
What part of speech is “team”

Learn all the parts of speech for different words and understand how to use them in the English language
Definition :
A team is a group of two or more people working together to achieve a common goal or purpose. Teams are often considered to be forms of collective social interaction and are often used in sports, work and other activities.
rules and use cases associated with the word 'team' in this part of speech is that it is a collective noun used to refer to a group of people, and it should always be used as a singular noun even though it is made up of multiple people.
1. The Sharks basketball team won their last game.
2. Our team worked together to solve the problem.
3. She is an integral part of the team.
When referring to teams, it is important to remember that although it is made of multiple people, it is still considered a singular noun and therefore verbs used in sentences with 'team' should always be in the singular form. For example, 'The team are discussing their plans' should instead be 'The team is discussing their plans'.
as an adjective, 'team' is used to describe something that is related to or characteristic of a group of people working together.
When 'team' is used as an adjective, it typically modifies nouns, providing more information about the nature of the noun in relation to a collective group.
1. The team effort was commendable, leading to the project's success.
2. They attended a team building workshop to improve their collaboration skills.
3. The coach praised the team spirit displayed during the match.
'Team' as an adjective often refers to activities, attributes, or events that involve or are intended for a group working together. It's important not to confuse the adjective form with the noun form. For instance, 'team effort' (adjective + noun) vs. 'the team' (noun).
as a verb, 'team' means to come together to achieve a common goal. It's often used in the phrasal verb form 'team up.'
When 'team' is used as a verb, it typically indicates the action of joining forces or collaborating.
1. The two companies decided to team up for the new project.
2. She teamed with her colleague to complete the assignment on time.
3. Local businesses are teaming up to support community events.
'Team up' is often followed by 'with' to indicate the parties involved in the collaboration. Be cautious not to confuse the verb form with the noun form. For instance, 'They teamed up' (verb) vs. 'They are a team' (noun). 'Team' as a verb is more colloquial and is often used in informal contexts.
Learn words and related parts of speech through practical exercises
Learn more about parts of speech.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
General Education
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

Home » All Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
All Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
Parts of speech are important in learning English because they help us understand how words work together in sentences. Just like puzzle pieces fit together to create a picture, parts of speech fit together to create meaningful sentences. When we know the different parts of speech, we can use them to build sentences correctly. It’s like having a set of rules or guidelines that show us how words should be used. For example, nouns are like the names of people, places, or things, while verbs show actions or states of being. By knowing the parts of speech, we can express ourselves clearly and accurately. We can choose the right words to describe things, show actions, or express ideas. It’s like having a toolbox of words that we can use to communicate effectively.
8 Parts of Speech
Types of nouns, types of pronouns, types of adjectives, types of verbs, all types of adverbs, types of prepositions, types of conjunctions, types of interjections, preposition, conjunction, interjection.
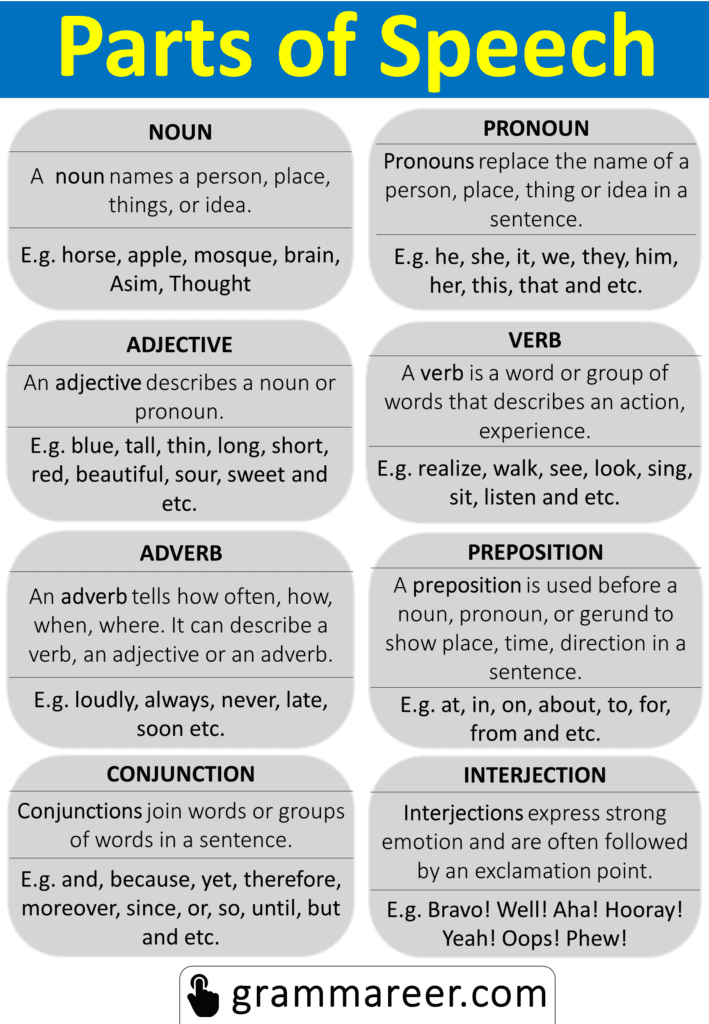
All Parts of Speech Chart with Examples
A noun is a word that gives a name to a person , place , thing , or idea . It helps us identify and talk about the stuff around us.
- People : teacher, doctor, student, friend, mother, father
- Places : city, park, school, restaurant, beach, home
- Things : book, table, chair, car, phone, computer
- Person: man, teacher, friend
- Place: city, park, school
- Thing: book, table, car
- Person: John, Mary, Michael
- Place: Paris, London, New York
- Thing: Coca-Cola, Nike, Titanic
- Dog, tree, house, ball, flower
- Love, happiness, courage, friendship, knowledge
- Team, family, flock, herd, swarm
- Cat (singular), cats (plural)
- Book (singular), books (plural)
- Chair (singular), chairs (plural)
- Water, happiness, information, sugar, knowledge
A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun . It helps us avoid repeating the same noun over and over again in a sentence. Instead, we can use a pronoun to refer to the noun.
- I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
- This, that, these, those
- Myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves
- Who, whom, whose, which, what
- Who, whom, whose, which, that
- Someone, anyone, nobody, everybody, something, anything, nothing, everything
- Each other, one another
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun . It provides more information about the qualities, characteristics, or attributes of the noun or pronoun it is describing.
- Beautiful, Few, These, Her, Which
