How to Write a Short Essay: Format & Examples
Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for personal statements where you need to write about yourself. It might seem easy, but it’s not half.

Expressing and elaborating your idea within the given word limit is the most challenging part of the task. In this article, we’ll explain how to write a great short essay. If you’re working on one of your assignments and need help, keep reading to learn more!
- 💡 What You Need to Know
- 📚 Essay Format
- 📝 Essay Template
- ✨ Guide & Useful Tips
- ✅ Essay Topics

🔗 References
💡 short essay: what you need to know, what is a short essay.
A short essay is an academic paper typically ranging between 200 and 750 words, providing a focused topic exploration. This type of essay follows a standard structure: intro-main body-conclusion, usually presented in a five-paragraph format.
How Long Is a Short Essay?
A short essay typically ranges from 200 to 750 words which can be covered in three to five paragraphs. This concise format translates to less than one page of typed content. However, it’s important to note that specific requirements may vary depending on the college, with some specifying a minimum of 150 words and a maximum of 650 words. Be sure to review the task instructions to ensure you meet the guidelines.
How Many Sentences Is a Short Essay?
In a short essay, the number of words is more important than the number of sentences. It means you can use any number of sentences as long as you stay within the required word limit. However, most of the time, a short essay consists of around 20 to 25 sentences.
📚 Short Essay Format
A short essay follows a standard essay structure : intro – main body – conclusion. You can be creative with the contents of your paper; however, it’s best to stick to the hamburger essay format when it comes to structure.
These are the benefits of having a standard essay structure:
- You always have a template that can help you organize your thoughts.
- You can estimate how many words each paragraph should include, making the writing process faster and easier.
- You can get a high grade by simply following the instructions.
Below you’ll find more detailed information on how to organize each short essay section.
How to Start a Short Essay
An introduction needs to grab readers’ attention and provide some background information . It’s best to start your essay with a hook. However, be careful and add only the necessary information since your word count is limited.
Here are a couple of tips on how to make your introduction work:
Body Paragraphs
In the body paragraphs, you present and develop the essay’s main points. Each section focuses on a specific idea related to the topic, providing evidence, examples, and analysis to support the overall thesis statement. Here’s the structure of a paragraph:
A summary aims to condense the key ideas and arguments presented in an essay, allowing readers to quickly grasp the essence of the paper without reading the entire content. A good summary should:

