Upload Meta
Happy Users 100% Satisfaction

30+ Expert team Members & associate partners

video library

Query Solutions

Topper's Talk

Explore—--- Learn —---Accomplish
Crack Competitive Exams under the guidance of India’s best faculty exam toppers for courses such as MPPSC, MPESB, MP POLICE, MPTET, SSC, BANK & RAILWAY.
Popular Courses
Paid courses (complete), paid courses [subject /part wise], paid test series, free test series, free e-book, free classes.

मैराथन ONLINE CLASSES [MP CURRENT AFFAIRS-2023]

MPPSC Free PDF Content
Free mppsc 2024 prelims test.

REASONING ABILITY TEST SERIES (BILINGUAL)

QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE TEST (BILINGUAL)

GENERAL STUDIES (BILINGUAL)

MPPSC 2024-Prelims MEGA Test Series

MCQ- Current Affairs Previous Years

उद्यमिता एवं प्रबंधन

समाजशास्त्र

अर्थव्यवस्था

ENTREPRENEURSHIP [ Paper 4- Part B]

Revision - वानिकी (यूनिट 1,2,3,4)

MPPSC Online Classes- English Medium

Batch 2.0- MPPSC ONLINE CLASSES- Hindi Medium

MPPSC Classes -HINDI MEDIUM
What vs education offer.
- Live and Recorded Lectures for MPPSC & MPESB (VYAPAM) Exam and other Government Exams.
- Top Educators will help You cover the full syllabus of MPPSC & MPESB (VYAPAM) Exam and other Government Exams.
- Books and Study materials for better preparation of All Competitive Exams.
- ONLINE & OFFLINE (MPPSC MEGA TEST SERIES) by VS EDUCATION & Associate Centers.
- Regular Mock tests for revising all topics.
- Get latest information Related to Civil Services Exams & Competitive Exams.
- Free Test Series for MPPSC & MPESB (VYAPAM) Exam and other Government Exams.
Every Student is Unique
We believe that every student learns differently and we work towards helping them learn better.
They learn with videos, concepts, tests & stories
Whether they want to start a new chapter or revise an old one, students learn at their own pace.
Learn better with individual learning paths
We provide multiple types of courses according to each students needs, they can choose courses according to his requirment.
Students experience all round academic growth
Our four modules work seam-lessly to boost every student's all-round academic growth, helping them learn better.
Course Categories
Become lifelong learners with India's best teachers, engaging video lessons and personalised learning journeys
- ALL CATEGORIES
- Engineering

VS Education App Features
VS EDUCATION is a technology based online learning initiative by VS EDUCATION . Add Power of Coaching to your Online learning with VS EDUCATION .
Live Online Interactive Classes
Online Test Series and feedback
Procure Printed SMP & Exercise Sheets
Free Stuff - Study material, eBooks, eDPPS etc
Live Online Doubt Removal
Recorded video lectures
Daily Dose - Important Questions. Quizzes & Study Tips
Live feed - Access to Important Videos, tricky Questions

Enter Registration ID Of Employment Department

Verify OTP To Continue
Resend OTP in sec.
Select Any One Job Role
Enter your details to continue
Don't have an account yet? SignUp
Enter Mobile Number To Continue
Complete Your Profile
Create Password To Continue
Windows Application

Select Classroom Center
No. data found.
.png)
- Current Students
- Faculty / Staff
- Paying for College
- Alumni Services
- Maine Transfer Guarantee
- Program Finder
- Affordable, Flexible, Accessible
- Distance Education
- All Online Courses & Degrees
- Bachelor’s Degrees Online
- Master’s Degrees Online
- Start Dates
- Admissions, Costs & Aid
- Partnerships
- Faculty and Contacts
- Academic and Career Support
- Student Testimonials
- Distance Education Advantage
- In-Person Education
- Sustainable Ventures
- Careers & Outcomes
- Strategic Plan
- Project Evolution
- Project Stratus
- About Unity
- Office of the President
- Our Evolution
- Sustainable Achievements & Initiatives
- Reinventing College
- Extended Reality (XR)
- Commencement
- Give to Unity Environmental University
- Institutional Communications
- Unity Environmental University News
- Unity Store
Frustrated with the 2024-2025 FAFSA ® Challenges? Unity Distance Education Is Here to Help and Support: Navigating the Issues and Finding Solutions

Frustrated with the 2024-2025 FAFSA ® Challenges?
Home / News / Training Vs. Education: What’s The Difference?

Training Vs. Education: What’s The Difference?
If you are looking to advance in your field or improve your earning potential, you may be wondering whether workforce training vs. education through a formal degree program is the best route for you.
Though the words training and education are often used interchangeably, they are fundamentally different. The biggest difference between training and education is that one focuses on building skills, and the other provides a foundation for further learning. Let’s explore these concepts in more detail to determine which is right for your professional goals.
What Is Workforce Education?
What is workforce training, education vs. training: the difference between education and training.

Universities like Unity offer formal education programs that can lay the framework for career advancement or change.
Workforce education (versus training) is a more continuous process of learning. While education may include learning new skills, it also is likely to provide context to those skills, such as a theoretical framework or relevant history. Education is typically focused on acquiring knowledge and the skills necessary to gain more knowledge about specific subjects. There are multiple levels of formal education with many professionals choosing to pursue a credential, certificate, associate degree , baccalaureate degree, or master’s degree .
Education usually occurs in classrooms at schools, colleges, and universities, but it can also occur online and in workplaces. For example, companies may invite educational speakers or provide a curated resource library to employees. Some companies will even pay the tuition for their employees to earn a baccalaureate or master’s degree because it is beneficial for them to invest in the education of a team member. Also, an educated individual is more likely to value and practice cultural competence in educational and professional settings.
Both training and education rely on purposeful instructional design to effectively teach and engage students.
Unity Environmental University’s Environmental Business Programs
Unity offers much more than environmental science degrees. We have several baccalaureate and Master’s programs that educate people on how to incorporate green practices into business.
Examples of business programs we offer include:
- Focus Area: Renewable Energy
- Focus Area: Adventure Ecotourism
- Focus Area: Sustainable Food and Farming
- Focus Area: Hemp Industry and Science
- Master’s in Environmental Marketing and Behavioral Economics
- SMBA in Sustainable Tourism & Hospitality

Ready To Learn More About Unity Environmental University?
Workforce training equips individuals with specific skills and/or knowledge. It is usually specific to an organization, job role, or task. For instance, a company may have all new employees complete the same onboarding training. New technologies or systems often require training current employees or specific teams.
Workforce training, like education, can occur online or in person . Yet, for many workforce development skills, in-person training is needed to provide hands-on practice or experiential learning . Some types of workforce training are optional, while others are required for all or certain employees. For example, all educators must complete several standardized trainings about laws and safety regulations regarding children.

Is educating the workforce about education or training? It’s actually about both. However, when deciding what type of professional development to pursue, it’s important to distinguish between training and education options. Consider their different approaches to learning and development within the context of the workforce.
Skills Vs. Knowledge
Short-term proficiency vs. long-term growth, specialized abilities vs. comprehensive insight, immediate use vs. progressive integration.
The main goal of workplace training is to gain practical skills that can be applied immediately on the job. The main goal of education is to instill knowledge. When skills are taught in education, they are often needed for further learning to take place. Workplace education can provide individuals with a broad, conceptual understanding of their field and industry, which can be advantageous to their careers.
In other words, education vs training is about learning to know vs learning to do. Quality education informs students of facts, concepts, and theories, whereas training focuses on applications.
When considering the average length of training vs education programs, training programs are usually shorter. They aim to achieve proficiency quickly in the trained individuals. On the other hand, education’s goal is to foster long-term personal and professional growth.
Research shows that formal higher education can transform an individual’s sense of self and interpersonal relationships. Other advantages of formal education for individuals and society as a whole include more:
- Environmental stewardship
- Technological literacy
- Financial stability
- Civic engagement
Discover popular green jobs and research the training and education required to succeed in them.
Training often concentrates on developing specialized abilities essential for particular tasks. Educational programs provide comprehensive insight aimed at developing a deeper understanding of a field. For example, if you work in the regenerative travel or sustainable hospitality industry and want to advance to management, you may have the choice between a manager-in-training program at your job or a tuition stipend to earn a bachelor’s degree in business management . Both could advance your career, but the approaches they take are very different.
The skills learned in workforce training are usually immediately applicable in the workplace. However, with education, there may not be a direct correlation between what you are learning and how you can apply it in your career. Instead, you may notice a gradual integration of knowledge from educational programs. This is part of the reason why both education and training are so important to professional success for individuals and businesses, as they operate on different timelines.
Unity Environmental University Offers Flexible Distance Education
Both education and workforce development are vital to individual and collective growth. The key is not to choose between them but to find the right balance at the right times. If you are leaning toward formal education, you can earn a bachelor’s or master’s degree completely online at Unity Environmental University . Just filter by Distance Education programs in our Program Search . We offer multiple start dates throughout the year, meaning you can begin your degree when you are ready.

Start Your Journey

Looking for Answers
Get More Info
© Unity Environmental University 2024. “America’s Environmental University.™”
Privacy Overview

Learning vs Education – The Difference and Why It Matters
I too often read articles or hear people talk about “learning” when what they are clearly referring to is education. The two are not the same, and I believe that recognizing and appreciating the difference – understanding learning vs education – is a critical part of becoming the effective lifelong learners we need to be in our current world.
Learning vs Education: How Are They Different?
I’ve previously defined learning as:
the lifelong process of transforming information and experience into knowledge, skills, behaviors, and attitudes
Education is just one option within this process. It is one approach to learning among many others. And, it’s usually a systematized approach that is developed, structured, and directed by people other than ourselves.
Education tends to be about taking classes, earning credentials, acquiring and proving the acquisition of knowledge and skills – again, all activities and outcomes governed by parameters set by others.
We tend to inflate the role of formal education, established knowledge, and the credentials associated because it produces relatively clear signals that can be seen and used as social and economic capital. All of our other experiences – that is, most of life – while often much more valuable, are much fuzzier and harder to convert into standardized signals.
By its very nature, education also tends to be conservative (in the non-political sense). It passes along and preserves what is already known – the established narrative – and it tends to treat the narrative as epistemological (the basis of knowledge and knowing) rather than instrumental (a means to an end). This sort of conservatism is at the very heart of traditional teaching (which nearly always benefits from a greater emphasis on epistemological modesty ).
Learning, on the other hand, is inherently progressive . It is always in the process of happening. The person who is learning is actively changing. Learning causes change, and change causes learning.
Learning is also a mindset .
Ideally, it’s what we bring to education, what helps us to move beyond what was and what is to what could be. There are so many ways in which we learn . Sometimes these are represented in education; very often they are under-represented or even actively suppressed.
Why does it matter?
There is nothing inherently negative about education. We very often need structures and systems to help us learn and clearly there can be significant benefits to passing along and preserving what is already known. But problems arise when we start treating education and learning as the same thing.
Well, when we equate learning with education, we’re more likely to focus on generating answers . On providing structure; on optimizing for performance and achievement.
Again, that’s not inherently bad, but we tend to over do it. We jump to conclusions too early and we inevitably provide solutions that work for only a subset – often a minority – of those we aim to serve, and often only for a limited time.
Worse, we provide answers that may be harmful to many of those we aim to serve. We wind up with a situation analogous to what we have in health care (at least in the U.S.) where interventions and treatments are prioritized over prevention and root causes.
Real learning, on the other hand, is about questions , about navigating ambiguity. To reference my definition again, it is as much about attitude and behavior as it is about knowledge and skills. Arguably it is more about these things in our current environment.
When we emphasize education as an approach to learning, our bias is to focus too much on cognition.
Again, the result is analogous to the situation in healthcare, where we tend to overemphasize the biological at the expense of the psychological and social, not fully appreciating that health – like learning – is multi-faceted.
We also tend to shift responsibility – and with it, freedom – away from the learner when we confuse education with learning. Too much responsibility gets placed on teachers and institutions, not enough on learners. As a result, we don’t really provide learners with the support they need. But learning doesn’t really happen without the learner’s involvement and effort, and the more the learner can take responsibility for the involvement and effort, the better.
In general, we simply miss a lot when we equate education with learning. Education isn’t the answer to everything. In fact, it is arguably becoming much less important, at least in its usual, traditional forms. Given the pace at which knowledge now flows and changes, and the ability for machines to learn nearly anything that has been systematized and structured, we arguably can’t educate ourselves fast enough .
Education remains useful, but learning is what is really needed to navigate our current world.
What needs to change?
So, if learning and education are different, and the learning vs education difference matters, what needs to change?
For starters, we – and particularly those in positions of influence – need to be more careful about language, more careful not to use the words “learning” and “education” interchangeably, but rather to use each in its proper place.
This may seem like a trivial or pedantic point, but language matters . Language shapes the world.
Next, we – as societies, as businesses, and certainly as educators – need to put much more emphasis on real learning, including educating (yes, that would be the proper word here) people about learning, about how to learn. As Malcom Knowles put it, it’s a tragic fact that most of us know only how to be taught. That needs to change.
Those of us in traditional educational roles – meaning not just teachers, but also parents, managers, and leaders of every stripe – need to focus less on teaching in the traditional sense and more on allowing for and generating contexts in which learning can happen. Allowing for ambiguity, for wasting of time, for tinkering, for questioning, risk taking, and failure. (All of the cliches of the business world apply here because business, when it is actually pursued productively, is a learning activity.)
Finally (for now), we need to appreciate much more deeply the degree to which learning and life are interwoven.
Learning is not confined within the walls of an institution or the structure of a class. It happens in the flow of life. It is rooted in physicality and emotion as much as in cognition. When we shift to seeing learning in this way, it becomes much easier to recognize and take advantage of the myriad opportunities for learning that we encounter daily.
Some of these opportunities will, of course, arise in the context education. But the vast majority will not – because education and learning are simply not the same thing.
Being insistent about understanding learning in its broadest and deepest sense is not just an academic exercise. It is critical for navigating the complexities of the world and making our way toward as much of a shared truth as we can find. If we take the parochial view of learning as merely education, we limit ourselves dangerously.
- This Is Learning
- Can we educate ourselves fast enough?
- 6 Disciplines of the True Learning Mindset
- A Short Collection of Powerful But Under Appreciated Learning Strategies
Related Posts

Are you truly available to learn?
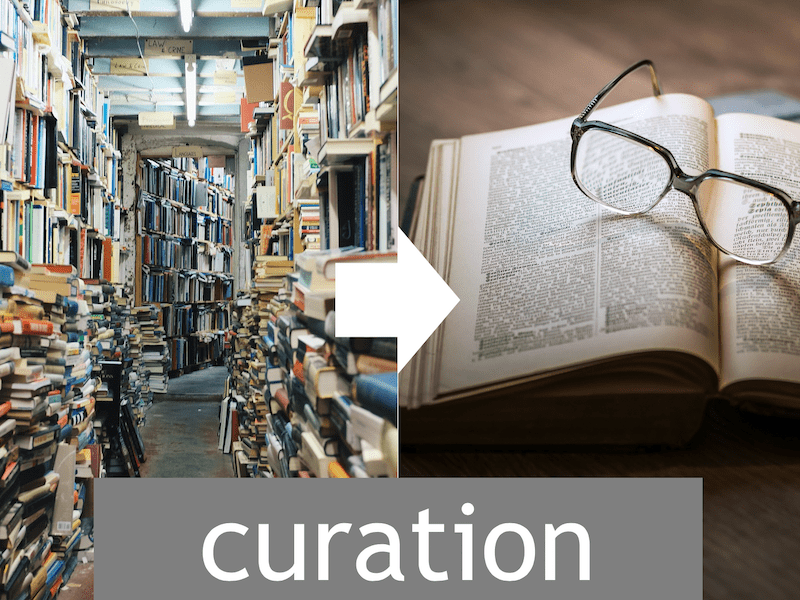
How to Curate Lifelong Learning

What is unlearning and what does it require?
2 thoughts on “learning vs education – the difference and why it matters”.
Something stuck out to me in this article when you said “Well, when we equate learning with education, we’re more likely to focus on generating answers.” This is really profound since the seed to an answer/s is asking the right question/s. I think education today is too focused on rewarding students for getting the right answers instead of rewarding them for asking questions that will help them arrive at an answer. They are missing half of the equation when answers are the priority.
I do think there is a difference – I’d frame it as learning is about the desire to obtain knowledge and improve one’s life and mindset, while education tends to be a structured, formal way to gain knowledge on a topic. So for one who is interested in learning, an education is one way to fulfill the desire to learn, but there are many other ways as well. Self-directed reading, hands-on experience, or taking a variety of local workshops are all alternative ways to learn without being an education.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
9 Core Difference Between Education and Training
- January 24, 2024

Although both these terms are used synonymously. Knowing the distinction is key to delivering efficient programs.
Education, in its broadest sense, is about learning. It’s a journey through theory, concepts & abstract knowledge that helps us understand our world & develop critical thinking.
In contrast to that, training is more focused. Its typically aimed at teaching specific skills or competencies needed for a particular job or activity.
In this article, we’ll unravel the difference between education and training. Shedding light on how they diverge and intersect.
What is Education?

