.
Rule 4: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Present Tense
If the Reporting Verb is in the Present Tense , there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room is dark.” Indirect: Arnab says that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room was dark.” Indirect: Arnab says that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “I shall finish the work.” Indirect: Arnab says that he will finish the work.
Direct: Mary says , “I am going to the party.” Indirect: Mary says that she is going to the party.
Direct: He tells us, “I will finish the project by tomorrow.” Indirect: He tells us that he will finish the project by tomorrow.
Rule 5: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Conversion of Future Tense
If the Reporting Verb is in the Future Tense , there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Sarah will say , “I am going to the store.” Indirect: Sarah will say that she is going to the store.
Direct: John will say, “I have completed the assignment.” Indirect: John will say that he has completed the assignment.
Direct: Arnab will say, “The room is dark.” Indirect: Arnab will say that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab will say , “The room was dark.” Indirect: Arnab will say that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab will say, “I shall finish the work.” Indirect: Arnab will say that he will finish the work.
Rule 6: Rules for Transforming Direct and Indirect Speech of Past Tense
If the Reporting verb of the Direct Narration is in the Past Tense , the Present Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech of Direct Narration is changed into the corresponding Past Tense in Indirect Narration .
Direct: Rohan said , “She works hard.” Indirect: Rohan said that she worked hard.
Direct: Rohan said, “She is singing a song.” Indirect: Rohan said that she was singing a song.
Direct: The guest said shouting, “We have arrived .” Indirect: The guest shouted that they had arrived.
Direct: My sister said , “It has been raining hard for 3 days”. Indirect: My sister said that it had been raining hard for 3 days.
Direct: Father said, “I visited the Taj yesterday.” Indirect: Father said that he had visited the Taj the previous day.
Direct: The boys said, “They were traveling in the park.” Indirect: The boys said that they had been traveling in the park.
Direct: The reporters commented , “The Kohinoor had been lost long ago”. Indirect: The reporters commented that the Kohinoor had been lost long ago.
Direct: Jyotsna said, “ She had been doing the work for 3 hours”. Indirect: Jyotsna said that she had been doing the work for 3 hours.
Rule: 7 Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Universal Truth or Habitual Fact or Scientific Truth.
The Tense of the Verb remains unchanged in Indirect Narration in cases of General Statements of Facts , Universal Truths , Commonplace Occurrences , and Habitual or Repeated Actions . No real change occurs in these cases. Only there will be present Tense alone.
Direct: The boy said to his mother, “ The sun rises in the East”. Indirect: The boy told his mother that the sun rises in the East. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The monk answered , “ Man is mortal”. Indirect: The monk answered that man is mortal. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The teacher told the students, “ Perseverance always leads to success.” Indirect: The teacher told the students that perseverance always leads to success.
Rule 8: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Personal Pronouns (I, We, You, He, She, They)
First person.
(a) If the subject of the reported speech of direct form is in the first person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the subject of the reporting verb in indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: She says, “ I am ill today.” Indirect: She says that she is ill that day.


Second Person
(b) If the subject of the reported speech in the Direct Form is in the second person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the object of the reporting verb in the indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: He says to me , ” You can do this work.” Indirect: He tells me that I can do that work.

Third Person
(c) If the subject of the reported speech of Direct Form is in the third person, there will be no change in the person of the Indirect Form.
Direct: I said, “ He will not wait for his friend.” Indirect: I said that he would not wait for his friend.

Pronouns Chart : direct and indirect speech rules
Rule 9: direct and indirect speech rules for demonstrative pronouns ( this, that ).
In the case of demonstrative pronouns, replace them with appropriate pronouns in indirect speech.
Direct: “ This is my book,” she said. Indirect: She said that this was her book.
Rule 10: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Commas with Reporting Verb
When introducing indirect speech with a reporting verb, use a comma to separate the reporting verb from the reported speech.
Example: She said, “I’ll be there on time.”
Rule 11: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Question Mark to Full Stop
If the direct speech is a question, change the question mark to a full stop when converting to indirect speech.
Direct: He asked, “Are you coming to the party ?” Indirect: He asked if I was coming to the party .
Rule 12: Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Exclamation Mark to Full Stop
In cases where the direct speech has an exclamation mark, replace it with a full stop in indirect speech.
