

Thesis Statement Formula for AP English Rhetorical Analysis Essays
A good thesis statement presents your topic to the reader and indicates how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter discussed in your essay. Think of it as a kind of road map, designed to help the reader know what to expect in the essay.
But an AP rhetorical analysis thesis statement is like nothing you’ve ever had to write in school before. Unlike other kinds of thesis statements, a rhetorical analysis thesis statement demands that you do three things:
Identify the rhetorical devices you will analyze in your essay
Identify the impact of those devices of the effectiveness of the text
Identify the author, genre, and name of the text
Sound daunting? Not to worry!
The below, fill-in-the-blank thesis statement formula, designed for use when writing rhetorical analysis essays, will make your life simpler, easier, and more successful!

create your own exam template and Directions

fully-aligned Language Reading and writing Multiple choice stems for units 1-9

Summer Reading
Literary , and specialty prompts.

General Writing Resources
Final projects, applied practice, sentence frames, youtube files.
*** Enter the $2,000 College Transitions No Essay Scholarship Contest ***
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023
Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- General Knowledge
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
$2,000 No Essay Scholarship
Presented by College Transitions
- Win $2,000 for college • 1 minute or less to enter • No essay required • Open to students and parents in the U.S.
Create your account today and easily enter all future sweepstakes!
Enter to Win $2,000 Today!
AP ® Lang teachers: looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Coach Hall Writes
clear, concise rhetorical analysis instruction.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Thesis
November 20, 2021 by Beth Hall
One of the first steps of writing a rhetorical analysis essay is knowing how to write a rhetorical analysis thesis.
Rhetorical analysis thesis statements can seem intimidating, but they do not have to be.
While the thesis is a small portion of an essay, it carries significant weight and impact, especially on the AP® Lang exam. For example, on AP® Lang rubric, a defensible thesis is one out of six possible points.
So, what is a defensible thesis and how do you write one for a rhetorical analysis essay?
A defensible thesis means that the thesis or position can be justified, proven, or defended.
You can craft a rhetorical analysis thesis statement with the following steps:
Step 1: As you are reading the passage, look for strategies or choices the author utilizes. Ask: What rhetorical choices does the writer/speaker make? (ie. juxtaposition, allusion, etc) This will be the basis of your thesis statement.
Step 2: Mention the author’s purpose in the thesis. Ask: Why did he/she make these choices? Why did he/she write this?
Step 3: Consider the effect on the audience. This step is not mandatory or always appropriate, but it can strengthen the thesis. The effect is looking at the author’s call to action. Ask: How does he/she want the audience to think/act?

Now that you understand the basis of a thesis statement, let’s talk about where this thesis goes in the essay.
The thesis is best placed in the introductory paragraph. By placing it in the introduction, it gives you a direction for your writing (and often where readers go looking for the thesis). The introduction contains the hook, context, and thesis statement. Often, the context and the thesis are combined together (look at the example below). The context identifies the specific passage you are talking about in your essay.
You can write only a thesis statement for an introductory paragraph if you are short on time, but it is better to have a well-developed introduction. If you want to know more about writing an introduction, you can watch the video here.
Let’s put this information together and look at an example of a thesis statement.
In Leonid Fridman’s passionate article “America Needs its Nerds,” ← context
he defines “geek” and contrasts America with other industrialized nations to develop his argument that America values athletes more than intellectuals. ← thesis
By doing so, Fridman urges readers to reprioritize the current social hierarchy. ← Effect
If you are feeling unsure about thesis statements or need a place to start, sentence frames are a great way to begin a thesis statement. Below are several sentence frames and examples to help you navigate thesis statements.
In SPEAKER/WRITER’S (tone) speech/letter/article (to AUDIENCE), he/she uses ___ and ____ to PURPOSE.
Note: The blanks in this sentence frame should be choices or strategies (nouns). For example, “he uses repetition and juxtaposition to…” Saying “uses” and then a device is rather simple. However, this sentence frame can lead to a defensible thesis. Once you understand this style of thesis writing, you can try more advanced styles.
In SPEAKER/WRITER’S (tone) speech/letter/article (to AUDIENCE), he/she ____ and ____ to PURPOSE.
Example: In his patriotic speech to Congress, President Roosevelt repeats “attacked” and “deliberate” as well as appeals to patriotism in order to convince Congress to declare war on Japan.
Example: In his patriotic speech to Congress, President Roosevelt repeatedly emphasizes the deliberate nature of the attack on Pearl Harbor and appeals to patriotism in order to convince Congress to declare war on Japan.
When you are ready to begin writing thesis statements on your own, remember to keep the following items in mind:
- A thesis identifies the strategies / choices AND purpose. Without both of these, it is not a defensible thesis.
- A thesis does not restate the prompt. Use the prompt as a guide, not as a thesis.
- A thesis answers the prompt. This may seem obvious, but it can be easy to get caught up in writing and lose track of your goal
Looking for more tips about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, check out this post here.
AP® Lang Teachers
Looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Latest on Instagram