It is a broad process. One that includes acquisition of knowledge, understanding, values, skills & moral habits. Focused on the holistic development of an individual. While encouraging critical thinking, creativity, and personal growth.
Furthermore, its not confined to just academic learning. It extends to understanding the world around us. And fostering intellectual and emotional maturity.
Also read about the difference between learning and training .
Key Points About Education
| : It covers a wide range of topics & theories. It provides a comprehensive understanding of subjects. | : It aims at long-term intellectual development. Added with the cultivation of a lifelong love for learning. | : Focuses on the all-round development of an individual. This includes moral, emotional & social aspects. | : Encourages exploration, questioning & understanding of various perspectives. |
Types of Education
| : A structured & systematic form. It includes primary, secondary & tertiary. | : Learning that occurs outside formal institutions. For instance learning from family, peers, or self-study. | : Organized learning outside the formal system. This includes adult classes or community workshops. |
What is Training?

Training is a systematic process focused on developing specific skills or practical knowledge. Aimed at improving performance in a particular task or job.
Often practical & job-specific, it’s focused at enhancing the efficiency & effectiveness in a professional context.
Training is more about application than theory. Hence, making it an essential component for vocational or technical learning.
You might also like to read about the difference between course and training .
Key Points About Training
| : Primarily a method of skill development. Centered around developing practical skills & competencies. | : Usually has a specific time frame with clear objectives. It’s often related to improving job performance. | : Involves practical exercises & real-world application. | : The success is often measured by one’s ability to perform specific tasks/functions. |
Types of Training
| : Practical training provided at the workplace while performing the actual job. | : Conducted outside the workplace, like workshops, seminars, or online courses. | : Focused on acquiring skills for a particular trade or profession. Often provided by technical or vocational schools. |
Explore the difference between teaching & learning .
9 Core Differences Between Education and Training (Education vs Training)
The former broadens our horizons & builds a foundation for critical thinking. While training equips us with the necessary tools & skills to apply in specific scenarios.
In the table below, we list down the key differences between education and training.
| Aspect | Education | Training |
|---|---|---|
| Broad learning and intellectual development. | Specific skill development for a task/job. | |
| Theoretical knowledge, comprehensive understanding. | Narrow scope, practical, job-related skills. | |
| Long-term process of intellectual growth and critical thinking. | Short-term skill enhancement for better job performance & productivity of employees. | |
| Holistic, fostering overall development. | Focused, task-oriented. | |
| Generally long-term and ongoing. | Often short-term, duration-specific. | |
| More exploratory, encouraging questioning and understanding. | Hands-on, practical application of skills. | |
| Based on understanding, critical analysis, and knowledge. | Based on performance and skill proficiency. | |
| Degree programs, liberal arts. | Workshops, vocational training programs, employee on-the-job training. | |
| Knowledge, critical thinking, and moral development. | Enhanced job performance, specific skill acquisition. |
Also read about teaching vs training .
Summary on Education vs Training
In conclusion, both education & training are distinct. And yet somehow interrelated in shaping both personal & professional landscapes.
While the former casts a wide net, training zeroes in on specific skill sets. This understanding is not just academic. But instrumental in guiding individuals and organisations. Towards more targeted and effective learning strategies.
By appreciating the difference between education and training, and where they intersect. We can better navigate our paths.
FAQs on Difference Between Training and Education
1.can someone receive education and training simultaneously.
Absolutely. Many programs incorporate elements of effective training. Particularly in fields where practical skills are essential. For instance, medical learning. It includes both comprehensive theoretical learning & practical training in clinical skills.
2.Can training be considered a part of education?
Yes. Particularly in the context of vocational or technical education. Where specific skills are taught as a part of a broader curriculum.
3.Is education more important than training?
Neither is inherently more important; they serve different purposes. Education is beneficial for a wide range of professions and life in general. Training, on the other hand, is essential for acquiring specific skills.
4.How do the methodologies of education and training differ?
Traditional education methodologies often involve exploratory and theoretical learning. Encouraging questioning and a deep understanding of subjects. Training methodologies are more practical. Focusing on hands-on skills and direct application of knowledge in specific scenarios.
5.Is online learning considered education or training?
Online learning can be both. Depending on the nature of the course. If the course is aimed at broad knowledge and theoretical understanding, it’s traditional education. If it’s focused on specific skills or tasks, such as coding bootcamps, it’s considered training.
6.Can training lead to personal growth similar to traditional education?
Yes, training can contribute to personal growth. Especially in terms of building confidence, honing specific skills, and improving job performance.
Nikhil Dutt
Nikhil, a seasoned writer, excels in content ranging from long-form content, ad copies, UX microcopies & scripts. With an in-depth understanding of social media algorithms, he's driven notable growth across platforms. Proficient in SEO & SMO, he champions holistic content creation with a mission to elevate businesses through powerful storytelling. Although an IT graduate, his writing passion defines him, making him a diverse professional. Outside work, Nikhil enjoys reading, journaling, and exploring new places. Volunteering as a Life & Relationship Coach, he's committed to helping individuals foster more joyful lives and relationships.
9 Major Difference Between Learning and Training
Difference between course and training: 12 factors, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Edmingle transcends the limitations of traditional learning management systems with its AI-powered analytics-focused LMS platform. An all-in-one SaaS training management platform for delivering training with impact.
Recent Posts

How to Improve Learner Experience in Online Training Programs with Edmingle

The Role of Real-Time Analytics in Live Training Programs with Edmingle

Insightful Learner Analytics with Edmingle: The Future of Training

Boost Learner Engagement with AI-Driven Sentiment Analysis on Edmingle

8 Best LMS in Dubai (UAE)

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
Prehistoric and primitive cultures
- Mesopotamia
- North China
- The Hindu tradition
- The introduction of Buddhist influences
- Classical India
- Indian influences on Asia
- Xi (Western) Zhou (1046–771 bce )
- Dong (Eastern) Zhou (770–256 bce )
- Qin autocracy (221–206 bce )
- Scholarship under the Han (206 bce –220 ce )
- Introduction of Buddhism
- Ancient Hebrews
- Education of youth
- Higher education
- The institutions
- Physical education
- The primary school
- Secondary education
- Early Roman education
- Roman modifications
- Education in the later Roman Empire
- Ancient Persia
- Elementary education
- Professional education
- Early Russian education: Kiev and Muscovy
- Influences on Muslim education and culture
- Aims and purposes of Muslim education
- Organization of education
- Major periods of Muslim education and learning
- Influence of Islamic learning on the West
- From the beginnings to the 4th century
- From the 5th to the 8th century
- The Irish and English revivals
- The cultural revival under Charlemagne and his successors
- Influences of the Carolingian renaissance abroad
- Education of the laity in the 9th and 10th centuries
- Monastic schools
- Urban schools
- New curricula and philosophies
- Thomist philosophy
- The Italian universities
- The French universities
- The English universities
- Universities elsewhere in Europe
- General characteristics of medieval universities
- Lay education and the lower schools
- The foundations of Muslim education
- The Mughal period
- The Tang dynasty (618–907 ce )
- The Song (960–1279)
- The Mongol period (1206–1368)
- The Ming period (1368–1644)
- The Manchu period (1644–1911/12)
- The ancient period to the 12th century
- Education of the warriors
- Education in the Tokugawa era
- Effect of early Western contacts
- The Muslim influence
- The secular influence
- Early influences
- Emergence of the new gymnasium
- Nonscholastic traditions
- Dutch humanism
- Juan Luis Vives
- The early English humanists
- Luther and the German Reformation
- The English Reformation
- The French Reformation
- The Calvinist Reformation
- The Roman Catholic Counter-Reformation
- The legacy of the Reformation
- The new scientism and rationalism
- The Protestant demand for universal elementary education
- The pedagogy of Ratke
- The pedagogy of Comenius
- The schools of Gotha
- Courtly education
- The teaching congregations
- Female education
- The Puritan reformers
- Royalist education
- The academies
- John Locke’s empiricism and education as conduct
- Giambattista Vico, critic of Cartesianism
- The condition of the schools and universities
- August Hermann Francke
- Johann Julius Hecker
- The Sensationists
- The Rousseauists
- National education under enlightened rulers
- Spanish and Portuguese America
- French Québec
- New England
- The new academies
- The middle colonies
- The Southern colonies
- Newfoundland and the Maritime Provinces.
- The social and historical setting
- The pedagogy of Pestalozzi
- The influence of Pestalozzi
- The pedagogy of Froebel
- The kindergarten movement
- The psychology and pedagogy of Herbart
- The Herbartians
- Other German theorists
- French theorists
- Spencer’s scientism
- Humboldt’s reforms
- Developments after 1815
- Girls’ schools
- The new German universities
- Development of state education
- Elementary Education Act
- Secondary and higher education
- The educational awakening
- Education for females
- New Zealand
- Education under the East India Company
- Indian universities
- The Meiji Restoration and the assimilation of Western civilization
- Establishment of a national system of education
- The conservative reaction
- Establishment of nationalistic education systems
- Promotion of industrial education
- Social and historical background
- Influence of psychology and other fields on education
- Traditional movements
- Progressive education
- Child-centred education
- Scientific-realist education
- Social-reconstructionist education
- Major trends and problems
- Early 19th to early 20th century
- Education Act of 1944
- The comprehensive movement
- Further education
- Imperial Germany
- Weimar Republic
- Nazi Germany
- Changes after World War II
- The Third Republic
- The Netherlands
- Switzerland
- Expansion of American education
- Curriculum reforms
- Federal involvement in local education
- Changes in higher education
- Professional organizations
- Canadian educational reforms
- The administration of public education
- Before 1917
- The Stalinist years, 1931–53
- The Khrushchev reforms
- From Brezhnev to Gorbachev
- Perestroika and education
- The modernization movement
- Education in the republic
- Education under the Nationalist government
- Education under communism
- Post-Mao education
- Communism and the intellectuals
- Education at the beginning of the century
- Education to 1940
- Education changes during World War II
- Education after World War II
- Pre-independence period
- The postindependence period in India
- The postindependence period in Pakistan
- The postindependence period in Bangladesh
- The postindependence period in Sri Lanka
- South Africa
- General influences and policies of the colonial powers
- Education in Portuguese colonies and former colonies
- German educational policy in Africa
- Education in British colonies and former colonies
- Education in French colonies and former colonies
- Education in Belgian colonies and former colonies
- Problems and tasks of African education in the late 20th century
- Colonialism and its consequences
- The second half of the 20th century
- The Islamic revival
- Migration and the brain drain
- The heritage of independence
- Administration
- Primary education and literacy
- Reform trends
- Malaysia and Singapore
- Philippines
- Education and social cohesion
- Education and social conflict
- Education and personal growth
- Education and civil society
- Education and economic development
- Primary-level school enrollments
- Secondary-level school enrollments
- Tertiary-level school enrollments
- Other developments in formal education
- Literacy as a measure of success
- Access to education
- Implications for socioeconomic status
- Social consequences of education in developing countries
- The role of the state
- Social and family interaction
- Alternative forms of education

What was education like in ancient Athens?
How does social class affect education attainment, when did education become compulsory, what are alternative forms of education, do school vouchers offer students access to better education.

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- World History Encyclopedia - Education in the Elizabethan Era
- Academia - Return on Education Using the Concept of Opportunity Cost
- National Geographic - Geography
- Table Of Contents

What does education mean?
Education refers to the discipline that is concerned with methods of teaching and learning in schools or school-like environments, as opposed to various nonformal and informal means of socialization .
Beginning approximately at the end of the 7th or during the 6th century, Athens became the first city-state in ancient Greece to renounce education that was oriented toward the future duties of soldiers. The evolution of Athenian education reflected that of the city itself, which was moving toward increasing democratization.
Research has found that education is the strongest determinant of individuals’ occupational status and chances of success in adult life. However, the correlation between family socioeconomic status and school success or failure appears to have increased worldwide. Long-term trends suggest that as societies industrialize and modernize, social class becomes increasingly important in determining educational outcomes and occupational attainment.
While education is not compulsory in practice everywhere in the world, the right of individuals to an educational program that respects their personality, talents, abilities, and cultural heritage has been upheld in various international agreements, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights of 1948; the Declaration of the Rights of the Child of 1959; and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966.
Alternative forms of education have developed since the late 20th century, such as distance learning , homeschooling , and many parallel or supplementary systems of education often designated as “nonformal” and “popular.” Religious institutions also instruct the young and old alike in sacred knowledge as well as in the values and skills required for participation in local, national, and transnational societies.
School vouchers have been a hotly debated topic in the United States. Some parents of voucher recipients reported high levels of satisfaction, and studies have found increased voucher student graduation rates. Some studies have found, however, that students using vouchers to attend private schools instead of public ones did not show significantly higher levels of academic achievement. Learn more at ProCon.org.
Should corporal punishment be used in elementary education settings?
Whether corporal punishment should be used in elementary education settings is widely debated. Some say it is the appropriate discipline for certain children when used in moderation because it sets clear boundaries and motivates children to behave in school. Others say can inflict long-lasting physical and mental harm on students while creating an unsafe and violent school environment. For more on the corporal punishment debate, visit ProCon.org .
Should dress codes be implemented and enforced in education settings?
Whether dress codes should be implemented and enforced in education settings is hotly debated. Some argue dress codes enforce decorum and a serious, professional atmosphere conducive to success, as well as promote safety. Others argue dress codes reinforce racist standards of beauty and dress and are are seldom uniformly mandated, often discriminating against women and marginalized groups. For more on the dress code debate, visit ProCon.org .
Recent News
education , discipline that is concerned with methods of teaching and learning in schools or school-like environments as opposed to various nonformal and informal means of socialization (e.g., rural development projects and education through parent-child relationships).
(Read Arne Duncan’s Britannica essay on “Education: The Great Equalizer.”)
Education can be thought of as the transmission of the values and accumulated knowledge of a society. In this sense, it is equivalent to what social scientists term socialization or enculturation. Children—whether conceived among New Guinea tribespeople, the Renaissance Florentines, or the middle classes of Manhattan—are born without culture . Education is designed to guide them in learning a culture , molding their behaviour in the ways of adulthood , and directing them toward their eventual role in society. In the most primitive cultures , there is often little formal learning—little of what one would ordinarily call school or classes or teachers . Instead, the entire environment and all activities are frequently viewed as school and classes, and many or all adults act as teachers. As societies grow more complex, however, the quantity of knowledge to be passed on from one generation to the next becomes more than any one person can know, and, hence, there must evolve more selective and efficient means of cultural transmission. The outcome is formal education—the school and the specialist called the teacher.
As society becomes ever more complex and schools become ever more institutionalized, educational experience becomes less directly related to daily life, less a matter of showing and learning in the context of the workaday world, and more abstracted from practice, more a matter of distilling, telling, and learning things out of context. This concentration of learning in a formal atmosphere allows children to learn far more of their culture than they are able to do by merely observing and imitating. As society gradually attaches more and more importance to education, it also tries to formulate the overall objectives, content, organization, and strategies of education. Literature becomes laden with advice on the rearing of the younger generation. In short, there develop philosophies and theories of education.
This article discusses the history of education, tracing the evolution of the formal teaching of knowledge and skills from prehistoric and ancient times to the present, and considering the various philosophies that have inspired the resulting systems. Other aspects of education are treated in a number of articles. For a treatment of education as a discipline, including educational organization, teaching methods, and the functions and training of teachers, see teaching ; pedagogy ; and teacher education . For a description of education in various specialized fields, see historiography ; legal education ; medical education ; science, history of . For an analysis of educational philosophy , see education, philosophy of . For an examination of some of the more important aids in education and the dissemination of knowledge, see dictionary ; encyclopaedia ; library ; museum ; printing ; publishing, history of . Some restrictions on educational freedom are discussed in censorship . For an analysis of pupil attributes, see intelligence, human ; learning theory ; psychological testing .
Education in primitive and early civilized cultures
The term education can be applied to primitive cultures only in the sense of enculturation , which is the process of cultural transmission. A primitive person, whose culture is the totality of his universe, has a relatively fixed sense of cultural continuity and timelessness. The model of life is relatively static and absolute, and it is transmitted from one generation to another with little deviation. As for prehistoric education, it can only be inferred from educational practices in surviving primitive cultures.
The purpose of primitive education is thus to guide children to becoming good members of their tribe or band. There is a marked emphasis upon training for citizenship , because primitive people are highly concerned with the growth of individuals as tribal members and the thorough comprehension of their way of life during passage from prepuberty to postpuberty.

Because of the variety in the countless thousands of primitive cultures, it is difficult to describe any standard and uniform characteristics of prepuberty education. Nevertheless, certain things are practiced commonly within cultures. Children actually participate in the social processes of adult activities, and their participatory learning is based upon what the American anthropologist Margaret Mead called empathy , identification, and imitation . Primitive children, before reaching puberty, learn by doing and observing basic technical practices. Their teachers are not strangers but rather their immediate community .
In contrast to the spontaneous and rather unregulated imitations in prepuberty education, postpuberty education in some cultures is strictly standardized and regulated. The teaching personnel may consist of fully initiated men, often unknown to the initiate though they are his relatives in other clans. The initiation may begin with the initiate being abruptly separated from his familial group and sent to a secluded camp where he joins other initiates. The purpose of this separation is to deflect the initiate’s deep attachment away from his family and to establish his emotional and social anchorage in the wider web of his culture.
The initiation “curriculum” does not usually include practical subjects. Instead, it consists of a whole set of cultural values, tribal religion, myths , philosophy, history, rituals, and other knowledge. Primitive people in some cultures regard the body of knowledge constituting the initiation curriculum as most essential to their tribal membership. Within this essential curriculum, religious instruction takes the most prominent place.

This device is not currently supported for these products.