Direct: She exclaimed, “What a beautiful day !” Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a beautiful day .
Rule 13: Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Rules of Modal Verbs
When dealing with modals like can, could, will, would, may, might, shall, should, must, etc., use the appropriate past form in indirect speech.
Direct: She said, “You should respect your elders. Indirect: She said that I should respect my elders.
Direct: She said, “I can speak French fluently. Indirect: She said that she could speak French fluently.
Direct: May I borrow your pen?” she asked. Indirect: She asked if she might borrow my pen.
Direct: He said, “You must complete the assignment by tomorrow. Indirect: He said that I must complete the assignment by the next day.
Rule 14: Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Rules of Conditional Sentences
In indirect speech, conditional sentences undergo specific changes, especially when they involve “will” or “would.”
Direct: He said, “I will help you.” Indirect: He said that he would help me.
Direct: He said, “I will help you with your project Indirect: He said that he would help me with my project.
Rule 15: Reporting Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Rules of Adverbs of Time
When using adverbs of time in indirect speech, adjust them to match the new timeframe.
Direct: “I will come tomorrow ,” she said. Indirect: She said that she would come the next day.
Rule 16: Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Rules of Adverbs of Place
Similar to adverbs of time, adverbs of place need modification in indirect speech.
Direct: ” I live here ,” he said. Indirect: He said that he lived there.
Rule 17: Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Rules of Adverbs of Manner
We can also use Adverbs of manner in indirect speech, requiring appropriate adjustments.
Direct: “He ran quickly,” she said. Indirect: She said that he ran quickly.
Rule 18: Time, Place, Manner, Distance, Direction Chart for Direct and Indirect Speech
In Indirect Narration, words denoting Time, Place, Manner, Distance, and Direction used in the quoted speech are correspondingly changed to conform to the point of view of the Reporter. Thus, the sense of nearness is changed into that of Distance, and so on.
Place Chart
Manner chart, distance chart, direction chart, rule 19: direct and indirect speech conversion rules for assertive sentences.
To convert Assertive sentences into indirect speech the following rules are applied.
(a) No comma and Inverted comma in Indirect Speech, only full stop at the end. (b) Reporting Verbs changed from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech ; ‘say – say’, ‘says – says’, ‘said – said’, ‘said to – told’, ‘say to – tell’, ‘says to – tells’. (c) Connective ‘that’ added before Reported Speech in indirect Narration.
Direct: He said to me, “I am ill.” Indirect: He told me that he was ill.
Direct: Mary said, “I am happy with my results.” Indirect: Mary said that she was happy with her results.
Direct: Tom said, “I will attend the meeting tomorrow.” Indirect: Tom said that he would attend the meeting the next day.
Direct: Alice said, “I have finished my homework.” Indirect: Alice said that she had finished her homework.
Direct: David said, “We are planning a trip to the mountains.” Indirect: David said that they were planning a trip to the mountains.
Rule 20: Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion Rules for Interrogative sentences
Forming indirect speech with questions necessitates some adjustments:
a. Reporting Yes/No Questions rules
When reporting yes/no questions, use “if” or “whether” and invert the subject and auxiliary verb in indirect speech.
Direct: John asked, “Are you coming to the party?” Indirect: John asked if I was coming to the party.
Direct: Sarah asked, “Do you like chocolate?” Indirect: Sarah asked if I liked chocolate.
Direct: Mike asked, “Have you finished your project?” Indirect: Mike asked if I had finished my project.
Direct: Emma asked, “Will you help me with my homework?” Indirect: Emma asked if I would help her with her homework.
Direct: “Will you be there?” he asked. Indirect: He asked if I would be there.
b. Reporting Wh-Questions rules
For reporting wh-questions, maintain the question word and adjust the word order in indirect speech.
(a) ‘Tell’ and ‘say’ in Direct Narration are changed to ‘ask’, ‘enquire of’, ‘question’, ‘want to know’ etc. in Indirect Narration. (b) In place of introductory ‘that’. ‘if’ or ‘whether’ should be used. (c) In Indirect Narration a full stop (.) must be put in place of a question mark(?) at the end of the sentence. (d) In Direct Narration the Reported Speech begins with W-word or how, in Indirect Narration the same Wh-word or how is retained.