- Big: a big house
- Red: a red car
- Beautiful: a beautiful sunset
- Many: many books
- Few: a few friends
- Several: several cups
- This: this book
- That: that pen
- These: these shoes
- Those: those flowers
- Your: your house
- His: his car
- Her: her cat
- Our: our team
- Which: which color
- What: what time
- Whose: whose bag
- Taller: a taller building
- More interesting: a more interesting movie
- Bigger: a bigger house
- Tallest: the tallest tree
- Most delicious: the most delicious cake
- Happiest: the happiest child
- American: American culture
- Italian: Italian cuisine
- French: French fashion
A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. It describes what someone or something does, experiences, or is.
- Feel, seem, taste, run, eat, jump, think, write, dance
Here are the types of verbs explained in easy language:
- Run, eat, jump, think, write, dance
- Be, appear, become, feel, seem, taste
- Can, will, must, should, have, may
- Could, would, should, might, must
- Eat (I eat an apple.), read (She reads a book.), kick (He kicks the ball.)
- Sleep, laugh, run, arrive
- Talk (present), talked (past), talked (past participle)
- Go (present), went (past), gone (past participle)
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb . It provides more information about how, when, where, why, or to what extent an action occurs or a quality is expressed.
- Always, often, Carefully, soon, never
- Yesterday, today, now, soon, always
- Here, there, inside, outside, nearby
- Carefully, quickly, happily, softly, loudly
- Very, extremely, quite, too, completely
- Always, often, sometimes, rarely, never
- Therefore, because, hence, thus, consequently
- To, in order to, so as to, for
- How, when, where, why, how often
- When, where, why
- However, therefore, furthermore, meanwhile, nevertheless
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and another word in a sentence. It indicates location, time, direction, manner, or other relationships.
- At, Before, From, Towards, By, For
- In: She is in the room.
- On: The book is on the table.
- At: They met at the park.
- Under: The cat is under the bed.
- Above: The bird is flying above the trees.
- Before: We had dinner before the movie.
- After: She arrived after the party started.
- During: I read a book during my vacation.
- At: They will meet at 7 p.m.
- On: The concert is on Friday.
- To: He walked to the store.
- From: She received a letter from her friend.
- Into: The children jumped into the pool.
- Out of: The cat jumped out of the box.
- Towards: He ran towards the finish line.
- With: She painted the picture with a brush.
- By: The book was written by the author.
- Like: He sings like a professional.
- In: She spoke in a soft voice.
- Because of: The game was canceled because of the rain.
- Due to: The flight was delayed due to bad weather.
- For: He received applause for his performance.
- Thanks to: Thanks to her help, I finished the project.
- Of: The pages of the book are torn.
- With: She entered the room with a smile.
- By: The song was written by John.
- With: The vase was made with clay.
- In: She is in good health.
- On: The dog is lying on the mat.
- For: She bought flowers for her mother.
- To: They went to the beach for relaxation.
- According to: According to the report, the sales increased.
- In front of: The car is parked in front of the house.
- Next to: The bookstore is next to the café.
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses together in a sentence. It helps to show relationships between these elements and coordinate their meaning within a sentence.
- But, Although, Whether…or, However, Where
- And: I like apples and oranges.
- But: He studied hard, but he failed the exam.
- Or: Would you like tea or coffee?
- So: She studied well, so she passed the test.
- Yet: He was tired, yet he continued to work.
- Because: He stayed home because he was sick.
- Although: Although it was raining, they went for a walk.
- If: If you study hard, you will succeed.
- While: She read a book while waiting for the bus.
- Either…or: You can either have pizza or pasta.
- Neither…nor: Neither he nor she attended the party.
- Both…and: She is both intelligent and hardworking.
- Whether…or: I haven’t decided whether to go or stay.
- However: She studied hard; however, she didn’t perform well.
- Therefore: It rained heavily; therefore, the match was canceled.
- Meanwhile: He cooked dinner; meanwhile, she set the table.
- Before: She left before I arrived.
- Where: I found a book where I least expected.
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotions, sudden reactions, or exclamations . It is used to convey feelings or add emphasis to a sentence.
- Ouch!, Hooray!, Bravo!, Fantastic!, Oh no!
- Wow! That’s an amazing view!
- Oh no! I forgot my keys!
- Ouch! That hurt!
- Yay! We won the game!
- Hi! How are you doing?
- Hello! Nice to meet you.
- Hey! What’s up?
- Hooray! We’re going on vacation!
- Yippee! It’s my birthday!
- Yahoo! I aced the exam!
- Whoa! That’s incredible!
- Oh my goodness! I can’t believe it!
- Good heavens! Look at the size of that!
- Bravo! Well done!
- Excellent! You did a great job!
- Fantastic! I love your idea!
- Ugh! I can’t believe this mess.
- Oh no! That’s not good.
- Yuck! This food tastes awful.
- Common Noun Definition and Examples
You may also like
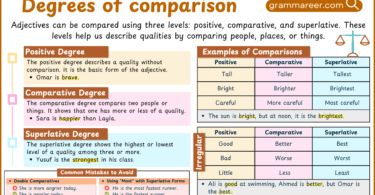
Degrees of Comparison of Adjectives with Examples