Start the year right with free, best-in-class developer tools
Let us know what you’re looking for:, an end-to-end development environment on pc to build any app, service, or game, visual studio 2022.
A complete development environment that will help you take your code from initial design to final deployment. Comes with support for many different languages, frameworks, and runtimes out of the box (such as .NET, Python, C++, Node.js, and TypeScript), with even more available as extensions. Add the GitHub Copilot extension to get a truly exceptional experience with code explanations and answers to docs in Github, among other features.
| Learn more
Get a simplified installer for your development type
You can always add or remove workloads and components
- .NET web & desktop
- Mobile with .NET
- Desktop with C++
Visual Studio Community 2022
Pick your own features with the full installer
A lightweight, powerful code editor on PC, Mac, or Linux
Visual studio code.
Comes with built-in support for JavaScript, TypeScript, and Node.js and has a rich ecosystem of extensions for other languages (such as C++, C#, Java, Python, Go). Customize the editing, building, debugging experience with extensions to optimize for your unique needs. Add the GitHub Copilot extension to get a truly exceptional experience with code explanations and answers to docs in Github, among other features.
- Windows x64 User Installer
- macOS Universal Package
- Linux x64 .deb
- Linux x64 .rpm
Learn how to use Visual Studio
Microsoft docs is the best place to find documentation for Microsoft products and technologies. Check out the sections highlighted below to learn how to use Visual Studio to develop applications, services, and games in the language of your choice.
Microsoft Learn

Visual Studio Dev Essentials
Get developer tools and services, Azure credit, downloads, and more – for free.
Azure for Students
Start building the future with Azure for Students! Get a $100 credit when you create your free Azure for Students account.
Developer Community
Documentation.
Rating Content
The 7 biggest differences between online learning vs classroom learning.

Table of contents
Share this article.
Online learning vs classroom learning is two popular options for acquiring knowledge and skills.
While both have their advantages and disadvantages, each approach offers a unique learning experience.
As technology continues to advance, online learning has become an increasingly popular alternative to traditional classroom learning.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the seven biggest differences between online learning vs classroom learning, including factors such as flexibility, cost, interaction, and more.
Whether you're a student or a teacher, understanding the differences between these two approaches can help you choose the best learning method for your needs.
So what are we waiting for? Let’s dive into all that you need to know about online learning vs classroom learning.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Online Learning

Let’s have a look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of online learning.
Advantages of Online Learning:
1. flexibility.
It allows learners to study at their own pace and on their schedule, making it an ideal option for those with busy lifestyles or other commitments.
2. Cost-Effective
Online courses are often less expensive than traditional classroom-based courses, making education more accessible to a wider range of learners.
3. Accessibility
It is available to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of geographic location or physical disabilities.
4. Personalized Learning
Online courses often offer personalized learning experiences, allowing learners to focus on their areas of interest or weaknesses.
Disadvantages of Online Learning
1. limited interaction.
It lacks the face-to-face interaction and socialization opportunities of traditional classroom learning, which may be a disadvantage for some learners.
2. Technical Issues
Technical difficulties such as internet connectivity issues, software glitches, or hardware malfunctions can disrupt the learning experience.
3. Self-Motivation
It requires a high degree of self-discipline and self-motivation, which may be challenging for some learners who require more structured learning environments.
4. Lack Of Feedback
It may offer limited feedback opportunities from instructors or peers, which can make it difficult for learners to gauge their progress and receive constructive criticism.
Now that we have discussed the advantages and disadvantages of online learning, let’s move on to those of classroom learning.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Classroom Learning

Advantages of Classroom Learning:
1. face-to-face interaction.
Classroom learning allows learners to engage in face-to-face interaction with their peers and instructors, facilitating collaboration and the exchange of ideas.
2. Structured Learning Environment
It provides a structured learning environment that may be beneficial for learners who require a more hands-on, guided approach to learning.
3. Immediate Feedback
It offers immediate feedback opportunities from instructors and peers, enabling learners to gauge their progress and receive constructive criticism.
4. Enhanced Socialization
It offers socialization opportunities that may help learners develop important social skills and networks.
Disadvantages of Classroom Learning:
1. limited flexibility.
Classroom learning may be less flexible than online learning, requiring learners to attend classes at specific times and locations.
2. Higher Cost
It may be more expensive than online learning due to costs associated with facilities, materials, and travel.
3. Distractions
It may be subject to distractions such as noise, disruptions, or interruptions, which can disrupt the learning experience.
4. Limited Customization
It may offer limited customization options, making it difficult for learners to focus on their specific areas of interest or weaknesses.
Online Learning Vs Classroom Learning

Let’s have a look at the top 7 differences between online learning vs classroom learning.
1. Learning Environment
The learning environment is one of the most significant differences between online learning and classroom learning.
Classroom learning takes place in a physical classroom, where students are present in-person with their teachers and peers.
The classroom provides a structured environment, which helps students stay on task, focus on their work, and receive immediate feedback from the teacher.
In contrast, online learning takes place in a virtual classroom, where students connect to a course via their computer or mobile device.
Online learners can access their course materials and assignments from anywhere, and at any time, making it a more flexible and convenient option.
2. Interaction
Another significant difference between online and classroom learning is the level of interaction between students and instructors .
In a classroom setting, students have the opportunity to interact with their peers and instructors face-to-face, which can help build strong relationships and a sense of community.
Classroom learning also allows for immediate feedback from the instructor, which can be very beneficial to students.
Online learning, on the other hand, relies on virtual communication, which can be less personal and less engaging than face-to-face interaction.
3. Schedule
One of the major benefits of online learning is the flexibility it offers.
Online courses are self-paced, which means that students can study when it's most convenient for them.
This makes it easier for students to balance their studies with work, family, and other commitments.
In contrast, classroom learning follows a set schedule, with specific times and locations for classes. This can be a challenge for students who have busy schedules or who live far from the school or university.
4. Teaching Methodology
Classroom learning and online learning differ in their teaching methodology. In a classroom setting, teachers use lectures, discussions, and group work to deliver the course material.
This can be very effective for students who learn best through social interaction and discussion. In contrast, online learning is more self-directed, with students responsible for reading the course materials and completing assignments on their own.
This can be beneficial for students who are more self-motivated or who prefer to work at their own pace.
Cost is another major difference between online and classroom learning.
Online courses are often less expensive than classroom courses, as there are fewer costs associated with facilities, materials, and travel.
This makes online learning a more accessible option for many students.
In contrast, classroom learning can be quite expensive, as students must pay for tuition, textbooks, transportation, and other expenses.
6. Technology
Technology plays a critical role in online learning, as students must have access to a computer and internet connection to participate in the course.
Online courses often incorporate a variety of technology tools, such as videos, podcasts, interactive quizzes, and online discussion forums.
In contrast, classroom learning may also use technology, but to a lesser extent.
7. Learning Style
Finally, online and classroom learning may be better suited to different learning styles.
Classroom learning may be more beneficial for students who learn best through social interaction and discussion, while online learning may be more effective for students who prefer self-directed learning and need to work at their own pace.
Ultimately, the best approach to learning will depend on each student's unique learning style, preferences, and circumstances.
Learn With Oreed
Experience enhanced learning capabilities in your workplace with Oreed's all-in-one platform.
- Gain a 360-degree understanding of your employees and better gauge their training needs.
- Oreed offers tailor-made training and courses to fit your organization's specific needs.
- You can measure the effectiveness of your training/courses with the platform's impact assessment feature.
So what are you waiting for? Book a demo with Oreed today to find out more.
Promote lifelong learning through Oreed by experiencing the most powerful all-in-one training and development intelligent platform that streamlines all your organization's learning, training, and development activities in one place.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, online learning vs classroom learning has its advantages and disadvantages.
While online learning offers flexibility and convenience, classroom learning provides face-to-face interaction and a structured learning environment.
Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on individual preferences and learning styles.
It is important to carefully consider the differences between online learning and classroom learning and choose the approach that best fits your needs and goals.
As technology continues to advance, the line between these two learning modes will likely continue to blur, creating even more options for learners in the future.
1. What is collaborative online learning?
Collaborative online learning is an approach to education that emphasizes collaborative group work and online communication tools to facilitate learning .
It involves students working together in virtual environments to complete learning activities and achieve shared learning goals.
Collaborative online learning allows students to engage in collaborative projects and activities regardless of their physical location, creating a sense of community and encouraging participation and engagement.
This approach can be implemented in various learning contexts, from traditional classroom settings to fully online courses, and is aimed at fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and teamwork skills.
2. What are some interesting facts about online learning?
Here are some interesting facts about online learning:
- Online courses are often more affordable than traditional in-person courses.
- It allows for greater flexibility and convenience, allowing students to learn at their own pace and on their schedule.
- Another fact about online learning is that online courses can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making education more accessible to a wider audience.
- It is just as effective, and in some cases more effective, than traditional in-person learning.
- It often offers a wide range of multimedia content, including videos, animations, and interactive simulations, which can enhance the learning experience.
Subscribe to our weekly email newsletter
Stay updated with the latest e-learning news and receive all the essential updates regarding the Oreed platform.
Please fix the following errors:
keep reading
![vs education Learning Experience Platform Market Size [2024]](https://oreed.org/cdn/1619638329_6089b83993722/1658391437_62d90b8d45216/1658391471_62d90baf0898f/1702465413_65798f85e1464/1702465413_65798f85e1078.jpeg)
Learning Experience Platform Market Size [2024]
Explore our in-depth analysis of the learning experience platform market size, trends, and forecasts for 2024. Dive into our expert LXP market insights.
![vs education What is a Learning Experience Platform [2024 Full Guide]](https://oreed.org/cdn/1619638329_6089b83993722/1658391437_62d90b8d45216/1658391471_62d90baf0898f/1702464014_65798a0ecf990/1702464014_65798a0ecf60a.jpeg)
What is a Learning Experience Platform [2024 Full Guide]
Learning Experience Platforms (LXPs) have revolutionized the field of learning and development, providing learners with innovative and personalized learning experiences.

AI In Recruitment
AI in recruitment enhances efficiency without replacing human recruiters. Discover Oreed for advanced employee development.
Supporting your growth every step of the way
Our support superheroes are a click away to help you get the most out of oreed.com, so you can focus on working without limits.
Support anytime, anywhere
Welcome to your new training intelligent platform
unlock your organization's potential and prepare to become a global leader of the future
- Request More Information
- Transfer Admissions
- Admitted? Enroll Now
- ADVANCEMENT
- FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE
- MISSION & MINISTRY
- STUDENT LIFE
- MyNU Portal
- MAPS & DIRECTIONS
- ALUMNI & FRIENDS
NeuPerspectives
A FRESH LOOK AT THE ROI OF EARNING AN ADVANCED DEGREE
MS vs. MA in Education — What’s the Difference?
Topics: Education Programs
Published on: 11/24/22 8:57 AM

Teachers who hold a master’s degree are sought after in many school environments, and if you are considering giving yourself a competitive edge with a graduate education degree — you should know that there are different degrees to choose from.
With different degrees come different abbreviations. Let’s break down the top two abbreviations you’ll encounter in your pursuit of a master's degree in education:
MA = Master of Arts
MS = Master of Science
There are differences between a Master of Science in Education and a Master of Arts in Education that are important to understand when planning your academic future. We’ve unpacked these differences so that you can make the best choice for your teaching goals.

What does the MA stand for in an education program?
A Master of Arts in Education will give you a deeper theoretical understanding of teaching and education. But it’s important to recognize that a Master of Arts in Education is specifically focused on the arts and humanities.
An MA in Education is a valuable option to pursue if you’re interested in obtaining an advanced degree that is rooted in the humanities and if you think you may want to teach subjects related to the liberal arts.
what is a master of science in education?
A Master of Science in Education will also give you a more technical understanding of the art of teaching. But a Master of Science in Education, compared to a Master of Arts in Education, is specifically focused on scientific and technical fields.
An MS in Education is an excellent choice for those interested in teaching subjects that are more technical in nature. And since this degree is rooted in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) ideology, many educators choose to obtain an MS in Education in order to jumpstart a teaching career that is specifically focused on STEM disciplines.
What is a STEM teacher?
The STEM fields are advancing more rapidly than ever, and for this reason, the need for competent and passionate STEM teachers has also increased at a rapid rate. Schools all over the country need data-minded educators who have specialized in one subject at the secondary level, such as biology or computer science.
With a Master of Science in Education , you can fill a significant talent gap by entering the classroom with the technical skills needed to teach the STEM disciplines that are so critical to the advancement of countless industries.
Your master's degree in education will equip you to work with the best in this impactful field and give you the tools to teach the next generation of STEM-focused professionals.
Here's why you should consider obtaining more credits (even if you already have a master's degree in education).
Did you know that teachers who obtain additional credits (on top of holding a master's degree) are actually eligible for higher salaries?
Many teachers who have invested in a master's degree in education choose to continue their education by earning a certification or endorsement — giving them more graduate-level credits, which in turn, leads to a salary increase. So, even if you have a master's degree already, there is value in achieving more credits through a certification or endorsement program.
Neumann University offers a variety of Master of Science in Education programs, certifications, and endorsements for educators who wish to advance their skills and for teachers who want to obtain additional credits in order to facilitate a salary increase.
Neumann University: Your Next Step into the STEM education field.
At Neumann University, we know the value of getting ahead of the competition, so we developed several graduate education programs to choose from — depending on your specific area of interest.
We offer a variety of Master of Science in Education programs (and certificates and endorsements) that are specifically designed for driven teachers looking to make a difference. The Master of Science in Education that you choose will sharpen your competitive edge and make you an excellent candidate for hire in diverse school environments.
Want to know more about our programs? Request more information or read some stories about how education impacts the world .
Ready to start your next steps into the graduate world? Apply now .
Explore our interactive education resource and take our quiz to find the master's program in education that's right for you.

WRITTEN BY: Bettsy McKlaine

About The Author: Bettsy McKlaine is the Executive Director of Enrollment Management, Degree Completion & Graduate Programs at Neumann University and a proud Alumna. The Neumann Community has become her second family and she loves to interact with students, both from the undergraduate and graduate population. Her favorite time of year is at the start of each semester as students begin classes!
RELATED STORIES

Why do Teachers Need a Master’s Degree in Education?

Which Master’s Degree in Education is Right for You?
Download our Guide to Neumann University’s MS in Education
Interested in receiving weekly advice and tips on earning an advanced degree, subscribe now, stay in the loop, we are excited to connect with you each week .
QUICK LINKS
- Academic Programs
- Accent Magazine
- Alumni & Friends
- Campus Ministry
- Campus Safety
- Career & Personal Development
- Center for Global Engagement
- Conferencing and Facilities
- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion
- Financial Assistance
- Giving to Neumann
- Guest Speakers
- Human Resources
- Incident Reporting
- ITR Help Desk
- Mission and Ministry
- News/Publications
- Request Information
- Student Health Services
- Student Life
- Study Abroad
- Sustainability at NU
- Job Opportunities
- Advancement
- Business Office
- Career & Professional Development
- Core Experience
- Digital Learning & Innovation
- International Student Support Services
- Live Stream
- #GradLife Podcast
- The Master It Series
- Student Success Center
One Neumann Drive Aston, PA 19014-1298
Phone: 610-459-0905

Neumann University participates in the State Authorization Reciprocity Agreements.
Neumann University © 2024. All Rights Reserved.