📝 Short Essay Template
Use this easy template to quickly structure any short narrative, argumentative, or informative essay.
Introduction
- Hook: an intriguing fact, question, or statistic to grab your readers’ attention.
- Background info: something that provides context.
- Thesis statement: the purpose or central argument of your essay presented in one sentence.
- Topic sentence: a paragraph’s opening sentence that expresses its main idea.
- Supporting sentences: evidence, facts, and examples supporting the topic sentence.
- Transition: phrases or sentences that ensure coherence and cohesion in the essay, allowing for a clear and logical progression of information.
- Summary: a brief recap and conclusion to an essay.
- Restated thesis: a restatement of the main ideas and arguments.
✨ How to Write a Short Essay: Useful Tips
Each essay format has different requirements. Below are some tips to help you ensure you’re on the right track with the short essay format.
1. Follow the Short Essay Format
Mastering the format requirements is crucial, especially when writing a concise argumentative essay. While the five-paragraph structure may not be commonly found in literature, it holds great significance in academic writing for several reasons:
- Adhering to this standardized template makes the writing process more manageable.
- The clear guidelines facilitate reading, checking, and evaluation.
- This format accommodates various essay types, allowing students to excel in most academic texts .
Each paragraph in the short essay format plays a distinct role, making it essential to include all components for a cohesive and impactful essay.
2. Make Your Introduction Meaningful
Here’s how you can make your introduction work:
- When writing the opening paragraph of your essay, be very specific about your topic. It will help you sharpen your argument and clarify your intentions.
- To avoid a generic introduction, consider providing an example of the evidence you will use to support your point.
- Lastly, make sure to place your thesis statement as the concluding sentence of the paragraph, signaling to your readers where they can find the main point of your essay.
3. Write a Strong Thesis
Much has been said about the importance of a thesis statement, but crafting a persuasive one can be challenging. In a short essay, a strong thesis statement plays a crucial role. It summarizes the argument you intend to defend in your paper, setting the stage for your essay. Your thesis statement should be specific, intellectually rewarding by presenting new information, and decisive in expressing your opinion . Let’s take a closer look at some examples to illustrate these principles:
- Bad example: There is a vast diversity of opinions regarding abortions.
- Good example: Every woman must have the right to control her pregnancy which means the right to control her own body, health, and life.
- Bad example: Prisons can harm a convict’s further career.
- Good example: Imprisonment deteriorates a convict’s self-confidence and motivation, lowering their chances for new employment.
- Bad example: Orphans become the beloved children in some families, while in others, they never become natives.
- Good example: This essay aims to confirm that the reasons why adopting families don’t accept children lie within the families’ unreadiness for change.
4. Keep Your Introduction & Conclusion Concise
In the realm of short essay writing, brevity is the key. While it may be tempting to use abstract statements as hooks or delve into distant considerations in the conclusion part, keep an eye on the word count. With a maximum of 75 words each, the introduction elucidates the topic and conveys its significance, while the conclusion reiterates the main claim and reinforces the supporting evidence .
5. Make Topic Sentences from Your Thesis
When it comes to short essays, brevity extends to the main body as well. Typically comprising only 3 to 4 paragraphs, each of them focuses on a distinct aspect of the overall argument. To ensure clarity, we suggest splitting the thesis into multiple parts and transforming them into topic sentences for each paragraph. This structured approach will help you avoid confusion and make the paper more digestible for your readers. Additionally, this method simplifies crafting a well-rounded conclusion.
6. Refer to Reliable Sources
When tackling a short essay, it’s crucial to avoid baseless claims and instead focus on substantiating your arguments. Pay special attention to the sources you cite, as even the slightest inconsistency can catch the reader’s eye.
Enhance your essay’s credibility by incorporating several quotations or research-based facts, demonstrating your awareness of the topic. Even in the case of an in-class essay where extensive research may not be feasible, include relevant information or paraphrase passages you have previously encountered. Use indirect quotations if you can’t remember the exact wording.
7. Revise Your Short Essay
With a 500-word count, every word counts! Here are a few tips you may find helpful:
- Take a moment to assess the length of your essay and eliminate any unnecessary words to ensure a faster and more polished result. Consider using our convenient summarizer to streamline your writing further.
- Sometimes it’s hard to spot your own mistakes while proofreading the essay. Our essay-to-speech tool feature can help you identify weak points by reading your paper out loud. This auditory perspective can help you quickly identify and rectify any areas that require improvement.
✅ Short Essay Topics
Selecting an engaging and captivating topic is vital if you want to showcase your writing skills in a single short essay. Below are some examples to inspire your creativity. They’ll help you brainstorm and find the perfect topic that aligns with your interests and allows you to demonstrate your writing skills .
Short Narrative Essay Topics
- How I see a day in my adult life .
- Personal Experience in the Covert Conflict.
- A loss that will never be replenished.
- The Author’s Personal Experience.
- Describe how you would change the school program.
- Higher Education: Personality and Academic Success.
- What is the critical element of success?
- Photography: Hobby of Millions Unique for Everyone.
- My first love and lessons learned from it.
- Mindfulness Practicing: Personal Experience.
- The longest day of my life.
- Writing: Personal Hobby Analysis.
- A place to find peace in the hurricane of events.
- The Sports Coaching Guidelines and Routines.
- An eye-opening situation that changed the way I treat others.
- Innovation in Operation Management – Personal Experience.
- The worst trait of my character.
- Chapter 8 of “Criminology Today” by F. Schmalleger.
- How I met my best friend.
- Importance of Friendships.
Short Argumentative Essay Topics
- Social media can kill a relationship.
- Smoking in Public Places: Should It Be Banned?
- Animals should live in their natural habitats .
- Should People Be Ashamed of Poverty?
- Mandatory Overtime for Nurses Should Be Eliminated.
- The third wave of feminism is about to end with a half-victory.
- The Importance of Variability in the Food Industry.
- Gender Stereotypes: Should Real Men Wear Pink?
- Pharmacies: A big lie that costs a fortune.
- Police Standards Should Be Modified.
- Genetic cloning is immoral.
- Should Smoking Be Illegal?
- College Athletes Should Not Be Paid.
- We will never be equal because we are all different.
- Mandatory Job Drug Test Should Be Allowed.
- The best economic system has not been developed yet.
- Why Marriage Should Be Based on Love and Not Arranged?
- Reasons Why Kids Should Not Play Tackle Football.
- Owning a gun means you can be killed by chance.
- Should Social Media Be Banned?
- The non-family-friendly TV screen.
- Why Immigrants Should Receive Social Services?
- There’s a lot more sport about video games than we think.
- Should Children Be Taught Sex Education in School?
Short Informative Essay Topics
- How have video games affected modern technologies ?
- Infidelity and Societal Impact on Family Values.
- Meaning of Life in “Half a Day” by Naguib Mahfouz.
- Sociological Research Evaluation: Effects of Parental Imprisonment on Children’s Social and Moral Aspects.
- Climate Change Impacts.
- Explain the importance of the Olympic Games for building intercultural links.
- The Importance of Strategic Management and Planning.
- The Network Strategy of USA Today.
- A prominent artist and their masterpiece.
- Organizational Vision and Its Importance for the Staff.
- How to develop reading habits that last.
- The Impact of Electronic Medical Records.
- New and Old Media: Form, Impact, and Accessibility.
- Declaration of Independence and Cultural Issues Today.
- How does alcohol impact the way we behave?
- The Importance of Diet Monitoring.
- Personal Philosophy of Nursing Care.
- Why do teachers need a study plan?
- The Introduction of a Four-Day Work Week.
- Journalist Profession, Its Pros and Cons.
- The role of capitalism in shaping our idea of democracy.
- Teju Cole Personality’s in Modern American Society.
- The Importance of Medical Ethics.
- Tell a story of a famous and successful startup.
- Power of Advertising: Good and Bad Balance’ Importance.
- Personal and Political Pacifism.
- The cultural importance of divination.
- Important Factors in Personal Investment.
- My way of organizing my daily schedule and staying productive .
- The Impact of “The Marrow of Tradition” on Future American Literature.
- Ray Bradbury’s “Fahrenheit 451”: Themes and Importance of the Book.
- Writing short essays – Concordia University
- Thesis Statements; The Writing Center – University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- What Is an Essay Structure? (With 4 Types and Tips) | Indeed.com
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Writing Guides: Writing Tutorial Services: Indiana University Bloomington
- Topic Sentences and Signposting | Harvard College Writing Center
- Using Topic Sentences | Writing Advice
- Beginning Proofreading – Purdue OWL® – Purdue University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