Linking Verbs in English with Example Sentences

Reflexive Pronouns: Definition, Uses and Examples
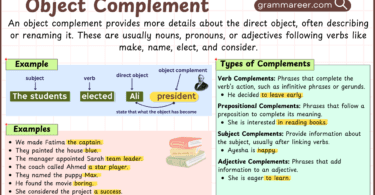
Object Complements in English with Examples

The Eight Parts of Speech in English (PDF)
In this article, we will provide a clear overview of the eight essential parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
What are the eight parts of speech?
Think of parts of speech as roles within a sentence. Just as individuals can hold various job titles—such as soldier, teacher, or baker—words can serve different purposes based on their functions. Whether a word acts as a noun, pronoun, verb, or any other part of speech determines its role in conveying meaning.
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
At the end of this article, you’ll find a downloadable PDF that includes examples of each part of speech, making it easier to apply your knowledge.
Parts of Speech Grammar Table
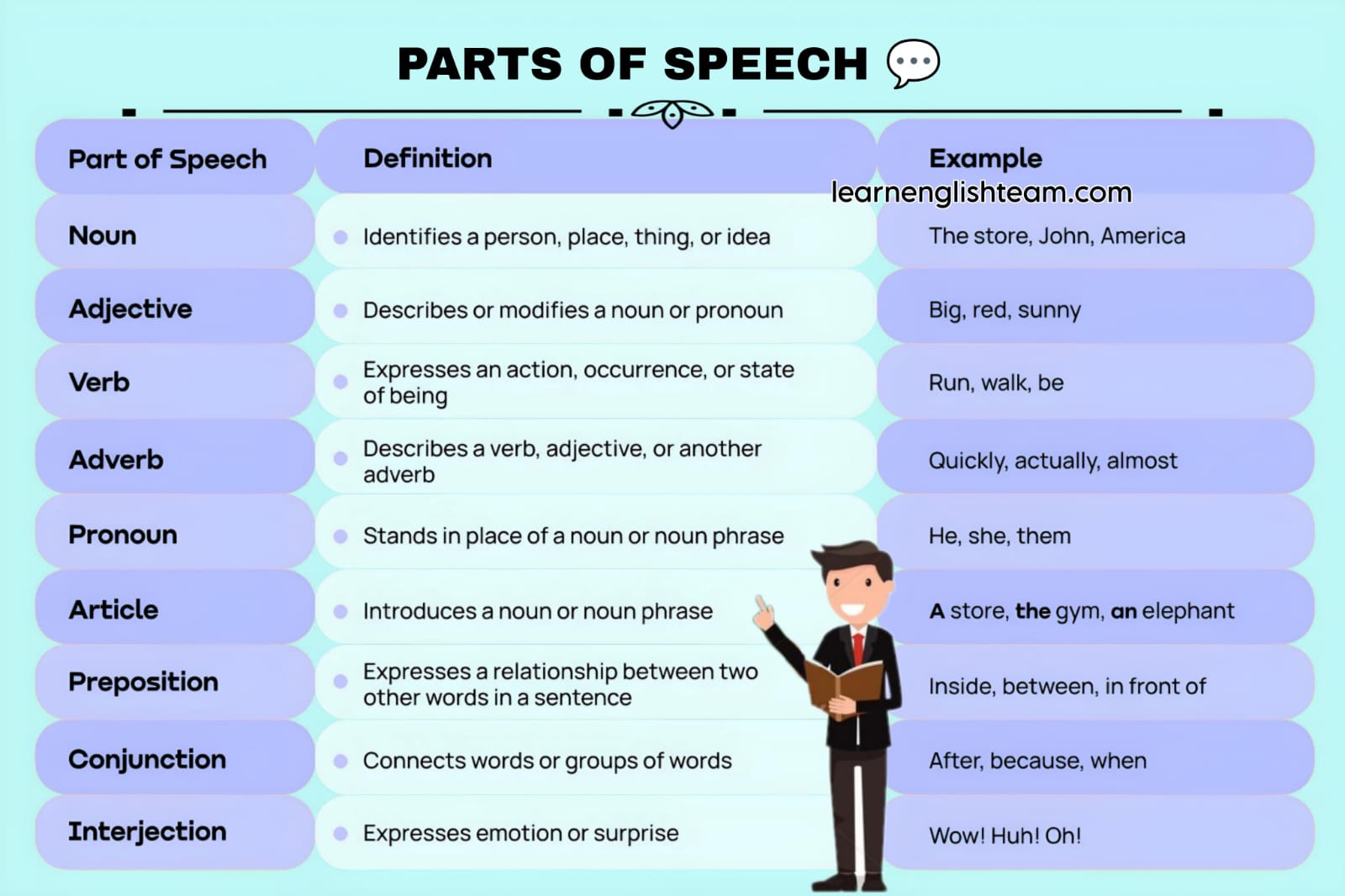
The 8 Parts of Speech

Nouns are separated into common nouns and proper nouns .
What is a common noun?
Common nouns are used for people, animals, places, or things.
Example: granny, mother, river, mountain, hotel, taxi, fox, camel.
He is an artist . Tom hates bananas . I love my mother . Her father is a doctor .
What is a proper noun?
Proper nouns are names for particular people, places or things. They always begin with a capital letter.
Example: Ali Baba, Harry Potter, Beethoven, Turkish, British, Malay, Hong Kong, India, The United Kingdom,the Pacific Ocean, the Eiffel Tower, Father’s Day, Ramadan, Halloween.
☛ The days of the week and months of the year are also proper nouns.
December is the last month of the year. Sunday is the last day of the week.
What is singular and plural noun?
When you are talking about one person, animal, place, or thing, use a singular noun .
Example: a ship, a teacher, a river, an apple, an umbrella.
When you are talking about two or more people, animals, places, or things, use plural nouns . Most nouns are made plural by adding -s at the end.
Example: ships, teachers, rivers, apples, umbrellas
Some exceptions: bus-buses. glass-glasses. watch-watches. brush-brushes. butterfly-butterflies. baby-babies. lady-ladies. story-stories.
☛ Nouns show possession by adding ‘s.
☛ Tom’s car. ☛ Car’s key.
What is concrete and abstract noun?
Concrete nouns are things you can experience (see, hear, smell, touch, or taste) with your senses. Here are some examples: tree, music, flowers, and chocolate.
Abstract nouns represent ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be perceived through the senses. Examples include love, honesty, joy, and freedom.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of nouns in English:
Check Also: Common and Proper Nouns Explained (Exercise and Examples) Masculine and Feminine Nouns in English 100 Most Common English Nouns A-Z List (PDF)

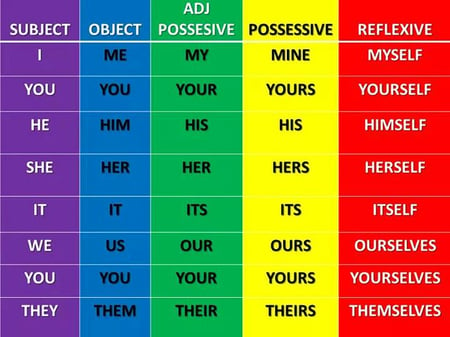
Personal Pronouns: The words I , you , he , she , it , we and they are called personal pronouns. He is a nice guy. You are welcome.
Possessive Pronouns: The words mine , yours , hers , his , its , theirs , ours , yours , theirs are called possessive pronouns. This car is mine . Time is yours .
Reflexive Pronouns: The words myself , yourself , himself , herself , itself , ourselves , yourselves and themselves are called reflexive pronouns. Maryam has hurt herself . Don’t cut yourself .
Demonstrative Pronouns: The words this , these , that and those are called demonstrative pronouns. This is my car. These are my flowers.
Interrogative Pronouns: The words who , whom , whose , what and which are called interrogative pronouns. We ask questions by using these pronouns. Who is she talking to? Which do you prefer?
Here’s a table with examples of different types of pronouns in English:
Check Also: Personal & Possessive Pronouns for English Learners Nobody, No one, None Difference & Examples Difference Between Who and Whom

Most verbs are action words. Verbs shows you what people, animals or things are doing.
Verbs can show actions or they can show states or situations.Those are the two types of verbs in English.
☛ I am eating. – verb (eat) shows an action. ☛ I am a student. verb (to be) shows a state.
☛ Verbs also change and take different forms to show tenses.
I drink a lot of water ☛ I drank a lot of water yesterday.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of verbs in English:
Check Also: 500+ English Verbs List (V1 V2 V3 Verb Forms) + PDF Most Common English Verbs & Synonyms List (PDF) All forms of the verb TO BE and Its Usage
4. ADJECTIVE

The red carpet. Deep thoughts. A busy street. She is beautiful today.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of adjectives in English:
Check Also: List of Opposite Adjectives in English (PDF) Positive Adjectives to Describe a Person (PDF) Comparative and Superlative Adjectives List + PDF

☛ A lot of adverbs end in -ly.
We are happily married. Tom calls me regularly . Suddenly , she knows. It’s love!
Here’s a table with examples of different types of adverbs in English:

Check Also: Types of Adverbs in English & Meaning and Examples (PDF) Common Suffixes in English (With Examples) & PDF
6. PREPOSITION

Prepositions tell us about time, position or place.
Some examples of prepositions are words like ‘ in ,’ ‘ at ,’ ‘ on ,’ ‘ of ,’ ‘ to ,’ ‘ from .’
She is in love. Book was on the table. I am from France. He is calling to you. Where are you at ?
Here’s a table categorizing types of prepositions with examples:
Check Also: Complete List of English Prepositions A-Z (Free PDF) Commonly Used Prepositions Lists in English Common Collocations in English With Prepositions (PDF) Prepositions of Location At, In & On (PDF)
7. CONJUNCTION

Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses together.
a teacher and students. a male or female?
☛ Words such as before , after , as , when , while , until , since , are conjunctions of time. Maryam could play guitar before she was four. She always brush her teeth after eating her meal.
There are four categories of conjunctions:

8.INTERJECTION
An interjection is a word that expresses an emotion, sudden, strong feeling such as surprise, pain, or pleasure.
☛ It is often followed by an exclamation point.
Check Also: Interjections in English Grammar & List Examples 1000+ Common Daily English Phrases for Beginners (PDF)

Parts of Speech PDF
Here you can download parts of speech PDF with examples.
Parts of Speech in English PDF – download
You May Also Like

Difference Between Race and Ethnicity in English ✍️

Conversational English – Greetings and Salutations Examples
Opposite Adjectives in English: A Guide for Learners (PDF)
Best examples for the students
Pratik dhamane
Useful lecture for whom studying English language from beginning. we hope you to upload more grammar lecture in pdf form
Sure! Don’t forget to subscribe our new lessons. 🙂
Very nice, thanks for the PDF.
Thanks for free PDF file.
I’m really enjoy Learning English.l find to the best to me

Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives, the top issue related to adverbs.
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Identify Parts of Speech
Last Updated: September 25, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Alexander Peterman, MA . Alexander Peterman is a Private Tutor in Florida. He received his MA in Education from the University of Florida in 2017. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 403,877 times.
Parts of speech are categories that are used to describe each word's function in a sentence. The best way to identify a word's part of speech is to think about what role the word plays in the sentence, but there are also a few clues that can help you figure out the part of speech if you are unsure about the word's function.
What Are the Parts of Speech?
- A noun is a word that names a person, place, or thing.
- Pronouns are words that stand in for nouns, like “he,” “she,” or “they.”
- Verbs are words that express an action, like “run” or “drive.”
- Adjectives are words that describe nouns, like “blue” or “pretty.”
- Adverbs are words that describe verbs or adjectives, like “happily.”
- Prepositions like “at” express the relationship between 2 words.
- Conjunctions are words that connect other words, like “and” or “but.”
- Interjections are exclamations of emotion, like “oh” or “wow!”
Analyzing the Word's Function

- Proper nouns are used to name a specific person, place, or thing, and the main words are always capitalized (Fred, New York, the Declaration of Independence).
- Nouns can be either singular or plural.
- Nouns can be possessive, in which case they typically end in 's or s'.

- Some pronouns stand in for people's names (he, our, they, hers, etc.).
- Other pronouns represent an object or idea (it, these, this, etc.).
- Pronouns may also stand in for very indefinite nouns that may be difficult to name without the use of a pronoun (everyone, no one, something, etc).

- Auxiliary verbs (also known as helping verbs) are words that are used to change the tense of the main verb (will, did, would, etc.). These are still considered verbs.

- Numbers are considered adjectives when they are used to answer the question "how many?"
- Articles (a, an, and the) are considered adjectives by many because they answer the question "which one?" However, some people consider articles to be a separate part of speech.

- Adverbs may also modify other adverbs. (I ran very quickly.)

- Coordinating conjunctions are used to join two clauses that are equally important to the sentence. There are 7 coordinating conjunctions: and, but, for, nor, or, so, and yet. (I like cats, but I don't like dogs.)
- Subordinating conjunctions are used to join a main clause and a subordinate clause, which is less important to the sentence. (I went outside, although it was raining.)

Using Word Placement and Punctuation Clues

- Both the subject and object of a sentence will contain a noun or pronoun. This means that a sentence that has both a subject and an object will contain a noun or pronoun both before and after the verb. ( I ate the apple .)
- The subject and object may contain modifiers such as adjectives as well.
- When the sentence has a direct object, it will come directly after the verb. (I like cookies .) When the sentence has an indirect object, it will come after a preposition. (I gave the card to Frank .)

- Adjectives are almost always found before nouns and pronouns (We look at a red dress.) or after the linking verb "to be" (The dress is red .)
- When adverbs are used to modify adjectives, they are almost always found right before the adjective. (The meal was truly delicious.)
- When adverbs are used to modify verbs, they may be found before the subject ( Later I will walk to school.), directly before the verb (I will carefully clean the artifacts .), or directly after the verb. (I go to the park frequently .)

- Conjunctions like "and" and "but" are sometimes used at the beginning of a sentence, although this is more rare. When it is done, you should be able to identify the other clause or phrase in the previous sentence.

- Not all interjections are marked by exclamation points. Don't rely on exclamations as the only way to recognize interjections.
- Another clue that a word might be an interjection is that it is used alone. If there are other words in the sentence, it is less likely to be an interjection.

- Keep in mind there may be an adjective, adverb, and/or article between the preposition and the noun or pronoun. These modifiers are all considered to be part of the noun or pronoun phrase. (We paid for the very expensive jeans.)
Using Suffix Clues to Identify Parts of Speech

- -ion (population)
- -sion (tension)
- -tion (attention)
- -acy (accuracy)
- -age (image)
- -ance (allegiance)
- -ence (permanence)
- -hood (childhood)
- -ar (scholar)
- -or (editor)
- -ism (idealism)
- -ist (realist)
- -ment (government)
- -ness (sadness)
- -y (beauty)
- -ity (capacity)

- -al (clerical)
- -ful (wonderful)
- -ly (friendly)
- -ic (chronic)
- -ish (squeamish)
- -like (childlike)
- -ous (contagious)
- -ate accurate
- -able (laughable)
- -ible (horrible)

- -ify (typify)
- -ate (proliferate)
- -ize (rationalize)
- -en (tighten)

- There are some words that end in -ly that are not adverbs (butterfly), so be careful not to overgeneralize.
- There are also a few adverbs that do not end in -ly (well, fast, very, etc.).
Practice Questions and Answers

Community Q&A
- Context is key, as some words can act as multiple different parts of speech, depending on their role in a sentence. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/nouns/
- ↑ https://www.thesaurus.com/e/grammar/what-are-the-types-of-pronouns/
- ↑ https://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/grammar/parts_of_speech.html
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/grammar/prepositions
- ↑ https://www.thesaurus.com/e/grammar/whats-a-conjunction/
- ↑ https://www.plainlanguage.gov/guidelines/concise/keep-the-subject-verb-and-object-close-together/
- ↑ https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/grammar/adjectives-and-adverbs/1/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/punctuation/independent_and_dependent_clauses/index.html
- ↑ https://www.thesaurus.com/e/grammar/what-is-an-interjection/
- ↑ https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/grammar/british-grammar/suffixes
About This Article

To identify different parts of speech, analyze the function that the word plays in a sentence. If the word names a person, place, thing, or idea, it is a noun. Label a word as a pronoun if it takes the place of a noun. If you see a word that expresses an action, that is a verb, and words that modify a verb are adverbs. If a word modifies a noun or pronoun, it is an adjective. To learn how to identify prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 26, 2017
Did this article help you?