Beyond the Classroom: School vs. Education Explained
- by ST Admin
- September 12, 2020

School vs. Education are two terms that have been misidentified, misinterpreted, and misconceptualized.
They are often used interchangeably and thought to mean the same thing, but they are different.
Education is the process of gaining knowledge formally and informally, while schooling is simply going to school to learn.
From these definitions, schooling can be said to be a branch of education, but education is not a branch of schooling.
When most people talk about education, they are talking about schooling. They want their children to go to the best schools, get the best “education,” and go on to get good jobs.
This article will highlight a few differences in schooling vs. education.
Table of Contents
What is Schooling?
Schooling is simply the process of learning or being taught within the four walls of a classroom or school. It is the process of receiving “education” or acquiring knowledge formally.
Here, the services of a teacher or lecturer are needed to instruct a group of people called pupils or students.
The teacher teaches them, considering their academic strengths and what they are supposed to know according to the curriculum, and at the end of the term, they take exams or tests.
In schooling, students move from level to level depending on how much they pass their exams or tests.
Read this: How many Colleges should I apply to? Quick Answer
- What is Schooling in Education?
“Schooling” in education refers to the formal process of instruction and learning in an institutional setting, such as a primary school, secondary school, or university.
It typically involves a structured curriculum, trained educators, and an organized environment where students learn specific subjects and skills.
Schooling is a subset of education, representing the formal, organized aspects of the broader educational experience.
While “education” encompasses all how individuals learn and grow throughout their lives (including informal and non-formal means), “schooling” is specifically the structured and institutionalized part of this process.
Reason Why School Is Important
1. school creates socialization:.
Schools provide most children the earliest opportunities to interact with peers outside the home.
As a result, they improve at communicating with others, paying attention in class, and solving issues independently.
Young children can benefit greatly from a solid groundwork in these social skills.
Teachers and other adults have to foster positive relationships among students. Furthermore, they need to deal with problems like bullying.
2. School teaches future goals:
The educational experience exposes children to several fields of study. It’s not uncommon for learners to feel a profound affinity for some material.
They can delve deeper into topics of interest, individually or as part of a group.
The students plan for the future and think about their potential profession. Any student can achieve their goals and pursue their interests with the help of their teachers.
3. School builds confidence:
Self-confidence in oneself and one’s abilities is essential for maintaining a healthy self-worth.
Those who lack self-assurance are easier to take advantage of and more susceptible to emotional distress. Children have early chances to develop self-assurance in a school environment.
They grow more assured of their talents by acquiring literacy skills such as reading, writing, and mathematics. A teacher’s influence in this situation is crucial.
Given that many students experience difficulty in one or more areas of study, it is their responsibility to recognize and appreciate even the smallest of victories.
What is Education?
Education is a lifelong process of learning and acquiring knowledge. It involves developing the ability to think, create, solve, understand, learn, act, and question. It also involves the development of the mind and character.
Education doesn’t deal only with learning or knowledge. It involves inculcating values, manners, and building habits. It prepares someone to face life and improves comprehension and encompassing.
Types of Education:
Education can be formal or informal and can happen anywhere, anytime.
1. Informal education
Informal education can be seen when parents or guardians teach children to talk, write, read, greet, be respectful, do chores, etc.
It can also be seen when children learn to do things and solve problems independently.
Informal education also includes online learning, self-learning, reading books, learning from friends, learning from life experiences and situations, and seminars.
2. Formal education
The term “formal education” describes a systematic approach to learning that begins with preschool (or earlier) and continues through higher education with specialized technical and professional development tracks.
Structured or synchronous learning are two more names for formal education. Teaching in a traditional classroom setting, online courses, remote labs, eLearning, workshops, seminars, and webinars are all types of formal education.
Formal education includes “schooling” at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels. It also includes graduate schools.
Read this: Internships for High School Students you can’t afford to miss
Reason Why Education Is Important
1. education encourages critical thinking:.
Students learn to think critically about life in general. These abilities can be used in any aspect of life, from professional to personal interactions.
2. Education strengthens societies:
For many individuals, their education becomes a vital social network. It could be the only place some people ever feel comfortable being themselves.
Having a sense of community and being a part of something greater than oneself is crucial for kids.
They will have a sense of belonging and security, motivating them to continue their community-building efforts when they graduate.
- Differences Between Education And School
| Definition | An institution where instruction is given, especially to young people. | The process of receiving or giving systematic instruction. |
| Scope | Limited to a specific environment and curriculum. | Broad and can occur in various settings, formal and informal. |
| Duration | Typically has a set duration (e.g., K-12, college years). | Lifelong – can be acquired at any age or stage. |
| Methodology | Structured, often standardized curriculum. | Can be structured or unstructured. Varies widely. |
| Evaluation | Regular assessments, grades, and feedback. | Not always assessed; can be self-directed. |
| Settings | Classroom, laboratories, or specific educational institutions. | Everywhere – classrooms, homes, workplaces, online, life experiences. |
| Objective | To provide a specific set of knowledge and skills, often leading to a degree or certificate. | Overall personal and intellectual development, skill acquisition. |
| Dependence on Instructors | Highly dependent on teachers and instructors. | Can be independent or dependent on mentors, instructors, or self-learning. |
| Flexibility | Often follows a strict timetable and calendar. | Can be pursued at one’s own pace and interest. |
| Influence | Primarily influenced by policies, governments, and institutional decisions. | Influenced by individual needs, society, culture, and personal experiences. |
Detailed Differences Between School and Education
- School : A structured, tangible institution. Schools function within boundaries, set routines, regulations, and a designated environment facilitating learning and interactions.
- Education : An expansive, intangible journey of growth. While formal schooling is a part, education embodies broader avenues of learning and self-exploration throughout one’s lifetime.
2. Methodology:
- School : Operates on a standardized framework, utilizing prescribed textbooks, regimented lesson plans, and a systematic evaluation mechanism. Emphasis is largely on a linear, objective approach.
- Education : Rich, diverse, and encompassing myriad avenues. It can emerge from experiential learning, digital platforms, personal introspection, cultural exchanges, and limitless other experiences.
3. Facilitators :
- School : Driven by trained educators like teachers, professors, and facilitators, who disseminate knowledge, mentor, assess, and play pivotal roles in students’ academic journeys.
- Education : A multifaceted journey steered by myriad influencers – parents, mentors, peers, authors, online educators, and even strangers, all contributing uniquely to an individual’s learning.
4. Freedom & Flexibility :
- School : Often constricted by time-bound schedules, academic calendars, set syllabi, and administrative guidelines, making it a regulated learning environment.
- Education : Boasts vast horizons offering boundless flexibility. Individual pursuits, curiosity-driven explorations, and self-paced modules reflect its adaptive nature.
5. Purpose & Outcome :
- School : Guided by measurable objectives: acquiring specific grades, mastering set curricula, or obtaining diplomas, societal benchmarks of academic success.
- Education : Dynamic in objectives. It caters to personal enrichment, understanding societal dynamics, fostering critical thinking, cultivating passions, and molding informed worldviews.
6. Environment :
- School : Predominantly held within the confines of classrooms, auditoriums, and physical campuses, fostering a sense of community and structured interaction.
- Education : Ubiquitous in essence. Beyond school walls, it thrives in parks, cafes, virtual forums, during travel, familial gatherings, and even in solitude.
7. Duration :
- School : Defines a stipulated time frame, marked by distinct milestones like enrollment, progression, and graduation, signaling different academic phases.
- Education : Perpetual and evolving, seamlessly intertwined with life’s continuum. Every moment, triumphant or challenging, contributes to the educational journey.
8. Validation :
- School : Validation is institutional. It’s channeled through scorecards, certificates, and accolades, often determining academic and sometimes societal standing.
- Education : Inherently personal and varied. Achievements might be self-realizations, acquired skills, or personal growth, not always needing external endorsements.
- Detailed Similarities Between School and Education
1. The objective of Knowledge Acquisition :
- School : Schools systematically provide foundational knowledge, focusing on critical thinking, reasoning, and cognitive skill development across multiple disciplines.
- Education : A holistic approach to understanding the world, education’s core objective remains knowledge enhancement, catering to diverse learning styles and individual inclinations.
2. Personal Development :
- School : Apart from academia, schools emphasize emotional intelligence, resilience, and adaptability, honing students into well-rounded individuals for society.
- Education : Encompassing more than just facts, education shapes attitudes, values, and beliefs, ensuring an individual’s growth aligns with societal and personal well-being.
3. Structured Learning :
- School : Offering organized lessons, clear guidelines, and progression paths, schools ensure sequential learning, allowing depth and breadth in subject matters.
- Education : Even in expansive settings, structured modules, syllabuses, or guidelines in formal education ensure systematic progression and comprehensive understanding.
4. Role of Instructors :
- School : Educators equipped with pedagogical expertise mentor students, tailor lessons, and provide a conducive environment for optimal learning experiences.
- Education : In diverse educational landscapes, facilitators, whether seasoned experts, peers, or digital platforms, drive knowledge dissemination and experiential learning.
5. Social Interaction :
- School : Schools act as social microcosms, teaching cooperation, negotiation, and empathy, enabling students to navigate larger societal frameworks effectively.
- Education : Beyond solitary learning, education thrives on collective wisdom, fostering group endeavors, collaborative projects, and shared knowledge platforms.
6. Continuous Evaluation :
- School : Through detailed feedback mechanisms, schools pinpoint strengths and areas of improvement, shaping pedagogical strategies for enhanced outcomes.
- Education : The broader realm of education emphasizes introspective evaluations, peer reviews, and tangible results, ensuring knowledge application and retention.
7. Encouragement of Curiosity :
- School : Teachers nurture an environment where inquiry is welcomed and exploration is rewarded, stimulating a student’s natural thirst for knowledge.
- Education : The backbone of education is an innate curiosity, pushing boundaries, challenging established norms, and seeking understanding beyond surface levels.
8. Foundation for Professional Growth :
- School : Through specialized subjects and vocational training, schools lay the groundwork for future academic pursuits and career aspirations.
- Education : Spanning life’s entirety, education equips individuals with adaptable skills, ensuring they navigate evolving professional landscapes with agility and competence.
9. Moral and Ethical Instruction :
- School : Through subjects like civic education, schools instill a strong sense of righteousness, societal responsibilities, and ethical decision-making.
- Education : In its broadest sense, education enlightens individuals on global ethics, moral compasses, and the intricate balance of rights and duties.
10. Adaptability :
- School : In this rapidly changing era, schools actively reform their practices, integrating technological advancements and addressing contemporary societal challenges.
- Education : Reflecting societal shifts, global challenges, and technological revolutions, education remains fluid, ensuring relevancy and applicability in ever-evolving contexts.
FAQs on Schooling vs. Education
The primary goal of public education in the United States is to help each student grow into an ethical, creative, and productive member of society.
Private School Satellite Programs
Personalized Learning Planning Process
Final tips:
School vs. Education will make you more focused as you study in college. It will help you manage your time and engage in extra and co-curricular activities to boost your self-esteem.
Schooling alone will not get you where you want to be because the school will not teach you self-development, leadership, critical thinking, and time management, but education through books will expose you to these pros of life.
Awesome one; I hope this article answers your question.
Editor’s Recommendations:
- How To Get Rid Of iboss On School Chromebook (FAQs)
- How To Play Games On A School Chromebook (FAQs)
- 13 Fun Games To Play On School Chromebook (FAQs)
- 15 Games you can play on your school Chromebook (FAQs)
- 20 Best Free Unblocked Game World Sites (FAQs)
- 10 Best Laptops For Online Teachers (FAQs)
- 5 Top Games That Are Not Blocked By Schools (FAQs)
If you find this article good, please share it with a friend.
- Detailed Difference Between School and Education
- is there a difference between education and schooling
- Schooling vs Education
- types of education
- what is education
- what is teaching in education
Hello, I am ST Admin! For five years, I began actively assisting students in Europe, the United States, and Canada in their pursuit of college advice and scholarship prospects. I am the Administrator of www.schoolandtravel.com at present.
How to Become a Substitute Teacher (Easy steps)
How long does it take to get a bachelor's degree (tips, benefits), you may also like.

Organised or Organized: Which is correct?
- by Paschal Uchechukwu
- October 28, 2020

Buisness or Business – Which is Correct?
- May 5, 2021

Fifthteen or Fifteen – Which is Correct? (FAQs)
- August 26, 2021


Advize vs Advice vs Advise – What’s the difference
- March 11, 2021
Omage vs. Homage – What’s the Difference?
- by Obiorah Esther
- December 24, 2020

Learnt vs Learned: Which is Correct?
- October 22, 2020

Education vs. Educational — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Education and Educational
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, application, usage in context, compare with definitions, educational, common curiosities, what is education, can education occur outside of educational institutions, what does educational mean, what is the goal of education, how do educational tools support education, what are educational methods, how do educational environments differ, how do educational standards affect education, what makes something educational, is all education formal, how do educational policies impact education, what is non-formal education, what is the difference between education and training, can educational experiences be non-academic, what role do educational psychologists play, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

Education vs. Schooling: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, education and schooling definitions, what is the main difference between education and schooling, is schooling necessary for a good education, does education end with schooling, can education happen outside of schooling, are education and schooling the same in different countries, what is the role of teachers in education and schooling, how does one measure the success of education and schooling, can schooling adapt to individual learning styles, what is the importance of extracurricular activities in education and schooling, how do social interactions contribute to education and schooling, what role does technology play in education and schooling, what is the difference between vocational schooling and traditional academic education, how do culture and society influence education and schooling, what is the future of education and schooling, how does education impact career development, how does one balance formal schooling with other forms of education, how do homeschooling and online schooling fit into these concepts, is schooling the same as academic education, can education be self-directed, what is the significance of lifelong learning in the context of education.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons
Education vs. Schooling
What's the difference.
Education and schooling are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Education refers to the process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes through various means, such as formal and informal learning, personal experiences, and self-study. It encompasses a broader scope and extends beyond the boundaries of a classroom. On the other hand, schooling specifically refers to the formal instruction and structured environment provided by educational institutions. While schooling is a crucial component of education, it is important to recognize that education can occur outside of traditional school settings, through real-life experiences, online courses, or vocational training. Therefore, education is a lifelong process that goes beyond the confines of schooling.
| Attribute | Education | Schooling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes through various methods such as teaching, training, or research. | A formal system of education provided by institutions such as schools, colleges, or universities. |
| Scope | Can be informal or formal, encompassing learning throughout life in various settings. | Primarily refers to the structured and organized learning that takes place within educational institutions. |
| Focus | Emphasizes holistic development, critical thinking, problem-solving, and personal growth. | Focuses on academic learning, following a curriculum, and achieving specific educational goals. |
| Methods | Can involve self-directed learning, experiential learning, online courses, apprenticeships, etc. | Relies on classroom instruction, lectures, textbooks, assignments, exams, and structured activities. |
| Flexibility | Allows for personalized learning paths, adapting to individual needs, interests, and learning styles. | Often follows a fixed schedule, curriculum, and standardized assessments, offering less flexibility. |
| Assessment | Assessment methods can vary, including projects, portfolios, presentations, or performance-based evaluations. | Assessment typically involves exams, quizzes, tests, and standardized assessments to measure academic progress. |
| Outcome | Focuses on overall knowledge, skills, personal growth, and lifelong learning. | Primarily aims to achieve academic qualifications and certifications. |
Further Detail
Introduction.
Education and schooling are often used interchangeably, but they are not synonymous. While both terms are related to the process of acquiring knowledge and skills, they have distinct attributes that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the differences between education and schooling, highlighting their unique characteristics and discussing their respective impacts on individuals and society.
Education: A Lifelong Journey
Education is a broad concept that encompasses learning throughout one's life, extending far beyond the confines of a classroom. It is a continuous process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes that shape an individual's intellectual, emotional, and social development. Education is not limited to a specific institution or timeframe; it can occur in various settings, such as homes, communities, workplaces, and even through self-directed learning.
One of the key attributes of education is its focus on holistic development. It aims to nurture individuals intellectually, emotionally, and morally, enabling them to become well-rounded and responsible members of society. Education encourages critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, and the ability to adapt to new situations. It fosters a love for learning and empowers individuals to pursue their passions and interests.
Furthermore, education goes beyond the acquisition of knowledge and skills; it also emphasizes the development of values and attitudes. It promotes empathy, respect, tolerance, and ethical behavior, fostering a sense of social responsibility and global citizenship. Education equips individuals with the tools to navigate the complexities of the world, make informed decisions, and contribute positively to their communities.
Schooling: Formal Instruction within Institutions
Schooling, on the other hand, refers to the formal instruction and structured learning that takes place within educational institutions, such as schools, colleges, and universities. It is a subset of education, focusing on the systematic delivery of curriculum-based knowledge and skills. Schooling typically follows a predetermined curriculum, which is designed to meet specific educational standards and objectives.
One of the primary attributes of schooling is its organized and structured nature. It provides a framework for learning, with designated subjects, timetables, and assessments. Schooling offers a standardized approach to education, ensuring that students receive a consistent level of instruction and evaluation. It also provides a social environment where students can interact with peers, fostering socialization and the development of interpersonal skills.
While schooling plays a crucial role in imparting foundational knowledge and skills, it is important to recognize that it is just one aspect of education. Schooling alone does not guarantee a well-rounded education, as it may not address individual learning styles, interests, or the development of values and attitudes. Additionally, the rigid structure of schooling may limit creativity, critical thinking, and the exploration of diverse perspectives.
Impacts on Individuals and Society
The differences between education and schooling have significant implications for individuals and society as a whole. Education, with its emphasis on lifelong learning and holistic development, equips individuals with the necessary tools to adapt to a rapidly changing world. It fosters creativity, innovation, and the ability to think critically, enabling individuals to navigate complex challenges and contribute meaningfully to society.
On the other hand, schooling, while providing a formal education, may sometimes fall short in preparing individuals for the realities of life beyond the classroom. The focus on standardized testing and rote memorization can hinder the development of essential skills, such as problem-solving, communication, and adaptability. This can lead to a mismatch between the skills acquired through schooling and the demands of the modern workforce.
Moreover, education extends beyond the individual level and has a profound impact on society. A well-educated population is essential for social progress, economic growth, and the advancement of democratic values. Education promotes social mobility, reduces inequality, and fosters social cohesion by providing equal opportunities for all individuals to reach their full potential. It also plays a crucial role in addressing societal challenges, such as poverty, discrimination, and environmental sustainability.
While schooling contributes to education by providing a formal structure, it is important to recognize that education is not limited to the confines of educational institutions. Education can occur in various forms and settings, including informal learning, vocational training, online courses, and community-based initiatives. Emphasizing the importance of education beyond schooling is crucial for fostering a lifelong love for learning and empowering individuals to take charge of their own educational journeys.
In conclusion, education and schooling are distinct concepts with unique attributes and impacts. Education encompasses lifelong learning, holistic development, and the acquisition of knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes. It extends beyond the boundaries of educational institutions and plays a crucial role in shaping individuals and society. On the other hand, schooling refers to the formal instruction within educational institutions, providing a structured approach to education. While schooling is an important component of education, it should not be seen as synonymous with education itself. Recognizing the differences between education and schooling is essential for fostering a comprehensive and inclusive approach to learning that empowers individuals and benefits society as a whole.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Education vs Training vs Development. What Is the Difference?
Education, training, and development are often used interchangeably. But what exactly do they mean? And why is it important to know the difference between the three?
To help clear the confusion about what each term signifies, we asked experts to discuss the difference between education, training, and development.
Here are their insights:

Vice President of Learning and Development, Kiddie Academy Educational Child Care
Development , education , and training are the concepts that may seem synonymous. Still, they are as different as the arts and sciences—yet work together in tandem to develop a curious mind.
Development is an abstract art
Development is an abstract art —it is the nature of watching a skill or person grow over time. It is a continual improvement toward an overarching goal that can be more informal and is observed relationally over time ( Example : a mentor observing a mentee).
Education is a science
If development is an art, education is a science . Education is the standardized practice of attaining a piece of knowledge or skill that will follow you throughout your life.
In education, there are facts in figures. There is a conceptual understanding that everyone should be able to reach when successfully trained.
Training is a vessel by which education is achieved
On the other hand, training is a vessel by which education is achieved. Training is meant to teach knowledge , skill , or attitude (KSA) that can be immediately understood and implemented.
Development is more informal and abstract to track
Assessment is the significant difference between training and development. You can assess learning through training immediately (through examination, such as a quiz). Development is more informal and abstract to track (such as mentor observing mentee).
The purpose of training is to have facts and figures that prove different outcomes because of the learning that happens in training.
Our academy aims to equip our franchisees (at nearly 300 locations around the country) to develop as impactful entrepreneurs in the educational child care industry through training, education, and development.
A team of operations, marketing, and education experts works with the franchisee to get to know them, their families , their professional backgrounds , and their goals .
We work with franchisees to provide regular training opportunities (pre-opening, regional, and at our annual conference). But we also help them develop and refine skillsets specific to their entrepreneurial goals in an ever-evolving one-on-one setting.
We also have the unique vantage point of impacting the education and development of young children in our classrooms. There are tangible benefits of a curriculum that prepares children for kindergarten, but more so in developing good character.
In an early childhood classroom, it’s easy to imagine the education opportunities we provide. But surprisingly, there is no lack of development opportunities.
You can familiarize a child with a skill (for example, sharing, working through conflicts with friends, etc.) through education and training, but how you approach the application of that skill relies upon development .
Development is contingent upon the teacher knowing the child
Development is contingent upon the teacher knowing the child and investing in their personal growth with one-on-one support and connection. Thus, genuinely successful development correlates with relational investment.
Training, development, and education are necessary throughout career and personal growth from grade school.
To be a lifelong learner is to pursue development constantly , and training and education are two practical tools by which we develop.
Eliana Levine

Co-founder, FindPeopleEasy
Training is the process of improving an employee’s knowledge and abilities for them to do a specific job.
Development is thought to be more general than training and more targeted to human requirements and organizational needs , and it is typically aimed at management personnel .
Education is the process of expanding a company’s workers’ general knowledge and comprehension.
Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world
According to Nelson Mandela, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” He says this because education is the key to gaining the knowledge, critical analysis, confidence, and skills necessary to improve the world.
Education is the process of acquiring and interpreting information
Education is the process of acquiring and interpreting information. It does not supply concrete answers but instead facilitates a logical and rational mind capable of telling links between relevant variables and, as a result, interpreting a situation .
Education teaches:
- intellectual and moral characteristics
- awareness of fundamental ideas
- the ability to analyze, interpret and evaluate information fairly
It has a more extensive range than training, which is more focused on organizational goals than individual goals.
Merits of education
- Leads to a healthier lifestyle.
- Gives access to socialization and better personal and professional networking.
- Allows people to pursue their passion.
- Provides an incredible feeling of accomplishment.
- The more a person is educated, the more their chances of securing a job.
- Encourages civic participation and citizenship.
- It provides a more significant opportunity to identify individual skills.
Related: Why Is Education Important in Our Life?
Training improves the employees’ knowledge and ability
Training improves the employees’ knowledge, ability, and abilities in performing a specific profession. It has a particular goal in mind: to enhance knowledge and skill .
In today’s global world, every corporation requires high-quality employee performance to stay in business; hence training is essential.
The training aims to transmit the essential knowledge , abilities , and attitudes to execute job-related tasks. It seeks to directly increase a person’s job performance and increase output with the better work quality.
Merits of training
- It leads to increased production in both terms of quantity and quality.
- It helps employees learn a variety of skills.
- Performances can improve through proper training.
- The organization’s cooperative environment.
- It instills trust in employees’ abilities to complete tasks.
- It reduces employee turnover.
- Mistakes at work are less likely to occur with good training.
The development includes activities that boost work performance
The development includes activities that boost work performance and those that promote personal growth, assisting employees in maturing and realizing their full potential so that they can become not only good employees but also great men and women to society.
Development is the process of preparing someone for a bigger and better career
In terms of the workplace, development aims to provide people with the skills to advance and take on more responsibilities. Development is the process of preparing someone for a bigger and better career.
This may entail the transmission of specific skills and knowledge and the installation of some personality characteristics and intellectual views.
Merits of development
- It helps improve performance.
- It improves one’s ability to deal with unforeseen circumstances.
- An organization’s development and learning culture help to recruit new employees and promote loyalty.
- It helps in the development of prospective good employees into exceptional leaders.
- With proper development programs, you can increase employee engagement and motivation.
- A company’s development programs will allow it to expand, develop, and successfully compete within its sector.
Differentiation and interactions in education, training, and development:
Though education and training are concerned with learning, education has a broader reach.
Education is a set of formal instructions received at a school or college
Since training and education often happen simultaneously, it’s challenging to distinguish between the two. Education is a set of formal instructions received at a school or college.
Training is more professional and is provided solely to do a specific job
At the same time, training is more professional and is provided solely to do a specific job. Training, rather than education, has a more immediate practical objective.
Many conventional technical school programs are solely job-oriented, whereas some training and development activities have a much broader reach and might be considered educational .
Development refers to how a person nurtures the skills to improve the overall performance
Education and development are closely linked. In other terms, development can easily be converted into education because it is more individual-oriented than training, which is more focused on the organization.
Development refers to how a person nurtures the skills to improve the overall performance in which a particular corporate sector achieves its desired outcomes.
The terms “training,” “education,” and “development” are widely employed. There could be no difference between them, but a closer examination reveals specific differences. There is little education in all training, and there is little training in all education.
Nance L. Schick, Esq.

Employment Lawyer, Third Ear Conflict Resolution | Workplace Mediator | Author, “ DIY Conflict Resolution ”
Education is a formal instruction toward a certificate
I am an employment attorney-mediator and diversity trainer based in New York City. I have gotten a lot of education, which I would describe as formal instruction toward a certificate (e.g., diploma, degree, license).
It was very knowledge-based and often focused on theory more than implementation. I struggled in law school until I shifted the focus of my responses from “real world” to theoretical.
I returned to school at age 29 after working as an operations supervisor, human resources supervisor, employee relations representative, sports marketing director, and minor league hockey agent.
It took me a couple of semesters to remember that my legal education was generally aspirational, if not idealistic.
It taught me how to think like a lawyer:
- Spot the issues
- Identify the laws that apply
- Gather the evidence in support of a client’s position
- Argue the client’s position
Training is more about building the skill necessary to apply the knowledge effectively
My education would not have been complete without training. While in law school, I received some of that training, but some of the best training I have ever gotten came from the management training program at United Parcel Service.
We reviewed laws , rules , regulations , policies , and procedures in that two-week program. Yet the focus wasn’t on memorizing them for an examination.
Related: What Is the Difference Between Law, Policy, and Regulation
We had discussions and participated in role plays to practice different techniques, see how they worked in different situations with other people, make mistakes, and try again. Training is more about building the skill necessary to apply the knowledge effectively.
Development builds on knowledge and skills
Finally, there is development, which is exactly what it sounds like. Development builds on knowledge and skills, usually more personal and individualized than education or training.
Development might include mentoring or coaching and education and training, depending on the person’s goals and needs. Sometimes the development is professional , such as reviewing an area of law or a new technique .
The development could be personal
At other times, the development could be personal , such as conflict resolution skills or communication skills (which are also arguably professional skills, yet many people still deem them personal).
When an employer offers the development, the individual’s goals will be aligned with the employer’s goals, which sometimes means it’s in everyone’s best interests to end the employment relationship.
Yet, in those cases, the separation is often much more amicable . I have twice unintentionally assisted employees in finding more compatible employment by discussing their personal and professional development goals.
In both, we ended the employment , but not all aspects of our relationship. That is possible in more cases than is often believed, and it is how I want to continue to run my business indefinitely.
Owen Wilcox

Financial Expert | Co-founder, USInstallmentLoans
The differences between training, education, and development are sublime , leading most communicators to interchange or use one instead of another wrongly.
That, however, doesn’t hinder the fact that their differences are as clear as day and night.
Differences in the objectives
Training is a learning process meant to teach a person skills.
Training is a learning process meant to teach a person skills necessary for a particular job or task. For example, training may involve teaching employees skills for operating machinery at a manufacturing plant.
Education refers to the learning process to sharpen a student’s intellect
Education refers to the learning process to sharpen a student’s intellect and thinking capacity .
To expound on the previous example, training fosters operational skills, and education leads to understanding why the machinery behaves and how to fix or improve its features.
Development is creating a holistic individual in tune with their mind, body, and soul
On the other hand, development is creating a holistic individual in tune with their mind, body, and soul. The aim is to enhance the recipients’ self-awareness , emotional intelligence , and creativity .
Differences in the teaching methodology
Training is undertaken through specialized courses, textbooks, and practices.
Training is undertaken through specialized courses , textbooks , and practices to transfer skills and competencies required to carry out particular tasks.
Organizations mainly train employees to:
- Appraise them for the company culture
- Improve their productivity
- Build confidence at work
- Foster a cooperative environment
Education is a lifelong process conducted through the exchange of knowledge
Education, on its part, is a lifelong process conducted through the exchange of knowledge and books other than textbooks. In education, the learner is encouraged to think and write to grasp the knowledge better and critique it to come up with better concepts.
Development may be undertaken with the help of teachers in the initial stages
On the other hand, development may be undertaken with the help of teachers in the initial stages. Still, it’s mainly a personal journey . Only the recipient can speak with certainty about whether they have reached their destination.
In this regard, development is comparable to eating , as only the one eating can state when they are satisfied.
Sasha Laghonh

Strategist | Author | Speaker, Sasha Talks
Education is acquiring knowledge through exploring ideas
Education is acquiring knowledge through exploring ideas and understanding how these concepts came into existence. This includes acknowledging the evolution of ideas that oversees the past , present , and future .
Education isn’t always categorized as non-fiction due to the genre of knowledge available, or else society’s identity would be limited without the presence of fictional elements and critical thinking .
Training is the step where individuals put their knowledge/ideas to good use
The latter seeds of knowledge yield their utility value through training and application . Training is the step where individuals put their knowledge/ideas to good use to produce results that align with their goals.
For example, if you’re a baker, you learn to make bread. This can be done through:
- taking classes
- apprenticeships
- watching videos
- reading books
- even word of mouth
The training stage welcomes the baker to put their acquired knowledge to good use
The training stage welcomes the baker to put their acquired knowledge to good use by creating their desired output (bread).
This process is not confined to a time frame because some students are fast learners while others require more time to process information before effectively applying it through practice.
The specific baking skills needed for making bread will require repetitive processes performed over time, which helps the baker refine their approach and technique to produce a result.
Sooner or later, the training milestone eventually transitions to the development phase . This is where the pre-existing and new knowledge, including practice, translates to custom strategies the baker can implement by exercising more creative control of their craft.
The baker hosts the fundamentals of making bread. They’ve learned what works through trial and error from experience; now, they’ve graduated to infusing their custom knowledge in “their” baking process.
It’s become a more sacred engagement for them, which began as a foreign concept that has become personalized to their preferences.
The baker may find better ways to optimize their time and resources in making bread by modifying the steps of baking different types of bread for different audiences under other circumstances.
Learning doesn’t cease because new aspects of education can be sought
Learning doesn’t cease because new aspects of education can be sought during the training and development phase . The latter stage allows the baker to develop and communicate their expertise through education mediums to teach others.
It’s important to remember some people host pre-existing knowledge on specific topics, but they haven’t had a reason or perhaps an opportunity to apply it through training and development .
Some people engage in learning for pleasure , while others may engage in fulfilling a required metric to meet academic or professional needs.

Founder and Head Of Design
Training is a crucial tool for every workforce
Training is a crucial tool for every workforce. This is true in all industries, not just oil and gas. Companies want their employees to be safer , more efficient , and more prepared than ever before, and they recognize the need for excellent training.
Training is mentioned whenever the workforce increases, a firm launches a new endeavor, or a crisis hits. New hires require training. Retrain current personnel. Employees depart due to a lack of training.
Education is acquiring information, skill, and development via study or training
By definition, education is acquiring information, skill, and development via study or training . The Cambridge English Dictionary defines training as the process of learning the abilities required to do a job or activity.
As these definitions show, while education and training are closely connected, they are not identical.
Education is the process of gaining broad information and skills in a classroom
Education is the process of gaining broad information and skills in a classroom or other educational setting. Educated skills and knowledge help kids build thinking and judgment around vast themes.
Education usually takes place throughout a semester or even years
Education usually takes place throughout a semester or even years. A student often seeks and pays for education to get a future job or advance in their profession.
Training refers to gaining technical information and abilities
Training refers to gaining technical information and abilities. It might take place in a classroom or out in the field. It is designed to increase employee performance and productivity by focusing on a specific skill set.
Training is frequently mandated, delivered, and sponsored by an employer after employment is gained.
Although some training courses might continue for weeks, they usually are considerably shorter than educational courses since they cover more precise and concentrated topics.
Simply defined, training is a specialized sort of education . Training and education focus on information acquisition, while training is significantly more task-oriented and skills-based.
Jim Wasserman

Litigation Attorney | Retired Teacher, ORCID
Training is helping to do a specific task
Training is helping to do a specific task, often by way of a good response/reaction. My students went into the test knowing that if they could eliminate one of five multiple-choice answers, the odds were in their favor to guess.
They also knew some great historical quotes (Abigail Adams’ “Remember the ladies” ) to use in essays.
Development was the improvement of students’ skills over time
Development was the improvement of their skills over time. Hopefully, between the beginning of the course and the test, my students learned how to read a question and understand what it was asking, come up with pertinent facts and insightful analysis , and then display those skills with a well-constructed essay.
I had students who began the course unable to write a tight introductory paragraph with a thesis that directly answered the question. They had developed that skill through their hard work during test time and then carried it into college.
Education understands the broader and deeper meaning of matters
Education understands the broader and deeper meaning of matters in the greater picture of life. For my course, that was the most important lesson, that how one score on one test on one day is a terrible metric of how good a student one is and, even more, how one will fare in life.
In fact, one’s high school career is not measured by where one goes to college but by what one takes with them wherever they go (including knowing and accepting yourself).
I used to have a student write down the names of people they admired in their life and then the university they attended (if they did) to see there was little correlation between leading an admirable life and where they enrolled.
In essence, I trained students for my paycheck, I helped develop students’ skills for them to realize their potential, and I educated them to make a better world .
Beverly Gearreald

College Counselor | Community Manager, Transizion
Education typically grants you a degree
This program typically grants you a degree, a high-school diploma, or a Ph.D. However, there is also a broader context in that one is generally considered “ educated” when one knows enough general knowledge, whether a formal education was involved.
Indeed, some people with a formal education still end up coming across as uneducated, depending on the quality of their education.
Training tends to be more specific and shorter than “getting an education”
This tends to be more specific and shorter than “getting an education.” For example, one can be trained to use a particular tool or software independent of one’s level of formal education.
This can result in taking a test and getting a certificate but typically does not involve getting a formalized degree.
The development includes improving any skill
Of all the titles used thus far, this is the hardest to define for me because it can be extensive. In particular, professional development can include improving any skill, especially soft skills, necessary for a job.
Get to Know Yourself Better with Our FREE Quizzes! (no email sign-up necessary):
- How Well Do You Know Yourself?
- Are You Living Your Full Potential?
- How Self-Motivated Are You?
- Is It the Right Time for a Big Change?
- Are You Living a Balanced Life?
- Are You Handling Stress Effectively?
Explore our quiz categories: Business Quizzes , Career Quizzes , Personality Quizzes, Relationship Quizzes , Well-Being Quizzes
One can also get certificates for participating in professional development programs, but these are generally not standardized and are not widely recognized.
That being said, depending on what you’re hoping to achieve in your career, professional development can be an extremely important component , such as improving language or communication skills .
One of the best ways to figure out how to advance your career is through mentorship . A mentor in the same field can help determine whether you need another degree, a certification, or just an improved skill set to help you get the promotion or new job you want.
As a mentoring company with professionals from various fields, our company can help you do just that.
Ellie Walters

CEO, FindPeopleFaster
It is easy to confuse the three or two of the three because they each speak of improvement . However, there is a difference between these three concepts and their applications within the language and organizational expectations.
Education is giving and receiving systematic instruction
Education is giving and receiving systematic instruction, typically concerning a particular field of knowledge. This process involves the indoctrination of concepts; students or employees read or are read to.
They are expected to show that they remember what they have been taught by being able to replicate that information on request.
Training involves undertaking or supervising actions
Training involves undertaking or supervising actions towards achieving a particular condition or acquiring a specific ability or skill.
This process involves routine actions taken by the participants to carry out specific tasks more effectively . Participants are then expected to carry out the skill for which they were trained as a test of the completion of their training.
Development is a change in a situation or subject
Development is a change in a situation or subject resulting in advancement or decline in the state of that situation or subject.
While education and training can be restricted to a field, development is more general. It refers to the improvement or decline of the subject’s general state, especially in other matters of the exact nature.
Differences between Education, Training and Development :
| Pursues knowledge | Pursues ability | Measures any changes | |
| Improves reasoning and clear judgement | Improves performance, ability and productivity | Improves or diminishes general conditions of the subject | |
| Wider focus on associated knowledge | Narrow focus on a skill | All round improvement of personality and relationships | |
| Students learn theory and concepts | Students apply theories and develop skill | Students observe trends within a field of knowledge | |
| Students learn through instruction | Students learn by practicing what they are shown | Students advance by solving problems | |
| Academic | Vocational or Professional | General or partial | |
| Students need education in order to complete a training | Students cannot start training without education | Students develop after applying their training and education has yielded changes in their contexts or situations |
Thomas Niemczewski

Owner, Stayyy
Development refers to changing something
The main difference between education and training is that the former involves learning something while the latter does not. This is different from development, which refers to changing something.
Education is a process by which people learn something new
Education is a process by which people learn something new. However, it does not mean that they have to go through all the learning steps. They can learn something in a short period of time in a few short sessions with no preparation or guidance.
Training refers to all the steps involved in learning and teaching someone new skills
On the other hand, training refers to all the steps involved in learning and teaching someone new skills. Education and training are sometimes confused with each other. They are not the same thing .
Sometimes education can be classified as training, but it is not educational in the sense of learning something new in a short period of time. It is more like learning how to do something or perform a specific task very well, such as driving or cooking at home.
Education as applied to learning new skills at school to enter adult life successfully
Education can be limited or unlimited . There are many different definitions of education and training, but they all use the same basic ideas. The first one is “education,” as applied to learning new skills at school to enter adult life successfully.
Education as applied to learning new skills beyond school
The second definition is education as applied to learning new skills beyond school; this means that during your working life, you need to learn new “skills” that you will need or will be able to use in business or society.
Education as applied to education itself
Finally, there is the third definition, which is education as applied to education itself. This definition emphasizes learning on your own time and needs; it includes learning skills useful for all aspects of lifelong learning and career development.
Mathew Bowley

Marketing Manager, Solmar Villas
Training is the process of mastering a set of pre-programmed actions
Training is the process of mastering a set of pre-programmed actions. Training is the use of knowledge . It makes people aware of the norms and procedures that will guide their actions. It aims to improve their current job performance or prepare them for future employment.
Development encompasses activities that boost job performance
A related process is a development. It encompasses activities that boost job performance and those that promote personality development; it assists individuals in maturing and realizing their full potential so that they can become not only good employees but also better men and women.
It is intended to provide people with the skills they need to advance in their careers and take on more responsibilities. Development is the process of preparing someone for a bigger and better job.
This may entail the transmission of specific skills and knowledge and the installation of certain personality traits and mental attitudes. In this way, development and education are very similar .
Education entails the comprehension and application of knowledge
Education entails the comprehension and application of knowledge. It does not provide definitive answers.
It fosters the development of a logical and rational mind capable of determining relationships among relevant variables and, as a result, character and an understanding of fundamental principles and the development of analytical, synthesis, and objectivity skills.
Typically, education is not part of an organization’s mission . It necessitates skills and knowledge that can only be acquired through formal education . Such institutions can help an organization assist and enhance its internal training and development activities.
Andrea M. Dey
Founder, Dey & Co. Design Living, LLC
Education helps many to learn and discover new things
In 2020 the difference between education, training, and development became less and less apparent to the point that it took on a new meaning; reinvention and reinvent fast!
Leaving many, especially those over the age of 50, scrambling to catch up, stay on pace, or just leave it altogether.
I remember two distinct things in April of 2020 while staying at my mom’s (an executive at a major broadcasting news company) house:
- The first is the constant barrage of boxes from Amazon and furniture stores to convert her bedroom into her home office.
- The second was her growing frustration as she spoke with her department to set up her new workstation and troubleshoot its glitches.
Her frustration grew even more as she had to learn new software and programs for team meetings that were now only taking place through video and group chat apps.
As a veteran in the finance industry, spreadsheets were second nature to her, and anything that wasn’t, there was an assistant to handle it.
Now amid a global pandemic that was disrupting everything we once knew, she had to gain a new education, get hands-on training, and develop new skills daily to sometimes hourly.
Learning a new language, apps, how to lead remote meetings, and more happened simultaneously. It became sink or swim, as life was happening, and this new way of doing business was not going to go away anytime soon.
Fast forward to now, April 2022. She has not only perfected the art of remote work, but now has tips and techniques for controlling the lighting to the right colors in clothing for the work, happy hours, and more events taking place virtually.
Education is the foundation that familiarizes one with the language and the basic formula
Education is the foundation that familiarizes one with the language and the basic formula. It’s the start of the conversation per se.
We then put it into practice through hands-on training. This allows us to gain experience and firsthand knowledge of navigating the subject matter or area of interest.
The development stage is a series of adapting, updating, and expanding on that knowledge
We hit the development stage, which is an ongoing process. It’s a series of adapting , updating , and expanding on that knowledge in changing times.
The pandemic has created a new language, formulas, and a new way of training and development.

CEO, WebSpero Solutions
Education is the formal teaching and learning environment
Education is the formal teaching and learning environment in schools , colleges , and universities . It means giving knowledge of the unknown, introducing the learners to new concepts/theories, and clearing their doubts about the previous learning.
Education consists of three important things:
- Reception (acquiring knowledge from different sources)
- Retention (retaining it in your mind to be stored in the brain’s long-term memory)
- Recall (to reproduce what is learned in tests and exams)
Without these three elements, education is incomplete.
Training means practicing and applying the skills learned in real-life situations
It means practicing and applying the skills learned in real-life situations . Training always comes after learning, for example, job training and internships.
Training enhances learning by doing . The more one practices the skill with their hands, the more perfect and able one becomes in doing that particular job efficiently .
Development is a blend of both education and training
Development is a blend of both education and training . For example, in an organization, when the training and development programs are run for the employees, they enhance the employee’s overall development.
First, he is educated about the new skills and then is trained practically in what he is taught. As a result, employees learn new capabilities that boost their self morale, and they grow on a professional and personal front.
Angedith Poggi, MPH, DHSc

Adjunct Professor | Educational Consultant
Education is a powerful tool for making informed decisions
Education is a powerful tool for making informed decisions related to personal , professional , and societal matters ; consequently, education impacts many people’s lives .
Learners pursuing higher education degrees are motivated not only by their personal goals but also by the contribution they may have to their field.
Earning a higher education degree may represent professional opportunities , a salary increase , and the privilege to contribute to research through projects related to a specific field.
However, formal education or higher education involves many expenses , sacrifices , and time . For instance, many learners struggle to balance their personal and professional life commitments while pursuing an academic degree.
Related: How to Live a Balanced Life? What Does it Really Mean?
Training and professional development represent viable options for adult learners
Therefore, training and professional development represent viable options for adult learners to acquire practical and relevant skills to advance their careers.
“Education is power.” Learning is crucial for individuals who seek professional opportunities, regardless of the duration and type of the program.
As a lifelong learner, I encourage everyone to maximize the opportunities to continue learning through formal , informal , and nonformal training.
James Chapman

Operations Manager, BELLA Bathrooms
In business, you will see the distinction between these three following concepts:
- Development
They are all necessary for you to succeed as an employee and employer.
Education is a process of gaining knowledge through the usage of a school system
Education is a highly acknowledged source of expertise that companies usually accept because the credibility of the person’s expertise is demonstrated through the diploma certificate issued , especially when the diploma comes from a prestigious institution .
Training is acquiring knowledge, skills, and competency for a specific purpose
Training is acquiring knowledge, skills, and competency for a specific purpose under the supervision of someone with superior authority or experience in the role. It is highly focused on the job taken.
Development is the act of growth you have acquired
Development is the act of growth you have acquired after being able to go through various situations. The progress will reflect on your actions in handling your job, embodying the knowledge, skills, and competency you have acquired from your training and education.
It is career-oriented and reflects on your entire performance as an employee. These three concepts can significantly impact your performance as an employee or an employer if used well.
Dr. Brian Harris

Lead Medical Advisor, SNOW
Education is the process of learning a new concept
Education is the process of learning a new concept and refers to a broader spectrum. It isn’t just limited to a concept or skill; it caters to developing a sense of judgment and reasoning skills.
Education is through books , lectures , and videos and is usually carried out in schools and universities.
Training usually refers to learning new skills that have immediate use
Training usually refers to learning new skills that have immediate use. Training is a more short-term process where you learn a new skill to be used in your career.
It is more vocational-oriented and is mainly carried out at work when you’re already in a role.
Development is usually a long-term process built upon your current education and training
Development is usually a long-term process built upon your current education and training. When you’re developing a skill, you’re enhancing your skills to be more efficient and effective.
This is a continuous process and includes both professional and personal growth.

Founder, Kimsadvice
Education is something that you don’t have knowledge of
Education is the knowledge the employee has to get at school in the computer field. Education is something that you don’t have knowledge of, and you seek that knowledge.
It is called education. For example, Bachelor’s degree in computer science is called education.
Training is when a person is about to finish their degree
Training is when a person is about to finish their degree. They have to do training in an organization to put into practice what they have learned in school.
It could also be training from any employee within an organization about a particular topic. Training is about putting your hand and doing the work with the supervision of some sort by someone else.
Development is when a person wants to acquire more knowledge in some area
Development is when this same person wants to acquire more knowledge in some area, either personal or professional . They can seek any course to enhance their learning.
This person already has some base, and when to improve this base is called development.
Agnieszka Goulin

Head of People, Spacelift
Training refers to expanding the knowledge, skill, attitude, abilities, and potential of the employee
Training refers to expanding the knowledge , skill , attitude , abilities , and potential of the employee to improve and hone the job performance.
It ensures better job performance and is crucial in the age of constant advancement in technology, wide use of computerization, and related culture.
Education has a broader objective as its purpose is to develop the individual
While training concerns the increase in knowledge, skills, and abilities for a particular job, i.e., has a narrow aim, education has a broader objective as its purpose is to develop the individual.
Education takes place in schools, colleges, and universities, while the place of work usually provides training. It enhances the individual’s general knowledge and motivates them to understand the environment.
Development refers to the growth of an individual in all respects
Training refers to the enhancement of skills for a particular job, and development refers to the growth of an individual in all respects. Training achieves immediate gains for the organization, while development focuses on the organization’s long-term needs.
A combination of training and development programs and an HR strategy allows for effective and efficient operation.
Dr. Ritesh Jain, MBBS, FRACP

Consultant Respiratory and Sleep Medicine | Co-Founder, WhatASleep
Education focuses more on theoretical knowledge and academic skills
The major difference between education, training, and development is each method’s opportunity to hone one’s skills. Education focuses more on theoretical knowledge and academic skills.
Training allows you to put that theoretical knowledge into practice
On the other hand, training allows you to put that theoretical knowledge into practice. As a result, you get to know how different the real world is compared to the academic world.
Development helps you further improve the skills you learned
Lastly, development is different from the other two because it helps you further improve the skills you learned during the education and training phase.
Education focuses on a systematic way of learning
The learning system that education, training, and development follow is entirely different. Education focuses on a systematic way of learning. This is usually done through a classroom setting and learning via theory .
Training emphasizes learning through practical application to boost one’s productivity and performance. Development also focuses on practice, but a more advanced form of it. People should concentrate on honing a wide range of skills in the development phase.
Lanny Tuchmayer

Lawyer | Director of Operations, Bergel Law
Training refers to learning to do something through performing or practicing
The major distinction between education and training is that they use different approaches to knowledge acquisition . Training refers to learning to do something through performing or practicing , whereas education refers to learning to do something theoretically .
They are both training two separate areas of the brain in this manner. The word education brings up images of children in classrooms for most people. However, the term can be applied in a variety of other settings.
Education refers to the act, process, or methodology of transmitting or gaining general knowledge
When used in this context, education refers to the act , process , or methodology of transmitting or gaining general knowledge, developing reasoning and critical abilities, and preparing oneself or others for a particular life role.
The term “training” has a variety of definitions. Some types of training are intended to help people learn specific work skills. Other types of training include instructing people on how to perform a given task for particular employment.
In general, training is the process of educating or instructing someone on how to perform various activities.
Elliot Lucas

Marketing Assistant, Portland Training Company
Education is learning to understand something
Education is learning to understand something. A lousy education is all about absorbing facts. You cram, cram, cram until you can regurgitate it. When you receive a good education, you’ll also understand how the facts interrelate and why they are true.
Training is learning to do something
Training is learning to do something. Unlike education, this usually has a hands-on component.
Development is learning to be something
Development is learning to be something. You can become competent at something with training alone. But you cannot become a master of it without action.
For example, you can receive training in painting, giving you the technical skills required, but you have to develop into an artist. I think this is true for all professions. By definition, development always involves rewriting who you are a little bit.
In practice, these three things usually come as a bundle. For example, my company is helping someone back into work as a forklift driver.
The learner needs education (health and safety, what does that button do etc.), training (we run them through an indoor maze on the forklift until they can navigate well), and development (the transition from long-term unemployment back into work requires grit and often a confidence boost).

Director of Marketing, Syntax Integration
Training is imparting knowledge and skills on precise, factual, and narrowly focused subject matter
Training is imparting knowledge and skills on precise , factual , and narrowly focused subject matter and skills. It is a structured learning activity that takes place in a classroom setting.
A broader intellectual or theoretical subject matter and the evolution of human attitudes are all included in the definition of development . There are many different learning activities, including both on and off-the-job training.
Education is the way professors provide content to pupils about a topic
There is also a formal classroom component. The primary purpose of education is for professors to provide content to pupils learning about the topic area they are teaching them.
The subject matter under research is well-known on a fundamental level. Teaching and training are examples of activities that fall within this category.
Learning is defined as acquiring new knowledge
Learning is defined as acquiring new knowledge or abilities through study, practice, or instruction. Learning can take place in any setting. It is an experience-based process that results in long-term changes in the potential for behavior.
When an individual has the potential to behave in a specific way to achieve a goal, this is referred to as their behavior potential .
Rodney Warner

Business Development Manager | CEO, Connective Web Design
Education is a brilliant way for the capitalist to control the working class
Education is a brilliant way for the capitalist to control the working class. They try to instill practices that will benefit them in the long and short run. This hidden agenda promotes social inequality among the working and ruling class.
Training allows individuals to develop some skills that are useful for everyday life
Training, unlike education, is more on the practical side. It allows individuals to develop some skills that are useful for everyday life.
As a result, they can enhance their existing knowledge and outshine others who focus on sticking to old practices, like rote learning.
The development allows individuals to grow and achieve their personal and professional goals
On the other hand, development is an informative process that allows individuals to grow and achieve their personal and professional goals. This is an attempt to overcome any future challenges and try to come up with practical solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can organizations support education, training, and development for their employees.
When it comes to nurturing employee growth, education, training, and development are critical components. Organizations that invest in their employees’ education and skill development benefit from improved productivity, increased employee satisfaction, and reduced turnover.
Here are some ways that organizations can support education, training, and development for their employees.
• Offer training programs : Organizations can provide structured training programs for employees to learn new skills or develop existing ones. This could involve in-person training sessions, online courses, or a combination of both.
• Provide mentorship opportunities : Pairing employees with mentors who have more experience and knowledge can help them develop professionally. This allows employees to learn from seasoned professionals who can offer guidance and insights.
• Encourage continuous learning : Encourage employees to continue learning by providing access to resources such as books, articles, and podcasts. Organizations can also provide support for employees who want to pursue additional education, such as degree programs or professional certifications.
• Create a culture of learning : Organizations can foster a culture of learning by promoting the value of education and development. Encouraging open communication and feedback, and providing opportunities for employees to share their knowledge and expertise, can help create a collaborative and learning-focused work environment.
• Offer career development programs : Organizations can offer career development programs that help employees identify their career goals and create a plan to achieve them. This could include coaching, workshops, and other resources to help employees advance in their careers.
• Provide job shadowing opportunities : Allowing employees to shadow their colleagues or leaders in different roles can help them gain a better understanding of different departments and roles within the organization. This can help employees develop a broader perspective and gain insights into how the organization operates.
• Provide feedback and recognition : Feedback and recognition are essential components of employee development. Providing constructive feedback and recognition for achievements can help employees improve their performance and feel valued.
How does education and training affect development?
Education and training play a critical role in the overall development of individuals, and have been found to impact various aspects of life. Here are some ways in which education and training affect development:
• Cognitive Development : Education and training help individuals develop better cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem solving, and decision making. They also aid in the development of literacy and numeracy skills.
• Personal Development : Education and training help individuals build self-confidence, self-esteem, and a sense of purpose. They also help individuals develop social skills, empathy, and emotional intelligence.
• Career Development : Education and training equip individuals with the skills and knowledge required to pursue a successful career. They also help individuals stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their fields.
• Economic Development : Education and training play a vital role in the economic development of a country. They help create a skilled workforce, increase productivity, and drive innovation and technological advancements.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The Editors
- Trivia Quizzes
- Memory Games
- Spot the Differences
- Sliding Puzzles
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Equity and Equality Aren’t the Same Thing. What Does That Look Like in Education?

- Share article
Today’s post is another in a series helping educators distinguish the differences between “equity” and “equality.”
‘Striving for Equity’
Jamie Wallace and Elaine V. Howes are co-editors of the book Culturally Responsive and Sustaining Science Teaching: Teacher Research and Investigation from Today’s Classrooms:
The terms “equity” and “equality” are often conflated. There are nuances and complexities in their interpretations and uses, further complicated by historical socio-cultural-racial inequities and structures of power and privilege in the United States. In our imperfect understanding of these ambiguous concepts, equality can be interpreted as “sameness,” particularly regarding opportunities and resources for students (Brayboy et al., 2007). This sameness or uniformity requires an eradication of all kinds of discrimination for equality to truly exist; thus, while equality is ideal, it is unlikely given long-standing histories of oppression and racism (Banks, 2021).
Equity refers to “fairness” and “justice” at a systemic level, regarding how individuals are seen and treated. In education, inequities are often viewed as unequal access to resources and opportunities. Yet, this interpretation omits the systems and processes that sustain inequities (Cochran-Smith & Keefe, 2022).
Thus, what is equal (same or uniform) differs from what is equitable (fair or just). In using an equality perspective, we would attempt to provide all students with identical opportunities. In striving for equity, we celebrate the multiple aspects of diversity in our pluralistic society and use these to center all students, especially those who have historically been poorly served by our education system.
Considering these terms, we highlight insights from our professional learning group (PLG) of teacher researchers exploring the equity pedagogy of culturally responsive and sustaining education (CRSE) in science. We draw on research by Ladson-Billings, Gay, Paris and Alim, and others to describe CRSE as valuing and connecting to students’ cultures and communities as assets; integrating them as resources; holding high expectations for learning; and adopting and supporting developing a critical stance (Howes & Wallace, 2022; Wallace et al., 2022). In our PLG, teachers research their own science teaching through a CRSE lens, working toward transforming teaching while addressing complex educational and social-cultural problems.
In our current climate with book bans and political attacks on discussing race, ethnicity, gender, power, and privilege in schools, equity-oriented, assets-based work like CRSE is critical. Below, we share examples from our work to help illuminate equity-focused approaches.
Imagine you are teaching in an urban high-need school and are responsible for preparing students for a standardized exam. Your students are recent immigrants and multilingual learners from numerous countries. You are teaching a lesson on natural hazards (earthquakes, tsunamis).
One option might be to take an equality-based perspective: Use a textbook outlining types of disasters, lectures about plate boundaries, and videos of volcanoes erupting. Alternatively, you could modify your teaching to support the students in your class, drawing on their diverse backgrounds, and meeting them where they are.
For instance, a teacher in our PLG developed a group research project in which students chose a natural hazard about which to design pamphlets detailing preparation and safety procedures. Students developed pamphlets in their primary language and English to support science and language learning.
This project incorporated students’ language assets and connected to their lived experiences, as students related firsthand interactions with natural disasters in their native countries and thought critically about the sociopolitical processes in places where hazards hit. This project communicated to students the importance of using their languages, experiences, and multiple identities as assets to support their learning. Modifying teaching in this way illustrates an equity-based approach to support all students’ learning.
Another teacher in our group taught about maps in a Manhattan high-need high school. She began with students developing memory maps of their neighborhoods and experiences. Using their memory maps, students learned about topographic changes accommodating modern infrastructure (including water sources), science specific to their communities, and inequities such as higher rates of asthma in cities. This place-based activity centered students’ identities by valuing and affirming their experiences and infusing them in learning.
Activities like these provide opportunities for students to integrate their lived experiences and communities into learning, creating spaces to uplift students’ stories and address social-justice issues. These approaches are customized to the individual students in the room, rather than an imaginary “every student,” setting high expectations and providing multiple entry points and worldviews. As Gorski (2016) argues, equity pedagogies must center students and their individual cultures, along with all students’ rights to equitable and just educational opportunities.

‘Equitable Access’
Courtney Rose, Ed.D., is a professor, educational consultant, culturally relevant/responsive educator, founder of Ivy Rose Consulting, and author of the upcoming book, Woven Together: How Unpacking Your Teacher Identity Creates a Stronger Learning Community . She currently serves as a visiting assistant teaching professor in the Educational Policy Studies department at Florida International University:
Much like “schooling” and “education, ” “equality” and “equity” get used interchangeably. In fact, in both cases, folks often actually lean into using one more often than the other. In the case of schooling/education, everything learning-related often gets lumped under education, and when it comes to equality/equity there is a far greater use of the word “equality,” with many pinpointing it as THE goal.
But as two of my favorite podcasters often say, words mean things , and understanding the definitions and distinctions between terms is the first step in aligning our goals with the policies and practices designed to attain them.
A clear, and highly discussed, example of the potential misalignments that can occur when one isn’t clear on whether they are working toward equality or equity is baked into the New York City public schools’ admissions process. For those who aren’t familiar, every 5th grade student in the district gets an application with a list of middle schools across the city they are eligible to attend, and they apply by ranking the schools in order of preference. Students then repeat this process in the fall semester of their 8 th grade year to apply to high schools. The process was designed to address the N.Y.C. school system’s long-standing position as one of the most segregated districts in the country. In fact, according to one 2018 study, New York City’s is the most segregated district for Black students and the second most segregated district for Latino students.
The admissions process is designed to level that playing field, opening up doors for students beyond their neighborhood school and utilizing “unbiased” programs that assess students’ eligibility based on attendance, grades, test scores, location/distance from schools, and availability of seats. However, with families spending years hiring tutors and touring schools in order to secure seats at the top schools in the district, many feel as though the system still prioritizes a wealthy and predominantly white subset of the population and maintaining educational inequities.
In the wake of the impact of COVID-19, which only exacerbated disparities and inequities, the district has partnered with organizations like IntegrateNYC to more accurately assess the disproportionate impact COVID-19 had across the district. Although it is not fully functioning as of yet, the new algorithm would use additional location-based and individual student circumstances to generate an admissions “priority score.” The higher the score, the more schools the student becomes eligible for.
While there are certainly many more questions to be answered, most of which won’t be determined until the new algorithm has been fully functioning for some time, the attempt to shift and redesign the algorithm shows the district’s acknowledgement that applying the same metrics across the board may create a system that seems to give students an equal shot at attending the best school for them but not equitable access or opportunity to secure a seat.

‘Differentiation Is a First Step’
Angela M. Ward, Ph.D., is an anti-racist educator with over 25 years of experience in education. She is a professional learning connoisseur focused on creating identity-safe schools and workplaces. Follow her @2WardEquity on Instagram and X and visit http://2wardequity.com/blog/ to subscribe to the 2Ward Equity newsletter:
The root word for equality is equal. If two students have different needs, yet the school provides the same or equal amounts of support, they are focused on equality for both students. One student will not receive support if another student does not receive the same support, otherwise known as fairness. Laws like the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, Title IX, and Title VI, for example, were passed to assist districts and other educational institutions with equity, not equality or fairness.
Equity acknowledges that every learner is not the same; that each learner’s lived experience is not the same; that location, space, and place is different for each; and, therefore, each learner will need something to support their learning that may differ from the needs of other learners. Special education students receive the most support with laws that ensure they receive equitable access to an education that directly meets their learning needs.
Differentiation is a first step to providing equitable access to a high-quality education to all students in a general education setting. Teachers differentiate strategies and engagement with students to provide each student the best chance at success with academic content. The Multi-Tiered System of Support (MTSS) is focused at the general education student who has not been labeled with an identified learning need. The MTSS provides educators with a process to learn more about supporting the learning needs of students, thereby offering students equitable access to a high-quality educational experience.
Public schools are required to educate all students. In addition to following the law and engaging in a successful MTSS, an equity-centered school district focuses budgets, staffing, buildings, and all resources on equitable distribution to ensure all students receive what they need to succeed in school regardless of social or cultural identity.
To learn more about equity and the law, visit Individuals with Disabilities Education Act , Education and Title VI , and/or Title IX and Sex Discrimination .

Thanks to Jamie, Elaine, Courtney, and Angela for contributing their thoughts!
Today’s post answered this question:
It’s not unusual for districts, schools, and educators to confuse “equality” with “equity.” What are examples, and ways, you would help them understand the difference?
Part One in this series featured responses from Jehan Hakim, Mary Rice-Boothe, Jennifer Cárdenas, and Shaun Nelms.
In Part Two , Karen Baptiste, PJ Caposey, and Denise Fawcett Facey contributed their perspectives.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email . And if you missed any of the highlights from the first 12 years of this blog, you can see a categorized list here .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for The Savvy Principal
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- MS in the Learning Sciences
- Tuition & Financial Aid

Qualitative vs. quantitative data analysis: How do they differ?

Learning analytics have become the cornerstone for personalizing student experiences and enhancing learning outcomes. In this data-informed approach to education there are two distinct methodologies: qualitative and quantitative analytics. These methods, which are typical to data analytics in general, are crucial to the interpretation of learning behaviors and outcomes. This blog will explore the nuances that distinguish qualitative and quantitative research, while uncovering their shared roles in learning analytics, program design and instruction.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is descriptive and includes information that is non numerical. Qualitative research is used to gather in-depth insights that can't be easily measured on a scale like opinions, anecdotes and emotions. In learning analytics qualitative data could include in depth interviews, text responses to a prompt, or a video of a class period. 1
What is quantitative data?
Quantitative data is information that has a numerical value. Quantitative research is conducted to gather measurable data used in statistical analysis. Researchers can use quantitative studies to identify patterns and trends. In learning analytics quantitative data could include test scores, student demographics, or amount of time spent in a lesson. 2
Key difference between qualitative and quantitative data
It's important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative data to both determine the appropriate research methods for studies and to gain insights that you can be confident in sharing.
Data Types and Nature
Examples of qualitative data types in learning analytics:
- Observational data of human behavior from classroom settings such as student engagement, teacher-student interactions, and classroom dynamics
- Textual data from open-ended survey responses, reflective journals, and written assignments
- Feedback and discussions from focus groups or interviews
- Content analysis from various media
Examples of quantitative data types:
- Standardized test, assessment, and quiz scores
- Grades and grade point averages
- Attendance records
- Time spent on learning tasks
- Data gathered from learning management systems (LMS), including login frequency, online participation, and completion rates of assignments
Methods of Collection
Qualitative and quantitative research methods for data collection can occasionally seem similar so it's important to note the differences to make sure you're creating a consistent data set and will be able to reliably draw conclusions from your data.
Qualitative research methods
Because of the nature of qualitative data (complex, detailed information), the research methods used to collect it are more involved. Qualitative researchers might do the following to collect data:
- Conduct interviews to learn about subjective experiences
- Host focus groups to gather feedback and personal accounts
- Observe in-person or use audio or video recordings to record nuances of human behavior in a natural setting
- Distribute surveys with open-ended questions
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative data collection methods are more diverse and more likely to be automated because of the objective nature of the data. A quantitative researcher could employ methods such as:
- Surveys with close-ended questions that gather numerical data like birthdates or preferences
- Observational research and record measurable information like the number of students in a classroom
- Automated numerical data collection like information collected on the backend of a computer system like button clicks and page views
Analysis techniques
Qualitative and quantitative data can both be very informative. However, research studies require critical thinking for productive analysis.
Qualitative data analysis methods
Analyzing qualitative data takes a number of steps. When you first get all your data in one place you can do a review and take notes of trends you think you're seeing or your initial reactions. Next, you'll want to organize all the qualitative data you've collected by assigning it categories. Your central research question will guide your data categorization whether it's by date, location, type of collection method (interview vs focus group, etc), the specific question asked or something else. Next, you'll code your data. Whereas categorizing data is focused on the method of collection, coding is the process of identifying and labeling themes within the data collected to get closer to answering your research questions. Finally comes data interpretation. To interpret the data you'll take a look at the information gathered including your coding labels and see what results are occurring frequently or what other conclusions you can make. 3
Quantitative analysis techniques
The process to analyze quantitative data can be time-consuming due to the large volume of data possible to collect. When approaching a quantitative data set, start by focusing in on the purpose of your evaluation. Without making a conclusion, determine how you will use the information gained from analysis; for example: The answers of this survey about study habits will help determine what type of exam review session will be most useful to a class. 4
Next, you need to decide who is analyzing the data and set parameters for analysis. For example, if two different researchers are evaluating survey responses that rank preferences on a scale from 1 to 5, they need to be operating with the same understanding of the rankings. You wouldn't want one researcher to classify the value of 3 to be a positive preference while the other considers it a negative preference. It's also ideal to have some type of data management system to store and organize your data, such as a spreadsheet or database. Within the database, or via an export to data analysis software, the collected data needs to be cleaned of things like responses left blank, duplicate answers from respondents, and questions that are no longer considered relevant. Finally, you can use statistical software to analyze data (or complete a manual analysis) to find patterns and summarize your findings. 4
Qualitative and quantitative research tools
From the nuanced, thematic exploration enabled by tools like NVivo and ATLAS.ti, to the statistical precision of SPSS and R for quantitative analysis, each suite of data analysis tools offers tailored functionalities that cater to the distinct natures of different data types.
Qualitative research software:
NVivo: NVivo is qualitative data analysis software that can do everything from transcribe recordings to create word clouds and evaluate uploads for different sentiments and themes. NVivo is just one tool from the company Lumivero, which offers whole suites of data processing software. 5
ATLAS.ti: Similar to NVivo, ATLAS.ti allows researchers to upload and import data from a variety of sources to be tagged and refined using machine learning and presented with visualizations and ready for insert into reports. 6
SPSS: SPSS is a statistical analysis tool for quantitative research, appreciated for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive statistical tests, which makes it ideal for educators and researchers. With SPSS researchers can manage and analyze large quantitative data sets, use advanced statistical procedures and modeling techniques, predict customer behaviors, forecast market trends and more. 7
R: R is a versatile and dynamic open-source tool for quantitative analysis. With a vast repository of packages tailored to specific statistical methods, researchers can perform anything from basic descriptive statistics to complex predictive modeling. R is especially useful for its ability to handle large datasets, making it ideal for educational institutions that generate substantial amounts of data. The programming language offers flexibility in customizing analysis and creating publication-quality visualizations to effectively communicate results. 8
Applications in Educational Research
Both quantitative and qualitative data can be employed in learning analytics to drive informed decision-making and pedagogical enhancements. In the classroom, quantitative data like standardized test scores and online course analytics create a foundation for assessing and benchmarking student performance and engagement. Qualitative insights gathered from surveys, focus group discussions, and reflective student journals offer a more nuanced understanding of learners' experiences and contextual factors influencing their education. Additionally feedback and practical engagement metrics blend these data types, providing a holistic view that informs curriculum development, instructional strategies, and personalized learning pathways. Through these varied data sets and uses, educators can piece together a more complete narrative of student success and the impacts of educational interventions.
Master Data Analysis with an M.S. in Learning Sciences From SMU
Whether it is the detailed narratives unearthed through qualitative data or the informative patterns derived from quantitative analysis, both qualitative and quantitative data can provide crucial information for educators and researchers to better understand and improve learning. Dive deeper into the art and science of learning analytics with SMU's online Master of Science in the Learning Sciences program . At SMU, innovation and inquiry converge to empower the next generation of educators and researchers. Choose the Learning Analytics Specialization to learn how to harness the power of data science to illuminate learning trends, devise impactful strategies, and drive educational innovation. You could also find out how advanced technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI) can revolutionize education, and develop the insight to apply embodied cognition principles to enhance learning experiences in the Learning and Technology Design Specialization , or choose your own electives to build a specialization unique to your interests and career goals.
For more information on our curriculum and to become part of a community where data drives discovery, visit SMU's MSLS program website or schedule a call with our admissions outreach advisors for any queries or further discussion. Take the first step towards transforming education with data today.
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from nnlm.gov/guides/data-glossary/qualitative-data
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from nnlm.gov/guides/data-glossary/quantitative-data
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation/pdf/brief19.pdf
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation/pdf/brief20.pdf
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from lumivero.com/solutions/
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from atlasti.com/
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from ibm.com/products/spss-statistics
- Retrieved on August 8, 2024, from cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-intro.html#Introduction-and-preliminaries
Return to SMU Online Learning Sciences Blog
Southern Methodist University has engaged Everspring , a leading provider of education and technology services, to support select aspects of program delivery.
This will only take a moment
Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/08/20/gcse-results-day-2024-number-grading-system/
GCSE results day 2024: Everything you need to know including the number grading system

Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.
Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren’t what you’re expecting.
When is GCSE results day 2024?
GCSE results day will be taking place on Thursday the 22 August.
The results will be made available to schools on Wednesday and available to pick up from your school by 8am on Thursday morning.
Schools will issue their own instructions on how and when to collect your results.
When did we change to a number grading scale?
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths.
By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
The numerical grading system was to signal more challenging GCSEs and to better differentiate between students’ abilities - particularly at higher grades between the A *-C grades. There only used to be 4 grades between A* and C, now with the numerical grading scale there are 6.
What do the number grades mean?
The grades are ranked from 1, the lowest, to 9, the highest.
The grades don’t exactly translate, but the two grading scales meet at three points as illustrated below.
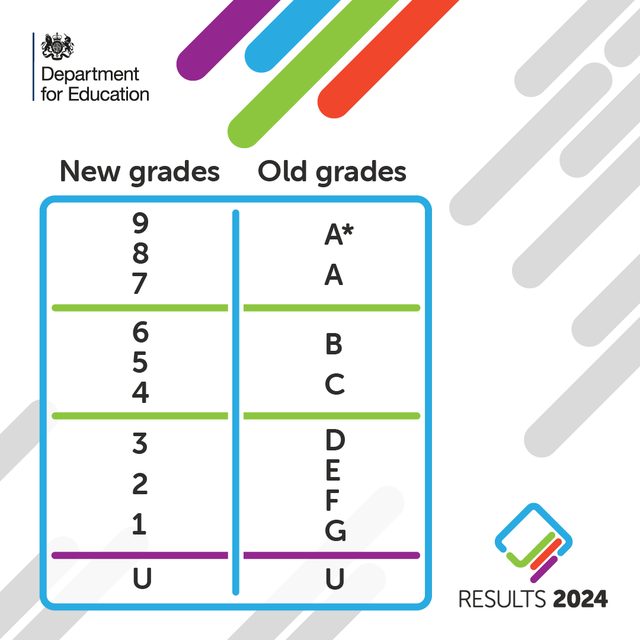
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, while the bottom of grade 4 is aligned to the bottom of grade C.
Meanwhile, the bottom of grade 1 is aligned to the bottom of grade G.
What to do if your results weren’t what you were expecting?
If your results weren’t what you were expecting, firstly don’t panic. You have options.
First things first, speak to your school or college – they could be flexible on entry requirements if you’ve just missed your grades.
They’ll also be able to give you the best tailored advice on whether re-sitting while studying for your next qualifications is a possibility.
If you’re really unhappy with your results you can enter to resit all GCSE subjects in summer 2025. You can also take autumn exams in GCSE English language and maths.
Speak to your sixth form or college to decide when it’s the best time for you to resit a GCSE exam.
Look for other courses with different grade requirements
Entry requirements vary depending on the college and course. Ask your school for advice, and call your college or another one in your area to see if there’s a space on a course you’re interested in.
Consider an apprenticeship
Apprenticeships combine a practical training job with study too. They’re open to you if you’re 16 or over, living in England, and not in full time education.
As an apprentice you’ll be a paid employee, have the opportunity to work alongside experienced staff, gain job-specific skills, and get time set aside for training and study related to your role.
You can find out more about how to apply here .
Talk to a National Careers Service (NCS) adviser
The National Career Service is a free resource that can help you with your career planning. Give them a call to discuss potential routes into higher education, further education, or the workplace.
Whatever your results, if you want to find out more about all your education and training options, as well as get practical advice about your exam results, visit the National Careers Service page and Skills for Careers to explore your study and work choices.
You may also be interested in:
- Results day 2024: What's next after picking up your A level, T level and VTQ results?
- When is results day 2024? GCSEs, A levels, T Levels and VTQs
Tags: GCSE grade equivalent , gcse number grades , GCSE results , gcse results day 2024 , gsce grades old and new , new gcse grades
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | ||
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
Comments and moderation policy
Education policy: How Harris and Trump differ on K-12, higher education and more
The two candidates differ vastly on education policy.
When it comes to education, Democratic presidential candidate Kamala Harris and former President Donald Trump have vastly different views for the nation.
Several unions representing educators and administrators -- including the National Education Association, the American Federation of Teachers, and the American Federation of School Administrators -- have endorsed Vice President Kamala Harris for president.
Former federal education leaders President Ronald Reagan's Secretary of Education William Bennett and Reagan's Under Secretary of Education Gary Bauer have registered their support for Trump for President. Trump's Secretary of Education Betsy DeVos has said she would work for Trump again but has stopped short of an endorsement.
Take a look at their record and what the two have said so far about their hopes and plans for both K-12 and higher education.
The Department of Education
Trump's Agenda47 campaign has proposed eliminating the U.S. Department of Education which, according to the DOE website, "establishes policy for, administers and coordinates most federal assistance to education." Trump, in a campaign video, has said he wants states, not the federal government, to have control over schools.
Throughout Trump's presidency, he proposed billions in cuts to the Department of Education's budget.
Harris' campaign as well as the Biden-Harris administration have criticized Trump for threatening to dismantle the department while expressing support for federal funding and policy initiatives from the agency.
Harris has been criticized for not putting forth many official policy positions, including education, since her campaign began roughly a month ago. Amid scrutiny, her campaign released an economic agenda with expectations of future policy rollouts to come in the final days on the campaign trail.

School choice
Trump has backed universal school choice programs, which allow a student's allotment of public education funds to be transferred to nonpublic schooling options -- including private and religious schools or homeschooling. Trump signed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act during his presidency, which his campaign states allowed parents to use up to $10,000 from a 529 education savings account to cover K-12 tuition costs at a school of their choice.
The Democratic 2025 platform opposes the use of private-school vouchers and tuition tax credits, opportunity scholarships, "and other schemes that divert taxpayer-funded resources away from public education."
Funding for low-income students and families
The Biden-Harris administration secured billions of dollars to increase federal funding for schools that largely serve low-income families, directing billions toward resources and funding for low-income schools but also increased funding to special education services, career and technical education and English-language learning programs.
In a 2019 bill, then-Sen. Harris proposed establishing “Family Friendly School” policies at 500 elementary schools to align the school day with the workday in support of working families.
Harris has spoken out in favor of 21st Century Community Learning Centers -- which host programs predominantly for students who are in high-poverty and low-performing schools and the Gaining Early Awareness and Readiness for Undergraduate Programs which provides yearslong grants for services at high-poverty middle and high schools.
Trump proposed cuts to both programs in annual budget proposals under his administration.
Both the Biden-Harris and Trump-Pence administrations have seen increases to Head Start , a program that provides federally subsidized preschool for low-income children.
The Biden-Harris administration increased funding for Head Start by roughly $2 billion since the start of their term. Trump's administration saw a roughly $1.3 billion increase during his term.
Trump also sought to "expand K-12 educational options for disadvantaged children impacted by the pandemic," and signed an Executive Order to provide emergency K-12 scholarships using Federal Community Service Block Grants so students could access in-person learning opportunities in December 2020.

K-12 curriculum
Trump's campaign has detailed a plan centering on prayer in public schools, an expansion of parental rights in education, patriotism as a centerpiece of education and the "American Way of Life."
This includes a dismantling of so-called "woke" or diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) initiatives in education and reinstating his administration's 1776 Commission which focuses education on the history and "values" of the founding of the United States of America. However, Trump has called for cutting federal funding for schools or programs that feature “critical race theory, gender ideology or other inappropriate racial, sexual, or political content onto our children.”
Trump plans to "promote positive education about the nuclear family, the roles of mothers and fathers, and celebrating rather than erasing the things that make men and women different and unique."
Harris has spoken out against efforts to ban books and restrict classroom content regarding race.
She called controversial Black history guidelines in Florida in 2023 "revisionist history" for requiring middle schoolers to learn "how slaves developed skills which, in some instances, could be applied for their personal benefit."
Teacher pay
When Harris first ran for president in 2019, she proposed closing "the teacher pay gap" between teachers and other professions that require a college degree -- which Harris said would be a $13,500 salary bump for teachers as schools nationwide continue to report staffing shortages and poor funding.
According to the National Education Association (NEA), the national average for starting teacher salaries is $44,530 and the national average teacher salary is $69,544. The Department of Education also found that 94% of teachers paid out of pocket for school supplies for their classrooms in a 2018 study.
Trump's Agenda47 states that he will support teacher merit pay, which ties a teacher's compensation to student performance. Some studies have shown that merit pay programs could improve student outcomes, while some argue there is not enough evidence , and that there are various factors that impact student performance -- including funding and resource inequity.
Teacher tenure and hiring
Trump's Agenda47 states he plans to put an end to teacher tenure laws. These laws are described by the United Federation of Teachers as state laws that prevent a school district from dismissing a tenured teacher without due process. Most states have tenure laws in place, however at least 10 states have zero or limited tenure laws, according to the NEA.
In a campaign video, Trump states he wants to abolish these policies "to remove bad teachers."
Trump also plans to create a credentialing body to certify teachers who "embrace patriotic values and support the American Way of Life" and encourage schools to allow trained teachers to carry concealed weapons at school.
The Biden-Harris administration has touted the tens of billions of dollars it has invested in staffing through the American Rescue Plan, which filled gaps in employment stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Biden-Harris administration's American Rescue Plan and the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act funded the hiring and training of more counselors, social workers and other staff in schools nationwide amid what has been called a mental health crisis.
Student loan forgiveness and free higher education
Harris has long been a proponent of free two-year college tuition for most students and for free four-year college and trade school tuition for students from lower- and middle-income families.
The Biden administration has touted student loan forgiveness as a central part of its education platform -- in July, the Department of Education laid out options for roughly 25 million borrowers to have some, or all, of their debt canceled.
This most recent proposal came after Biden and Harris' initial effort to cancel some or all debt for 43 million people was overturned by the Supreme Court. Despite the roadblock, the administration says it has forgiven more than $144 billion for millions of Americans through other programs.

More than 940,000 of these are public servants who have their federal student loans forgiven through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program -- up from the 7,000 recipients enrolled in the program before the Biden-Harris administration took office.
During Trump's time in office, he proposed eliminating the PSLF and making cuts to the Pell Grant program.
Trump's agenda for 2025 focuses on plans to create a new, free university called the "American Academy" and fund it by "taxing, fining and suing" private universities.
"Its mission will be to make a truly world-class education available to every American, free of charge, and do it without adding a single dime to the federal debt," said Trump. "This institution will gather an entire universe of the highest quality educational content, covering the full spectrum of human knowledge and skills, and make that material available to every American citizen online for free."
Recent Title IX changes
The Biden-Harris administration recently issued new rules that say Title IX protects students from discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity, and expanded protections from sex-based harassment to include “sexual violence and unwelcome sex-based conduct that creates a hostile environment by limiting or denying a person’s ability to participate in or benefit from a school’s education program or activity.”
The regulations update also enhances protections for students, employees and applicants against discrimination "based on pregnancy, childbirth, termination of pregnancy, lactation, related medical conditions, or recovery from these conditions." However, parts of it have been blocked from enforcement by conservative-led lawsuits.
Trump has said he would overturn the new regulations connected to what he has called "gender insanity."
Historically Black Colleges and Universities
Both Trump and Harris have invested in HBCUs, which have long been underfunded by the federal government, throughout the years.
During Trump's time in office, he signed into law the bipartisan FUTURE Act to permanently send $255 million in annual funding for HBCUs, forgave $322 million in disaster loans to four HBCUs in 2018, and signed legislation that included more than $100 million for scholarships, research and centers of excellence at HBCU land-grant institutions.
Harris proposed increased funding for HBCUs in her first presidential run -- particularly focusing on training for Black educators. The Biden-Harris administration sent more than $16 billion in funding and investments to these schools from 2021 to 2024.
Related Topics
- Kamala Harris
- Donald Trump
Trending Reader Picks

NASA astronauts must return on different craft
- Aug 24, 2:40 PM

Anthony Fauci hospitalized with West Nile virus
- Aug 24, 11:30 AM

HS football player dies after game injury
- Aug 25, 11:21 AM

Tim Walz gives rural Democrats renewed hope
- Aug 24, 6:11 AM
RFK Jr. suspending campaign, backing Trump
- Aug 23, 8:02 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events

This blog is about to help those who preparing for Civil Services (IAS, MPPSC & Other State PSC's), PEB (Vyapam), SSC and Banking. We make and effort to provide the quality material and useful information and easy to learn techniques for the students.
- Exam Specific Contents
- General Studies
- Hindi / English / Computer
- Aptitude & Reasoning
- Question Papers
- Special Content / Current affairs
- Registration Form
- VS Education by vikram singh
Thursday, February 23, 2017


Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.

- Education News
Karnataka’s leading medical colleges in NIRF Ranking 2024

| | | | |
| National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences, Bangalore | 4 | 71.92 | Between Rs. 30,000 to Rs. 1.5 Lakh (full course) |
| Kasturba Medical College, Manipal | 9 | 67.42 | Between Rs. 1.5 lakh to Rs. 16.5 lakh (first year) |
| St. John's Medical College | 28 | 58.03 | Between Rs. 90,000 to Rs. 10 lakh (first year) |
| Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore | 33 | 57.12 | Between Rs. 1 Lakh to Rs. 70 Lakh (full course) |
| JSS Medical College, Mysore | 39 | 55.00 | Between Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 19 Lakh (first year) |
| M. S. Ramaiah Medical College | 46 | 51.76 | Between Rs. 4.5 lakh to Rs. 22 lakh (first year) |
Why is Karnataka a good option in medical courses?
Why is medical a top choice for many science students, visual stories.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Visual Studio Code for Education is free and completely online, so you can access it across devices and platforms. Choose from short bite-size lessons of varying difficulty levels, or full courses that include interactive assessments and coding challenges. With built-in accessibility features like Immersive Reader, zoom, screen reader support ...
VS EDUCATION is a technology based online learning initiative by VS EDUCATION . Add Power of Coaching to your Online learning with VS EDUCATION . Live Online Interactive Classes . Online Test Series and feedback . Procure Printed SMP & Exercise Sheets . Free Stuff - Study material, eBooks, eDPPS etc .
Python: flexible, easy, popular. Use it for web, software, data, QA, and more. Learn Python today! Learn front-end web design using HTML/CSS/JavaScript to make your own web pages. Show off your skills! Build a Python game to match English and Spanish words. Visual Studio Code for Education. Powering the next generation of developers.
Connect with VS Education in an efficient and transparent manner. Updated on. Jul 15, 2024. Education. Data safety. arrow_forward. Safety starts with understanding how developers collect and share your data. Data privacy and security practices may vary based on your use, region, and age. The developer provided this information and may update it ...
Microsoft Visual Studio Code for Education is a free online computer science education platform for students and teachers built on Visual Studio Code. With no software to install or configure, VS ...
Quality education informs students of facts, concepts, and theories, whereas training focuses on applications. Short-term Proficiency Vs. Long-term Growth. When considering the average length of training vs education programs, training programs are usually shorter. They aim to achieve proficiency quickly in the trained individuals.
Learn how learning and education are different, and why it matters for becoming effective lifelong learners in a complex world. Explore the benefits and limitations of education, and the importance of learning as a mindset, process, and outcome.
Education provides a structured framework for holistic development, while literacy enables individuals to access information, communicate effectively, and participate actively in society. Both education and literacy are interconnected and mutually reinforcing, playing a vital role in personal and societal development.
VS Education has been successful in helping thousands of aspirants so far and will continue to do so in the days to come. With a simple user interface, design, and exciting features, the VS ...
9 Core Differences Between Education and Training (Education vs Training) The former broadens our horizons & builds a foundation for critical thinking. While training equips us with the necessary tools & skills to apply in specific scenarios. In the table below, we list down the key differences between education and training.
VS EDUCATION. 10K+ Downloads. Everyone. info. Share. Add to wishlist. About this app. arrow_forward. Get the most reliable learning experience. Updated on. Jul 17, 2024. Education. Data safety. arrow_forward. Safety starts with understanding how developers collect and share your data. Data privacy and security practices may vary based on your ...
Education is a discipline that is concerned with methods of teaching and learning in schools or school-like environments as opposed to various nonformal and informal means of socialization (e.g., rural development projects and education through parent-child relationships).
A lightweight, powerful code editor on PC, Mac, or Linux. Comes with built-in support for JavaScript, TypeScript, and Node.js and has a rich ecosystem of extensions for other languages (such as C++, C#, Java, Python, Go). Customize the editing, building, debugging experience with extensions to optimize for your unique needs.
It allows learners to study at their own pace and on their schedule, making it an ideal option for those with busy lifestyles or other commitments. 2. Cost-Effective. Online courses are often less expensive than traditional classroom-based courses, making education more accessible to a wider range of learners. 3.
Introduction. Education and learning are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct attributes that set them apart. While education is a formal process of acquiring knowledge and skills through structured institutions, learning is a broader concept that encompasses acquiring knowledge through various means, including formal education, personal experiences, and self-directed exploration.
A Master of Science in Education will also give you a more technical understanding of the art of teaching. But a Master of Science in Education, compared to a Master of Arts in Education, is specifically focused on scientific and technical fields. An MS in Education is an excellent choice for those interested in teaching subjects that are more ...
Education might include sharing how to develop and maintain company culture, problem-solving philosophies, or best practices for team conflict. While training can occur on the job, education is typically delivered in a dedicated learning environment. It's usually wide in scope and pertains to abstract concepts.
September 12, 2020. School vs. Education are two terms that have been misidentified, misinterpreted, and misconceptualized. They are often used interchangeably and thought to mean the same thing, but they are different. Education is the process of gaining knowledge formally and informally, while schooling is simply going to school to learn.
The focus of education is on the act of imparting knowledge, developing skills, and fostering critical thinking. Whereas, educational often modifies nouns, describing tools, content, or environments that aid in educational processes, such as educational software or educational standards. Education as a concept can be formal or informal and ...
It is a broad concept that shapes an individual's perspective and understanding of the world. Schooling, meanwhile, is more focused on academic achievement, following a structured system intended to provide students with specific knowledge and qualifications. 8. Education can be self-directed, and its success is often measured by personal ...
Education refers to the process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes through various means, such as formal and informal learning, personal experiences, and self-study. It encompasses a broader scope and extends beyond the boundaries of a classroom. On the other hand, schooling specifically refers to the formal instruction and ...
Education is the process of gaining broad information and skills in a classroom . Education is the process of gaining broad information and skills in a classroom or other educational setting. Educated skills and knowledge help kids build thinking and judgment around vast themes. Education usually takes place throughout a semester or even years
Angela M. Ward, Ph.D., is an anti-racist educator with over 25 years of experience in education. She is a professional learning connoisseur focused on creating identity-safe schools and workplaces.
In this data-informed approach to education there are two distinct methodologies: qualitative and quantitative analytics. These methods, which are typical to data analytics in general, are crucial to the interpretation of learning behaviors and outcomes. ... (interview vs focus group, etc), the specific question asked or something else. Next ...
Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.. Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren't what you're expecting.
Trump's Agenda47 campaign has proposed eliminating the U.S. Department of Education which, according to the DOE website, "establishes policy for, administers and coordinates most federal ...
Thursday, February 23, 2017. YOUTUBE CHANNEL. MPPSC Mains 2018. Important Study Material in Text [hindi] Discussion forum- UPSC/MPPSC/SSC. For SSC/ Railway Discussion. Discussion forum- For MP exams 2018. Posted by Education VS at 12:52 AM. Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to FacebookShare to Pinterest.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would "eliminate the U.S. Department of Education" — and that's accurate.
During the 2024 Democratic National Convention, Illinois Gov. JB Pritzker criticized former President Donald Trump, urging voters to listen to an actual billionaire rather than Trump's rhetoric.
The 2024 NIRF rankings, released on August 12, highlighted six Karnataka institutes among India's best medical colleges. Notably, the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences secured ...