

Essay on Impact Of Globalization On Communication
Students are often asked to write an essay on Impact Of Globalization On Communication in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Impact Of Globalization On Communication
Introduction.
Globalization is the process of integrating the world’s economies, cultures, and societies. It has greatly influenced how we communicate. This essay will explore the impact of globalization on communication.
Global Connectivity
Globalization has made the world a smaller place. With the help of the internet and technology, we can now communicate with anyone, anywhere, at any time. This has made sharing ideas and information easier and quicker than ever before.
Language and Communication
Globalization has also affected language use. English has emerged as a global language, making communication between different cultures more efficient. It has also led to the mixing of languages, creating new forms of communication.
Cultural Exchange
Globalization has led to a greater exchange of cultures. This cultural exchange has influenced the way we communicate, introducing new words, phrases, and styles of communication from different cultures into our own.
Despite the benefits, globalization also brings challenges. The rapid pace of communication can lead to misinformation spreading quickly. Additionally, the dominance of English can undermine other languages and cultures.
In conclusion, globalization has significantly impacted communication. It has brought us closer, influenced language use, and facilitated cultural exchange. But it also presents challenges that need to be addressed.
250 Words Essay on Impact Of Globalization On Communication
Globalization is the system of interaction among the countries of the world to develop the global economy. This has a big impact on how people communicate.
Global Communication
Globalization has made communication easier and faster. Before, it was hard to talk to someone far away. Now, with the internet and mobile phones, we can talk to anyone, anywhere, anytime. This is because of globalization.
Language and Culture
Globalization has also changed the way we use language. English has become a global language. It helps people from different countries to talk to each other. Also, we learn about other cultures through communication. This helps us understand and respect each other more.
Business Communication
In business, globalization has made it easy to share ideas and information. Companies can now work with people from different countries. They can also sell their products to customers all over the world. This has helped businesses grow and succeed.
Even though globalization has made communication easier, it also brings challenges. For example, not everyone has access to the internet. Also, there can be misunderstandings because of language and cultural differences.
In conclusion, globalization has changed the way we communicate. It has made it easier and faster, but also brought challenges. We need to work on these challenges to make the most of global communication.
500 Words Essay on Impact Of Globalization On Communication
The meaning of globalization and communication.
Globalization is the process of making something worldwide in scope or application. It means that people, ideas, and goods move more easily and quickly across the world. Communication, on the other hand, is the way we share or exchange information. So, when we talk about the impact of globalization on communication, we’re talking about how globalization changes the way we share and receive information.
Before globalization, communication was limited. People could only talk face-to-face or send letters that took weeks to arrive. But, with globalization, we now have the internet, mobile phones, and social media. These tools make it easy for us to talk to someone on the other side of the world in real-time.
Breaking Down Barriers
Globalization breaks down communication barriers. Before, language differences made it hard for people from different countries to talk. But now, we have translation tools that can translate languages in real-time. This means we can talk to people from different parts of the world without knowing their language.
Sharing of Cultures
Globalization also impacts the way cultures share information. Through the internet, we can learn about different cultures without leaving our homes. We can watch videos, read articles, and even talk to people from different cultures. This helps us understand and appreciate different cultures better.
Increased Business Opportunities
Globalization has also made it easier for businesses to communicate with customers and other businesses from different parts of the world. Through emails, video calls, and social media, businesses can reach more people and expand their market.
The Downsides
Despite the many benefits, globalization also has its downsides. The ease of communication can lead to information overload. We’re constantly bombarded with news, messages, and updates. This can be overwhelming and can make it hard for us to focus.
Additionally, while globalization allows us to learn about different cultures, it can also lead to cultural homogenization. This is when cultures become more similar to each other because of the influence of dominant cultures.
In conclusion, globalization has a big impact on communication. It has made communication easier, faster, and more accessible. It has broken down barriers, allowed us to learn about different cultures, and increased business opportunities. But, it also has its downsides like information overload and cultural homogenization. As we continue to live in a globalized world, it’s important for us to learn how to navigate these changes in communication.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Impact Of Food Consumption On Health
- Essay on Impact Of Food Advertising
- Essay on Impact Of Everyday Racism
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay
Introduction, social media: a brief history, positive and negative effects of social media in globalization, recommendations, reference list.
Globalization is the metamorphosis of the world from a vast unexplored space to a fairly big village where everyone seems to be connected. It refers to the integration and connection of the world in many areas, including technology, information, culture, business (Jan 2009, p. 66; Stevenson 1999, p. 40).
It is the delocalization of space and time, enabling real-time communication between persons who are thousands of miles apart from one another (Chan 1994, p. 76). It connects and unites the world (Robertson 1992, p.112). Advances in communication and transportation have facilitated globalization.
Economies and culture across the world are now collectively linked by new trends in communication (Robertson 1992, p. 112). But, globalization can be like a double-edged sword; with certain populous cultures exerting strong influences on the global community and vice versa (Flew 2007, p.86).
Globalization of media facilitates the sharing of home grown content with a worldwide audience via various media organizations (Liebes &Katz 1990, p. 106). Media globalization influences different cultures through propagation of information. This is because many media organizations control economic and social resources giving them considerable influence over global culture (Curran 2002, p. 218).
This paper will analyse and discuss the issues relating to globalization and its impact on social media. It will look at the advantages and disadvantages of globalization and the response of social media to the global phenomena.
Social media are sites on the internet that are used to share multimedia information, data, discussions and personal interactions (Traber, 1986, p. 84).
Individuals and groups create and share content on these sites where they can also have personal conversations. Social media takes many forms, including blogs, forums, message boards, social networks, virtual worlds, digital storyboards, social bookmarks, video, data and content-sharing sites, to name a few (Kim et al 2011, p. 368). There are many social networking sites, the most popular among which are Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Wikipedia, and Wetpaint (Kim et al 2011, p. 370).
Social media can be loosely defined as a platform bringing together people from different backgrounds who share a common interest for the purpose of discussing issues of interest. It is where technology meets the social needs of people, since human beings are social beings.
Social media can be traced back to the late 1960s. CompuServe was all the rage then; it used dial-up technology to establish connections to a network (Boyd 2007, p. 226). After delivery of the first email in 1971, two computer enthusiasts invented the first platform for a virtual community.
It was known as the bulletin board system (BBS) (Traber 1986, p. 84). The purpose of BBS was to alert friends about meetings, make announcements and post information (Boyd 2007, p. 218). In 1993, CERN, a nuclear research organization in Switzerland, donated the World Wide Web technology to the world and in the same year, Mosaic, the first graphical server, was launched. Mosaic’s launch gave rise to web pages and changed the internet scene (Curtis 2011, p. 62).
Geocities was launched in 1994 and it enabled users to create their own websites modelled after urban areas. The web hit the millionth-site mark in 1997 and in the same year, blogging and online chatting began (Curtis 2011, p. 62). Google opened shop in 1998 as an internet search engine and index. Wikipedia, the world’s largest wiki was started in 2001 as an online encyclopaedia (Kim et al 2011, p. 368).
Social networking websites have mushroomed in recent years, with the emergence of MySpace, LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, digg and YouTube, among others. By 2011, social media was accessible from almost everywhere and social media business was increasing. The development of multimedia-capable mobile devices enabled more people from around the world to access social media from anywhere at any time (Curtis 2011, p. 62).
Advances in social media have brought about massive changes in business, education, politics, entertainment, employment and human interaction (Giddens 1990, p.174). It is now possible to study, work, watch programs, listen to music, vote and follow the latest news without having to leave one’s home.
Actually, one does not need to be tied down to a home in the traditional sense since technology has occasioned virtual homes. With the advent of social media, the world has been transformed into a huge village where news items from a seemingly insignificant corner of the globe can be spread across the planet in just a few clicks and seconds.
This paper sets out to expound on the many positive and negative impacts of the globalization of social media.
The massive number of ideas that people share through such platforms as Twitter and Facebook has noticeably influenced a change in lifestyles, preferences, political ideologies and academic achievements, both for the positive and negative.
Product sales
Social media is now an instrumental tool in the success of a business today. Social media inventions have increased business sales due to their far reaching effects on the global market. According to different surveys, social media is responsible for attracting customers on a global scale and increasing business worth, among other positive factors (Bellamkonda 2012, par. 2 ).
Social media as a business
A recent trend of note is the formation of companies that are run using the internet. As an illustration, the social media phenomenon, Facebook, has transformed from a social network to a public corporation, with its Initial Public Offering doing very well in the first few days of trading.
Marketing methods
Social media as a marketing tool is almost unrivalled because of its ability to reach a universal audience at a click of a button. Users share information about a product with friends. It is an ideal tool in this regard, since it is not only effective, but cheap and easy to use. On the flip side, this also means that negative information about a product or company will spread with the same speed and efficacy reducing sales.
Non-adoption
Those businesses that are keen about the use of social media to augment their business operations have been successful. However, those that do not adopt such tools or cannot successfully use them have not been as successful. This is especially true for small businesses where those organizations that cannot afford to advertise on social media platforms become less competitive and lose potential customers to those effectively using social media.
Foreign investment
The connectivity that globalization of social media has accomplished has become a conduit for the dissemination of information. Such sharing has presented opportunities that have hitherto been unavailable to individuals (Curran 2002, p. 218).
These opportunities have empowered many communities through the availability of employment opportunities and the improved infrastructure, especially in developing countries where multinational corporations have relocated their operations in a bid to maximize their profits by taking advantage of the cheap available labour and the low costs of doing business.
With the main base of operations still situated in the mother country, communication with the operations in foreign lands is maintained using many forms of media, including social media.
Job seekers
Globalization of social media has become a significant factor in networking for those seeking jobs and has opened opportunities for employers to outsource their work, providing employment opportunities to those who may be disadvantaged geographically.
As well, search for work using traditional means in today’s market is an elusive venture, as most firms, realizing the advantages of social media, now recruit employees online. And, while social networking provides a great way to network, make friends and share information, some information that people reveal about themselves on social networking sites is very personal.
The privacy terms provided by use licences may dispel their fears, but care should be taken when posting information that may not be welcome by all since some practices by employers have raised ethical concerns about job recruitment through social media sites.
These concerns include racism, gender discrimination, sexual discrimination and religious intolerance based on information found during or after the hiring process. What employers forget is that employment laws still apply in the context of social media just as they apply to any other method used for recruitment (Jan 2009, p. 67).
Literacy and artistic talent
Social media can be used to improve literacy and fine-tune artistic talents through the features available on social networking sites that enable quick and easy upload of self-made multimedia productions and materials.
Skill building
Social media sites are filled with new advancements that are user friendly. When students spend a lot of time on social networking sites, they become tech savvy and the skills they learn from these sites will benefit them in their future endeavours.
Study methods. The rate at which students gather and share information on social sites improves their productivity and instils team-building spirit within them. However, too much time spent on social networking sites can result in the development of poor face-to-face interpersonal skills and low self-esteem (Kim et al 2011, p. 370). Face-to-face communication assists a student to develop the use of body language and other non-verbal cues to communicate effectively. Students who lack these skills will have less confidence in themselves.
In addition, student study time is consumed by browsing social sites to chat with friends and update their pages due to the ease with which these sites are accessed and the availability of technology. Social media has also been accused of encouraging moral decadence because children can easily access pornographic sites and other uncensored materials and may try to ape what they see.
Student research
One major area in which social media has made a negative impact is academia. Students resort to regurgitation of information that is easily accessed through Facebook, Twitter, blogs and other forums without taking time to establish the veracity and authenticity of their sources (Jones 1995, p. 66).
The ability to research and retain information is compromised as students come to rely on copying and pasting information. This also encourages plagiarism, a form of academic cheating (Jones 1995, p. 66).
Social media has been used for political gossip, conversations, debates and analyses, especially during election periods. Political activists and analysts have paid keen attention to these hotspots of political innuendo, especially during crises. In effort to make the incumbent look bad the analysts have tended to exaggerate situations for political expediency.
On a positive note, social media has been used by some politicians as platforms for launching their campaigns and as tools for wooing voters as well as instruments for gauging political strength. For instance, in 2008, Barrack Obama embraced social media as a tool to source funds and as a strategic instrument for wooing young American voters (Curtis 2011, p. 64).
Social media have been used by politicians to strengthen and reinforce the political beliefs of their fans and supporters. This make their campaigns very effective compared to mass media. This is because it is easy to narrow down to the targeted audience for maximum impact. A case that clearly demonstrates the impact of globalization of social media is the Arab spring revolutions that erupted across the Middle East and North Africa (Bellamkonda 2012, par 2).
During the Egyptian revolution, after the government shut down all non-government broadcasting stations, communication was facilitated by social media sites such as Facebook and Twitter, among others. Social media provided a means by which aggrieved Egyptians could voice their disappointment and to show the world the atrocities committed against them by the Mubarak regime.
Despite the positive impact that social media has had in the area of politics to keep the populace informed, it has also been an effective tool used to end dictatorial regimes.
One of biggest impacts that the globalization of social media has had is in connection with mass media. In the past, the collection and distribution of information was solely in the hands of mainstream media. With the rise of social media, this domination of information by mass media has been on the decline (Curran 2002, p. 218).
Domination of information is the propagation of ideology through media. The domination of information by mass media can be likened to the domination of knowledge in the dark ages, when the ruling elite controlled all access to books and education at the expense of masses of illiterate peasants (Curran 2002, p. 222).
From a philosophical perspective, mass media ensured that theirs’ was the dominant ideology. Ideology lasts as long as the interests of the dominant are satisfied. It is the ideas of the prevailing class that are entrenched into the social order (Curran 2002, p. 218).
Mass media has had a cunning way of presenting relevant information so that it is generally accepted by the public. In addition, the information distributed by mass media is intended to suit the vested interests of the elite few. Since the emergence of social media, the marginalized populace has managed to liberate itself from the onslaught of misinformation propagated by mass media (Boyd 2007, p. 218).