Shop My TPT Store
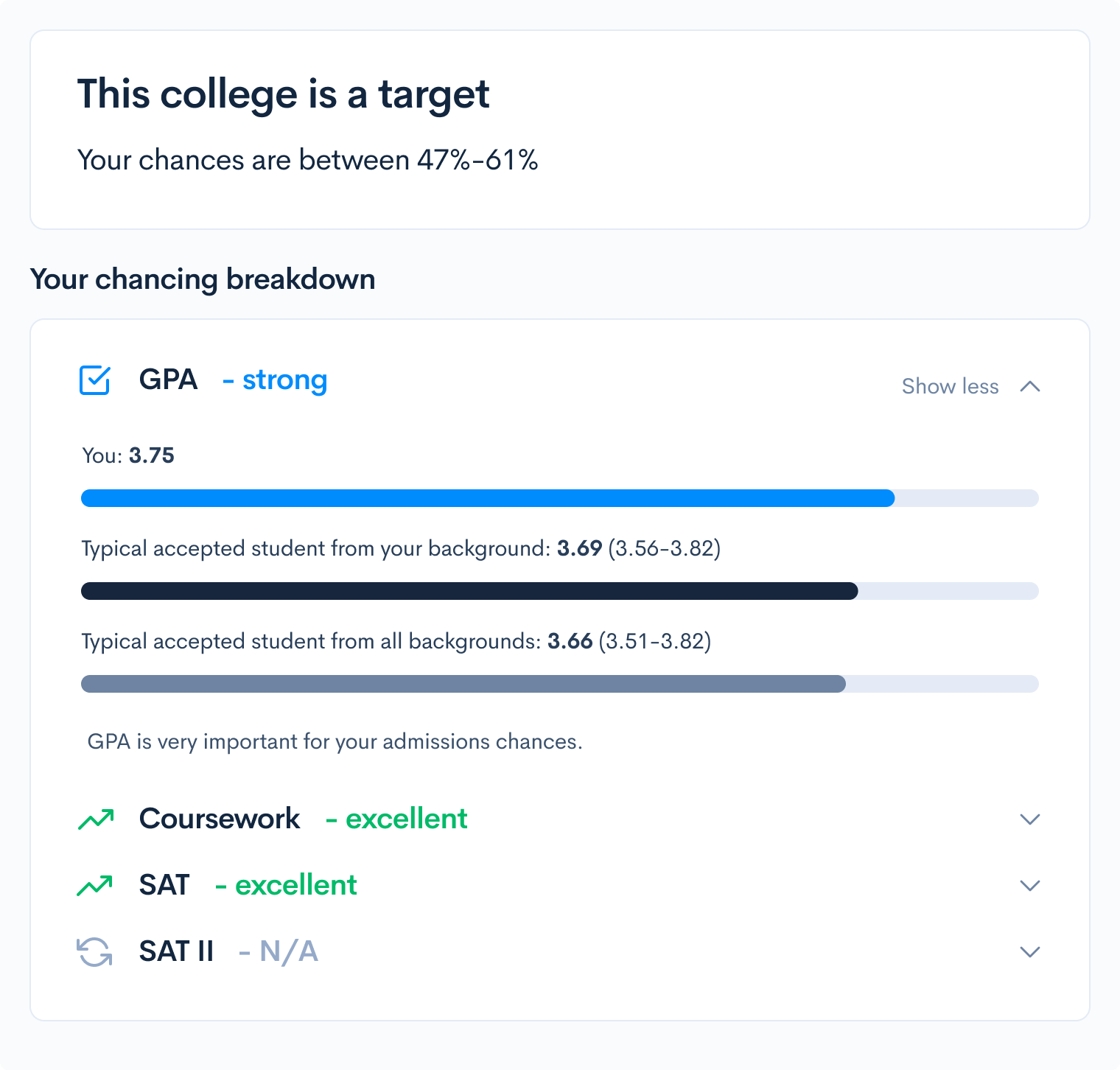
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Essay
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
What is the ap lang rhetorical essay, tips for writing the ap lang rhetorical essay.
- AP Lang Rhetorical Essay Example
How Will AP Scores Affect College Chances?
The AP English Language Exam is one of the most common AP exams you can take. However, the average score on the exam in 2020 was a 2.96 out of 5. While this may seem a bit low, it is important to note that over 550,000 students take the exam annually. With some preparation and knowing how to study, it is totally possible to do well on this AP exam.
The AP Lang Rhetorical Essay is one section of the AP English Language Exam. The exam itself is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, and is broken into two sections. The first part of the exam is a 60 minute, 45-question multiple-choice section. The questions on this part of the exam will test your ability to read a passage and then interpret its meaning, style, and overall themes. After the multiple-choice section, there is a section lasting 2 hours and 15 minutes with three “free response” essays. This includes the synthesis essay, the rhetorical analysis essay, and the argument essay.
- In the synthesis essay , you will have to develop an argument using pieces of evidence provided to you.
- The argumentative essay will have you pick a side in a debate and argue for or against it.
- The rhetorical essay requires that you discuss how an author’s written passage contributes to a greater meaning or theme.
The rhetorical essay is perhaps the most unique of all AP Lang exam essays because it requires the test taker to analyze and interpret the deeper meanings of the passage and connect them to the author’s writing style and writing syntax in only 40 minutes. This essay can be the trickiest because it requires you to have knowledge of rhetorical strategies and then apply them to a passage you’ve never seen before.
1. Outline Your Essay Before Writing
One of the most important parts of the AP Lang essays is structuring your essay so that it makes sense to the reader. This is just as important as having good content. For this essay in particular, you’ll want to read the passage first and write a brief outline of your points before you begin the essay. This is because you will want to write the essay using the passage chronologically, which will be discussed in detail below.