Haven Weldem
Nov 1, 2017
May 7, 2022
Pannindriya Lam
Nov 18, 2019
Rohane Nayak
Jun 10, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Definition & Examples
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyse how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, ‘laugh’ can be a noun (e.g., ‘I like your laugh’) or a verb (e.g., ‘don’t laugh’).
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, other parts of speech, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Upload my document
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., ‘jump’), occurrence (e.g., ‘become’), or state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., past simple ), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding’-ed’ to the end of the word (or ‘-d’ if the word already ends in ‘e’). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
‘I’ve already checked twice’.
‘I heard that you used to sing ‘.
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., ‘a red hat’), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like ‘to be’ (e.g., ‘the hat is red ‘).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding ‘-ly’ to the end of an adjective (e.g., ‘slow’ becomes ‘slowly’), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., ‘at’) or phrase (e.g., ‘on top of’) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., ‘the door’, ‘the energy’, ‘the mountains’).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., ‘a poster’, ‘an engine’).
There’s a concert this weekend.
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., ‘a dog’, ‘an island’).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., ‘ in the field’)
- Noun (e.g., ‘I have an in with that company’)
- Adjective (e.g., ‘Tim is part of the in crowd’)
- Adverb (e.g., ‘Will you be in this evening?’)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., ‘a cup and plate’), or two adjectives (e.g., ‘strong and smart’). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use 'The', 'A' or 'An'
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
- teammate: a person who is on a team with you.
- teamwork: work done together with others.
- Humanities ›
- English Grammar ›
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). Open classes can be altered and added to as language develops, and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , parts of speech are generally referred to as word classes or syntactic categories. The main difference is that word classes are classified according to more strict linguistic criteria. Within word classes, there is the lexical, or open class, and the function, or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below, and practice identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, and they're called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence . They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became.
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Many adjectives can be turned into adjectives by adding the suffix - ly . Examples: softly, quickly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spatial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples of articles: a, an, the ; examples of determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun (or converted adjective) work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject, and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a verb command with an understood "you" noun.
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- What Are Word Blends?
- Figure of Speech: Definition and Examples
- Definition and Examples of Adjectives
- Subjects, Verbs, and Objects
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples
- What Is The Speech Act Theory: Definition and Examples
- A List of Exclamations and Interjections in English
- Definition and Examples of Discourse
- What Is Nonverbal Communication?
- Examples and Usage of Conjunctions in English Grammar
- Definition and Examples of Ambiguity
- Linguistic Variation
- Definition and Examples of Interjections in English
- Understanding the Types of Verbs in English Grammar
- Complex Words in English
- Definition and Examples of Jargon
- Encyclopedias
Definitions
- Word Finders
- Letterpress
- Spelling Bee
- Words with friends
- Apalabrados
- Words of Wonders
- Text to speech
Parts of speech
- Numbers to words
- Phonetic spelling
- Terms of use
Modal title
What part of speech is team.
Team can be categorized as a noun and a verb .
- 1. team is a verb, present, 1st person singular of team (infinitive).
- 2. team is a verb (infinitive).
- 3. team is a noun, singular of teams .
Inflections
- Infinitive Present Simple Past Past Participle Gerund
- (to) team team / teams teamed teamed teaming
- Infinitive : (to) team
- Present : team / teams
- Simple Past : teamed
- Gerund : teaming
- Singular Plural
- team teams
- Singular: team
- Plural: teams
What does team mean?
Examples of team, last searches.
The 8 Parts Of Speech In English
There are eight major parts of speech .
- Nouns name persons, places, things, ideas, or qualities, e.g., Franklin, boy, Yangtze River, shoreline, Bible, desk, fear, happiness.
- Pronouns usually substitute for nouns and function as nouns, e.g., I, you, he, she, it, we, they, myself, this, that, who, which, everyone.
- Verbs express actions, occurrences, or states of being, e.g., be, become, bunt, inflate, run.
- Adjectives describe or modify nouns or pronouns, e.g., gentle, helpful, small.
- Adverbs describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, e.g., almost, gently, helpfully, someday.
- Prepositions relate nouns or pronouns to other words in a sentence, e.g., about, at, down, for, of, with.
- Conjunctions link words, clauses, and phrases. There are coordinating conjunctions that link words, clauses, or phrases of equal importance, and there are subordinating conjunctions that introduce subordinate clauses and link them to main clauses.
- Interjections express feeling or command attention, either alone or in a sentence, e.g., darn, hey, oh, wow.
Some words ( adjectives , adverbs , interjections , nouns , verbs ) are productive classes allowing new members; others, with functional rather than lexical meaning ( articles , conjunctions , prepositions ) are nonproductive and have a limited number of members.
Some grammarians consider articles , quantifiers , and numerals to also be parts of speech.
Language Stories

Trending Words
Hobbies & Passions
Word Origins
[ daw -gid-lee ]
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Parts of Speech
- Sentence Structure
- Sentence Types
- Rules & Usage
- Punctuation
- How to Diagram
- Diagramming Index
- Diagramming Together
- Contact & FAQ
- Stream the Documentary
- Testimonials
- What part of speech is this?
If you've ever found yourself wondering what part of speech a word is, you're not alone. In this lesson, we'll explore how to answer that question as well as why that answer can seem a bit confusing. You'll also find a quiz at the bottom of the page so that you can test yourself, along with a free PDF download. Jackpot!
Would you like to make this lesson more interactive? Download the free ebook.

If you'd like to fill out your answers as you move through this lesson, download the guide before you watch the video.
If you'd like to print it out and you're serious about conserving the ink in your printer, print only pages 4, 9, 10, and 11.
Pop quiz, hot shot! Let's say you're at the grocery store deciding between chunky and creamy peanut butter (tough choice) when someone walks up to you and asks, "What part of speech is the word love ?"
Obviously, the first thing to do is run away from this person. But then, your mind might linger on that question, and you might start to wonder Hmm ... what part of speech is the word love anyway?
At that point, you would probably think of some example sentences to figure it out.
I love peanut butter.
From this sentence, you might conclude that love is a verb since you know that verbs express action, and love is showing an action in this sentence.
You wouldn't be wrong, but then you might think of this sentence:
Love for peanut butter brought me to the store today.
Wait a minute! Here, love is a noun. It's an idea, and it's the subject of the sentence. What's the deal? How can love be a verb and a noun?
Here's a secret about the parts of speech that many people don't realize:
Many words can function as more than one part of speech.
They will only be doing one part-of-speech job at a time, though. In our example sentences above, we can see that love can be a verb and a noun, and we can also see that it's doing just one of those jobs in each sentence.
How can you figure out what part(s) of speech a word can be, and how will you know what the word is acting as in any given sentence?
The first thing to do is to study the parts of speech and understand how they work.
Here's what you can do after you have a sense of what the parts of speech are and how they work:
What part(s) of speech can this word be?
Look up the word in a dictionary. Dictionaries will show you the possible parts of speech that a word can function as. You can use a dictionary that's an actual book, an online dictionary, or your device's built-in dictionary. The dictionary will list each word's possible part of speech, and it will give you definitions for all of the meanings of a word within each part of speech.
What part of speech is this word in this sentence?
In order to figure out how a word is functioning, w e need to look at the word within the context of a sentence. Look over your sentence, and then open up your dictionary. Match the meaning of the word in your sentence with the most fitting dictionary definition. Then you'll be able to tell what part of speech it is in your sentence.
Let's look at two examples of words acting as different parts of speech.
We'll look at the words for and iron , and we'll see them acting as different parts of speech. We'll also take a peek at what the dictionary says for each word.
What part of speech are the words in bold?
I asked for pie.
I cried, for I knew that the pie was gone.
Where is the iron ?
Please iron my shirt.
I asked for pie. (preposition)