In fact, globalization of social media has given the masses a medium for voicing their protests against the domination of the ruling class. At the same time, social media has provided a common, unrestricted platform where both the elite and the subordinate class can freely interact, thus removing the barriers of class and status (Ellison 2007, p.1150).
Humanitarian crises
Social media is an essential tool for observers of humanitarian crises as it provides an unedited view of the situation. Although the benefits of social media cannot be definitively measured, its contributions cannot go unnoticed (Boyd 2007, p. 214). Globalization of social media has brought positive changes in the response to humanitarian crises worldwide. It is now possible to receive first hand communication from afflicted regions.
Social media also provides raw unadulterated footage of the situation on the ground (Ellison, 2007, p.1144). It provides a constructive platform for volunteers to contribute to rescue efforts. Social media can also provide nominal advantages to citizens in times of war by facilitating communication when communication lines have been damaged (Chen 2011, p. 5). Social media has proved to be an effective medium for getting assistance to those facing humanitarian crises.
Cultural influence
Just as globalization facilitates social media, social media facilitates cross-cultural interaction. Culture is influenced through contact with other cultures (Allwood 2000, p. 9). In this regard, social media cannot be discussed independently of other forms of media like mass media. In the same way that mass media has a strong influence on global culture, social media also does, and it may be more effective since information transferred by social media is transmitted practically in real time and is first hand.
Until now, people have been forced to operate on two planes: the local and the global. There is a need to encourage healthy cross-cultural interactions through social media without compromising self-identity that can only be established through one’s local culture (Croucher 2011, p. 259).
The interaction platform offered by social media is a breeding ground for cross-fertilization of cultures. Each culture picks what it considers good from other cultures. This has had positive effects on democracy and human rights, where the international community has advocated for universalism.
However, there have been some negative effects in countries like China, which struggles to protect its national culture from what it considers to be the bad influence of the global community (Zhang 2006, p. 113).
When the negative effects of interacting at the global level through social media are felt at the municipal, familial and individual level, the effect has always been that global culture has eroded the culture of the person involved (Kim et al 2011, p. 364). However, influence works both ways and other cultures can influence the global culture (Hall 1976, p. 14).
Personal dialogue
Globalization and technology have met in social media to render time and space irrelevant and ensure that people of different parts of the world can meet and discuss the most intimate issues (Morris 2002, p. 283). Consequently, the security of the individual has been compromised when personal information is given to a total stranger; an action that may have disastrous results, as has been illustrated above.
Social connection
While social media provides many ways to virtually connect with the world, it ironically has the effect of eroding the social skills of an individual who begins to rely on it exclusively. When one spends the majority of time with virtual friends, there is the risk of losing the skills to interact with friends and family in the community (Englehardt 2001, p. 205).
Terrorism and crime
Social media has been used to advance the activity of international crimes and global terrorism. Through these sites, the masterminds of terrorist attacks have been able to easily influence individuals of impressionable minds to join their groups and do their bidding. This has affected the security of individuals, forcing governments back to the drawing board to strategize how to provide security in the modern world (Ellison 2007, p. 1149).
Legal issues
Legal challenges also arise from the use of materials that are shared online through the social sites. Data protection, intellectual property infringement and defamation are legal issues that challenge social media platform owners. Due to its virtual nature, it is easy for users to ignore relevant laws, assuming they do not.
The virtual nature of social media gives a false sense of security, which is not the reality (Jones 1995, p. 68). This trend is encouraged since laws relating to social media are developing slowly compared with the pace of technological development and growth of social media.
Another challenge is controlling the content of social media. What one culture considers offensive and inappropriate could be acceptable to another; or what the global culture finds very interesting might make an individual uncomfortable (White 1980, p. 3). The advent of mobile phones makes the situation more challenging, because while it is possible to control computer networks, it is virtually impossible to control transmission by mobile phones.
Computer and data security
Finally, threats of malware, worms and phishing are real and cannot be under-rated. Social media users need to appreciate the dangers involved with sharing personal information in these platforms. They must first address privacy and security concerns before opening up to their virtual friends.
As has been demonstrated, social media has permeated many aspects of life. For one to maximize the benefits of social media on the global plane, participation in social media workshops is critical, as is attending seminars that offer training on security, networking strategies and how to increase visibility globally.
This paper has reviewed the effects of globalization on social media. It has also highlighted the impact that social media has on different aspects of daily life, including politics, economics, culture, moral values, lifestyle, employment and communication.
The paper has established that there are both positive and negative effects of globalization on social media, presenting a variety of challenges for us all.
Allwood, J & Schroeder, R 2000, ‘Intercultural Communication in a Virtual Environment’, Intercultural Communication , vol. 4, pp. 1-15.
Bellamkonda, S 2012, ‘Small Business See Business Increase through Mobile Marketing’, Washington Business Journal, vol. 2, pp. 23-45.
Boyd, D & Ellison, N 2007, ‘Social Network Sites: Definition, History, and Scholarship’, Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 210-230.
Chan, J.M 1994, ‘Media Internationalization in China’, Journal of Communication , vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 72-80.
Chen, G 2005, ‘A Model of Global Communication Competence’, China Media Research, vol. 1, pp. 3-11.
Croucher, S 2011, ‘Social Networking and Cultural Adaptation: A Theoretical Model’, Journal of International and Intercultural Communication, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 259-264.
Curran, JD 2002, Media and Power , Academic Press, New York.
Ellison, N, Steinfield, C & Lampe, C 2007, ‘The Benefits of Facebook “Friends”: Social Capital and College Students’ Use of Online Social Network Sites’, Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, vol. 12, pp. 1143-1168.
Englehardt, E (ed.) 2001, Ethical Issues in Interpersonal Communication: Friends, Intimates, Sexuality, Marriage, and Family , Harcourt College Publishers, Fort Worth.
Flew, T 2007, Understanding Global Media , Palgrave Macmillan, New York.
Giddens, A 1990, The Consequences of Modernity, Polity, Cambridge.
Hall, E 1976, Beyond Culture , Doubleday, New York.
Jan, M 2009, ‘Globalization of Media: Key Issues and Dimensions’, European Journal of Scientific Research , vol. 29, no.1, pp. 66-75. Web.
Jones, S (ed.) 1995, Cyber-society: Computer-mediated Communication and Community , Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Kim, Y, Sohn, D & Choi, S 2011, ‘Cultural Difference in Motivations for Using Social Network Sites: A comparative study of American and Korean College Students’, Computers in Human Behavior, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 365-372.
Liebes, T & Katz, E 1990, The Export of Meaning: Cross-Cultural Readings of Dallas , Oxford University Press, New York.
Morris, N 2002, ‘The Myth of Unadulterated Culture Meets the Threat of Imported Media’, Media, Culture and Society , vol. 24 no. 2 pp. 278-289. Web.
Robertson, R 1992, Globalization: Social Theory and Global Culture , Sage, London.
Stevenson, N 1999, The Transformation of the Media: Globalization, Morality and Ethics , Longman, New York.
Traber, M (ed.) 1986, The Myth of the Information Revolution: Social and Ethical Implications of Communication Technologies , Sage, London.
White, R, 1980, ‘The Search for Values in Media Ethics’, Communication Research Trends , vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-6.
Zhang, Z 2006, Globalization and the National Cultural Security , Chinese University of Communications, Beijing.
- Social Media Crises
- Intimacy and Sexuality Behaviors in Social Media
- Facebook: Change and Innovation
- Facebook's Marketing and Communication Patterns
- Facebook's Negative and Positive Effects on Children
- Scandal in Burson-Marstelle Firm
- Media and Technologies as Agents of Socialization
- Social Networking Tools in Business
- Social Media Issues Relating To Race and Religion
- Impacts of Social Media on Lives
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, May 16). Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-globalization-on-social-media-essay/
"Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay." IvyPanda , 16 May 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-globalization-on-social-media-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay'. 16 May.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay." May 16, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-globalization-on-social-media-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay." May 16, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-globalization-on-social-media-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Social Media and Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects Essay." May 16, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-globalization-on-social-media-essay/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Globalization - Education and Management Agendas
The Impact of Globalization on Cross-Cultural Communication
Submitted: 21 December 2011 Published: 17 August 2012
DOI: 10.5772/45816
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Globalization - Education and Management Agendas
Edited by Hector Cuadra-Montiel
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
27,848 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Overall attention for this chapters
Author Information
Lowell c. matthews.
- Southern New Hampshire University, Manchester, NH, USA
Bharat S. Thakkar
- PREMGroup, Inc. and Faculty, College of Business, Walden University, USA
*Address all correspondence to:
1. Introduction
In a global environment the ability to communicate effectively can be a challenge. Even when both parties speak the same language there can still be misunderstandings due to ethic and cultural differences. Over the last decade, there have been countless examples from the business sector that demonstrate how poor communication can lead to poor organizational performance. Understanding the impact of globalization on cross-culture communication is imperative for organizations seeking to create a competitive advantage in the global market. Recent economic challenges further highlight the need for organizations to develop the internal communication capacity necessary to control and monitor external threats. As society becomes more globally connected the ability to communicate across cultural boundaries has gained increasing prominence. Global businesses must understand how to communicate with employees and customers from different cultures in order to fulfill the organization’s mission and build value for stakeholders. The use of technology has had a profound impact on how businesses communicate globally and market their products and services. However, with the advancements in technology organizations must still be cognoscente of the culture nuisances that can potentially present obstacles in trying to increase profits and market share. According to Genevieve Hilton, “cultural proficiency doesn't mean memorizing every cultural nuance of every market. It's knowing when to listen, when to ask for help, and when—finally—to speak” [ 1 ].
For companies involved in global business operations the relationship of managers and subordinates in multinational firms is important. In research conducted by Thomas and Ravlin [ 2 ] it was found that participants to whom nationality was more important indicated lower perceptions of similarity with the manager, lower intentions to associate, and lower perceptions of managerial effectiveness. The results of the study strongly indicate that teaching members of different cultures to behave like each other is an ineffective approach to improving intercultural interactions in business settings [ 2 ]. Focus should be placed on using individual differences to create innovation. Training and development of individuals involved in intercultural interactions should involve more than simply promoting cultural adaptation
Communication is vital for businesses to effectively explain how their products and services differ from their competitors. Companies that are successfully able to communicate cross-culturally have a competitive advantage because they can devote more time and resources to conducting business and less time on internal and external communication issues [ 1 ]. Communication is necessary for individuals to express themselves and to fulfill basic needs. The same holds true for businesses, governments, and countries. Without the ability to communicate and understand each other, there would be chaos.Communication that is based on cultural understanding is more apt to prevent misunderstandings caused by personal biases and prejudices.
To illustrate the importance of communication on building relationships globally consider the example of the United States and South Korea. The relationship between these two countries is one built upon a rich history. In 1884, the United States government became the first foreign entity to purchase property in Korea [ 3 ]. Before this time no foreigner was permitted to live inside Seoul. Despite significant cultural differences, South Korea and the United States have been able to develop a communication process that other countries seek to replicate. The American Chamber of Commerce in Korea was established in 1953 with the chief purpose to promote the advancement of trade and commerce between Korea and the United States. Article II of the Chamber’s constitution outlines the following six objectives [ 4 ]:
To promote the development of commerce between the United States of America and Korea;
To promote measure calculated to benefit and protect the interests in Korea of member companies and citizens of the United States;
To represent, express, and give effect to the opinions of the Chamber business community of the United States regarding trade, commerce, finance, industry, and related questions;
To collect, evaluate, and disseminate among its members statistical and other information concerning commerce or other undertakings of interest to them;
To associate and cooperate with other organizations sharing mutual interests;
To do any and all other things incidental or related to the attainment of the above objectives.
When countries are able to exchange ideas and communicate in an open society everyone benefits. Kathleen Stephens, U.S. Ambassador to the Republic of Korea, summed it up by saying, “we must use our shared interests and values to compliment and transform each other’s growth” [ 5 ]. The main purpose of this study is to develop a cross-cultural communication model that can be applied by companies that communicate with employees from different cultures. The aim is to identify the steps that leaders of organizations competing in a global environment should consider when communicating to different cultures. This study uses a group a college students participating in the 2 nd Korea America Student Conference (KASC) as the main research source for creating the model. KASC is supported by the International Student Conferences, a non-profit organization located in Washington, D.C., which sponsors student-run educational and cultural exchange programs for university students from the United States, Japan, and Korea [ 6 ]. The researchers used a mix of qualitative and quantitative research methodologies to generate the model. A comparative literature review is conducted and organizational examples of Samsung and Hyundai are considered to demonstrate the impact of globalization on cross-culture communication practices. The study also highlights the action research methodology that was employed to design the cross-culture communication model. In conclusion, the 4 C’s Global Leadership Model is introduced to demonstrate how organizational leaders can create innovation in a global environment by managing conflict, communication, creativity, and connectivity.

2. Literature review
Research on cross-cultural communication often focuses on understanding how individual differences influence our ability to communicate with others. Since most individuals grow up within a single culture having to interact with others from a different culture or background can represent a challenge [ 7 ]. Exposure to different cultures affects our ability to communicate with others in a way that leads to positive outcomes. Fink, Neyer, and Kölling propose that researchers involved in cross-cultural studies should develop an understanding of the interrelations between cultural dimensions, cultural standards, and personality traits [ 7 ]. This increased awareness helps an individual to manage their own cross-cultural behavior as well as that of others.
Reza Najafbagy refers to co-orientation, the ability to familiarize all aspects of one’s own life in relation to someone of a different culture, as a primary component of intercultural communication [ 8 ]. Individuals that have experienced different cultures are more cognizant of how to alter their communication style so that others understand the information they are trying to transfer. Research conducted by Seak and Enderwick revealed the importance of providing cross-cultural communication and training skills for expatriates assigned to foreign locations in particularly, China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Japan and South Korea [ 9 ]. Now more than ever global organizations must ensure that their employees have the skills required to communicate across cultural boundaries. Cross-cultural communication enhances innovation by allowing for collective problem solving and the open dissemination of information [ 10 ].
Cohen and Levinthal define the term absorptive capacity as an organization’s ability to identify and recognize the value of new external information, absorb it, and implement it into their business operations [ 11 ]. Organizations that understand the importance of external information are better able to use their core competencies to create a competitive advantage. Cross-culture communication enhances an organization’s absorptive capacity because it provides a new of perspective for satisfying the needs of stakeholders.Communication is the life-blood of organizations and must be allowed to flow throughout the entire organization. However, when information flows are random and there is no apparent directive of how to apply the outside knowledge the organization will not benefit [ 11 ]. Productivity decreases when organizational leaders are not able to communicate clear and concise expectations. Furthermore, conflict and tension arises when employees do not understand how their personal efforts contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Culture can affect how we perceive the actions of others. Ambassador Stephens gave the example of a “cheerleading group from North Korea that was participating in a sports competition in South Korea. When the group was heading to the venue one of the cheerleaders yelled for the bus stop. She then proceeds to get off the bus in the rain to get a poster of the North Korean leader that was getting wet. Why? Usually, 70% of Americans would say it was for show. 70% of Koreans would respond that the cheerleader really felt something” [ 5 ]. Our perception of others directly affects how we interpret their behavior and actions. Effective cross-culture communication requires that we base our perceptions on facts and not merely on personal biases and prejudices. The Global Leadership and Organizational Behavior Effectiveness Project (GLOBE) examined cultural values of organizational practices and leadership. The study focuses on identifying cultural influences on leadership and management practices. Some scholars believe that as society becomes more interconnected cultural differences will converge [ 12 ]. Even though some convergence may occur over time, countries will still maintain distinct cultural differences that will transcend technology and external influences.
Successful business leaders must be able to balance organizational objectives with external global challenges. As organizations become more interconnected the role of leaders in managing global teams is becoming increasingly important. Being able to navigate through different cultural nuances is a key skill for global leaders. Rabotin defines cultural intelligence as “the ability to interact with others from diverse cultural backgrounds, being aware of our cultural values that drive our attitudes, behaviors, and beliefs” [ 13 ]. Regardless of their geographic location leaders must be able to communicate across borders in order to create a competitive advantage and achieve results. It is clearly apparent that physical boundaries are increasingly becoming transparent. A global leader must be aware of their personal cultural biases and be willing to change their opinions by learning from those that are different from them [ 13 ].
In research conducted by Choi and Chang it was noted that organizational culture directly impacts the attitudes and motivation of employees towards innovation [ 14 ]. The researchers identified three organizational factors of management support, resource availability, and support for learning as key enablers for innovation [ 14 ]. All three factors were found to be significantly correlated to implementation, however; only management support was determined to be a significant predictor of innovation [ 14 ]. This research supports the conclusion that when employees are fully engaged in the process of innovation success is more likely to be achieved. Organizations must have in place procedures that encourage innovation throughout the entire company. Every employee must feel vested in the company and continually seeking ways to improve processes.
3. Methodology
A qualitative and quantitative research strategy consisting of group observations, interviews, and surveys were used to gather information. These methods are most appropriate because of the complexity involved in studying culture and communication from an individual perspective. By using these methods the researchers were able to ascertain underlying factors that are relevant to understanding the affects of culture on communication when two different groups interact with each other.
Participants were undergraduate and graduate students from South Korea and the United States selected to participate in the 2 nd Korea America Student Conference (KASC). Selection to KASC is based on a competitive process. Participation in the study was completely voluntary and students were asked to complete a consent form. A total of 46 students attended KASC and 65% were female. 52% of the students resided in South Korea and 48% in the United States. Interestingly, 73% of all the students identified Korean as part of their ethnicity. 91% of the students were 19 to 23 years of age.
The researchers focused on collecting data from participants to assist in the development of a cross-cultural communication model. The researcher addressed the differences and similarities in communication strategies and the affect on building relationships. Previous research on culture has applied a field-based approach that allows for the exchange of information from multiple sources. The researchers followed a similar structure when participating in KASC over a two-week period.
The role of the researchers was that of consultants that sought to serve as a bridge between the participants and the administrators of the conference. It was important for the researcher to develop a level of trust with the participants quickly. To accomplish this, the researchers assisted staff with administrative tasks during the conference and shared in activities with the participants. The researchers used current programs established by KASC to expand opportunities to exchange information. For example, the researcher attended lectures, group discussions, and roundtable sessions.
The topics discussed during interviews included: a) reasons for participating in KASC, b) individual experiences and interactions with different cultures, c) reactions to changes that occurred during the conference, and d) discussion of how culture affects the communication between American and Korean students. During group observations the researchers focused on key words and phrases that were used by the students and categorized them according to relevant themes. Based on the words and phrases a concept map was created that helped to identify the predictors used in the study.
Five cultural measurements of acceptance, conflict, individualism, risk, and sharing were used to predict the country of residence. Table 1 defines the variables used in the study. The country of residence index was selected as the dependent variable because it is directly affected by culture.
Rigor and validity were addressed by continuously redefining the key issues identified by participants. Participant feedback was vital to this study and was used to form and shape the cross-cultural communication model. The survey that was developed for this study consisted of 23 items that were rated on five point Likert scale with 1=strongly disagree to 5=strongly agree. Each of the items assessed one of the cultural measurements of acceptance, conflict, individualism, risk, or sharing.
Variables in Cross-Cultural Communication Study
A multiple regression analysis was conducted to evaluate how well the five independent variables for culture predict the country of residence. The linear combination of culture measures was significantly related to the country of residence index, F (5, 17) = 3.57, p <.01. The sample multiple correlation coefficient was.71, indicating that approximately 51% of the variance of the country of residence index in the sample can be accounted for by the linear combination of culture measures.
Model Summary
The partial regression plots for conflict and sharing exhibit the best correlations for predicting the country of residence index. Table 3 presents indices to indicate the relative strength of the individual predictors. As expected all of the bivariate correlations between the country of residence index were positive.
The Bivariate and Partial Correlations of the Predictors with the Country of Residence Index
5. Cross-cultural communication model
The purpose of communication is to transfer ideas and knowledge from one entity to the other. The first step in communication is input; someone must say something that is received by someone else. The communication loop is successful when the receiver demonstrates that he or she understands what was being communicated. From an organizational perspective there are many barriers than can impede the flow of communication. These barriers include culture, technology, language, workforce, and environment. For the purpose of this model culture refers to the traditions and customs that are prevalent in the country where each company is located. These traditions and customs influence policies and procedures implemented by businesses. Technology is simply the use of mediums such as email, Internet, text messaging, and cell phones to communicate. When a company does not have experience using a particular technological medium to communicate it may rely on older methods that the other company views as inadequate. Language is what is spoken in the country where the company is located. If the languages of the two companies are different, then one company must learn the other’s language or a new language must be created. Workforce refers to the internal structure of the company, including employees, managers, and organizational leaders. Environment refers to the external forces that affect the company. For example, the economy can have an adverse impact on an organization and present an obstacle to cross-culture communication.
As illustrated in Figure 1 , when these barriers are eliminated companies are able to experience innovation, reduced conflict, and better dissemination of information. J. Ku-Hyun (personal communication, July 20, 2009) stated “to be successful as a global corporation communication is critical.” Without communication organizations will cease to be. The challenge for organizations that must communicate cross-culturally is to ensure that their message is understood the way that it was intended. When communication barriers are not removed it is easy to make assumptions about what is being communicated. Our assumptions of what we thought was being communicated can be very different from the original message. Communication takes effort, it is much easier to sit back and simply assume what we think others are trying to tell us. To actively engage in communication takes time and energy. Organizations must be willing to invest the resources needed to support cross-culture communication.
Successful cross-cultural communication creates a dialogue, a continuous transfer of information. This exchange of information addresses our assumptions and clarifies points we do not understand. It also provides the opportunity for us to ask questions and confirm the information that was received. Having a dialogue reduces conflict because cultural misunderstandings can be dealt with when they arise. The dialogue only occurs when both parties agree to share information and ensure that the transfer of information is not blocked.

Cross-Culture Communication Model
6. Samsung and Hyundai
To illustrate how companies can utilize the cross-culture communication model to improve business practices consider the examples of Samsung and Hyundai. Samsung is unique because of its focus on human resources and risk taking initiatives. The company was founded in 1938 and is the world’s largest conglomerate. Samsung is recognized as a global industry leader because of its inner capacity to take advantage of distinct initiatives (J. Ku-Hyun, personal communication, July 20, 2009). It hires a small percentage of non-Koreans inside Korea but employs a higher percentage off non-Koreans outside of Korea. The culture of the organization is very family centric. Decisions occur in a collective atmosphere that allows for communication at all levels of the organization. However, even when decisions are clearly communicated throughout the organization employees may not always show support.
The workforce can represent a barrier to cross-cultural communication when employees feel they are not valued. This presented an issue at Samsung. The expectation was that you stayed at job until your assignment was completed. However, with the increase of younger employees entering the workforce who had different expectations, Samsung had to make a change. Management made the decision to change the workday from five-to-nine to seven-to-four [ 15 ]. The reason for Samsung’s change was to get employees to be more team oriented and more productive. Changing the hours of the workday required employees to work together and it also required managers and supervisors to have a more active role in completing daily tasks. The seven-to-four schedule was a cultural shift that was instigated by new employees entering the company with a different outlook towards work and personal time. Prior to the change, employees were expected to stay on the job until it was completed. With the change the office closed at four and everything stopped. Now employees have to proactively plan their workday in order to ensure that everything is accomplished in a timely fashion.
Samsung has been able to become a global leader because of its commitment to the development of technological capabilities [ 16 ]. Management’s objective is to “develop technology capabilities for value creation in diverse business areas” that will ultimately support growth in global competition [ 16 ]. The focus on innovation requires the sharing of business practices and technology throughout the organization. Samsung must communicate with employees and customers simultaneously to ensure that company objectives are met.
J. Ku-Hyun (personal communication, July 20, 2009) reports that Samsung’s competitive advantages include 1) commitment to work that is translated into speed advantages, 2) highly skilled engineers and technicians, and 3) management talent and experience. Samsung has used these competitive advantages to enhance its relationship with customers and expand globally.
Hyundai Motor Company was formed in 1967 and has established itself as company that focuses on quality improvement and innovation [ 17 ]. From the small beginning in Seoul, Korea the company has now expanded to more than ten countries including the United States, Canada, India, China, Turkey, Russia, Malaysia, Sudan, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, and Japan [ 17 ]. For this expansion to take place requires effective communication that is able to overcome cultural barriers and accomplish global management initiatives. Research conducted by Wright, Suh, and Leggett revealed that Hyundai’s achievement at globalization depended upon its ability to expand international sales as it gained experience in international markets [ 18 ]. The move from domestic to global production means Hyundai must operate in “unfamiliar and uncertain economic and cultural contexts” [ 18 ].
Over the years Hyundai has learned valuable lessons on the importance of knowing and valuing the needs of its customers. In the early 1990s, Hyundai experienced problems when trying to expand production to Canada. The primary issue was that the company did not adapt the design of the Sonata for North American customers [ 18 ]. Consequently, the company lost market share to Toyota’s Camry and Honda’s Accord. Another important lesson was learned when Hyundai made the decision to start production in Turkey because of the lower cost for workers. Because of the lower wages management decided to use more hand-operated technology instead of the automated manufacturing processes utilized in its domestic plants. As a result, the production rate of the Turkish plant was 25% lower than that in Korea [ 18 ]. From these experiences Hyundai learned the importance of researching the culture of a country before making profound business decisions. Cross-culture communication involves adapting organizational policies to fit the context of where business transactions will occur.
Key to Hyundai’s success is its corporate philosophy that places the needs of customers as top priority in all business areas. This customer-oriented management style requires organizational leaders to be receptive to new ideas and to think outside the box. To encourage employees to expand their cultural awareness the company encourages three-month assignments to its overseas sites. For example, when the company was building a site in Alabama it allowed employees to visit and study the culture [ 19 ].The company promotes an employee backpack travel program around the globe where teams of three design their cultural experience. The teams compete for a company sponsorship of 15-day expeditions by writing what they hope to learn [ 19 ]. More than 47 teams have traveled to 70 countries, including Peru, Turkey, and Greece [ 19 ]. Employees that participate bring back what they learn and share it with their colleagues.
“Hyundai Motor Company is strengthening its position as a global brand, establishing local production systems on a global scale and supplying automobiles that meet the needs and tastes of customers in each specific region” [ 17 ]. During a visit to the Asan Plant located in Chungchungnam-do, Korea, it was very apparent of how the company is being innovative. The plant has a production capacity of 300,000 units and utilizes the latest in robotic technology to assemble vehicles (Tour Guide, personal communication, July 27, 2009). One unit is produced every 57 seconds and 100% of all the welding is completely automated. The Asan plant has 34,000 employees; the average annual salary is $50,000. The plant operates two ten-hour shifts and provides numerous incentives for employees that are innovative on the job.
7. Conclusion
The researchers proposed attending the 2nd Korea-America Student Conference in order to develop a relationship with participants that have a vested interest in global issues and to define the criteria for the proposed cross-culture communication model by using various qualitative methods. These objectives were accomplished and much insight gained into understanding how culture affects communication.
Samsung and Hyundai are only two examples of organizations that are effectively communicating cross-culturally. Both organizations have been able to learn from their past mistakes and create strategies that support their growth in the global market. The sharing of information makes it possible for other organizations to also benefit from the mistakes made by these organizations.
During one of the group observations a Korean participant stated, “A smile is a basic tool of communication” (personal communication, July 16, 2009). How true it is that a simple smile can break down communication barriers and build bridges of understanding. Cross-culture communication is not easy, especially when we are unfamiliar with the receiver of the information. Organizational leaders that have to communicate cross-culturally can use the following steps:
Develop clear and concise expectations for how the organization will accomplish its mission;
Ensure that employees understand their role in the organization;
Be willing to invest time to communicate;
Remember that communication is a two-way process, listen before you speak.
“Many misunderstanding have occurred, not only because of mistakes in the usage of words or expressions, but also because of the lack of goodwill and cultural knowledge” [ 8 ]. Mistakes are a normal part life and at times if we are not careful our mistakes can have lasting consequences. “We can make mistakes as long as we can correct mistakes. We can get feedback from the global market” [ 10 ]. The cross-culture communication model developed from this study provides a mechanism for obtaining feedback from the global market. The model identifies the barriers to cross-culture communication and summarizes the outcomes that can be achieved when these barriers are tackled.
The results of study verified that the five independent variables of acceptance, conflict, individualism, risk, and sharing could be used to predict country residence. A limitation to this study was the small sample size that used. In order to validate the validity and reliability of the study a larger sample size should be used in future studies. The participants of the study were also aware of the need to increase cultural awareness and displayed a desire to gain a deeper understanding of American and Korean relations. The study adds to the current body of knowledge on cross-culture communication by demonstrating the importance of culture in business settings.
Organizational cross-functionality or connectivity is essential to innovation because it brings together a diverse group of people from different functional backgrounds [ 20 ]. Management must take steps to ensure that cross-functionality does not create conflict and hinder communication within the team [ 20 ]. To effectively generate innovation the level of expertise and individual skill set of each team member must be ascertained. The innovation process is supported when members share a common vision and goal. Research indicates that cross-functional teams are more effective at new produce development that is valued by the customer [ 21 ].
Leadership is the foundation to cross-functionality because it provides the oversight and direction necessary for it to work. Leaders that are innovators are receptive to change and value feedback from those around them. They recognize that they cannot be successful unless those around them are successful. For innovative organizations it is necessary for management to develop innovative leaders. This is done by having in place recruitment strategies that target successful applicants that possess the skills necessary to the organization to the next level [ 22 ]. There should also be in place a well-developed talent-management process that identifies innovators, connects them to the mission of the organization, and provides the necessary internal resources for them to be successful.

The 4 C’s Global Leadership Model
A comparison of leadership strategies between Samsung and Hyundai provides the basis for developing the 4 C’s Global Leadership Model that can be employed by organizations to make certain that they have the right person for the job. The model consists of four key factors: communication, conflict, creativity, and connectivity. Being aware of what types of individuals make good global leaders allows the organization to develop HR policies to support recruitment and succession. By creating a pipeline of capable global leaders the organization is able to sustain innovation and change.
Leaders are the main link responsible for harnessing the ideas of employees to create innovation. They must also assess the development of their competitors and the needs of customers. Bringing together individuals from different cultural backgrounds will lead to conflict; however, this does not have to be perceived as a negative. The challenge for global leaders is to use the conflict as a benefit for the organization. Gehani and Gehani define conflict as simply the result of natural differences that occur between people from different backgrounds [ 23 ]. Different ideas and views lead to innovation and new products and services. From this perspective leaders should encourage healthy conflict. “Conflict between diverse groups of people can be used to drive the growth of their organizations” [ 23 ]. If there were no conflict to spark discussion there would be no innovation.
Communication helps to moderate the relationship between conflict and innovation. This fact is furthermore impacted by the complexity of competing in global environment. Leaders must be aware of the communication styles that are needed when working with multicultural teams. The use of the email, conference calls, and other technological innovations to communicate need to be addressed to ensure that all members are able to participate fully. When members feel they are not able to communicate openly innovation is hindered and the organization suffers.
As global competition continues to increase, successful organizations must evolve to meet the changing needs of consumers. Innovation provides the opportunity for organizations to think outside the box and “produce better product, faster, cheaper and more efficiently than competitors [ 24 ]. Creativity is directly linked to communication and innovation. Increased attention on innovation has caused organizational leaders to develop systems to manage the process and support the efforts of employees. According to Dooley & O’Sullivan being able to identify the correct process for implementing innovation will directly impact the success [ 24 ]. It is easier to implement innovation when the culture of the organization allows for employee feedback, planning, and evaluation.
Employees play a vital role in innovation. In research conducted by Barnett and Storey it was found that there was a strong connection between learning and innovation in organizations [ 25 ]. The researchers studied 220 employees at a manufacturing company, Tensator, located in the United Kingdom. Key to Tensator’s success is their ability to integrate succession planning with sustaining innovation [ 25 ]. Instead of focusing solely on keeping top management positions filled, the organization seeks to keep the pipeline of skilled laborers in amble supply to support innovation. Tensator follows a growth strategy that centers on “grow-your-own” [ 25 ]. This strategy requires the company to continually provide learning and development opportunities for employees to ensure that they remain at the top of their game.
Microsoft is applying a holistic approach to innovation in seeking to compete with Yahoo and Google in the development of search engines [ 26 ]. Management is aware they must do more than simply try to catch up with their competitors; they must redesign the way that search engines are viewed and utilized. The holistic approach is further supported by Porter in work done with organizations to help them improve their supply chains [ 27 ]. Organizations that use a holistic approach are able to obtain a broader view of how they fit into the global market. Instead of focusing on small segments of their business operations, attention is given to the entire process. This allows for the organization to implement innovation that will create value for customers.
Connectivity is defined as the ability to orchestrate organizational networks to move in the same direction in order to accomplish the company’s mission. Employees must feel contacted to the organization and understand how their individual effort contributes to the bottom line. Global leaders must look for opportunities to connect everyone within the organization to the overall goals and objectives. When employees understand the big picture and the direction the organization is taking innovation and change are supported.
The 4 C’s Global Leadership Model is designed to provide a basis for organizational leaders to use in mapping out strategies for working globally with multicultural teams. The business environment is continually evolving and global leaders must persistently develop new organization strategies to meet global challenges. Although, Samsung and Hyundai both compete in different industries there are parallels that can be gleamed from how they communicate and inspire innovation from their employees. The Cross-Culture Communication Model and 4 C’s Global Leadership Model are tools designed to assist organizational leaders to compete in the ever-changing global environment.
The core aspects of global leadership critical to leading innovation and change are vision, communication, and responsibility. In 2008 a group of scholars and business leaders identified twenty-five factors that are important for managers in implementing innovation [ 28 ]. Key among them was that management must have a clear vision for the organization. The organizational vision provides a roadmap for employees by defining what the organization hopes to accomplish.Communication is important because it allows for the exchange and refinement of ideas. Effective communication requires that organizations not become bogged down with hierarchal thinking that can typically slow down the communication process. Large organizations must operate like small organizations and be able to respond quickly to organizational and market changes [ 28 ].
Successful organizations must focus on goals that are socially responsible [ 28 ]. Innovation is not just creating the coolest new gadget but it is creating the coolest new gadget that serves the environment in a sustainable manner. As organizations become more global the focus on corporate social responsibility increases. Organizations can no longer operate within a silo. The actions of one organization can affect many others. According to Westlund it is no longer sufficient for organizations only to make a profit and comply with the law [ 29 ]. They must also be socially responsible and give something back to the global community that they serve.
- 3. Habbi House. The American Embassy Residence Seoul, Korea. 2009
- 4. American Chamber of Commerce in Korea. AMCHAM Korea’s Constitution. http://amchamkorea.org/about/constitution.jsp accessed 15 August 2009
- 6. ICS. International Student Conferences. http://www.iscdc.org/ (accessed 17 August 2009).
- 10. Lim, Wonhyuk. Korea export-oriented industrialization. Lectured presented at Korea Development Institute. Seoul, South Korea. 2009
- 15. Lee, H., Lee, J., Lee, J., Choi, C. Time to change, time for change: How was time used to change a global company? Academy of Management Proceedings, August 2005.
- 17. Hyundai Motor Company. Hyundai Motor Company PR Brochure 2008 1 60
© 2012 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Globalization.
Published: 17 August 2012
By Douglas E. Mitchell and Selin Yildiz Nielsen
8730 downloads
By James Campbell
2828 downloads
By Verónica López, Romina Madrid and Vicente Sisto
2115 downloads
IntechOpen Author/Editor? To get your discount, log in .
Discounts available on purchase of multiple copies. View rates
Local taxes (VAT) are calculated in later steps, if applicable.
Support: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 23 March 2022
Communication competencies, culture and SDGs: effective processes to cross-cultural communication
- Stella Aririguzoh 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 9 , Article number: 96 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
39k Accesses
36 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Business and management
- Cultural and media studies
Globalization has made it necessary for people from different cultures and nations to interact and work together. Effective cross-cultural communication seeks to change how messages are packaged and sent to people from diverse cultural backgrounds. Cross-cultural communication competencies make it crucial to appreciate and respect noticeable cultural differences between senders and receivers of information, especially in line with the United Nations’ (UN) recognition of culture as an agent of sustainable development. Miscommunication and misunderstanding can result from poorly encrypted messages that the receiver may not correctly interpret. A culture-literate communicator can reduce miscommunication arising from a low appreciation of cultural differences so that a clement communication environment is created and sustained. This paper looks at the United Nations’ recognition of culture and how cultural differences shape interpersonal communication. It then proposes strategies to enhance cross-cultural communication at every communication step. It advocates that for the senders and receivers of messages to improve communication efficiency, they must be culture and media literates.
Similar content being viewed by others

Assessment of the impacts of artificial intelligence (AI) on intercultural communication among postgraduate students in a multicultural university environment
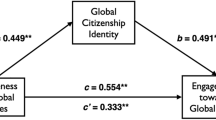
Global citizenship identity mediates the relationship of knowledge, cognitive, and socio-emotional skills with engagement towards global issues
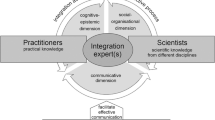
Communication tools and their support for integration in transdisciplinary research projects
Public interest.
The United Nations has recognized culture as a causal agent of sustainability and integrated it into the SDG goals. Culture reinforces the economic, social, and communal fabrics that regulate social cohesion. Communication helps to maintain social order. The message’s sender and the receiver’s culture significantly influence how they communicate and relate with other people outside their tribal communities. Globalization has compelled people from widely divergent cultural backgrounds to work together.
People unconsciously carry their cultural peculiarities and biases into their communication processes. Naturally, there have been miscommunications and misunderstandings because people judge others based on their cultural values. Our cultures influence our behaviour and expectations from other people.
Irrespective of our ethnicities, people want to communicate, understand, appreciate, and be respected by others. Culture literate communicators can help clear some of these challenges, create more tolerant communicators, and contribute to achieving global sustainable goals.
Introduction
The United Nations established 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015 to transform the world by 2030 through simultaneously promoting prosperity and protecting the earth. The global body recognizes that culture directly influences development. Thus, SDG Goal 4.7 promotes “… a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development.” Culture really matters (Seymour, 2007 ). Significantly, cultural cognition influences how people process information from different sources and suggests policies they may support or oppose (Rachlinski, 2021 ). Culture can drive sustainable development (United Nations, 2015 ; De Beukelaer and Freita, 2015 ; Kangas et al., 2017 ; Heckler, 2014 ; Dessein et al., 2015 ; and Hosagrahar, 2017 ).
UNESCO ( 2013 , p.iii ; 2017 , p.16; 2013a , p. 30) unequivocally states that “culture is a driver of development,” an “enabler of sustainable development and essential for achieving the 2030 Agenda” and as “an essential pillar for sustainable development.” These bold declarations have led to the growth of the cultural sector. The culture industry encourages economic growth through cultural tourism, handicraft production, creative industries, agriculture, food, medicine, and fisheries. Culture is learned social values, beliefs, and customs that some people accept and share collectively. It includes all the broad knowledge, beliefs, art, morals, law, customs, and other experiences and habits acquired by man as a member of a particular society. This seems to support Guiso, Paola and Luigi ( 2006 , p. 23) view of culture as “those customary beliefs and values that ethnic, religious, and social groups transmit fairly unchanged from generation to generation.” They assert that there is a causality between culture and economic outcomes. Bokova ( 2010 ) claims that “the links between culture and development are so strong that development cannot dispense with culture” and “that these links cannot be separated.” Culture includes customs and social behaviour. Causadias ( 2020 ) claims that culture is a structure that connects people, places, and practices. Ruane and Todd ( 2004 ) write that these connections are everyday matters like language, rituals, kingship, economic way of life, general lifestyle, and labour division. Field ( 2008 ) notes that even though all cultural identities are historically constructed, they still undergo changes, transformation, and mutation with time. Although Barth ( 1969 ) affirms that ethnicity is not culture, he points out that it helps define a group and its cultural stuff . The shared cultural stuff provides the basis for ethnic enclosure or exclusion.
The cultural identities of all men will never be the same because they come from distinctive social groups. Cultural identification sorts interactions into two compartments: individual or self-identification and identification with other people. Thus, Jenkins ( 2014 ) sees social identity as the interface between similarities and differences, the classification of others, and self-identification. He argues that people would not relate to each other in meaningful ways without it. People relate both as individuals and as members of society. Ethnicity is the “world of personal identity collectively ratified and publicly expressed” and “socially ratified personal identity‟ (Geertz, 1973 , p. 268, 309). However, the future of ethnicity has been questioned because culture is now seen as a commodity. Many tribal communities are packaging some aspects of their cultural inheritances to sell to other people who are not from their communities (Comaroff and Comaroff, 2009 ).
There is a relationship between culture and communication. People show others their identities through communication. Communication uses symbols, for example, words, to send messages to recipients. According to Kurylo ( 2013 ), symbols allow culture to be represented or constructed through verbal and nonverbal communication. Message receivers may come from different cultural backgrounds. They try to create meaning by interpreting the symbols used in communication. Miscommunication and misunderstanding may arise because symbols may not have the same meaning for both the sender and receiver of messages. If these are not efficiently handled, they may lead to stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination. Monaghan ( 2020 ), Zhu ( 2016 ), Holmes ( 2017 ), Merkin ( 2017 ), and Samovar et al. ( 2012 ) observe that inter-cultural communication occurs between people from different cultural groups. It shows how people from different cultural backgrounds can effectively communicate by comparing, contrasting, and examining the consequences of the differences in their communication patterns. However, communicating with others from different cultural backgrounds can be full of challenges, surprises, and re-learning because languages, values, and protocols differ. Barriers, like language and noise, impede communication by distorting, blocking, or altering the meaning.
Communication patterns change from one nation to the next. It is not uncommon, for example, for an American, a Nigerian, a Japanese national, or citizens of other countries to work together on a single project in today’s multi-cultural workplace. These men and women represent different cultural heritages. Martinovski ( 2018 ) remarks that both humans and virtual agents interact in cross-cultural environments and need to correctly behave as demanded by their environment. Possibly too, they may learn how to avoid conflicts and live together. Indeed, García-Carbonell and Rising ( 2006 , p. 2) remark that “as the world becomes more integrated, bridging the gap in cultural conflicts through real communication is increasingly important to people in all realms of society.” Communication is used to co-ordinate the activities in an organization for it to achieve its goals. It is also used to signal and order those involved in the work process.
This paper argues that barriers to cross-cultural communication can be overcome or significantly reduced if the actors in the communication processes become culture literates and competent communicators.
Statement of the problem
The importance of creating and maintaining good communication in human society cannot be overemphasized. Effective communication binds and sustains the community. Cross-cultural communication problems usually arise from confusion caused by misconstruction, misperception, misunderstanding, and misvaluation of messages from different standpoints arising from differences in the cultures of the senders and receivers of messages. Divergences in cultural backgrounds result in miscommunication that negatively limits effective encrypting, transmission, reception, and information decoding. It also hinders effective feedback.
With the rapid spread of communication technologies, no community is completely isolated from the rest of the world. Present-day realities, such as new job opportunities and globalization, compel some people to move far away from their local communities and even their countries of origin to other places where the cultures are different. Globalization minimizes the importance of national borders. The world is no longer seen as a globe of many countries but as a borderless entity (Ohmae, 1999 ) and many markets (Levitt, 1983 ) in different countries with different cultures. As a matter of necessity, people from other countries must communicate.
The United Nations ( 2015 ) recognizes culture’s contribution to sustainable development and promotes local cultures in development programmes to increase local population involvement. Despite the United Nations’ lofty ideals of integrating culture into development, culture has hindered development at different levels. Interventions meant to enhance development are sometimes met with opposition from some people who feel that such programmes are against their own culture.
Gumperz ( 2001 , p. 216) argues that “all communication is intentional and grounded in inferences that depend upon the assumption of mutual good faith. Culturally specific presuppositions play a key role in inferring what is intended.” Cross-border communications reflect the kaleidoscope of the diverse colours of many cultures, meeting, clashing, and fusing. Like Adler ( 1991 , p. 64) observes, “foreigners see, interpret, and evaluate things differently, and consequently act upon them differently.” Diversities in culture shape interpersonal communication. Yet the basic communication process is the same everywhere. It is in these processes that challenges arise. Therefore, this study seeks to examine how each of these steps can be adapted to enhance cross-cultural communication, especially in today’s digitized era of collapsing cultural boundaries. Barriers to cross-cultural communication can be significantly reduced if the actors in the communication processes become culture literates and competent communicators.
Study objectives
The objectives of this study are
To examine United Nations efforts to integrate culture into sustainable development.
To suggest modifications to each communication process step to improve effective cross-cultural communication.
Literature review
Some authors have tried to link culture, communication, and sustainable goals.
The need to know about people’s culture
There are compelling reasons to learn about other people’s cultures.
Cultural literacies: Difficulties in cross-cultural communication can be reduced when senders of messages understand that the world is broader than their ethnocentric circles. It demands that senders of messages know that what they believe may not always be correct when communicating with receivers of these messages who are from different cultures. Logical reasoning will expect increased exposure to different cultures to increase understanding. When people of different groups communicate frequently, it is anticipated that they should understand each other better. This is what Hirsch ( 1987 ) labels as cultural literacy . In the ordinary course of things, common knowledge destroys mutual suspicion and misinterpretation that often generate conflicts.
To protect the earth: It is essential to point out that at “the most global level, the fate of all people, indeed the fate of the earth, depends upon negotiations among representatives of governments with different cultural assumptions and ways of communicating” (Tannen, 1985 , p. 203). If the world is to be protected, it is necessary to understand other peoples’ cultures who live and interact with us at different fronts and in this same world. The world is still our haven. Nevertheless, Vassiliou et al. ( 1972 ) find that increased exposure can increase people’s mutual negative stereotyping. Tannen ( 1985 , p. 211) remarks that stereotypes of ethnic groups partly develop from the poor impressions that people from other cultures have about the natives because they hold different meanings for both parties. Stereotyping is detrimental to cross-cultural communication, and its dismissal is necessary for any successful cross-cultural exchange.
Spin-offs from globalization: Bokova ( 2013 ) observes that globalization transforms all societies and brings culture to the front. She remarks that communities are increasingly growing diverse and yet interconnected. The spin-offs from globalization open great doors for exchanges, mutual enrichment of persons from different cultures, and pictures of new worlds.
The dynamics of cross-cultural communication
Different cultures emphasize different values. The emphasis on one value by one culture may lead to difficulties in cross-cultural communication with another person who does not see that particular value in the same light, for example, timeliness. It is crucial to note Sapir’s ( 1956 , p. 104) insistence that “every cultural pattern and every single act of social behaviour involves communication in either an explicit or implicit sense.” Even though Hofstede ( 2005 , p. 1) comments that “cultural differences are nuisance at best and often a disaster,” UNESCO ( 1998 , 1999 ) recognizes cultural diversity as an “essential factor of development” and an issue that matters. This makes cultural diversity a blessing rather than a disaster. The various shades of cultural values influence how we behave and communicate with others outside our cultural environment. Our ideals and biases also influence communication.
Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner ( 1997 ) developed a culture model with seven dimensions. They are universalism versus particularism (rules versus relationships); individualism versus communitarianism (the individual versus the group); specific versus diffuse (how far people get involved); neutral versus emotional (how people express emotions) ; achievement versus ascription (how people view status); sequential time versus synchronous time (how people manage time); and internal direction versus outer direction (how people relate to their environment). These cultural models signify how people from these areas communicate. People from different backgrounds may have difficulties communicating as their values may be significantly different. A good communicator must take note of this distinctiveness in values because they impact the communication processes. For example, a person who is particular about upholding written rules may not be interested in knowing who the culprit is before administering sanctions. But the other person interested in maintaining a good relationship with others may re-consider this approach.
Hofstede ( 1980 ) identifies five significant values that may influence cross-cultural communication:
Power distance: This is the gap between the most and the least influential members of society. People from different cultures perceive equality in various ways. The social hierarchy or status determines where individuals are placed. Status is conferred by inheritance or by personal achievement. Some cling to societal classification and its hierarchy of power. Others value and cherish the equality of all people. Yet, other cultures see other people as dependents and somehow inferior beings. A king in an African community is seen as far more powerful and important than his servants, who are expected to pay obeisance to him. Most countries in Europe are egalitarian. Arabic and Asian countries are high on the power index.
Individualism versus collectivism: This explains the extent to which members of a particular culture value being seen first, as individuals or as members of a community. As individuals, they are entirely held accountable for their errors. They are also rewarded as individuals for their exploits. However, in some cultures, the wider community is involved. Suppose a person makes an inglorious error. The whole community where that individual comes from shares in it. The same goes if he wins laurels and awards. The individual does not exist primarily for himself. African, Japanese, Indian, and most Asiatic nations follow the collective approach. A Chinese man has his Guanxi or Guanshi. This is his network of influential and significant contacts that smoothen his business and other activities (Yeung and Tung, 1996 ). He succeeds or fails based on his personal relationships. In other words, the basis of business is friendship. This is clear evidence of collectivism. Most people from America and Europe are individualistic. It must be pointed out that personal values mediate both community and individualistic spirit. Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner’s communitarianism vs. individualism appears very similar to this Hofstede’s individualism/collectivism orientation. The information receiver who values his individuality will be offended if he is seen as just a group member or if his negative performance on the job is discussed openly. The message sender who appreciates his subordinates would send personalized messages and expect their feedback.
Uncertainty avoidance: This shows the degree to which a particular culture is uncomfortable with uncertainties and ambiguities. Some cultures avoid or create worries about how much they disclose to other people. A culture with high uncertainty avoidance scores wants to avoid doubts by telling and knowing the absolute truth in everything. For them, everything should be plainly stated. When situations are not like this, they are offended, worried, and intolerant of other people or groups they feel are hiding facts by not being plain enough. Hofstede and Bond ( 1988 ) write that this trait is very peculiar to western Europeans. This means that people from countries like Greece, Turkey, and Spain are very high on uncertainty avoidance. Communication between people with high or low uncertainties may be hindered. Some people may appear rude and uncouth because of their straightforward ways of talking. Some Africans may see some Americans and people from Europe as too wide-mouthed because they feel they do not use discretion in talking. They say things they may prefer to keep silent about and hide from the public’s ears. On the other hand, some Americans may see some Africans as unnecessarily secretive. Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner’s ( 1997 ) universalism/particularism explains why some cultures insist on applying the rule of law no matter who the offender is.
Masculinity/feminity roles : Hofstede ( 2001 ) defines masculinity as society’s preference for success, heroism, assertiveness, and material rewards for success. Conversely, femininity is seen as the preference for co-operation, diffidence, caring for the weak and quality of life. The male-female contradiction affects communication. Females are expected to be meek homemakers that tend and nurture their family members. Like Sweden and Norway, cultures that favour females do not discriminate between the sexes. Japan and Nigeria have cultures that are predominantly masculine in orientation. Competitive and aggressive females are frowned at and seen as social deviants. In the other cultures where females are more favoured, a man may land in court and face public condemnation for domestic violence. Hofstede ( 1998 ) believes that how different cultures see the male/female roles influence how they treat gender, sexuality, and religion.
Long-time orientations: A particular society accepts some degree of long or short associations. Japanese culture scores high in long-term orientation values, commitments, and loyalty. They respect tradition, and therefore, changes in their society take a longer time to happen. Cultures with low long-term orientation do not value tradition much, nor do they go out of their way to nurture long-standing relationships. Literally, changes occur in rapid succession. There appears to be more attachment to the pursuit of immediate self-satisfaction and simple-minded well-being. Baumeister and Wilson ( 1996 , pp. 322–325) say that meaning comes from a sense of purpose, efficacy, value, and a sense of positive self-worth. Thus, if you communicate with somebody with a short-term orientation, you may think that he is too hasty and intemperate, while he may feel that you are too sluggish and not ready to take immediate action.
Hall ( 1983 ) introduces two other factors:
Time usage: Some cultures are monochronic, while others are polychronic. Monochronic cultures are known for doing one thing at a time. Western Europe is monochronic in time orientation, as illustrated by the familiar adage that says, “There is a time and place for everything!” Persons from this cultural background are very punctual and strictly adhere to plans. They are task-oriented. Polychronic cultures schedule multiple tasks simultaneously, even though there may be distractions and interruptions while completing them. Plans may often change at short notice. Such different time management and usage may constrict effective communication. A London business entrepreneur will find it difficult to understand why his business partner from Nigeria may be thirty minutes late for a scheduled meeting. The answer is in their perception of time. Some Nigerians observe what is referred to as African time , where punctuality is tacitly ignored.
Low and high context: This refers to how much a culture depends on direct or indirect verbal communication. According to Hall ( 1976 ), low context cultures explicitly refer to the topic of discussion. The speaker and his audience know that the words mean exactly what they say. In high context cultures, the meanings of words are drawn from the context of the communication process. The words may never mean what they say. For example, the sentence: I have heard . In the low context culture, it merely means that the listener has used his ears to listen to what the speaker is saying. In the high context culture, the listener knows more than what the speaker is saying and may be planning something unpleasant. Europeans and North Americans have low contexts. African and Asian nations have high contexts.
Vaknin ( 2005 ) brings in another value:
Exogenic and endogenic: This shows how people relate to their environment. Deeply exogenic cultures look outside themselves to make sense of life. Hence, they believe in God and His power to intervene in the affairs of men. Endogenic cultures draw on themselves when searching for the meaning of life. They think they can generate solutions to tackle the problems facing them. While the endogenic person may exert himself to find a solution to a challenge, his exogenic partner may believe that supernatural help will come from somewhere and refuses to do what is needed. Of course, this provides a problematic platform for effective communication.
The United Nations’ sustainable development goals and culture
The United Nations recognizes that culture is implicitly crucial to the achievement of the SDGs. No meaningful development can occur outside any cultural context because every person is born into a culture. To a large extent, our cultural foundations determine what we do and how we see things. Therefore, culture must be integrated into sustainable development strategies. Some specific goals’ targets acknowledge that culture drives development. Sustainable development revolves around economic, social, and environmental objectives for people. These goals are implicitly or explicitly dependent on culture because culture impacts people.
There are 17 Sustainable Development Goals. However, there are four specific ones that refer to culture are:
SDG 4 focuses on quality education
By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development
In other words, quality education is most effective if it responds to a place and the community’s cultural context and exactitudes. This target hinges on education promoting peace, non-violence, and cultural diversity as precursors to sustainable development. Encouraging respect for cultural diversity within acceptable standards facilitates cultural understanding and peace.
SDG 8 focuses on decent work and economic growth
By 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products
Strengthening trade in cultural goods and services will provide growth impetus for local, national, and international markets. These will create employment opportunities for people whose work revolves around cultural goods. Cultural tourism generates revenues that improve the economy. In this sense, culture facilitates the community’s well-being and sustainability.
SDG 11 focuses on sustainable cities and communities
Target 11.4
Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage
When our cultural heritage is carefully managed, it attracts sustainable investments in tourism. The local people living where this heritage is domiciled ensure that it is not destroyed and that they themselves will not damage the heritage areas.
SDG 12 focuses on responsible consumption and production
Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products
Several indigenous livelihoods and crafts are built on local knowledge and management of the ecosystem, natural resources, and local materials. If natural resources are depleted, production will be endangered. Local livelihoods that utilize low technology and energy generate less waste and keep their environment free from pollution. In other words, proper management of the ecosystem prevents biodiversity loss, reduces land degradation, and moderates adverse climate change effects. Where there are natural disasters, traditional knowledge already embedded in the people’s culture helps them become resilient.
Theoretical framework
The social construction of reality is hinged on the belief that people make sense of their social world by assembling their knowledge. Scheler ( 1960 ) labels this assemblage the Sociology of Knowledge . Berger and Luckmann ( 1966 , p.15) contend that this “knowledge is concerned with the analysis of the social construction of reality.” Social construction theory builds on peoples’ comprehension of their own life experiences. From there, people make assumptions about what they think life is or should be. Young and Collin ( 2004 ) present that social constructionism pays more attention to society than individuals. Communities determine what they feel is acceptable. What is widely accepted by a particular community may be unacceptable to other people who are not members of this group. Therefore, people see an issue as good or bad based on their group’s description. Thus, what is a reality in Society A may be seen as illegal in Society B . Berger and Luckmann ( 1966 ) claim that people create their own social and cultural worlds and vice versa. According to them, common sense or basic knowledge is sustained through social interactions. These, in turn, reinforce already existing perceptions of reality, leading to routinization and habitualization. Berger and Luckmann ( 1991 ) say that dialogue is the most important means of maintaining, modifying, and reconstructing subjective reality.
Burr ( 2006 ) writes that the four fundamental tenets of social constructionism are: a critical instance towards taken-for-granted knowledge, historical and cultural specificity; knowledge sustained by social processes; and that knowledge and social action go together. This taken-for-granted knowledge is a basic common-sense approach to daily interactions. Historical and cultural specificities look at the peculiar but past monuments that have shaped the particular society. Knowledge is created and sustained by socialization. Good knowledge improves the common good. However, whoever applies the knowledge he has acquired wrongly incurs sanctions. This is why convicted criminals are placed behind bars.
Social constructions exist because people tacitly agree to act as if they do (Pinker, 2002 ). Whatever people see as realities are actually what they have learnt, over long periods, through their interactions with their society’s socialization agents such as the family, schools and churches. Cultural realities are conveyed through a language: the vehicle for communication. Language communicates culture by telling about what is seen, spoken of, or written about. However, groups construct realities based on their cultures. The media construct realities through the production, reproduction, and distribution of messages from which their consumers give meaning to their worlds and model their behaviours.
The method of study
The discourse analysis method of study is adopted for this work. Foucault ( 1971 ) developed the ‘discursive field’ to understand the relationships between language, social institutions, subjectivity, and power. Foucault writes that discourses relate to verbalization at the most basic level. The discursive method explores the construction of meanings in human communication by offering a meaningful interpretation of messages to enhance purposeful communication. Discourse analysis examines how written, or spoken language is used in real-life situations or in the society. Language use affects the creation of meaning; and, therefore, defines the context of communication. Kamalu and Isisanwo ( 2015 ) posit that discourse analysis considers how language is used in social and cultural contexts by examining the relationship between written and spoken words. Discourse analysis aims to understand how and why people use language to achieve the desired effect. The discursive method explores the construction of meanings in human communication by offering a meaningful interpretation of messages to enhance purposeful communication. Gale ( 2010 ) says that meaning is constructed moment by moment. Garfinkel ( 1967 ) explains this construction as the common-sense actions of ordinary people based on their practical considerations and judgments of what they feel are intelligible and accountable to others. According to Keller ( 2011 ), a peoples’ sense of reality combines their routinized interactions and the meanings they attach to objects, actions, and events. It is in this understanding of the natural use of language that some barriers to effective cross-cultural communication can be reduced.
Messages may assume different meanings in different situations for other people. These meanings affect social interactions. They either encourage or discourage further human communication. As Katz ( 1959 ) has written, interpersonal relationships influence communication. To make meaning out of messages and improve human relationships, it is necessary to understand that content and context may not represent the same thing to people in different situations. Waever ( 2004 , p. 198) states that “things do not have meaning in and of themselves, they only become meaningful in discourse.” Since people’s perspectives are different, it becomes extremely difficult to form a rigid basis on specific ideas. Ideas are discussed on their merits. Discursive analysis inspects the ways individuals construct events by evaluating language usage in writing, speech, conversation, or symbolic communication (Edwards, 1997 ; Harre and Gillet, 1994 ). Language is the carrier of culture. According to Van Dijk ( 1995 , p. 12), this approach is used to study descriptive, explanatory, and practical issues in “the attempt to uncover, reveal or disclose what is implicit, hidden or otherwise not immediately obvious in relations of discursively enacted dominance or their underlying ideologies.” The media play fundamental roles in the processes of constructing or reconstructing reality. They can do these because of Aririguzoh’s ( 2004 ) observation that the press impacts the political and socio-cultural sub-systems.
Culture at the international galleries
The affairs of culture came into international prominence at the UNESCO’s World Conference on Cultural Policies held in Mexico in 1982. This conference gave a broad definition of culture to include “the whole complex of distinctive spiritual, material, intellectual and emotional features that characterize a society or social group. It includes not only the arts and letters but also modes of life, the fundamental rights of the human being, value systems, traditions and beliefs” (UNESCO, 1982 , p. 1).
The United Nations World Commission on Culture and Development, led by J. Perez de Cuellar, published our Creative Diversity’s Landmark Report (UNESCO, 1995 ). This report points out the great importance of incorporating culture into development. Although the Commission recognizes cultural diversities, it sees them as the actual vehicles driving creativity and innovation. During the World Decade on Culture and Development (1988–1998), UNESCO stepped up again to campaign for greater recognition of culture’s contribution to national and international development policies. In 1998, Stockholm hosted an Inter-governmental Conference on Cultural Policies for Development. Its Action Plan on Cultural Policies for Development reaffirmed the correlation between culture and development (UNESCO, 1998 ). In 1999, UNESCO and the World Bank held the Inter-governmental Conference, Culture Counts , in Florence. Here, ‘cultural capital’ was emphasized as the tool for sustainable development and economic growth (UNESCO, 1999 ).
The United Nations General Assembly adopted the 2005 World Summit Outcome Document . Here, cultural diversity was explicitly admitted as a contributor to the enrichment of humankind. The United Nations General Assembly Resolutions on Culture and Development adopted in 2010 and 2011 (65/166 and 66/208) recognize culture as an “essential component of human development” and “an important factor in the fight against poverty, providing for economic growth and ownership of the development processes.” These resolutions called for the mainstreaming of culture into development policies at all levels. The UN System Task Team on the Post 2015 Development Agenda issued a report, Realizing the Future We Want for All ( 2012 , p. ii), with a direct charge that culture has a clear role to play in the “transformative change needed for a rights-based, equitable and sustainable process of global development.” Paragraph 71 of the report declares:
It is critical to promote equitable change that ensures people’s ability to choose their value systems in peace, thereby allowing for full participation and empowerment. Communities and individuals must be able to create and practice their own culture and enjoy that of others free from fear. This will require, inter alia, respect for cultural diversity, safeguarding cultural and natural heritage, fostering cultural institutions, strengthening cultural and creative industries, and promoting cultural tourism (p. 33).
In 2005, the Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions member states agreed that cultural diversity “increases the range of choices and nurtures human capacities and values. Therefore, it is a mainspring for sustainable development for communities, peoples and nations” (UNESCO, 2005 , p. 1). The Convention reiterated the importance of the link between culture and development. UNESCO also steers an International Fund for Cultural Diversity to promote sustainable development and poverty reduction among the developing and least developed countries that are parties to the Convention.
UN Resolution 2347 of 2017 focuses exclusively on protecting cultural heritage and its necessity for peace and security. This Resolution brings a thorough awareness of culture’s role as a source of stability, inclusion, driver of reconciliation, and resilience. This Resolution reinforces Resolution 2199, adopted in February 2015, partly to fight against international terrorism financing and prohibit the illicit trafficking of cultural goods from Iraq and Syria.
Communication processes for overcoming difficulties in cross-cultural communication
The primary risk in cross-cultural communication is distortion, which creates misunderstanding or even misrepresentation of the conveyed information. Baumgratz ( 1990 , pp. 161–168) shares the opinion that relevant cultural dimensions of what he calls a social communication situation should be mapped out for individuals or groups who are from different nations or cultural origins but who have realized the need to contribute to the achievement of social, institutional, organizational, group, and personal aims. The tactics to overcome difficulties in cross-cultural communication lie in the communication processes. Any of the steps can become a barrier since culture influences the behaviour of both senders and receivers of messages. Barriers impede communication by distorting, blocking, or creating misunderstandings. Hence, it is necessary to create an enabling environment that will make communicating easier. Each of the communication steps can be strategized to enhance communication.
He is the source or initiator of the message. He can be a person or an organization. If the sender is a person, Malec ( 2018 ) refers to him as the carrier of intangible culture and the creator of the tangible ones. Messages are conveyed through spoken or written words. Nevertheless, messages can also be non-verbal. The encoding includes selecting words, symbols, or gestures in composing a message. The sender should encrypt, transfer meaning, or package his messages in ways that the receivers can access them. He should use symbols that the receiver would comprehend. The first thing he should do is use a language that his receiver understands. For example, it is useless to send a message written in English to another person who only understands French. Not only is the effort wasted, but it might also generate hostility. In Nigeria, Mexican soaps are freely watched. However, their producers avoided the obvious language challenge by dubbing in English voice-overs.
Words mean different things in different languages. For example, a British boss would answer yes to a question. However, his American subordinate would answer, yeah . The boss would think that he is disrespectful and impolite. Meanwhile, the American employee would be bewildered by the boss’s apparent coldness. British people use words that have different meanings from their American counterparts. For example, the word, pant , means underwear to a Briton but a pair of trousers to an American. The Englishman may still run into trouble with other nationals because his words have different meanings to these listeners. For example, the English phrase fart means a different thing among the Danish. For them, the word means speed ! The English word gift means poison in German. If an Englishman calls somebody a brat , his Russian friend will conclude that he is calling him his brother , which is what the word means in his language. Igbo children of south-eastern Nigeria call the hawk leke . But for the Yorubas in the southwest, this is the name given to a male child.
The sender, too, must know that even body language may mean different things. He should not assume that non-verbal messages mean the same in every part of the world. In Japan, nodding the head up and down means disagreement. In Nigeria, it means the opposite. Even though his own culture invariably influences the message’s sender, he should understand that his message is intended for a cross-cultural audience. He must also realize that the contents are no longer meant for ethnic communities defined by geographical locations but for an audience connected by frequent interactions that are not necessarily in the same physical place. A message sender that values esprit de corps will incorporate this into his messages by telling them that the laurel does not go to any person in particular but to the winning team. He thus encourages everybody to join in to win, not as individuals but as members of a group. If he is high on doubt avoidance, he makes his messages very direct and unambiguous and leaves no room for misinterpretation. However, a male sender who wants to assert his masculinity may wish to sound harsh. The sender who regularly attends church services may unconsciously put some words of Scripture in his messages because of his exogenic roots. The sender with monochronic orientation will send one message and expect the task to be completed as scheduled. His linear cultural background will be offended if the result is the contrary. Similarly, the sender who places a high value on rules and regulations would send messages of punishment to those who break them but reward those who keep them without minding his relationships with them. An effective sender of messages to a cross-cultural society should state his ideas clearly, offer explanations when needed, or even repeat the whole communication process if he does not get the appropriate feedback.
This is the information content the sender wants to share with his receivers. These include stories, pictures, or advertisements. He should carefully avoid lurid and offensive content. A French man may see nothing wrong in his wife wearing a very skimpy bikini and other men ogling at her at a public beach. His counterpart from Saudi Arabia will be upset if other men leer at his wife. In addition, the wife would be sanctioned for dressing improperly and appearing in public. If a person has a message to share with others from a different cultural background, he should be careful. His listeners may not isolate his statement as being distinct from his personality.
Societies with high context culture usually consider the messages they send or receive before interpreting them. Messages are hardly delivered straightforwardly. The message is in the associated meanings attached to the pictures and symbols. Thus, those outside that community find it very difficult to understand the meaning of the messages. In low-context communication, the message is the information in words. The words mean what they say. However, a corporate sender of messages, for example, the head of the Human Resources Department of a multi-cultural company interested in building team spirit, may organize informal chit-chats and get-togethers to break the proverbial ice as well as create a convivial atmosphere where people can relate. The message he is passing across is simple: let colleagues relax, relate, and work together as team members irrespective of where they come from. All of these are communicative actions.
The channel’s work is to provide a passage for the sender to guide his message to the receiver. While face-to-face communication is ideal for intimate and close group conversations, it is impossible to talk to everybody simultaneously. Different channels of passing across the same message may be used. For example, the same message may be passed through radio, adapted for television, put online, or printed in newsletters, newspapers, and magazines. The hope is that people who missed the message on one channel may see it on another somewhere else. A pronounced media culture will hasten cross-cultural communication. Many people consume media content. However, these consumers are expected to be media literates. Aririguzoh ( 2007 , p. 144) writes that:
media literacy is the systematic study of the media and their operations in our socio-political systems as well as their contributions to the development and maintenance of culture. It is the information and communication skill that is needed to make citizens more competent. It is the ability to read what the print media offer, see what the visual media present, and hear what the aural media announce. It is a response to the changing nature of information in our modern society.
Official messages should be passed through defined routes and are best written. This would close avenues of possible denials by others if the same message were passed across verbally. It could be difficult to misinterpret the contents of a written document. Written documents have archival values. As much as possible, rumours should be stamped out. A good manager should single out regular gossips in a multi-cultural organization for special attention. Equally, an effective manager heading widely dispersed employees can co-ordinate their activities using communication technologies with teleconferencing features. Aririguzoh ( 2007 , p. 45) notes, “information and communication technologies have transformed the range and speed of dispersing information and of communicating. Today, the whole world lies a click away!”
The media of communication are shaped by the culture of the people who produce them. What they carry as contents and the form they assume are defined by the culture of the sender. In low-context societies, it is common for messages to be written. In high context societies, it is common for statements to be verbal. Importantly, Aririguzoh ( 2013 , pp. 119–120) points out that “… the mass media can effectively be deployed to provide pieces of information that enhance communication, build understanding and strengthen relationships in our rapidly changing environment dictated by the current pace of globalization. The mass media assiduously homogenize tastes, styles, and points of view among many consumers of its products across the globe. They have effectively helped in fading away national distinctions and growing mass uniformity as they create, distribute and transmit the same entertainment, news, and information to millions of people in different nations.”
The receiver is the person the sender directs his message to. In a workplace, the receiver needs the message or information to do his job. The receiver decodes or tries to understand the meaning of the sender’s message by breaking it down into symbols to give the proper feedback. If the message is verbal, the receiver has to listen actively. The message receiver must understand a message based on his existing orientations shaped by his own culture. Even the messages that he picks are selected to conform to his existing preconceptions.
Oyserman et al. ( 2002 ) make an interesting discovery: that receivers from different cultures interpret the message senders’ mannerisms. For an American, a speaker talking very quickly is seen as telling the uncensored truth. In other words, the speaker who talks too slowly implicates himself as a liar! However, for the Koreans, slow speech denotes careful consideration of others. In some cultures, particularly in Asia, the receiver is responsible for effective communication. Kobayashi and Noguchi ( 2001 ) claim that he must become an expert at “understanding without words.” Miyahara ( 2004 , p. 286) emphasizes that even children literarily learn to read other people’s minds by evaluating the subtle cues in their messages and then improvising to display the expected and appropriate social behaviour and communication. Gestures involve the movements of the hands and head of the sender. The receiver clearly understands these body movements. As painted by Sapir ( 1927 , p. 556), “we respond to gestures with an extreme alertness and, one might almost say, in accordance with an elaborate and secret code that is written nowhere, known by none, and understood by all.”
Receivers who value individualism appreciate personal freedom, believe that they can make their own decisions, and respect their performance. Those who prefer communitarianism would prefer group applause and loyalty. A monochromatic receiver would start and finish a task before starting another one. He would be offended when colleagues do not meet deadlines, are late to appointments, and do not keep rigid schedules. His co-worker, who synchronizes his time, develops a flexible working schedule to work at two or more tasks.
This is the final process. Ordinarily, the sender wants a response to determine if the message he sent out has been received and understood. Acknowledging a message does not indicate a clear understanding of its contents. Feedback can be positive or negative. Positive feedback arises when the receiver interprets the message correctly and does what the sender wants. Negative feedback comes when messages are incorrectly interpreted, and the receiver does not do what the sender of the information has intended him to do. Cross-cultural communication recognizes that people come from different backgrounds. Therefore, feedback on diverse messages would be different. A sensitive communicator would be careful how he designs his messages for a heterogeneous audience so that he can elicit the desired feedback.
It must be emphasized that no culture is superior to another as each culture meets the needs of those who subscribe to it. To a large extent, our culture influences our behaviours and expectations from other people. Although there are noticeable similarities and differences, what separates one culture from another is its emphasis on specific values. As the United Nations has affirmed, there is diversity in cultures. These diversities add colour and meaning to human existence. This suggests that particular policies should be carved out to attend to specific locations and supports Satterthwaite’s ( 2014 ) proposition that local actors should be empowered to help achieve the SDGs. What the local populace in one community may appreciate may be frowned upon and even be fought against by residents in another place. As Hossain and Ali ( 2014 ) point out, individuals constitute the societies where they live and work. While Bevir ( 1996 ) describes this relationship as that of mutual dependence, he recognizes that people are influenced by their particular social structures and therefore do not go against them. Bevir believes that social systems exist for individuals.
Societies are built on shared values, norms and beliefs. These, in turn, have profound effects on individuals. Society’s culture affects individuals while the individuals create and shape the society, including initiating sustainable development. Development rests on the shoulders of men. Thus, culture influences the ways individuals behave and communicate. The effective communicator must actively recognize these elements and work them into communication practices. As Renn et al. ( 1997 , p. 218) point out, “sustainable practices can be initiated or encouraged by governmental regulation and economic incentives. A major element to promote sustainability will be, however, the exploration and organization of discursive processes between and among different actors.”
To achieve the United Nations sustainable goals, the competent communicator has to recognize that the culture of the actors in a communication process is the basic foundation for effective communication. For example, while one individual may discuss issues face-to-face and is not afraid to express his feelings candidly, another person may not be so direct. He may even involve third parties to mediate in solving a problem. Either way, their approaches are defined by their cultural backgrounds. It may be counterproductive to assume that either of these approaches is the best. This assertion is supported by the study of Stanton ( 2020 ), who explored intercultural communication between African American managers and Hispanic workers who speak English as a second language. He finds managers that follow culturally sensitive communication strategies getting more work done. Cartwright ( 2020 ) also observes that intercultural competence and recognition of cultural differences in East and Central Europe are foundation pillars for business success. This lends credence to Ruben and Gigliotti ( 2016 ) observation that communication with people from different cultures reduces the barriers associated with intercultural communication and enhances the communication process.
Irrespective of our ethnicities, people want to communicate, understand, appreciate, and be respected by others. Effective communication is the foundation of good human relationships among team members, whether their cultural backgrounds differ or not. Good feedback is achieved when both the sender and receiver of messages create common meanings. This is what discourse is all about. Messages must be meaningful, meaningfully constructed and meaningfully interpreted. Georgiou ( 2011 ) labels this the communicative competence : acknowledgement of the intercultural dimension of foreign language education and successful intercultural interactions that assume non-prejudiced attitudes, tolerance and understanding of other cultures, and cultural self-awareness of the person communicating. An efficient communicator must understand that culture shapes people, and the people then shape society. In other words, communication shapes the world. Therefore, appropriately chosen communication strategies help blend the different cultures.
According to Bokova ( 2013 ), there is “renewed aspirations for equality and respect, for tolerance and mutual understanding, especially between peoples of different cultures.” This means that if all parties respect other team members’ cultures, a clement work environment is inevitable. Cultural literacy creates more tolerant and peaceful work environments. Achieving this starts with a re-examination of the whole communication process. The crux of cross-cultural communication is developing effective ways to appreciate the culture of others involved in the acts of communication. Understanding these differences provides the context for an enhanced understanding of the values and behaviours of others. Reconciling these differences confers competitive advantages to those who communicate effectively. The media must provide the links between senders and receivers of messages in the context of their socio-cultural environments.
The United Nations appreciates the distinctiveness in cultures and has incorporated it as a significant factor in achieving sustainable development goals. This global body has produced different documents championing this. Every development takes place in an environment of culture. The heart of sustainable development is the man. The SDGs will be more meaningful and easily achievable by recognizing that actions should be both locally and culturally relevant. Cultural differences can be effectively managed if senders and receivers of messages understand that culture shapes how people communicate and, by extension, the relationship with other people who may not necessarily be from their tribal communities. Breaking down the barriers to cross-cultural communication lies in understanding these distinct differences and consciously incorporating them into the communication processes to enhance communication competencies.
Data availability
All data analysed are contained in the paper.
Adler N (1991). International dimensions of organizational behavior, 2nd edn. Pws-Kent Publishing Company
Aririguzoh S (2004) How the press impinges on the political and socio-cultural sub-systems. Nsukka J Humanit 14:137–147. http://www.unnfacultyofarts.com/download.php?download_file=UFAJH192.pdf
Aririguzoh S (2007) Media literacy and the role of English language in Nigeria. Int J Commun 6:144–160
Google Scholar
Aririguzoh S (2013) Human integration in globalization: the communication imperative. Niger J Soc Sci 9(2):118–141
Barth F (1969) Introduction. In: Barth F (ed.) Ethnic groups and boundaries: the social organization of culture difference. Little, Brown & Company, pp. 9–30
Baumeister R, Wilson B (1996) Life stories and the four needs for meaning. Psychol Inq 7(4):322–325
Article Google Scholar
Baumgratz G (1990) Personlichkeitsentwicklung und Fremdsprachenerwerb. Transnationale Kommunikationsfthigkeit im Franzosischunterricht (Personality development and foreign language acquisition: transnational communication skills in French lessons). Schoningh
Berger P, Luckmann T (1966) The social construction of reality: a treatise in the sociology of knowledge. Penguin Books Ltd
Berger P, Luckmann T (1991) The social construction of reality. Penguin Books.
Bevir M (1996) The individual and society. Political Stud 44(1):102–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9248.1996.tb00759.x
Bokova I (2013) The power of culture for development. http://en.unesco.org/post2015/sites/post2015/files/The%20Power%20of%20e%20fCulturor%20Development.pdf
Bokova I (2010) 2010 International year for the rapprochement of culture: message from Irina Bokova, Director-General of UNESCO https://www.un.org/en/events/iyrc2010/message.shtml
Burr V (2006) An introduction to social constructionism. Routledge, Taylor & Francis e-Library
Cartwright CT (2020) Understanding global leadership in eastern and central Europe: the impacts of culture and intercultural competence. In: Warter I, Warter L (eds.) Understanding national culture and ethics in organisations. Emerald Publishing Limited, Bingley, pp. 63–74
Causadias JM (2020) What is culture? Systems of people, places, and practices. Appl Dev Sci24(4):310–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2020.1789360
Comaroff J, Comaroff J (2009) Ethnicity , inc. University of Chicago Press
De Beukelaer C, Freita R (2015) Culture and sustainable development: beyond the diversity of cultural expressions. In: De Beukelaer C, Pyykkönen MI, Singh JP (eds.) Globalization, culture, and development: the UNESCO convention on cultural diversity. Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 203–221
Dessein J, Soini K, Fairclough G, Horlings L (2015) Culture in, for and as sustainable development. Conclusions of COST ACTION IS1007 investigating cultural sustainability. European Cooperation in Science and Technology, University of Jyvaskyla https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.3380.7844
Edwards D (1997) Discourse and cognition. Sage
Field L (2008) Abalone tales: Collaborative explorations of sovereignty and identity in native California. Duke University Press Books
Foucault M (1971). The order of discourse. In: Young R (ed.) Untying the text: a post-structuralist reader. Routledge and Kegan Paul Limited
Gale J (2010) Discursive analysis: a research approach for studying the moment-to-moment construction of meaning in systemic practice. Hum Syst21(2):7–37
García-Carbonell A, Rising B (2006) Culture and communication. College of Management Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, pp. 23–40
Garfinkel H (1967) Studies in ethnomethodology. Prentice-Hall
Geertz C (1973) The interpretation of cultures. Basic Books
Georgiou M (2011) Intercultural competence in foreign language teaching and learning: action inquiry in a Cypriot tertiary institution. Doctoral Thesis, University of Nottingham
Guiso L, Paola S, Luigi Z (2006) Does culture affect economic outcomes?. J Econ Perspect20(2):23–48. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.20.2.23
Gumperz JJ (2001) Interactional sociolinguistics: a personal perspective. In: Schiffrin D, Tannen D, Hamilton HE (eds.) The handbook of discourse analysis. Blackwell Publishers Ltd., pp. 215–228
Hall E (1976) Beyond culture. Doubleday
Hall E (1983) The dance of life: the other dimension of time. Doubleday
Harre R, Gillet G (1994) The discursive mind. Sage
Heckler S (2014) On the importance of culture in sustainable development. In Sillitoe P (ed.) Sustainable development: an appraisal from the Gulf region. Berghahn Books, pp. 436–459
Hirsch ED (1987) Cultural literacy: what every American needs to know. Houghton Mifflin
Hofstede G (2001) Culture’s consequences: comparing values, behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations, 2nd edn. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA
Hofstede G (1980) Culture’s consequences: international differences in work-related values. Sage
Hofstede G (1998) Masculinity and femininity: the taboo dimension of national cultures. Sage
Hofstede G (2005) Cross-cultural communication. http://encyclopedia.laborlawtalk.com/Cross-cultural_communication
Hofstede G, Bond MH (1988) The Confucius connection: from cultural roots to economic growth. Organ Dyn 16(4):4–21. http://www.clearlycultural.com/geert-hofstede-culturaldimensions/masculinity/
Holmes P (2017) Intercultural communication in the global workplace, critical approaches. Critical intercultural communication theories, issues, and concepts. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118783665.ieicc0051
Hosagrahar J (2017) Culture: at the heart of SDGs. The UNESCO Courier, 1 (April–June). https://en.unesco.org/courier/april-june-2017/culture-heart-sdgs
Hossain FMA, Ali MK (2014) Relation between individual and society. Open J Soc Sci 2:130–137. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2014.28019
Jenkins R (2014). Social identity. Routledge
Kamalu I, Osisanwo A (2015) Discourse analysis. In: Kamalu I, Tamunobelema I (eds.) Issues in the study of language and literature: theory and practice. Kraft Books, pp. 169–195
Kangas A, Duxbury N, De Beukelaer C (2017) Introduction: cultural policies for sustainable development. Int J Cult Policy 23(2):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286632.2017.1280790
Katz E (1959) Mass communications research and popular culture. Stud Public Commun 2:10–19
Keller R (2011) The sociology of knowledge approach to discourse (SKAD). Hum Stud 34(1):43–65
Kobayashi Y, Noguchi Y (2001) Consumer insight, brand insight, and implicit communication: successful communication planning cases in Japan. In Roberts M, King R (eds.) The Proceedings of the 2001 special Asia-Pacific conference of the American Academy of Advertising. pp. 29–40
Kurylo A (2013) Inter/Cultural communication: representation and construction of culture. Sage Publications, Inc.
Levitt T (1983, May) The globalization of markets. Harv Bus Rev 92–102
Malec TE (2018) Introduction to theory of culture-related spatial development. Cogent Arts Humanit 1557583. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311983.2018.1557583
Martinovski B (2018) A model of culture-based communication. In: Faucher C (ed.) Advances in culturally-aware intelligent systems and in cross-cultural psychological studies. Intelligent Systems Reference Library, vol 134. Springer, Cham, pp. 335–350
Merkin RS (2017) Cross-cultural communication theory and research overview. In: The international encyclopedia of intercultural communication. John Wiley & Sons, pp. 1–10
Miyahara A (2004) Toward theorizing Japanese interpersonal communication competence from a non-western perspective. In: Jandt FE (Ed.) Cross-cultural communication. Sage, pp. 279–292
Monaghan L (2020) Intercultural communication: teaching nonverbal communication. In: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Monaghan L (ed.) The international encyclopedia of linguistic anthropology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 1–6
Ohmae K (1999) The borderless world. Harper Business.
Oyserman D, Coon H, Kemmelmeier M (2002) Rethinking individualism and collectivism: evaluation of theoretical assumptions and meta-analyses. Psychol Bull 128:3–72
Pinker S (2002) The blank slate: the modern denial of human nature. Penguin Books
Rachlinski JJ (2021) What is cultural cognition, and why does it matter? Annu Rev Law Soc Sci17(1):277–291. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-lawsocsci-011921-060754
Renn O, Blattel-Mink B, Kastenholz H (1997) Discursive methods in environmental decision making. Bus Strategy Environ 6:218–231
Ruane J, Todd J (2004) The roots of intense ethnic conflict may not in fact be ethnic: categories, communities and path dependence. Eur J Sociol 45(2):209–232
Ruben BD, Gigliotti RA (2016) Leadership as social influence: an expanded view of leadership communication theory and practice. J Leadersh Organ Stud 23:467–479. https://doi.org/10.1177/1548051816641876
Samovar LA, Porter RE, McDaniel ER (2012) Intercultural communication: a reader. Wadsworth Cengage Learning
Sapir E (1927) The unconscious patterning of behavior in society. In: Mandelbaum D (ed.) Selected writings of Edward Sapir. University of California Press, pp. 544–559
Sapir E (1956) Selected writings in language, culture and personality. University of California Press
Satterthwaite D (2014) Guiding the goals: empowering local actors. SAIS Rev 34(2):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1353/sais.2014.0025
Scheler M (1960) Die Wissensformen und die Gesellschaft. The forms of knowledge and society. A. Francke AG
Seymour J (2007) Culture does matter. Relig Educ 102(2):105–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/00344080701285147
Stanton RA (2020) Intercultural communication between African American managers and Hispanic workers with ESL. Doctoral Dissertation, Walden University
Tannen D (1985) Cross-cultural communication. In: Adrianus van Dijk T (ed.) Handbook of discourse analysis , vol 4. Academic Press, pp. 203–215
Trompenaars F, Hampden-Turner C (1997) Riding the waves of culture. Nicolas Brealey
UNESCO (2017) UNESCO moving forward the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development https://en.unesco.org/creativity/sites/creativity/files/247785en.pdf
UNESCO (2013) Communication & development, No. 9. Regional Office for Culture in Latin America and the Caribbean, Havana, Cuba
UNESCO (2013a). Activity report 2012 – 2013 . Regional Office for culture in Latin America and the Caribbean, Havana
UNESCO (1999) Proceedings of the seminar measuring culture and development: prospects and limits of constructing cultural indicators. In: Culture counts conference organized by the World Bank and the government of Italy in co-operation with UNESCO, Florence, Italy, 4–7 October. http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0011/001191/119138eo.pdf
UNESCO (1998) Action plan on cultural policies for development adopted in by the Intergovernmental Conference on Cultural Policies for Development, Stockholm, Sweden, 2 April. http://www.unesco.org/cpp/uk/declarations/cultural.pdf
UNESCO (1995) Our creative diversity: report of the world commission for culture and development. http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001429/142919e.pdf
UNESCO (1982) Mexico city declaration on cultural policies. World conference on cultural policies. UNESCO, Mexico City, Paris, 26 July–6 August
UNESCO (2005) The convention on the protection and promotion of the diversity of cultural expressions https://en.unesco.org/creativity/convention
United Nations (2012) Realizing the future we want for all: report to the secretary-general. www.un.org/millenniumgoals/pdf/Post_2015_UNTTreport.pdf
United Nations (2015) Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development http://www.unesco.org/new/en/brasilia/culture/culture-and-development/culture-in-sustainable-development/
Vaknin S (2005) The classification of cultures. http://samvak.tripod.com/class.html .
Van Dijk TA (1995) Aims of critical discourse analysis. Jpn Discourse 1:17–27
Vassiliou V, Triandis H, Vassiliou G, McGuire H (1972) Interpersonal contact and stereotyping. In Triandis H (ed.) The analysis of subjective culture. Wiley, pp. 89–115
Waever O (2004) Discursive approaches. In: Wiener A, Diez T (eds.) European integration theory. Oxford University Press, pp. 197–215
Yeung I, Tung R (1996) Achieving business success in Confucian societies: the importance of guanxi (Connections). Organ Dyn 25(2):54–65
Young R, Collin A (2004) Introduction: constructivism and social constructionism in the career field. J Vocat Behav 64(3):373–388
Zhu H (2016) Research methods in intercultural communication: a practical guide. Routledge
Download references
Acknowledgements
I acknowledge: Dr. Emmanuel Mogaji of Greenwich University for reading and pointing out helpful corrections; Professors Innocent Chiluwa, Abiodun Gesinde, David Imhonopi and Dr Evaristus Adesina of Covenant University, who went through the manuscript, suggested corrections and encouraged me not to give upe and my daughter, Victoria-Grace Onyekachi Miracle Aririguzoh, who proofread this manuscript and brought in sunshine when the clouds were grey.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mass Communication, Covenant University, Ota, Nigeria
Stella Aririguzoh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stella Aririguzoh .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Ethical approval
There was no ethical approval or informed consent approval sought as neither applies to this paper.
Informed consent
This article does not have human participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Aririguzoh, S. Communication competencies, culture and SDGs: effective processes to cross-cultural communication. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9 , 96 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01109-4
Download citation
Received : 28 May 2021
Accepted : 14 February 2022
Published : 23 March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01109-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Cultural competence in the nursing, dentistry, and medicine professional curricula: a qualitative review.
- Maura Klenner
- Rodrigo Mariño
- Carlos Zaror
BMC Medical Education (2022)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
The Globalization of Communication | A Reflection Paper by Paulo Habla

As I sit down and reflect on how communication flourished over the last centuries, I realized how fortunate we are as citizens of the Digital Age to grasp the privilege to be able to send messages across the entire globe with the power of a single click. At the same time I wondered, when was the last time people primarily send their handwritten letters enclosed within an envelope to those they want to relay their message to? Perhaps it has quite been a long time, dating from years and years prior to this time. Although some are still doing so, the vast majority of the population now relies to the ever-changing comfort technology offers.
Related papers
Revista CS, 2025
In short, this call for papers seeks to gather reflections and studies that address the complexity, speed and uncertainty of the communicative practices of contemporary societies and communities and include basic, primary and simple forms of human communication as well as those mediated by the development and reach of technology and artificial intelligence. Therefore, we will give priority to participative articles within any of the following areas: 1) Communication, artificial intelligence, digital media and transmedia and multiplatform storytelling. 2) Technology, activism and new models of creation, collection, circulation and analysis of information, know-how and scientific knowledge. 3) Communication, memories, narratives and media, and their relationships with social and citizen mobilization. 4) Communication and politics, communication policies, democracy, liberty, and power practices. 5) Impact and transformation of communication in the intimate and collective experience of groups, communities and territories, Submission deadline: November 30, 2023
The electronic “global village” envisioned by McLuhan 50 years ago is now fully operational. Communications technologies are expanding our connectivity at an accelerating rate. Yet despite their obvious impact on how we all live and work, it’s not easy to grasp the depth of this transformation or its implications for our future, in part because our social and economic institutions are evolving much more slowly. This essay focuses on one specific consequence of the shift to electronic media – that they’re changing how we understand communication itself, both conceptually and in our everyday lives. As background, I compare the emergence of computerized media with the much slower transition that took place in ancient times, from oral to literate culture. As written text gradually became the dominant medium of cultural evolution, it fostered a distanced, objective mode of thought that made deeper levels of interpersonal connection seem irrelevant to the serious business of civilization. Today the new media vastly extend the power of published text, but they also revive the immediacy of real-time participation that belongs to oral culture. They make possible a new appreciation of the depth and complexity of communications systems, both at the physical level and in human interaction.
If we were to stand at the orbit of the communications satellites, at night e would see an earth with deep dark areas and intensely illuminated areas and inhabited by a race of compulsive communicators. This need to communicate with our fellow human beings has forced us t find ways to span the distances that separate us. Just the blink of an eye ago, or so it seems t anyone born before 1970, our planet was rotating comfortably in its well-established orbit of political and social relations. Peoples and societies were neatly divided into communities identified as much by ideologies and enemy images as by nationality or race. But suddenly in the mid-1980s, someone pressed the fast-forward button and life has careened ahead topsy-turvy through a cavalcade of changes. This article looks back into ancient history and brings us up to the recent past telling the story of how we humans fought geography and distance to communicate across the planet. Though much of the world as yet to make a single telephone call, every person is affecting by our collective ability to span t e time zones and communicate meaningfully. From time immemorial we have been separated one from another by time, distance, culture and language. Have things really changed? Let's travel back in time now and look at how our ancestors succeeded and sometimes failed in their compulsion o communicate with one another.
The history of human communication can be measured by a series of paradigm shifts: speaking, writing, printing, and now, interconnecting globally. Government and business need to invest in research and innovation to explore how the communicative context is changing, how individuals will be affected by their interconnection with electronic objects, and what transcendent values will define the collective vision of reality.
Routledge, 2020
The harnessing of steam and electricity in the mid-nineteenth century created a new world of possibilities in business, politics, and public life. In no realm was this transformation more momentous than in communications, an activity commonly understood at this time to embrace not only the trans-local circulation of information, but also the long-distance transportation of people and goods (Matterlart 1996, 2000). For the first time in world history, merchants could convey overseas large quantities of goods on a regular schedule and exchange information at a speed greater than a ship could sail. New organizations sprang up to take advantage of this "communications revolution," as this transformation has come to be known (John 1994). Some were public agencies; others were private firms. Each was shaped not only by the harnessing of new energy sources, but also by the institutional rules of the game. These rules defined the relationship of the state and the market, or what economic historians call the political economy. This chapter surveys this transformation, which we have come to view with fresh eyes following the commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s. It features case studies of two well-documented global communications organizations that originated in the nineteenth century - undersea cable companies and news agencies - which we have supplemented by a brief discussion of other important global communications organizations: radio, telephony, and the mail. We have not surveyed film, a topic addressed by Peter Miskell's chapter in this Handbook.
Teresa, 2017
ECO WEB TOWN JOURNAL of SUSTAINABLE DESIGN, 2019
Fronteiras: Revista Catarinense de História
Virginia Fusco y Andrea Greppi (eds). Democracia radical. Madrid: Lengua de Trapo, 2024, 2024
Pathogens and Disease, 2013
International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Nanotechnology, 2012
Revista Brasileira de Física Médica
Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 2008
Frontiers in Psychology, 2022
Ciencias Marinas, 1996
Journal of Radiation Oncology, 2017
Revista Odontológica do Brasil Central, 2010
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2005
Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
100 Words Essay on Impact Of Globalization On Communication Introduction. Globalization is the process of integrating the world’s economies, cultures, and societies. It has greatly influenced how we communicate. This essay will explore the impact of globalization on communication.
The impact of globalization on communication & education. As technology advances, the world is both getting larger and smaller. Today we are able to communicate with people across the...
Global communication is directly affected by the process of globalization, and helps to increase business opportunities. Although globalization has many benefits for international communication and world trade. Globalization also have its side effects.
This paper has reviewed the effects of globalization on social media. It has also highlighted the impact that social media has on different aspects of daily life, including politics, economics, culture, moral values, lifestyle, employment and communication.
International Communication and Globalization supplies a much needed and well-timed overview, with its writers examining how communication between countries has developed and laying out new ways to approach the study of the expanding media and communication studies area.
Understanding the impact of globalization on cross-culture communication is imperative for organizations seeking to create a competitive advantage in the global market. Recent economic challenges further highlight the need for organizations to develop the internal communication capacity necessary to control and monitor external threats.
This essay reviews the impact and policy implications of global communication in international relations in the following seven arenas: theory, military, political, economic, educational, scientific, and cultural.
Globalization has made it necessary for people from different cultures and nations to interact and work together. Effective cross-cultural communication seeks to change how messages are packaged...
In this essay, I review this intersection of journalism and globalization by considering the communication field’s approach to ‘media globalization’ within a broader interdisciplinary perspective that mixes the sociology of globalization with aspects of geo-graphy and social anthropology.
This essay focuses on one specific consequence of the shift to electronic media – that they’re changing how we understand communication itself, both conceptually and in our everyday lives. As background, I compare the emergence of computerized media with the much slower transition that took place in ancient times, from oral to literate culture.