2. Understand Rhetorical Strategies
If you feel like you don’t know where to start as you prepare to study for the rhetorical essay portion of the exam, you aren’t alone. It is imperative that you have a grasp on what rhetorical strategies are and how you can use them in your essay. One definition of rhetoric is “language carefully chosen and arranged for maximum effect.” This can include types of figurative language (metaphor, simile, personification, pun, irony, etc.) elements of syntax (parallelism, juxtaposition, anthesis, anaphora, etc), logical fallacies, or persuasive appeals. Overall, there are many elements that you can analyze in an essay and having a good grasp on them through practice and memorization is important.
3. Keep the Essay Well Structured
Even if you understand the various rhetorical strategies you can use, where do you begin? First of all, you’ll want to write a strong introduction that outlines the purpose of the piece. At the end of this introduction, you will write a thesis statement that encapsulates all the rhetorical strategies you discuss. Perhaps these are style elements, tone, or syntax. Be sure to be specific as you list these.
Next, you will create your body paragraphs. As you discuss the rhetorical elements in the piece and tie them back to the work’s meanings, be sure to discuss the points in chronological order. You don’t have to discuss every single strategy, but just pick the ones that are most important. Be sure to cite the line where you found the example. At the end of the essay, write a short conclusion that summarizes the major points above.
4. Be Sure to Explain Your Examples
As you write the essay, don’t just list out your examples and say something like “this is an example of ethos, logos, pathos.” Instead, analyze how the example shows that rhetoric device and how it helps the author further their argument. As you write the rhetorical essay, you’ll want to be as specific and detail-focused as possible.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Below is a prompt and example for a rhetorical essay, along with its score and what the writer did well and could have improved:
The passage below is an excerpt from “On the Want of Money,” an essay written by nineteenth-century author William Hazlitt. Read the passage carefully. Then write an essay in which you analyze the rhetorical strategies Hazlitt uses to develop his position about money.