1. Just below the word that you look up, you'll find a listing for a part of speech. The first listing is usually the most common way that the word is used. For is most commonly used as a preposition .
2. Next, you'll find definitions of the word for each part of speech. If there is more than one definition, they'll be numbered. There are many definitions for for as a preposition, and here you can see two.
3. After the definition, you'll often find an example of how to use the word as that part of speech and definition. You can see the examples in italics.
I cried, for I knew that the pie was gone. (conjunction)

1. Below all of the definitions for for as a preposition, we can see a listing for another part of speech. It's here that we see that for can also be a conjunction .
2. Here's the definition. It's not numbered because there is only one entry for for as a conjunction.
3. Here is an example sentence for us. (It's strange, though, that they also used for as a preposition in this example as well as a conjunction!)
Where is the iron ? (noun)

1. The first part of speech listed under iron is noun .
2. The first two definitions of iron as a noun weren't the ones used in the sentence above, but the third entry was what I was looking for.
3. They don't give us an example sentence. Boohoo!
Please iron my shirt. (verb)
1. Underneath all of the definitions for iron as a noun, I came here which let me know that iron can also be used as a verb .
2. There's only one definition for iron as a verb, so they didn't number this entry.
3. Again, there's no example sentence. Perhaps everyone at the dictionary company called in sick on the day that they had to write example sentences for iron .
Test Yourself
I. Label the Parts of Speech
Directions : Name the part of speech for the underlined word in each sentence. Use a dictionary if you need one. For extra credit, diagram the sentences . :) Scroll down to see the answers.
a) I will light the fire.
b) Can you see that red light ?
c) This light jacket isn't warm enough.
2. FAST
a) Hadley is a fast runner.
b) The 12-hour fast cleared my mind.
c) He drives fast !
a) I had a general sense of how it works.
b) The general sank low in his chair.
a) Practice piano before you play with your friends.
b) Practice piano before dinner.
a) Roll the dice.
b) I will eat the soup with a roll .
a) I like old books.
b) They acted like old friends.
c) The boys had like interests.
a) The kids were awake till midnight.
b) Open the till and count the money.
c) My grandpa, a farmer, would till his soil in the spring.
a) Cup your hands around your mouth and yell.
b) I'll use the red cup .
a) The long drive through the countryside lifted my spirits.
b) I always drive within the speed limit.
a) Everyone in the family photo wore blue .
b) Jackie lives in the blue house.
Would you like to download this lesson?

- 20 Pages
- Includes all of the instructions and exercises on this page
- 4 pages with blank space to write answers
- 7 pages of answers (All 24 sentence diagrams included)
- Printable
- If you only want to print out the pages where you'll be writing (I'm looking at you, expensive ink cartridges.), print pages 4, 9, 10, and 11.
II. Write Your Own Sentences
Directions : Write your own sentences using the words below. Make sure the word is being used as the part of speech indicated on the left side. Underline the word in your sentence. The first one is done for you. Feel free to use a dictionary!
Noun: The long drive through the countryside lifted my spirits.
Verb: I always drive within the speed limit.
Noun: ___________________________________
Adjective: ________________________________
Verb: ___________________________________
Preposition: ________________________________
Adverb: ___________________________________
1. LIGHT
a) I will light the fire. VERB
b) Can you see that red light ? NOUN
c) This light jacket isn't warm enough. ADJECTIVE
6. LIKE
a) I like old books. VERB
b) They acted like old friends. PREPOSITION
c) The boys had like interests. ADJECTIVE
2. FAST
a) Hadley is a fast runner. ADJECTIVE
b) The 12-hour fast cleared my mind. NOUN
c) He drives fast ! ADVERB
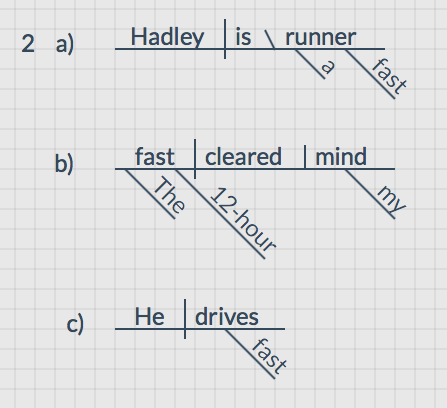
7. TILL
a) The kids were awake till midnight. PREPOSITION
b) Open the till and count the money. NOUN
c) My grandpa, a farmer, would till his soil in the spring. VERB
3. ABOVE
a) I had a general sense of how it works. ADJECTIVE
b) The general sank low in his chair. NOUN
8. CUP
a) Cup your hands around your mouth and yell. VERB
b) I'll use the red cup . NOUN
4. BEFORE
a) Practice piano before you play with your friends. CONJUNCTION
b) Practice piano before dinner. PREPOSITION
9. DRIVE
a) The long drive through the countryside lifted my spirits. NOUN
b) I always drive within the speed limit. VERB
5. ROLL
a) Roll the dice. VERB
b) I will eat the soup with a roll . NOUN
10. BLUE
a) Everyone in the family photo wore blue . NOUN
b) Jackie lives in the blue house. ADJECTIVE
* The sentence diagrams for 4, 5, 9, and 10 are available in the downloadable version of this lesson.
Answers for II. Write Your Own Sentences are also available in the free, downloadable version of this lesson.
Would you like to see another example of this concept? Let's look at how the word balance can be a noun or a verb , and how it can help you think about your life.