When you hear the phrase “spiritual leadership,” you probably think it’s only associated with religion. But did you know that this form of leadership can also be found in business? The book Spiritual Leadership: Moving People on to God’s Agenda by Henry and Richard Blackaby is a good starting point...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

“If a tree falls in the forest, does it make a sound?” is one of the most debatable philosophical questions regarding observation and perception. Many tried to answer it, including the English philosopher John Locke. Do you need to explore Locke’s perspective on this question in your essay? You are on the right...

The long-standing debate surrounding abortion has many opponents and advocates. Groups known as Pro-Choice and Pro-Life argue which approach is better, with no easy solution in sight. This ethical complexity is what makes abortion a popular topic for argumentative writing. As a student, you need to tackle it appropriately. If...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay is not exactly a piece of cake. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to...

Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from varying perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

Discourse is the way people talk about any specific topic. It’s also the way in which language is used to convey social and historical meanings. Discourse analysis is the process that helps to understand the underlying message of what is being said. Sounds interesting? Keep reading to learn more. This in...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Short Essay
Short essay generator.

A short essay is a concise piece of writing, typically between 250 and 500 words, that presents a focused argument or reflection on a specific topic. Unlike longer essay writing , a short essay requires a clear, narrow topic and a precise thesis statement due to its limited length. It includes an introduction, body, and conclusion, aiming to express ideas effectively within a compact structure. Short essays often prioritize clarity, coherence, and brevity, making every sentence impactful. They are commonly used in academic settings, examinations, and other contexts where concise and well-organized responses, like a free essay , are required to convey information or opinions succinctly.
What is a Short Essay?