Student essay example:
In his essay, Hazlitt develops his position on money through careful use of adjectives and verbs, hypothetical situations, and images. His examples serve to impress upon the reader the highly negative consequences of being in “want of money.”
Hazlitt’s word choice in his opening phrase provides an example of his technique in the rest of the essay. It is not necessary to follow “literally” with “truly” yet his repetition of the same ideas emphasizes his point. In his next sentence, one that lasts forty-six lines, Hazlitt condignly repeats similar ideas, beating into his audience the necessity of having money in this world. The parallelism throughout that one long sentence, “it is not to be sent for to court, or asked out to dinner…it is not to have your own opinion consulted or sees rejected with contempt..” ties the many different situations Haziltt gives together. What could have become a tedious spiel instead becomes a melodious recitation, each example reminding you of one before it, either because of the similarities in structure or content. Hazlitt addresses many different negative effects of not having money but manages to tie them together with his rhetorical strategies.
The diction of the passage fully relays Hazlitt’s position about money. In every example he gives a negative situation but in most emphasizes the terrible circumstance with strong negative adjectives or verbs. “Rejected,” “contempt,” “disparaged,” “scrutinized,” “irksome,” “deprived,” “assailed” “chagrin;” the endless repetition of such discouragement shows how empathetically Hazlitt believes money is a requisite for a happy life. Even the irony of the last sentences is negative, conveying the utter hopelessness of one without money. Through one may have none in life, pitiless men will proceed to mock one’s circumstances, “at a considerable expense” after death!
In having as the body of his essay one long sentence, Hazlitt creates a flow that speeds the passage along, hardly giving the reader time to absorb one idea before another is thrown at him. The unceasing flow is synonymous with Hazlitt’s view of the life of a person without money: he will be “jostled” through life, unable to stop and appreciate the beauty around him or to take time for his own leisure.
The score on this essay was a 6 out of 6. This essay started out very strong as the student had a concrete thesis statement explaining the strategies that Hazlitt used to develop his position on money as well as Hazlitt’s belief on the topic. In the thesis statement, the student points out that adjectives, verbs, hypothetical situations, and images help prove Hazlitt’s point that wanting money can be problematic.
Next, the student broke down their points into three main subsections related to their thesis. More specifically, the student first discusses word choice of repetition and parallelism. When the student discusses these strategies, they list evidence in the paragraph that can be found chronologically in Hazlitt’s essay. The next paragraph is about diction, and the student used specific adjectives and verbs that support this idea. In the last paragraph, the student emphasized how the speed and flow of the essay helped describe Hazlitt’s viewpoint on life. This last concluding sentence is particularly thoughtful, as it goes beyond the explicit points made in the essay and discusses the style and tone of the writing.
It is important to remember that in some ways, the rhetorical essay is also an argumentative essay, as the student must prove how certain rhetorical strategies are used and their significance in the essay. The student even discussed the irony of the paragraph, which is not explicit in the passage.
Overall, this student did an excellent job organizing and structuring the essay and did a nice job using evidence to prove their points.
Now that you’ve learned about the AP Lang rhetorical essay, you may be wondering how your AP scores impact your chances of admission. In fact, your AP scores have relatively little impact on your admissions decision , and your course rigor has much more weight in the application process.
If you’d like to know your chances of admission, be sure to check out our chancing calculator! This tool takes into account your classes, extracurriculars, demographic information, and test scores to understand your chances at admission at over 600 schools. Best of all, it is completely free!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's look at an example of an excellent AP rhetorical analysis thesis statement: In her indignantly critical and cleverly crafted speech given to the National Association for Women's Suffrage, Florence Kelley clearly articulates and emotionally persuades her audience through the use of parallelism and inclusive language to advocate for changes to child labor laws.
verbs and cause/effect language in this section of your text: because, due to, since, so, consequently, etc.). Constructing Conclusion Paragraphs: 1. Identify 2-3 key ideas—singular abstract words—to which the essay relates. (Don't write these down.) 2. Generating a sentence that establishes the relationship between the ideas considered in
AP Lang Summer Reading: Thank You For Arguing. Literary and Rhetorical Verbs. Literary Analysis. Rhetorical Analysis. Lit Templates with Examples (Q 1-3) How to Write Rhetorical Analysis. How to Write Rhetorical Analysis. Rhetorical Analysis Templates and Guide. RA Templates & Guide Without Examples ... & Thesis. Lit Q2- Body Paragraphing ...
A strong thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis is NOT… A simple statement of your topic A broad statement A statement of facts or statistics A summary of the author's essay you are analyzing A statement of what you're going to do in the essay Examples of weak rhetorical analysis thesis statements:
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication. At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category.
rhetorical analysis essay. Below is one way that is a good, simple format to help you get started. You may find as you become more comfortable with analysis that you want to deviate from this format. That's fine as long as you are still focusing on numbers 1-3 from above. Introduction The introductory paragraph to an analysis essay is usually ...
While the thesis is a small portion of an essay, it carries significant weight and impact, especially on the AP® Lang exam. For example, on AP® Lang rubric, a defensible thesis is one out of six possible points. So, what is a defensible thesis and how do you write one for a rhetorical analysis essay? A defensible thesis means that the thesis ...
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Template Title: [Your Essay Title] Introduction 1. Hook: Start with an engaging statement or question to grab the reader's attention. 2. Background Information: Provide context about the text you are analyzing, including the author, title, and main argument or purpose. 3.
The rhetorical essay is perhaps the most unique of all AP Lang exam essays because it requires the test taker to analyze and interpret the deeper meanings of the passage and connect them to the author's writing style and writing syntax in only 40 minutes. This essay can be the trickiest because it requires you to have knowledge of rhetorical ...
D:\My Documents\Orlando Teacher docs\AP LANG and COMP\2 Close Reading The Art and Craft of Analysis HOW TO WRITE: AP Rhetorical Analysis Paragraphs and Essays Things you must know in order to accurately analyze a text: 1. SOAPS 2. Rhetorical Strategies a. Appeals (ethos, logos, pathos) b. Style (diction, syntax, details, imagery, tone, etc.) 3.