I can help you teach or learn grammar.
This is original content from https://www.english-grammar-revolution.com/what-part-of-speech.html

Our Free Guide Gives You A Fun Way
To Teach And Learn The Basics v

Elizabeth O'Brien is the creator of Grammar Revolution.
Her lessons are guaranteed to give you more confidence in your communication skills and make you smile. :)
Other Helpful Resources
- I used the website https://www.letsdiagram.com to make my sentence diagrams.
Sentences & Diagrams
Shop & log in.
Home BLOG SHOP Contact PRIVACY POLICY Your Purchases
Copyright © 2009 - 2024 Grammar Revolution. All Rights Reserved.
JOIN OUR PRIVATE FACEBOOK GROUP RSS INSTAGRAM

- Character Traits
- Compare and Contrast
- Read Alouds
- Point of View
- Reading Response Ideas
- Summarizing
- Text Features
- Text Structures
- Find the Fib
- Reusable Ideas
- Writing Ideas
- Opinion Writing Ideas
- Monster Ideas
- TPT Resources
- Disclosure Policy
- Dollar Deals
- Lifetime Access

Teaching Parts of Speech: 6 Activity Ideas

Activities to Help You Teach Nouns, Adjectives, Verbs, and Adverbs
1. introduce each part of speech separately .
Teaching each part of speech in isolation will keep your upper elementary students from becoming overwhelmed. Make sure they have a solid understanding of one part of speech before moving on to the next. Start by teaching nouns - using these free noun worksheets!
Of course, students will develop a more solid understanding of if they understand how the different parts of speech relate to each other. Students need to understand, for example, that adjectives modify nouns. But instead of trying to teach nouns and adjectives at the same time, make sure your upper elementary students have a solid understanding of nouns before introducing them to adjectives.
2. Write Sentences Without Different Parts of Speech
Help your students better understand the purposes of different parts of speech by writing sentences that exclude a specific part of speech.
For example, you could write the following sentence 4 different ways, excluding a noun, adjective, verb, or adverb in the different sentences.
Complete Sentence: The lazy cat snored loudly.
- Without a noun: The lazy snored loudly.
- Without an adjective: The cat snored loudly.
- Without a verb: The lazy cat loudly.
- Without an adverb: The lazy cat snored.
This activity helps 3rd, 4th, and 5th grade students better understand what role each part of speech plays in sentences. Sentences need nouns and verbs to make sense, but adjectives and adverbs make sentences more interesting.
This Parts of Speech Resource includes this activity - and it also has a fun sort with missing nouns, adjectives, verbs, and adverbs that helps students think carefully about the purpose of each part of speech!
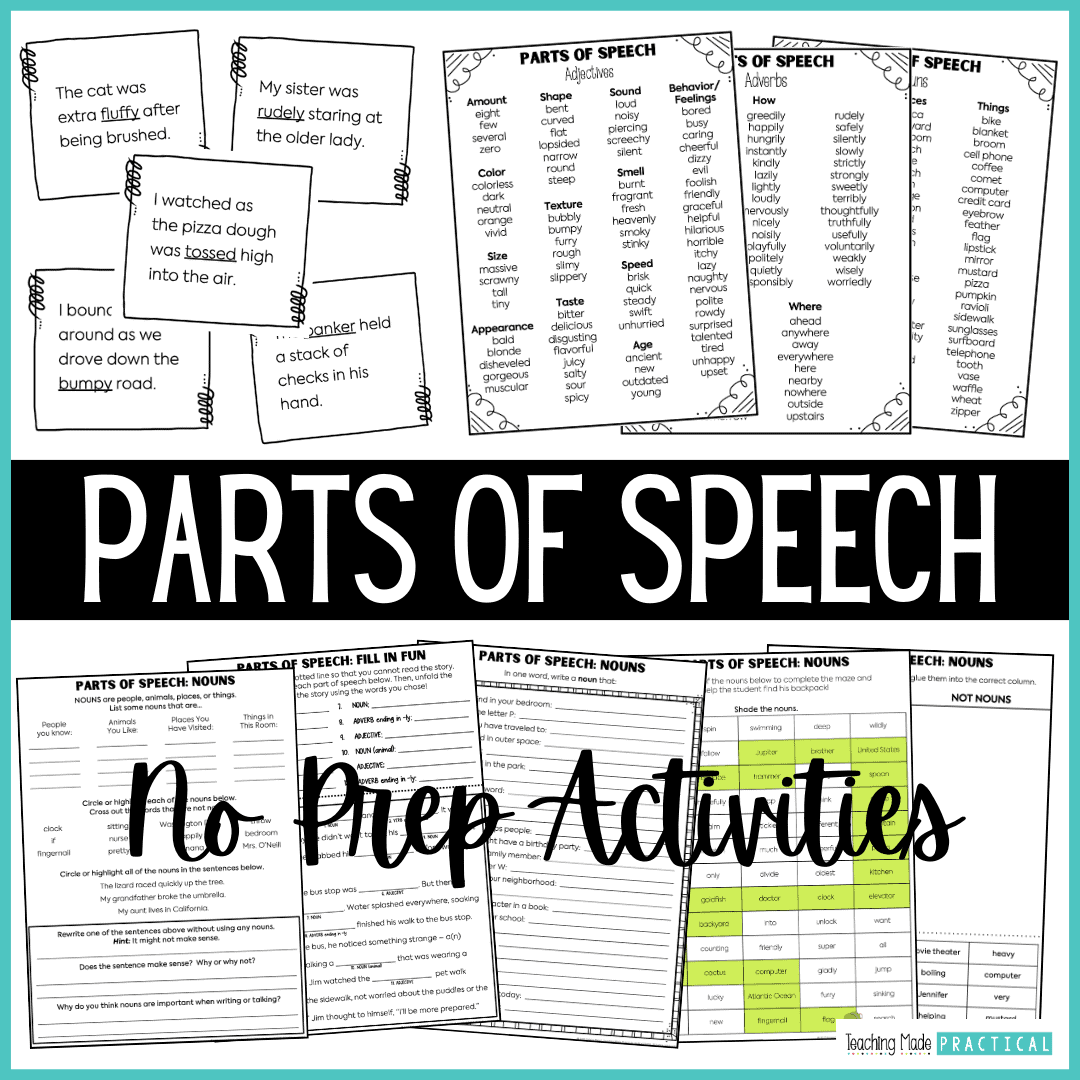
3. Create a Parts of Speech Anchor Chart
As you teach each part of speech in isolation, add to a parts of speech anchor chart that you create with your 3rd, 4th, and 5th grade students. A quick Pinterest search can provide anchor chart inspiration.
By creating an anchor chart together, referring to it throughout your grammar lessons, and then leaving it up as a reminder to students, you will help your students retain what they have learned.
4. Provide Parts of Speech Word Lists

Ideas for Practicing and Reviewing Parts of Speech
5. word sorts.
Provide upper elementary students with a list of words and have them sort them into groups based on their parts of speech. This is an engaging activity that also makes a great word wall for upper elementary classrooms that you can add to regularly!
This Parts of Speech Resource includes a variety of sorts - as well as some fun maze sort activities - to make this no prep for you.
6. Go on a Scavenger Hunt
Send your 3rd, 4th, and 5th grade students on a hunt for words that are a certain part of speech. They could search your classroom library, posters, anchor charts, or textbooks.
This can be a bit overwhelming to students who are just being introduced to the different parts of speech - trying to figure out the part of speech for every word they came across can be overwhelming. Provide a little direction for students so that they have a starting point.
For example, if you are sending students on a hunt for adjectives, ask them to find a word that:
- describes an animal
- describes their favorite movie
- describes their bedroom
This Parts of Speech Resource includes scavenger hunt worksheets like this that are no prep for you!
Want This Noun Freebie?
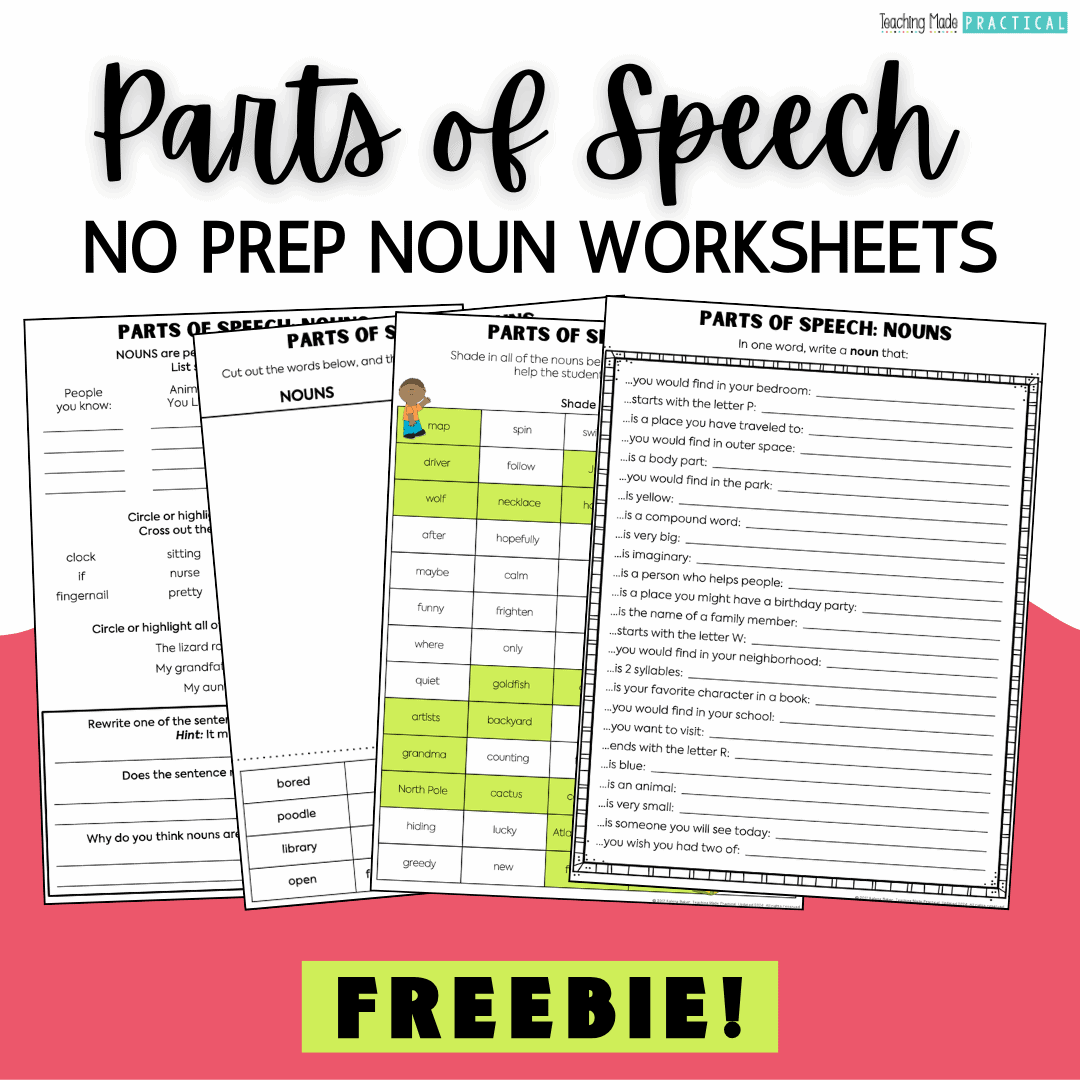

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
rules and use cases associated with the word 'team' in this part of speech is that it is a collective noun used to refer to a group of people, and it should always be used as a singular noun even though it is made up of multiple people. Examples: 1. The Sharks basketball team won their last game. 2. Our team worked together to solve the problem.
Learn what a part of speech is and how to identify the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. See examples, types, and grammar tips for each part of speech.
Learn how to classify words into eight parts of speech based on their roles in sentences. Find out the definitions, categories, and examples of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and articles.
Learn the categories and functions of words in English grammar with this comprehensive guide to the 8 parts of speech. Find out the subclasses of nouns, verbs, adjectives, and more with examples and quizzes.
Learn the 8 parts of speech in English grammar with definitions, examples, and rules. Nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and articles are the building blocks of language.
Parts of speech are important in learning English because they help us understand how words work together in sentences. Just like puzzle pieces fit together to create a picture, parts of speech fit together to create meaningful sentences. ... Team, family, flock, herd, swarm; Countable Nouns: Cat (singular), cats (plural) Book (singular), books ...
Download a PDF that includes examples of each part of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Learn the definitions, types, and functions of each part of speech with clear explanations and tables.
Learn the basics of the eight parts of speech in English: verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. See how to use them correctly in your writing and speaking with examples and explanations.
Learn the definition and function of each part of speech in English: nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections. See how they modify, describe, or connect words and sentences with examples and printable worksheets.
Learn the nine parts of speech in English with definitions, examples, and video lessons. Find out how to classify words according to their functions in sentences and why determiners are different from adjectives.
Parts of speech are categories that are used to describe each word's function in a sentence. The best way to identify a word's part of speech is to think about what role the word plays in the sentence, but there are also a few clues that can help you figure out the part of speech if you are unsure about the word's function.
Learn about the eight parts of speech in English grammar and how to use them correctly. Find examples, explanations, and tips for common words and phrases such as and, was, the, in, on, and by.
Learn the definition and examples of the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Find out how to use and analyse words in sentences with this comprehensive guide.
Learn the meaning, pronunciation, and usage of the word team in English. Find synonyms, related words, and word combinations for team in different contexts and levels of language.
Learn the nine parts of speech in English grammar and how to identify them in sentences. Find out the difference between open and closed word classes, and see examples of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections.
Parts of speech. Scrabble Words with friends Wordfeud Apalabrados Letterpress Wordle Wordscapes Words of Wonders Spelling Bee Crossword Definitions Thesaurus Proverbs Abbreviations Verb conjugator Sentences Quotes Syllables Parts of speech Numbers to words Phonetic Spelling Rhymes Text to speech
Learn the definitions and examples of nouns, verbs, adjectives, and other parts of speech in English. Adjectives describe or modify nouns or pronouns, e.g., gentle, helpful, small.
Learn how to identify the possible parts of speech of a word and how to determine its function in a sentence. Use dictionaries, definitions, and examples to practice and test yourself.
Send your 3rd, 4th, and 5th grade students on a hunt for words that are a certain part of speech. They could search your classroom library, posters, anchor charts, or textbooks.. This can be a bit overwhelming to students who are just being introduced to the different parts of speech - trying to figure out the part of speech for every word they came across can be overwhelming.
Parts of Speech for Team. Team is used as a Noun . Team is used as a ...
Every sentence contains at least one verb. Similarly, every sentence must have at least one noun. The process of these and other parts of speech working together is known as grammar.. In a sentence, is refers to the action of being.That's a little different from how we normally think of verbs, which are usually described as "action words."