Procedure, Example Solved Problem | Operations Research - Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method) | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th business maths and statistics : chapter 10 : operations research.
Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method)
First check whether the number of rows is equal to the numbers of columns, if it is so, the assignment problem is said to be balanced.
Step :1 Choose the least element in each row and subtract it from all the elements of that row.
Step :2 Choose the least element in each column and subtract it from all the elements of that column. Step 2 has to be performed from the table obtained in step 1.
Step:3 Check whether there is atleast one zero in each row and each column and make an assignment as follows.
Step :4 If each row and each column contains exactly one assignment, then the solution is optimal.
Example 10.7
Solve the following assignment problem. Cell values represent cost of assigning job A, B, C and D to the machines I, II, III and IV.
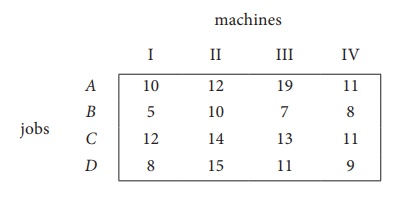
Here the number of rows and columns are equal.
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced. Now let us find the solution.
Step 1: Select a smallest element in each row and subtract this from all the elements in its row.
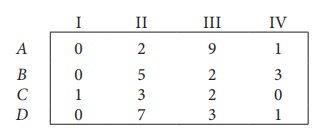
Look for atleast one zero in each row and each column.Otherwise go to step 2.
Step 2: Select the smallest element in each column and subtract this from all the elements in its column.
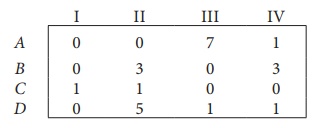
Since each row and column contains atleast one zero, assignments can be made.
Step 3 (Assignment):
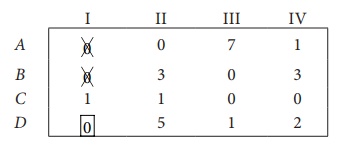
Thus all the four assignments have been made. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
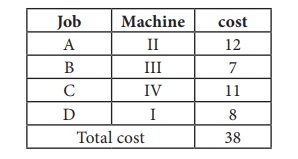
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost
Example 10.8
Consider the problem of assigning five jobs to five persons. The assignment costs are given as follows. Determine the optimum assignment schedule.
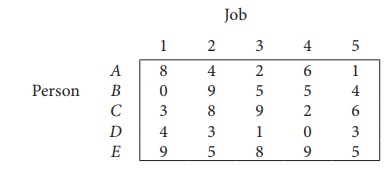
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced.
Now let us find the solution.
The cost matrix of the given assignment problem is
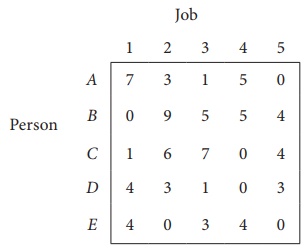
Column 3 contains no zero. Go to Step 2.
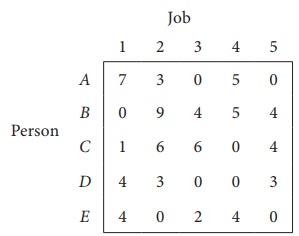
Thus all the five assignments have been made. The Optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
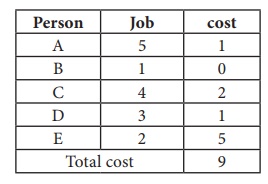
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ` 9
Example 10.9
Solve the following assignment problem.
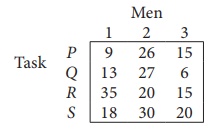
Since the number of columns is less than the number of rows, given assignment problem is unbalanced one. To balance it , introduce a dummy column with all the entries zero. The revised assignment problem is
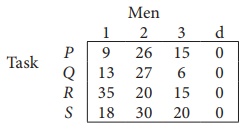
Here only 3 tasks can be assigned to 3 men.
Step 1: is not necessary, since each row contains zero entry. Go to Step 2.
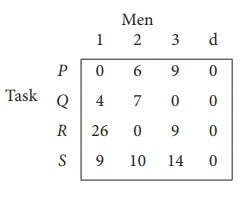
Step 3 (Assignment) :
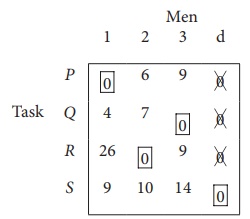
Since each row and each columncontains exactly one assignment,all the three men have been assigned a task. But task S is not assigned to any Man. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
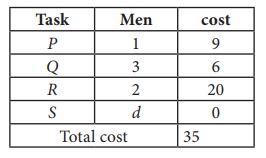
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ₹ 35
Related Topics
Privacy Policy , Terms and Conditions , DMCA Policy and Compliant
Copyright © 2018-2023 BrainKart.com; All Rights Reserved. Developed by Therithal info, Chennai.

COMMENTS
ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM Dr. K . Bharathi ... EXAMPLE OF ASSIGMENT PROBLEMS QUESTION TO ANSWER MCQ QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER K.BHARATHI,SCSVMV. ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM 2 / 55 ... Solution: The given problem is balanced with 5 job and 5 machine. A = 2 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 4 9 22 58 11 19 43 78 72 50 63 41 28 91 37 45 74 42 27 49 39
The total setup time associated with this solution is 11 hours. This completes the solution of the problem. As noted earlier, every basic feasible solution in an assignment problem is degenerate. Since degeneracy is known to impede progress toward an optimal solution, other algorithms have been developed for the solution of assignment problems.
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ` 9. Example 10.9. Solve the following assignment problem. Solution: Since the number of columns is less than the number of rows, given assignment problem is unbalanced one. To balance it , introduce a dummy column with all the entries zero. The revised assignment problem is
Module 4: Transportation Problem and Assignment problem Prasad A Y, Dept of CSE, ACSCE, B'lore-74 Page 3 Since the supply from row O1 is completed cancel the row O1. The demand for column D2 remain 350 - 50 = 50. From the remaining table the north-west corner cell is (O2, D2). The minimum among the supply
Jobs with costs of M are disallowed assignments. The problem is to find the minimum cost matching of machines to jobs. Fig 1 Matrix model of the assignment problem. The network model is in shown in Fig.2. It is very similar to the transportatio external flows are all +1 or -1. The only relevant parameter for the assignment model is arc cost
Lesson 20 :Solving Assignment problem Learning objectives: • Solve the assignment problem using Hungarian method. • Analyze special cases in assignment problems. Writing of an assignment problem as a Linear programming problem Example 1. Three men are to to be given 3 jobs and it is assumed that
Several problems of management have a structure identical with the assignment problem. For example: Example I: A manager has four persons (i.e. facilities) available for four separate jobs (i.e. jobs) and the cost ... The solution of the assignment problem should take into account these restrictions so that the infeasible assignments can be ...
1. Row D has only one "0", so make assignment to it (D4). And cross all other 0 in the corresponding column. 2. After Assignment of D on machine 4, now Row B and C both have only one Zero. So assignment are made to these rows ( C1 and B2) and zeros in columns are crossed. 3. Finally only one Zero is left in Row A where Machine three has a Zero
Chapter 17 The Assignment Problem 301 These problems are all examples of problems which may be solved as as-signment problems. In this chapter we will derive an efficient algorithm for solving assignment problems, and then discuss several problems which may be solved using this algorithm. The assignment problem will then be described in terms ...
Unbalanced Assignment Problem: Any assignment problem is said to be unbalanced if the cost matrix is not a square matrix, i.e. the no of rows and the no of columns are not equal. To make it balanced we add a dummy row or dummy column with all the entries as zero. Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method) First check whether the number ...