Download Short Essay Examples Bundle
Short Essay Format
A well-organized short essay includes three main parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion. Here’s a breakdown of each section:
Introduction
Purpose: The introduction presents the topic and includes a clear thesis statement to outline the essay’s main point. Length: Usually 2-3 sentences. Tips: Start with a hook to grab attention. Provide some background information before stating the thesis.
Purpose: The body elaborates on the thesis, supporting it with evidence , examples, and explanations. Length: Typically 1-3 paragraphs, depending on the essay’s length. Tips: Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea that supports the thesis. Use transitions to maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs.
Purpose: The conclusion summarizes the main points and reinforces the thesis. Length: Usually 2-3 sentences. Tips: Restate the thesis in a fresh way . Provide a final thought or suggest a call to action , if appropriate.
Short Essay Example
The Importance of Daily Exercise Maintaining a daily exercise routine is essential for a healthy lifestyle. Exercise not only improves physical health by reducing the risk of chronic diseases, but it also enhances mental well-being. Regular physical activity, even for just 30 minutes a day, can boost energy levels, improve mood, and increase overall life satisfaction. For instance, studies show that individuals who engage in daily exercise report higher levels of happiness and lower stress. Additionally, daily exercise promotes better sleep and cognitive function. In conclusion, incorporating daily exercise into one’s routine can lead to substantial health benefits, making it a worthwhile investment in personal well-being.
Short Essay for Students

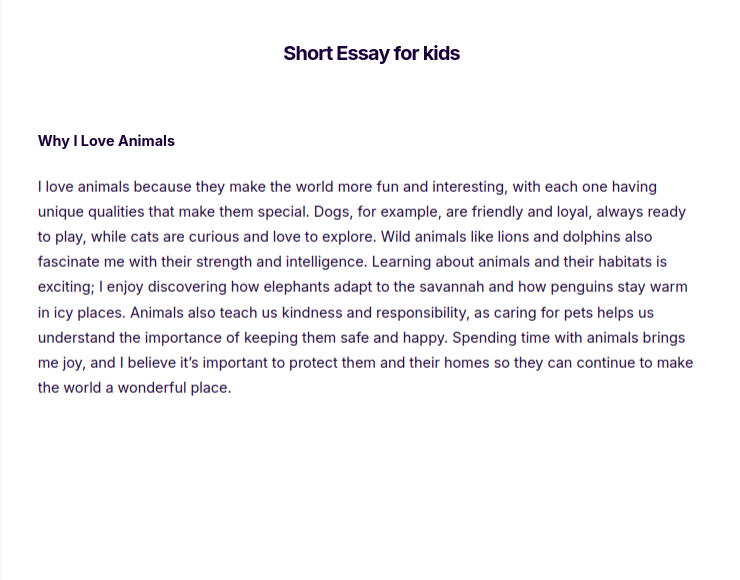
Short Essay for Kids
Short Essay for high school Students

- Short Essay about myself for Students
- Short Essays for Class 5
- short Essays for Class 2
- Short Essay for Scholarship
- Short Essay for Job Interview
- short essay on mother
- short essay on importance of education
- short essay on nature
- short essay on rainy day
- short essay on mobile phone
- short essay on village life
Essays usually become a channel for a person to express emotions and ideas about something or someone. A writer can be creative in presenting topics that he/she thinks is relevant and from which people can infer important lessons in life. Thus, there are many ways to write an essay .
Some of the few types of essays are informative essay , analysis essay , concept essay , reflective essay , and many more. These are all different in the way that they are written as well as their objective. Each is unique in its own way. An essay could also be written short or long, which of course, depends on the writer.
Short Narrative Essay Example