Direct: Lisa asked, “Where are you going?” Indirect: Lisa asked where I was going.
Direct: Mark asked, “What time does the movie start?” Indirect: Mark asked what time the movie started.
Direct: Jennifer asked, “Why did you leave early?” Indirect: Jennifer asked why I had left early.
Direct: Tom asked, “How do you solve this problem?” Indirect: Tom asked how I solved that problem.
Direct: “Where are you going?” she asked. Indirect: She asked where I was going.
Direct: The teacher said to me, “Why are you late?” Indirect: The teacher asked me why I was late.
Rule 21: Imperative Sentences Rules for shifting Direct and Indirect Speech
The indirect speech also involves reporting imperatives, which are commands, requests, or advice:
Reporting Commands
When reporting commands, use the reporting verb “tell” and change the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: The teacher said, “Open your books.” Indirect: The teacher told the students to open their books.
Reporting Requests
For reporting requests, employ the reporting verb “ask” and convert the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: She said, “Please help me with this.” Indirect: She asked for help with that.
(a) Reporting verbs of Direct Speech changed into order or command, advise, or request according to sense in Indirect Speech. (b) ‘To’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration; for the negative imperative sentence ‘not to’ is used. (c) ‘not to’ can also be replaced by ‘forbid’, or ‘prohibit’. (d) ‘Let’ implies ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘suggest’ or ‘propose’ in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration (e) ‘Let’ without ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘tell’, or ‘wish’ according to sense in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: Mother said to me, “Don’t run in the sun.” Indirect: Mother advised me not to run in the sun.
Direct: She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic.” Indirect: She suggested that we should go for a picnic.
Rule 22: Optative Sentences Rules Converting Direct into Indirect Speech
The following rules are used to change an optative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech
(a) Reporting verbs changed to ‘ wish ’, ‘ pray’ , and ‘ bless ’ in Indirect Speech. (b) Linker, ‘ that ’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: The monk said to me, “ May God bless you.” Indirect: The monk wished that God might bless me.
Rule 23: Exclamatory Sentences Rules Transforming Direct to Indirect Speech
(a) The reporting verb is changed into exclaim (in joy), exclaim (in grief), cried out (in sorrow), pray, wish, etc. (b) Examinations are turned into statements. (c) Interjections (Alas, Oh, Hurrah) are omitted. (d) ‘What’, and ‘How’ used in exclamation should be replaced by great, great, very, very much, and big.
Direct: The boys said, “Hurrah! we have won the match.” Indirect: The boy exclaimed in joy that they had won the match.
Solved Exercises Direct and Indirect Speech following rules
Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
Q: Ratan said to Anita, “I don’t like your brother”.
Ans: Ratan told Anita that she did not like her brother.
Q: The hermit said to the boys, “God is present everywhere.”
Ans: The hermit told the boys that God is present everywhere.
Q: :He said to you, “You shouldn’t play in my garden.”
Ans: He told you that you should not play in his garden.
Q: The class teacher said to the students. “The inspector will visit our school today.”
Ans: The class teacher told the students that the inspector would visit their school that day.
Q: He said to me, “I don’t believe you.”
Ans: He told me that he didn’t believe me.
Q: She said to her son, “I’ve often told you not to play with fire.”
Ans: She told her son that she had often told him not to play with fire.
Q: Sitesh said to Lina, “I want you to go to Patna with me.”
Ans: Sitesh told Lina that he wanted her to go to Patna with him.
Q: “We can’t be quite happy in life,” he said.
Ans: He said that they couldn’t be quite happy in life.
Q: He said, “The Muslims bury their dead.”
He said that the Muslims bury their dead.
Q: “You’ve overcooked the steak again, Mary”, he said.
Ans: He told Mary that she had overcooked the steak again.
Q: Ramen said to Bina, “I’m going to your house this, week.”
Ans: Ramen told Bina that he was going to her house that week.
Q: He said, “We will discuss this tomorrow.”
Ans: He said that they would discuss that the next day
Turn the following sentences into direct speech.
Q: He said to me, “You are wicked; so I shall not mix with you.”
Ans: He told me that I was wicked; so he would not mix with me.
Q: He said to you, “I was much struck by your eloquence.”
Ans: He told you that he had been much struck by your eloquence.
Q: We remarked, “God is gracious.”
Ans: We remarked that God is gracious.
Q: I said to my mother, “I shall always obey you.”
Ans: I told my mother that I should always obey her.
Q: He said to Gopal, “You were a mere boy when I saw you last.”
Ans: He told Gopal that he was a mere boy when he had seen him last.
Q: I said to him, “The sky is blue.”
Ans: I told him that the sky is blue.
Q: He said to me, “You will feel the consequences.”
Ans: He told me that I should feel the consequences.
Q: She said to you, “I am not angry with you.”
Ans: She told you that she was not angry with you.
Q: I said to them, “You have done wrong.”
Ans: I told them that they had done wrong.
Q: He said, “I visit the temple every day.”
Ans: He said that he visited the temple every day.
Direct and Indirect Speech Sample MCQ Questions Answers
Fill in the blanks with proper direct and indirect speech rules.
- d) had been
- Answer: a) was
- c) will like
- d) had liked
- Answer: a) liked
- a) will visit
- b) would visit
- d) had visited
- Answer: b) would visit
- Answer: c) was
- c) will have
- Answer: b) had
- Answer: b) could
- a) revolves
- c) revolved
- d) is revolving
- Answer: a) revolves
- b) had been
- Answer: b) had been
- Answer: b) would
FAQs : Direct and Indirect Speech
Q : what is the key difference between direct and indirect speech.
Ans: The main difference lies in the quoting style. Direct speech involves repeating someone’s exact words, while indirect speech reports what was said without quoting verbatim.
FAQ 2: Is it always necessary to backshift the tense in indirect speech?
Ans: While backshifting is common, some exceptions exist, especially in cases where the statement’s truth remains constant.
FAQ 3: How do I handle multiple speakers in indirect speech?
Ans: When reporting multiple speakers, use appropriate reporting verbs and introduce each person’s dialogue in a logical sequence.
FAQ 4: Can I mix direct and indirect speech in the same sentence?
Ans: Combining direct and indirect speech in a sentence is possible, but it requires precision to avoid confusion.
FAQ 5: What are some reporting verbs commonly used in indirect speech?
Ans: Reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” “claimed,” and “explained” are frequently employed.
FAQ 6: How can I ensure my writing maintains a natural flow when switching between direct and indirect speech?
Ans: Focus on maintaining consistency in style and verb tense to ensure a smooth transition between direct and indirect speech.
FAQ 7: How do I identify direct and indirect speech in a sentence?
Ans: Direct speech is usually enclosed within quotation marks and directly quotes someone’s words. Indirect speech, on the other hand, reports those words without quotation marks, often using reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” etc.
FAQ 8: Can reporting verbs change the meaning of indirect speech?
Ans: Yes, the choice of reporting verbs can convey the speaker’s attitude or emotions towards the reported speech. Different reporting verbs can modify the meaning slightly.
FAQ 9: What are the common reporting verbs for indirect speech?
Ans: Common reporting verbs for indirect speech include “say,” “tell,” “ask,” “inquire,” “explain,” “describe,” and more.
FAQ 10: How do I change tenses in indirect speech?
Ans: The tense in indirect speech is generally shifted back one step. For example, present simple becomes past simple, present continuous becomes past continuous, and so on.
FAQ 11: Is it essential to use quotation marks in indirect speech?
Ans: No, quotation marks are not used in indirect speech as they report the speech without directly quoting it.
FAQ 12: Can you give an example of indirect speech in narratives?
Ans: Certainly! In the story, he said, “I love you,” to which she replied that she loved him too.
FAQ 14: Can we omit the reporting verb in indirect speech?
Ans: It is possible to omit the reporting verb in some cases, especially in informal contexts, but including it adds clarity and structure to the reported speech.
FAQ 15: Do all tenses change in indirect speech?
Ans: Most tenses change in indirect speech, but the changes depend on the context and the tense of the original statement.
FAQ 16: Can you provide more examples of direct and indirect speech transformations?
Ans: Certainly! Here are a few more examples:
Direct: “I am reading a book,” she said. Indirect: She said that she was reading a book.
Direct: “We have completed the project,” they exclaimed. Indirect: They exclaimed that they had completed the project.
FAQ 17: How can I practice using direct and indirect speech effectively?
Ans: Practice by converting direct speech to indirect speech and vice versa using various reporting verbs, tenses, and pronouns. Additionally, read books or articles and identify the reported speech used by the authors.
Recommended Articles:


Reported Speech
Learn how to use reported speech in English. Reported speech is also known as indirect speech and is used to tell somebody else what another person said. Using reported speech in English can sometimes be difficult for non-native speakers as we (usually) change the verbs, pronouns and specific times.
Keep reading to understand how to use reported speech and download this free English lesson!

Let’s study reported speech !
Reported speech vs. direct speech.
When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech or reported speech .
When we use d irect speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, “_”. For example:
Scott said, “I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now.”
When we use r eported speech, we usually change the verbs, specific times, and pronouns. For example:
Scott said that he was coming to work. He said that he would be late because there was a lot of traffic at that time.
How do we use reported speech ?
Since reported speech is usually talking about the past, we usually change the verbs into the past. It is always necessary to change the verbs when the action has finished or is untrue.
We do not always change the verbs. When you are reporting an action that is still current or true, it is not necessary to change the verb tense. For example:
How old are you? “ I am twenty-seven years old .” She said she is twenty-seven years old.
We usually follow the rules below. When we are reporting speech, we are usually talking about the past; therefore, we change the verbs into the past.
Reporting Questions
We use a special form when we report questions:
WH-Questions:
Where is + Tom’s house ? He asked where Tom’s house + was.
Where does Tom live? He asked where Tom lived.
Yes/No Questions:
Does Tom live in Miami? She asked if Tom lived in Miami.
Is Tom happy? She asked if Tom was happy.
Say vs. Tell
Say Something
June: “I love English .”
June said (that) she loved English.
Tell Someone Something
June: “I love English.”
June told me (that) she loved English.
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Must, might, could, would, should , and ought to stay the same in re ported s peech . We usually change may to might .
Infinitives and Reported Speech
Infinitives stay the same in reported speech:
“ I am going to the store to buy milk.” He said he was going to the store to buy milk.
We also use infinitives when reporting orders and commands, especially when using tell .
“ Do your homework. Don’t use a dictionary!!” He told me to do to my homework and not to use a dictionary.
Reporting Suggestions
When we are reporting another speakers suggestions, we can use a special form with suggest, recommend, or propose .
SUGGEST/ RECOMMEND/PROPOSE + (*THAT) + SUBJECT PRONOUN + **V1
SUGGEST/ RECOMMEND/PROPOSE + V1 + ING
“I think you should visit Viscaya.” → He suggested we visit Viscaya. He suggested visiting Viscaya.
“Try to get there early to get good seats.” → He recommended we get there early to get good seats.
*That is often omitted in speech.
**The verb is always in the base form. We do not use third person.
Reporting Statements
A reported statement begins with an introductory clause and is followed by the ‘information’ clause. The speaker may choose different words, but the meaning remains unchanged. Some formal words to introduce a reported statement or response are: declared, stated, informed, responded, replied, etc.
“I don’t agree with these new rules. I am not going to accept this change!” → He declared that he was in disagreement with the new rules and stated that he would not accept the changes.
Free English Lesson PDF Download
Reported Speech ~ Exercises and Practice
A. Change each direct speech example into the reported speech . The first one has been done for you.
- Michelle said, “I love my Chihuahua, Daisy.”
Michelle said that she loved her Chihuahua, Daisy.
2. Republicans said, “We don’t support Obama’s plan to raise taxes.”
__________________________________________________________.
3.With her mouth full, Sarah said, “I am eating mashed potatoes.”
4. John Lee said, “This year, I will not pay my taxes.”
5. Lebron said, “I am going to win the championship next year.”
6. Patty said, “I can’t stomach another hamburger. I ate one yesterday.”
B. Rewrite the sentences/questions below using reported / indirect speech . Always change the tense, even though it is not always necessary. You can use ‘said’, ‘told me’ , or ‘asked’ .
1. Sarah: “I am in the shower right now.”
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. John: “I dropped my son off at school this morning.”
3. Samuel: “I am going to the beach with my sister this afternoon.”
4. John: “Jessica will call you later.”
5. The girls: “Who does John live with?”
6. Our classmate: “Did we have any homework last night?”
7. Sarah: “I am moving to Tokyo because I want to learn Japanese.”
8. John: “Why do you have an umbrella?”
9. The students: “Our teacher can’t find her books anywhere.”
10. Sarah and Jillian: “Is John British?”
11. Steve: “I’m going to the beach so that I can play volleyball.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
12. Ann: “Where is the bathroom?”
13. My parents: “What are you going to do with your life?”
14. Sarah: “I ate breakfast before I came to school.”
C. Your friend Megan is very nosy (she always wants to know what’s going on) so she constantly asks questions about your life and the lives of your friends. Rewrite her questions using the reported questions form. The first one has been done for you .
1. Why do you date Ryan?
She asked me why I dated Ryan.
2. How much money do you make at your new job?
________________________________________________________________________________
3. Does Ryan think I’m pretty?
4. Where is your favorite restaurant?
5. Do I look good in these jeans?
6. Can I borrow some twenty bucks?
D. Your American grandfather is telling you about how things used to be. Using the reported speech , tell your friends what he said.
“In the 1930s, people were very poor. They ate watery soup and hard bread. Many people lost their jobs. To make matters worse, a horrible drought ruined most of the farmland in the American midwest. People went to California to look for a better life. They picked strawberries in the hot California sun.”
Did you download this lesson? If not, don’t forget to download this free English lesson.
If you have any questions about English grammar, please contact us via email us or just comment below. I hope this lesson helped you understand how to use reported speech in English.
Click here to subscribe to our newsletter! #TurnYourLanguageOn
Do you need to improve your English? See the locations of our English language schools in the United States.

Take our FREE Proficiency Test and
Discover your English Proficiency Level!
Get in Touch and Turn Your LANGUAGE ON
Join our mailing list

Proud partners with National Geographic Learning

Privacy Overview

IMAGES
COMMENTS
‘I have a German lesson this afternoon and I haven’t done my homework yet,’ said the boy. 5. ‘If you let the iron get too hot you will scorch your clothes.’
Sentences are given in direct speech. Change them into indirect speech. 1. The teacher said to the boys, ‘Have you done your homework?’. 2. The little girl asked the man, ‘Will you help me?’. 3. Janaki said, ‘I have been reading this book.’. 4. Mother said to the daughter, ‘Go and change your dress.’. 5.
Direct: He said, “She has finished her homework.” Indirect: He said that she had finished her homework. Simple Present changes to Simple Past.
"Do your homework first, and then you can go to the cinema", said Jamie's mother LONG Jamie's mother agreed to let him go to the cinema .....his homework first. As long as he did Harry thought of throwing a surprise party for katie's birthday.
Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph that follow : Son : Mummy, Where have I put my wallet ? Mother: I don’t know. Ask your father. Son : He will say the same thing. Mother : Why don’t you put things in their proper place ? A son asked his mother (a) _________ ?
Mother: Ok, in what subjects do you have homework? Son: I have homework in English, math, history, science and socal studies. Mother: Ok, that is a lot of homework.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like "Do your homework first, and then you can go to the cinema", said Jim's mother., Jim's mother agreed to let him go to the cinema, so long as he did his homework first., "Yes, I took the money, but Ned told me to do it!"
Understanding Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for conversion is crucial for effective communication. This updated guide explains the key rules, including how to choose the right reporting verbs, handle tense changes, and accurately convert speech.
Reported speech is also known as indirect speech and is used to tell somebody else what another person said. Using reported speech in English can sometimes be difficult for non-native speakers as we (usually) change the verbs, pronouns and specific times. Keep reading to understand how to use reported speech and download this free English lesson!
Sentences are given in the direct speech. Change them into indirect speech. 1. ‘My Lord, is any of your silver missing?’ the Sergeant said to the Bishop. 2. ‘Did you see the exhibition?’ the teacher said to me. 3. ‘My son, when will you come back?’ said the mother. 4. ‘Can I get supper and lodging here for a night?’ said Jean Val Jean. 5.