Short Essay Plan Example

Sample Narrative Essay Example

High School Narrative Essay Example

Biographical Narrative Essay Example


Free Visual Essay Example
Argumentative Essay Writing

Sample Opinion Essay Example

Scholarship Essay Example

Short Expository Example

Short Narrative Essay Example

Short Argumentative Sample Example

Persuasive Short Essay Example

Descriptive Short Essay Example

College Short Essay Example

Critical Essay Example

Importance of Short Essay
A short essay is usually contained in just a page and not lengthy words or explanations in necessary to express the main point of the topic. Short essays are important when one is trying to present an important topic without having to write a lot of words or using multiple pages. You may also like concept essay examples & samples.
It presents just the right amount of data or knowledge necessary to feed a hungry mind. As scientific researches has put it, the mind can retain more data when the details are presented in a brief and concise manner. Some people have short attention span so you need to have the writing skills to make your point with just a few words.
How to write a short essay
Writing a short essay involves focusing on clarity and conciseness. With a limited word count, each sentence must add value and effectively convey your ideas. Follow these steps to craft a compelling short essay:
- Understand the Topic Read the prompt carefully to grasp what is required. Identify the main question or theme you need to address.
- Create a Thesis Statement Develop a clear thesis that states your main point or argument. Keep it concise, as this will guide the focus of your entire essay.
- Outline Your Essay Plan the structure: A short essay usually has an introduction, body, and conclusion. List the main points for each section. This helps maintain a logical flow.
- Write the Introduction Start with a hook to grab attention. This could be a question, fact, or a brief anecdote. Introduce your topic briefly and end with your thesis statement.
- Develop the Body Paragraphs Focus on one main idea per paragraph to ensure clarity. Use evidence or examples to support your points. This can include facts, quotes, or personal experiences. Keep paragraphs concise: Aim for around 3–5 sentences per paragraph.
- Write the Conclusion Summarize your main points briefly. Restate the thesis in a new way to reinforce your argument. End with a closing thought or a call to action, if appropriate.
- Revise and Edit Check for clarity and conciseness: Remove unnecessary words and redundant ideas. Proofread for grammar and spelling errors. Ensure your ideas flow logically, with smooth transitions between sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing short essays
Writing a short essay can be challenging due to the limited space available to convey your ideas. Here are some helpful tips to ensure your essay is concise, focused, and impactful:
- Be clear and specific about your main argument or point.
- Make sure your thesis is concise and sets the direction for the entire essay.
- Keep each paragraph dedicated to a single point that supports your thesis.
- Use topic sentences to introduce the paragraph’s main idea.
- Avoid unnecessary words and fluff. Get straight to the point.
- Choose words that convey your meaning accurately and efficiently.
- Even in a short essay, examples can strengthen your argument.
- Select only the most impactful evidence to support your points.
- Plan your word count for each section (introduction, body, and conclusion) to stay within the limit.
How is a Short Essay Structured?
A short essay usually includes an introduction, one or two body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each section should be concise, with the introduction presenting the thesis, the body paragraphs supporting it, and the conclusion summarizing the main points.
How Do You Choose a Topic for a Short Essay?
Choose a focused and manageable topic that can be effectively explored within the word limit. The topic should be specific enough to allow for depth without requiring extensive background information.
What is the Purpose of a Short Essay?
The purpose of a short essay is to express a clear and concise argument, analyze a specific topic, or share insights on a subject. It encourages critical thinking and allows for concise communication of ideas.
How Do You Write a Strong Thesis for a Short Essay?
A strong thesis in a short essay should be clear, specific, and directly answer the essay prompt. It should convey the main argument or point of the essay in one or two sentences, setting the tone for the entire piece.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a Short Essay on the importance of teamwork.
Create a Short Essay discussing the impact of climate change.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Short Essay
Last Updated: September 11, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 124,184 times.
Essay writing is a common assignment in high school or college courses, especially within the humanities. You’ll also be asked to write essays for college admissions and scholarships. In a short essay (250-500 words), you will need to provide an introduction with a thesis, a body, and a conclusion, as you would with a longer essay. Depending on the essay requirements, you may also need to do academic or online research to find sources to back up your claims.
Picking a Topic and Gathering Research
- If you have any questions about the topic, ask your instructor. If your essay doesn't respond to the prompt, you likely won't receive full credit.

- If you're writing an essay for an in-class test or for an application, tailor the essay to the given prompt and topic. Quickly brainstorm a few ideas; for example, think of positive things you can say about yourself for a college-entrance essay.
- For example, the topic “depression in American literature” is far too broad. Narrow down your topic to something like “Willie Loman’s depression in Death of a Salesman .”
- Or, you could write about a narrow topic like “the increase in the USA’s national debt in the 1950s” rather than a broad topic like “the American economy in the 20th century.”

- Depending on the field in which you’re writing the essay—e.g., hard sciences, sociology, humanities, etc.—your instructor will direct you towards appropriate databases. For example, if you’re writing a high-school or college-level essay for your English class, visit online literary databases like JSTOR, LION, and the MLA Bibliography.
- If you're writing the essay for a college or graduate-school application, it's unlikely that you'll need to include any secondary sources.
- If you're writing a timed or in-class essay, you may not be able to find research articles. But, still do draw information from texts and sources you've studied both in and out of class, and build from points made in any provided reading passages.

- If you’re writing about current events or journalism topics, read articles from well-known news sites like CNN or the BBC.
- Avoid citing unreliable websites like blogs or any sites that have a clear bias about the topic they’re reporting on.
Composing the Essay

- If you write the essay without outlining, the essay will be poorly organized.

- This thesis statement is far too weak: “ Death of a Salesman shows the difficulty of living in America after WWII.”
- Instead, hone your thesis to something like: “Arthur Miller uses Death of a Salesman to show that the American Dream is materialist and impractical.”

- So, avoid beginning the paragraph by writing something like, “Since the beginning of time, all people have been consumed with the desire for their father’s approval.”
- Instead, write something like, “In the play Death of a Salesman , Willie Loman’s sons compete for their father’s approval through various masculine displays."
- Then, you can say, "To examine this topic, I will perform a close reading of several key passages of the play and present analyses by noted Arthur Miller scholars."

- In a short essay, the conclusion should do nothing more than briefly restate your main claim and remind readers of the evidence you provided.

- So, take the example about Death of a Salesman . The first body paragraph could discuss the ways in which Willie’s sons try to impress him.
- The second body paragraph could dive into Willie’s hopelessness and despair, and the third paragraph could discuss how Miller uses his characters to show the flaws in their understanding of the American Dream.

- Always cite your sources so you avoid charges of plagiarism. Check with your instructor (or the essay prompt) and find out what citation style you should use.
- For example, if you’re summarizing the inflation of the American dollar during the 1930s, provide 2 or 3 years and inflation-rate percentages. Don’t provide a full-paragraph summary of the economic decline.
- If you're writing an in-class essay and don't have time to perform any research, you don't need to incorporate outside sources. But, it will impress your teacher if you quote from a reading passage or bring up pertinent knowledge you may have gained during the class.

- If no one agrees to read the essay, read over your own first draft and look for errors or spots where you could clarify your meaning. Reading the essay out loud often helps, as you’ll be able to hear sentences that aren’t quite coherent.
- This step does not apply to essays written during a timed or in-class exam, as you won't be able to ask peers to read your work.

- It’s always a mistake to submit an unrevised first draft, whether for a grade, for admissions, or for a scholarship essay.
- However, if you're writing an essay for a timed exam, it's okay if you don't have enough time to combine multiple drafts before the time runs out.
Condensing Your Essay

- So, if you’re writing about Death of a Salesman , an article about symbolism in Arthur Miller’s plays would be useful. But, an article about the average cost of Midwestern hotels in the 1940s would be irrelevant.
- If you’re writing a scholarship essay, double-check the instructions to clarify what types of sources you’re allowed to use.

- A common cliche you might find in an essay is a statement like, "I'm the hardest working student at my school."
- For example, this sentence is too verbose: “I have been a relentlessly stellar student throughout my entire high school career since I am a seriously dedicated reader and thoroughly apply myself to every assignment I receive in class.”
- Shortened, it could read: “I was a stellar student throughout my high school career since I was a dedicated reader and applied myself to every assignment I received.”

- Avoid writing something like, “Willie Loman can be seen as having achieved little through his life because he is not respected by his sons and is not valued by his co-workers.”
- Instead, write, “Arthur Miller shows readers that Willie’s life accomplishments have amounted to little. Willie’s sons do not look up to him, and his co-workers treat him without respect.”

- For example, if you’re trying to prove that WWII pulled the USA out of the Great Depression, focus strictly on an economic argument.
- Avoid bringing in other, less convincing topics. For example, don’t dedicate a paragraph to discussing how much it cost the USA to build fighter jets in 1944.
Short Essay Template and Example

Expert Q&A
- When composing the text of your essay, resist the temptation to pull words from a thesaurus in an attempt to sound academic or intelligent. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If your high school or college has an online or in-person writing center, schedule an appointment. Taking advantage of this type of service can improve your essay and help you recognize structural or grammatical problems you would not have noticed otherwise. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://monroecollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=589208&p=4072926
- ↑ https://www.library.illinois.edu/hpnl/tutorials/secondary-sources/
- ↑ https://www.utep.edu/extendeduniversity/utepconnect/blog/march-2017/4-ways-to-differentiate-a-good-source-from-a-bad-source.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/essay-outline/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay/essay-introduction
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evidence/
- ↑ https://mlpp.pressbooks.pub/writingsuccess/chapter/8-3-drafting/
- ↑ https://www.trentu.ca/academicskills/how-guides/how-write-university/how-approach-any-assignment/writing-english-essay/using-secondary
- ↑ https://www.antioch.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Academic-Tone-for-Formal-Writing.pdf
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/ccs_activevoice/
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/academicwriting
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
D. L. Smith
Sep 9, 2019
Did this article help you?

Aug 15, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO