Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples

How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean—any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs. discussion vs. conclusion, checklist: research results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like “appears” or “implies.”
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe store: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the sneakers, boots, sandals, etc.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarize or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to be positively correlated with donation intention, t (98) = 12.19, p < .001, with the donation intention of the high social distance group 0.28 points higher, on average, than the low social distance group (see figure 1). This contradicts the initial hypothesis that social distance would decrease donation intention, and in fact suggests a small effect in the opposite direction.
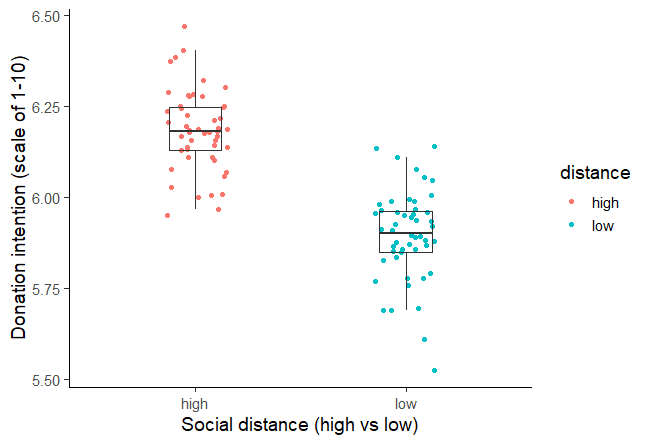
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organizations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
When asked about video games as a form of art, the respondents tended to believe that video games themselves are not an art form, but agreed that creativity is involved in their production. The criteria used to identify artistic video games included design, story, music, and creative teams.One respondent (male, 24) noted a difference in creativity between popular video game genres:
“I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.”
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 6, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/results/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Guide to Writing the Results and Discussion Sections of a Scientific Article
A quality research paper has both the qualities of in-depth research and good writing ( Bordage, 2001 ). In addition, a research paper must be clear, concise, and effective when presenting the information in an organized structure with a logical manner ( Sandercock, 2013 ).
In this article, we will take a closer look at the results and discussion section. Composing each of these carefully with sufficient data and well-constructed arguments can help improve your paper overall.

The results section of your research paper contains a description about the main findings of your research, whereas the discussion section interprets the results for readers and provides the significance of the findings. The discussion should not repeat the results.
Let’s dive in a little deeper about how to properly, and clearly organize each part.
How to Organize the Results Section
Since your results follow your methods, you’ll want to provide information about what you discovered from the methods you used, such as your research data. In other words, what were the outcomes of the methods you used?
You may also include information about the measurement of your data, variables, treatments, and statistical analyses.
To start, organize your research data based on how important those are in relation to your research questions. This section should focus on showing major results that support or reject your research hypothesis. Include your least important data as supplemental materials when submitting to the journal.
The next step is to prioritize your research data based on importance – focusing heavily on the information that directly relates to your research questions using the subheadings.
The organization of the subheadings for the results section usually mirrors the methods section. It should follow a logical and chronological order.
Subheading organization
Subheadings within your results section are primarily going to detail major findings within each important experiment. And the first paragraph of your results section should be dedicated to your main findings (findings that answer your overall research question and lead to your conclusion) (Hofmann, 2013).
In the book “Writing in the Biological Sciences,” author Angelika Hofmann recommends you structure your results subsection paragraphs as follows:
- Experimental purpose
- Interpretation
Each subheading may contain a combination of ( Bahadoran, 2019 ; Hofmann, 2013, pg. 62-63):
- Text: to explain about the research data
- Figures: to display the research data and to show trends or relationships, for examples using graphs or gel pictures.
- Tables: to represent a large data and exact value
Decide on the best way to present your data — in the form of text, figures or tables (Hofmann, 2013).
Data or Results?
Sometimes we get confused about how to differentiate between data and results . Data are information (facts or numbers) that you collected from your research ( Bahadoran, 2019 ).

Whereas, results are the texts presenting the meaning of your research data ( Bahadoran, 2019 ).

One mistake that some authors often make is to use text to direct the reader to find a specific table or figure without further explanation. This can confuse readers when they interpret data completely different from what the authors had in mind. So, you should briefly explain your data to make your information clear for the readers.
Common Elements in Figures and Tables
Figures and tables present information about your research data visually. The use of these visual elements is necessary so readers can summarize, compare, and interpret large data at a glance. You can use graphs or figures to compare groups or patterns. Whereas, tables are ideal to present large quantities of data and exact values.
Several components are needed to create your figures and tables. These elements are important to sort your data based on groups (or treatments). It will be easier for the readers to see the similarities and differences among the groups.
When presenting your research data in the form of figures and tables, organize your data based on the steps of the research leading you into a conclusion.
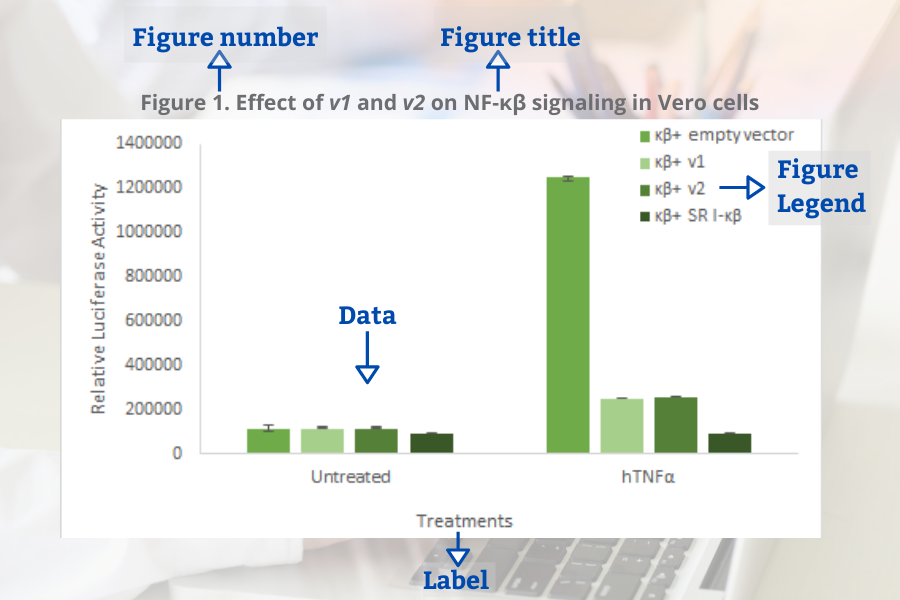
Common elements of the figures (Bahadoran, 2019):
- Figure number
- Figure title
- Figure legend (for example a brief title, experimental/statistical information, or definition of symbols).
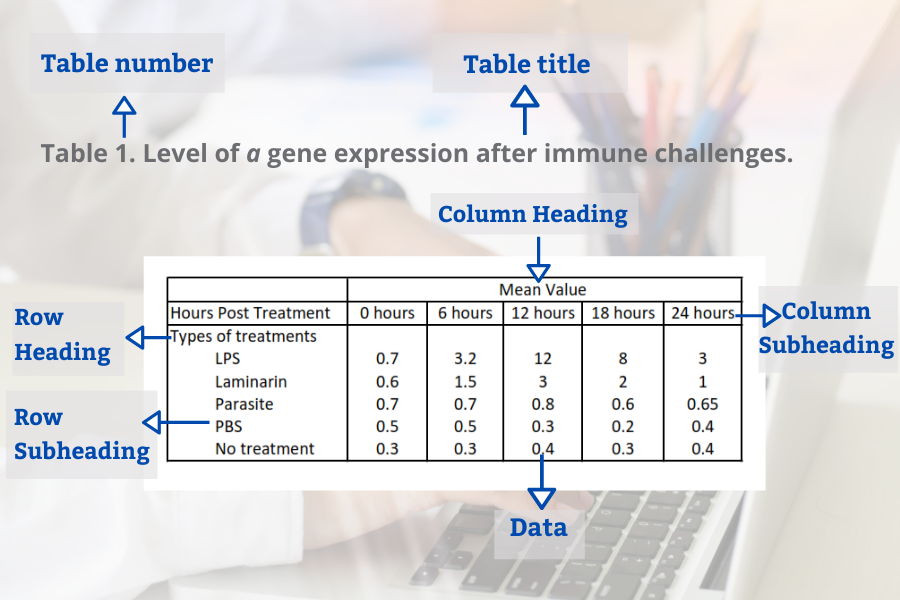
Tables in the result section may contain several elements (Bahadoran, 2019):
- Table number
- Table title
- Row headings (for example groups)
- Column headings
- Row subheadings (for example categories or groups)
- Column subheadings (for example categories or variables)
- Footnotes (for example statistical analyses)
Tips to Write the Results Section
- Direct the reader to the research data and explain the meaning of the data.
- Avoid using a repetitive sentence structure to explain a new set of data.
- Write and highlight important findings in your results.
- Use the same order as the subheadings of the methods section.
- Match the results with the research questions from the introduction. Your results should answer your research questions.
- Be sure to mention the figures and tables in the body of your text.
- Make sure there is no mismatch between the table number or the figure number in text and in figure/tables.
- Only present data that support the significance of your study. You can provide additional data in tables and figures as supplementary material.
How to Organize the Discussion Section
It’s not enough to use figures and tables in your results section to convince your readers about the importance of your findings. You need to support your results section by providing more explanation in the discussion section about what you found.
In the discussion section, based on your findings, you defend the answers to your research questions and create arguments to support your conclusions.
Below is a list of questions to guide you when organizing the structure of your discussion section ( Viera et al ., 2018 ):
- What experiments did you conduct and what were the results?
- What do the results mean?
- What were the important results from your study?
- How did the results answer your research questions?
- Did your results support your hypothesis or reject your hypothesis?
- What are the variables or factors that might affect your results?
- What were the strengths and limitations of your study?
- What other published works support your findings?
- What other published works contradict your findings?
- What possible factors might cause your findings different from other findings?
- What is the significance of your research?
- What are new research questions to explore based on your findings?
Organizing the Discussion Section
The structure of the discussion section may be different from one paper to another, but it commonly has a beginning, middle-, and end- to the section.
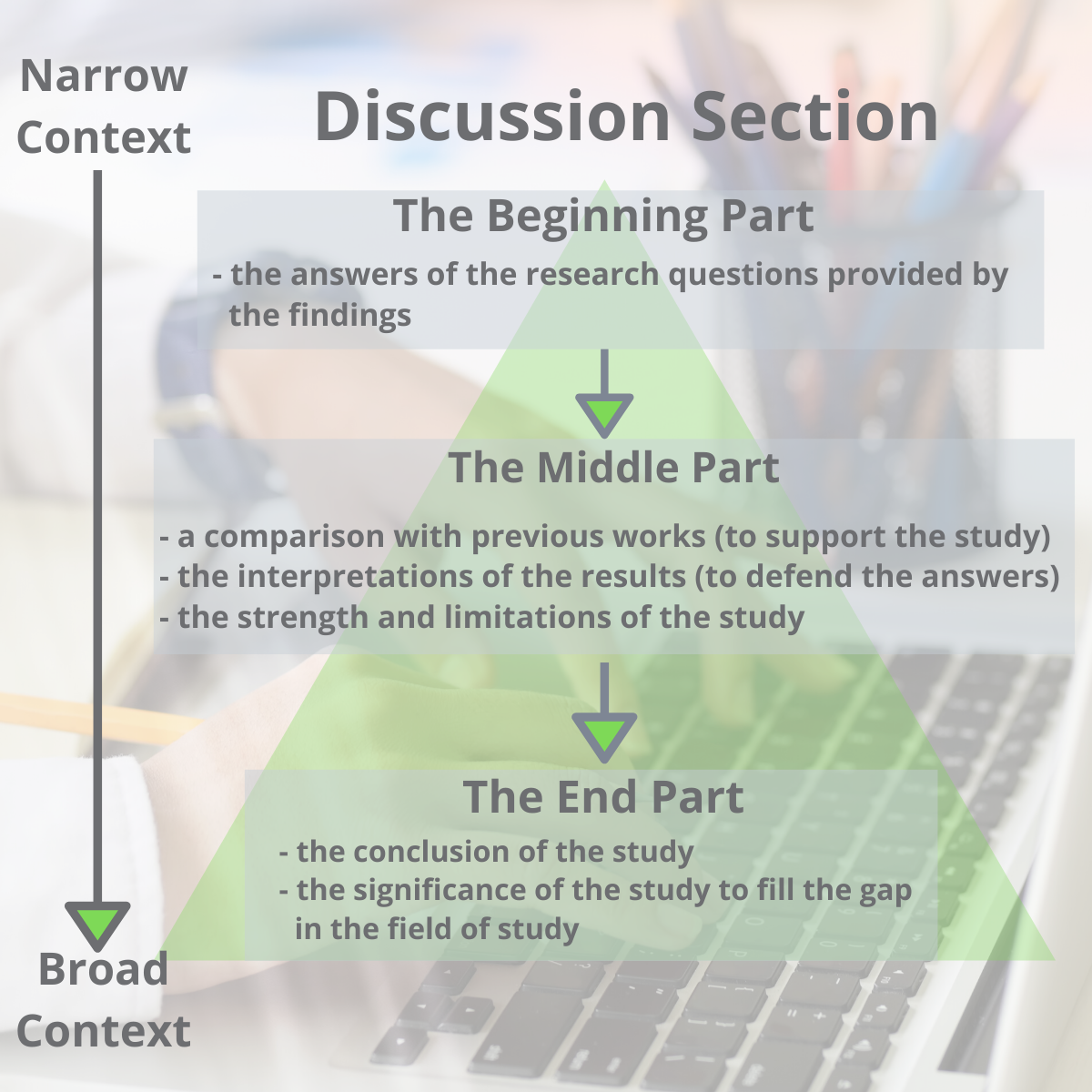
One way to organize the structure of the discussion section is by dividing it into three parts (Ghasemi, 2019):
- The beginning: The first sentence of the first paragraph should state the importance and the new findings of your research. The first paragraph may also include answers to your research questions mentioned in your introduction section.
- The middle: The middle should contain the interpretations of the results to defend your answers, the strength of the study, the limitations of the study, and an update literature review that validates your findings.
- The end: The end concludes the study and the significance of your research.
Another possible way to organize the discussion section was proposed by Michael Docherty in British Medical Journal: is by using this structure ( Docherty, 1999 ):
- Discussion of important findings
- Comparison of your results with other published works
- Include the strengths and limitations of the study
- Conclusion and possible implications of your study, including the significance of your study – address why and how is it meaningful
- Future research questions based on your findings
Finally, a last option is structuring your discussion this way (Hofmann, 2013, pg. 104):
- First Paragraph: Provide an interpretation based on your key findings. Then support your interpretation with evidence.
- Secondary results
- Limitations
- Unexpected findings
- Comparisons to previous publications
- Last Paragraph: The last paragraph should provide a summarization (conclusion) along with detailing the significance, implications and potential next steps.
Remember, at the heart of the discussion section is presenting an interpretation of your major findings.
Tips to Write the Discussion Section
- Highlight the significance of your findings
- Mention how the study will fill a gap in knowledge.
- Indicate the implication of your research.
- Avoid generalizing, misinterpreting your results, drawing a conclusion with no supportive findings from your results.
Aggarwal, R., & Sahni, P. (2018). The Results Section. In Reporting and Publishing Research in the Biomedical Sciences (pp. 21-38): Springer.
Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Zadeh-Vakili, A., Hosseinpanah, F., & Ghasemi, A. (2019). The principles of biomedical scientific writing: Results. International journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 17(2).
Bordage, G. (2001). Reasons reviewers reject and accept manuscripts: the strengths and weaknesses in medical education reports. Academic medicine, 76(9), 889-896.
Cals, J. W., & Kotz, D. (2013). Effective writing and publishing scientific papers, part VI: discussion. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 66(10), 1064.
Docherty, M., & Smith, R. (1999). The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers: Much the same as that for structuring abstracts. In: British Medical Journal Publishing Group.
Faber, J. (2017). Writing scientific manuscripts: most common mistakes. Dental press journal of orthodontics, 22(5), 113-117.
Fletcher, R. H., & Fletcher, S. W. (2018). The discussion section. In Reporting and Publishing Research in the Biomedical Sciences (pp. 39-48): Springer.
Ghasemi, A., Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Hosseinpanah, F., Shiva, N., & Zadeh-Vakili, A. (2019). The Principles of Biomedical Scientific Writing: Discussion. International journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 17(3).
Hofmann, A. H. (2013). Writing in the biological sciences: a comprehensive resource for scientific communication . New York: Oxford University Press.
Kotz, D., & Cals, J. W. (2013). Effective writing and publishing scientific papers, part V: results. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 66(9), 945.
Mack, C. (2014). How to Write a Good Scientific Paper: Structure and Organization. Journal of Micro/ Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS, 13. doi:10.1117/1.JMM.13.4.040101
Moore, A. (2016). What's in a Discussion section? Exploiting 2‐dimensionality in the online world…. Bioessays, 38(12), 1185-1185.
Peat, J., Elliott, E., Baur, L., & Keena, V. (2013). Scientific writing: easy when you know how: John Wiley & Sons.
Sandercock, P. M. L. (2012). How to write and publish a scientific article. Canadian Society of Forensic Science Journal, 45(1), 1-5.
Teo, E. K. (2016). Effective Medical Writing: The Write Way to Get Published. Singapore Medical Journal, 57(9), 523-523. doi:10.11622/smedj.2016156
Van Way III, C. W. (2007). Writing a scientific paper. Nutrition in Clinical Practice, 22(6), 636-640.
Vieira, R. F., Lima, R. C. d., & Mizubuti, E. S. G. (2019). How to write the discussion section of a scientific article. Acta Scientiarum. Agronomy, 41.
Related Articles

A quality research paper has both the qualities of in-depth research and good writing (Bordage, 200...

How to Survive and Complete a Thesis or a Dissertation
Writing a thesis or a dissertation can be a challenging process for many graduate students. There ar...

12 Ways to Dramatically Improve your Research Manuscript Title and Abstract
The first thing a person doing literary research will see is a research publication title. After tha...

15 Laboratory Notebook Tips to Help with your Research Manuscript
Your lab notebook is a foundation to your research manuscript. It serves almost as a rudimentary dra...
Join our list to receive promos and articles.

- Competent Cells
- Lab Startup
- Z')" data-type="collection" title="Products A->Z" target="_self" href="/collection/products-a-to-z">Products A->Z
- GoldBio Resources
- GoldBio Sales Team
- GoldBio Distributors
- Duchefa Direct
- Sign up for Promos
- Terms & Conditions
- ISO Certification
- Agarose Resins
- Antibiotics & Selection
- Biochemical Reagents
- Bioluminescence
- Buffers & Reagents
- Cell Culture
- Cloning & Induction
- Competent Cells and Transformation
- Detergents & Membrane Agents
- DNA Amplification
- Enzymes, Inhibitors & Substrates
- Growth Factors and Cytokines
- Lab Tools & Accessories
- Plant Research and Reagents
- Protein Research & Analysis
- Protein Expression & Purification
- Reducing Agents

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Results and Discussion
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
- Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Study Skills
- Exam Skills
- How to Write a Research Proposal
- Ethical Issues in Research
- Dissertation: The Introduction
- Researching and Writing a Literature Review
- Writing your Methodology
- Dissertation: Results and Discussion
- Dissertation: Conclusions and Extras
Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis eBook

Part of the Skills You Need Guide for Students .
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Writing your Dissertation: Results and Discussion
When writing a dissertation or thesis, the results and discussion sections can be both the most interesting as well as the most challenging sections to write.
You may choose to write these sections separately, or combine them into a single chapter, depending on your university’s guidelines and your own preferences.
There are advantages to both approaches.
Writing the results and discussion as separate sections allows you to focus first on what results you obtained and set out clearly what happened in your experiments and/or investigations without worrying about their implications.This can focus your mind on what the results actually show and help you to sort them in your head.
However, many people find it easier to combine the results with their implications as the two are closely connected.
Check your university’s requirements carefully before combining the results and discussions sections as some specify that they must be kept separate.
Results Section
The Results section should set out your key experimental results, including any statistical analysis and whether or not the results of these are significant.
You should cover any literature supporting your interpretation of significance. It does not have to include everything you did, particularly for a doctorate dissertation. However, for an undergraduate or master's thesis, you will probably find that you need to include most of your work.
You should write your results section in the past tense: you are describing what you have done in the past.
Every result included MUST have a method set out in the methods section. Check back to make sure that you have included all the relevant methods.
Conversely, every method should also have some results given so, if you choose to exclude certain experiments from the results, make sure that you remove mention of the method as well.
If you are unsure whether to include certain results, go back to your research questions and decide whether the results are relevant to them. It doesn’t matter whether they are supportive or not, it’s about relevance. If they are relevant, you should include them.
Having decided what to include, next decide what order to use. You could choose chronological, which should follow the methods, or in order from most to least important in the answering of your research questions, or by research question and/or hypothesis.
You also need to consider how best to present your results: tables, figures, graphs, or text. Try to use a variety of different methods of presentation, and consider your reader: 20 pages of dense tables are hard to understand, as are five pages of graphs, but a single table and well-chosen graph that illustrate your overall findings will make things much clearer.
Make sure that each table and figure has a number and a title. Number tables and figures in separate lists, but consecutively by the order in which you mention them in the text. If you have more than about two or three, it’s often helpful to provide lists of tables and figures alongside the table of contents at the start of your dissertation.
Summarise your results in the text, drawing on the figures and tables to illustrate your points.
The text and figures should be complementary, not repeat the same information. You should refer to every table or figure in the text. Any that you don’t feel the need to refer to can safely be moved to an appendix, or even removed.
Make sure that you including information about the size and direction of any changes, including percentage change if appropriate. Statistical tests should include details of p values or confidence intervals and limits.
While you don’t need to include all your primary evidence in this section, you should as a matter of good practice make it available in an appendix, to which you should refer at the relevant point.
For example:
Details of all the interview participants can be found in Appendix A, with transcripts of each interview in Appendix B.
You will, almost inevitably, find that you need to include some slight discussion of your results during this section. This discussion should evaluate the quality of the results and their reliability, but not stray too far into discussion of how far your results support your hypothesis and/or answer your research questions, as that is for the discussion section.
See our pages: Analysing Qualitative Data and Simple Statistical Analysis for more information on analysing your results.
Discussion Section
This section has four purposes, it should:
- Interpret and explain your results
- Answer your research question
- Justify your approach
- Critically evaluate your study
The discussion section therefore needs to review your findings in the context of the literature and the existing knowledge about the subject.
You also need to demonstrate that you understand the limitations of your research and the implications of your findings for policy and practice. This section should be written in the present tense.
The Discussion section needs to follow from your results and relate back to your literature review . Make sure that everything you discuss is covered in the results section.
Some universities require a separate section on recommendations for policy and practice and/or for future research, while others allow you to include this in your discussion, so check the guidelines carefully.
Starting the Task
Most people are likely to write this section best by preparing an outline, setting out the broad thrust of the argument, and how your results support it.
You may find techniques like mind mapping are helpful in making a first outline; check out our page: Creative Thinking for some ideas about how to think through your ideas. You should start by referring back to your research questions, discuss your results, then set them into the context of the literature, and then into broader theory.
This is likely to be one of the longest sections of your dissertation, and it’s a good idea to break it down into chunks with sub-headings to help your reader to navigate through the detail.
Fleshing Out the Detail
Once you have your outline in front of you, you can start to map out how your results fit into the outline.
This will help you to see whether your results are over-focused in one area, which is why writing up your research as you go along can be a helpful process. For each theme or area, you should discuss how the results help to answer your research question, and whether the results are consistent with your expectations and the literature.
The Importance of Understanding Differences
If your results are controversial and/or unexpected, you should set them fully in context and explain why you think that you obtained them.
Your explanations may include issues such as a non-representative sample for convenience purposes, a response rate skewed towards those with a particular experience, or your own involvement as a participant for sociological research.
You do not need to be apologetic about these, because you made a choice about them, which you should have justified in the methodology section. However, you do need to evaluate your own results against others’ findings, especially if they are different. A full understanding of the limitations of your research is part of a good discussion section.
At this stage, you may want to revisit your literature review, unless you submitted it as a separate submission earlier, and revise it to draw out those studies which have proven more relevant.
Conclude by summarising the implications of your findings in brief, and explain why they are important for researchers and in practice, and provide some suggestions for further work.
You may also wish to make some recommendations for practice. As before, this may be a separate section, or included in your discussion.
The results and discussion, including conclusion and recommendations, are probably the most substantial sections of your dissertation. Once completed, you can begin to relax slightly: you are on to the last stages of writing!
Continue to: Dissertation: Conclusion and Extras Writing your Methodology
See also: Writing a Literature Review Writing a Research Proposal Academic Referencing What Is the Importance of Using a Plagiarism Checker to Check Your Thesis?
- How it works

How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter – A Quick Guide with Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On July 12, 2024
Dissertation discussion is the chapter where you explore the relevance, significance, and meanings of your findings – allowing you to showcase your talents in describing and analyzing the results of your study.
Here, you will be expected to demonstrate how your research findings answer the research questions established or test the hypothesis .
The arguments you assert in the dissertation analysis and discussions chapter lay the foundations of your conclusion . It is critically important to discuss the results in a precise manner.
To help you understand how to write a dissertation discussion chapter, here is the list of the main elements of this section so you stay on the right track when writing:
- Summary: Start by providing a summary of your key research findings
- Interpretations: What is the significance of your findings?
- Implications: Why are your findings important to academic and scientific communities, and what purpose would they serve?
- Limitations: When and where will your results have no implications?
- Future Recommendations : Advice for other researchers and scientists who explore the topic further in future.
The dissertation discussion chapter should be carefully drafted to ensure that the results mentioned in your research align with your research question, aims, and objectives.
Considering the importance of this chapter for all students working on their dissertations, we have comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation discussion chapter.
The discussion and conclusion chapters often overlap. Depending on your university, you may be asked to group these two sections in one chapter – Discussion and Conclusion.
In some cases, the results and discussion are put together under the Results and Discussion chapter. Here are some dissertation examples of working out the best structure for your dissertation.
Alternatively, you can look for the required dissertation structure in your handbook or consult your supervisor.
Steps of How to Write Dissertation Discussion Chapter
1. provide a summary of your findings.
Start your discussion by summarising the key findings of your research questions. Avoid repeating the information you have already stated in the previous chapters.
You will be expected to clearly express your interpretation of results to answer the research questions established initially in one or two paragraphs.
Here are some examples of how to present the summary of your findings ;
- “The data suggests that”,
- “The results confirm that”,
- “The analysis indicates that”,
- “The research shows a relationship between”, etc.
2. Interpretations of Results
Your audience will expect you to provide meanings of the results, although they might seem obvious to you. The results and their interpretations should be linked to the research questions so the reader can understand the value your research has added to the literature.
There are many ways of interpreting the data, but your chosen approach to interpreting the data will depend on the type of research involved . Some of the most common strategies employed include;
- Describing how and why you ended up with unexpected findings and explaining their importance in detail
- Relating your findings with previous studies conducted
- Explaining your position with logical arguments when/if any alternative explanations are suggested
- An in-depth discussion around whether or not the findings answered your research questions and successfully tested the hypothesis
Examples of how you can start your interpretation in the Discussion chapter are –
- “Findings of this study contradict those of Allen et al. (2014) that”,
- “Contrary to the hypothesized association,” “Confirming the hypothesis…”,
- “The findings confirm that A is….. even though Allen et al. (2014) and Michael (2012) suggested B was …..”
3. Implications of your Study
What practical and theoretical implications will your study have for other researchers and the scientific community as a whole?
It is vital to relate your results to the knowledge in the existing literature so the readers can establish how your research will contribute to the existing data.
When thinking of the possible consequences of your findings, you should ask yourself these;
- Are your findings in line with previous studies? What contribution did your research make to them?
- Why are your results entirely different from other studies on the same topic?
- Did your findings approve or contradict existing knowledge?
- What are the practical implications of your study?
Remember that as the researcher, you should aim to let your readers know why your study will contribute to the existing literature. Possible ways of starting this particular section are;
- “The findings show that A….. whereas Lee (2017) and John (2013) suggested that B”, “The results of this study completely contradict the claims made in theories”,
- “These results are not in line with the theoretical perspectives”,
- “The statistical analysis provides a new understanding of the relationship between A and B”,
- “Future studies should take into consideration the findings of this study because”
“Improve your work’s language, structure, style, and overall quality. Get help from our experienced dissertation editors to improve the quality of your paper to First Class Standard. Click here to learn more about our Dissertation, Editing, and Improvement Services .
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue, then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across various disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

4. Recognise the Limitations of your Research
Almost every academic research has some limitations. Acknowledging them will only add to your credibility as a scientific researcher.
In addition to the possible human errors, it’s important to take into account other factors that might have influenced the results of your study, including but not limited to unexpected research obstacles, specific methodological choices , and the overall research design.
Avoid mentioning any limitations that may not be relevant to your research aim, but clearly state the limitations that may have affected your results.
For example, if you used a sample size that included a tiny population, you may not generalise your results.
Similarly, obstacles faced in collecting data from the participants can influence the findings of your study. Make a note of all such research limitations , but explain to the reader why your results are still authentic.
- The small sample size limited the generalisability of the results.
- The authenticity of the findings may have been influenced by….
- The obstacles in collecting data resulted in…
- It is beyond the framework of this research…
5. Provide Recommendations for Future Research
The limitations of your research work directly result in future recommendations . However, it should be noted that your recommendations for future research work should include the areas that your own work could not report so other researchers can build on them.
Sometimes the recommendations are a part of the conclusion chapter . Some examples;
- More research is needed to be performed….
The Purpose of Dissertation Discussion Chapter
Remember that the discussion section of a dissertation is the heart of your research because a) it will indicate your stance on the topic of research, and b) it answers the research questions initially established in the Introduction chapter .
Every piece of information you present here will add value to the existing literature within your field of study. How you structured your findings in the preceding chapter will help you determine the best structure for your dissertation discussion section.
For example, it might be logical to structure your analysis/discussions by theme if you chose the pattern in your findings section.
But generally, discussion based on research questions is the more widely used structure in academia because this pattern clearly indicates how you have addressed the aim of your research.
Most UK universities require the supervisor or committee members to comment on the extent to which each research question has been answered. You will be doing them a great favour if you structure your discussion so that each research question is laid out separately.
Irrespective of whether you are writing an essay, dissertation, or chapter of a dissertation , all pieces of writing should start with an introduction .
Once your readers have read through your study results, you might want to highlight the contents of the subsequent discussion as an introduction paragraph (summary of your results – as explained above).
Likewise, the discussion chapter is expected to end with a concluding paragraph – allowing you the opportunity to summarise your interpretations.
The dissertation analysis & discussion chapter is usually very long, so it will make sense to emphasise the critical points in a concluding paragraph so the reader can grasp the essential information. This will also help to make sure the reader understands your analysis.
Also Read: Research Discussion Of Findings
Useful Tips
Presentation of graphs, tables, and figures.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, students spent days creating graphs and charts for their statistical analysis work . Thanks to technology, you can produce even more accurate graphs and figures today in a shorter period.
Using Microsoft Word, STATA, SPSS, Microsoft Excel and other statistical analysis software, we can now draw beautiful-looking figures, tables , and graphs with just a few clicks and make them appear in our document at the desired place. But there are downsides to being too dependent on technology.
Many students make the common mistake of using colours to represent variables when really they have to print their dissertation paper final copy in black and white.
Any colours on graphs and figures will eventually be viewed in the grayscale presentation. Recognizing different shades of grey on the same chart or graph can sometimes be a little confusing.
For example, green and purple appear as pretty much the same shade of grey on a line chat, meaning your chart will become unreadable to the marker.
Another trap you may fall into is the unintentional stuffing of the dissertation chapter with graphs and figures. Even though it is essential to show numbers and statistics, you don’t want to overwhelm your readers with too many.
It may not be necessary to have a graph/table under each sub-heading. Only you can best judge whether or not you need to have a graph/table under a particular sub-heading as the writer.
Relating to Previous Chapters
As a student, it can be challenging to develop your own analysis and discussion of results. One of the excellent discussion chapter requirements is to showcase your ability to relate previous research to your research results.
Avoid repeating the same information over and over. Many students fall into this trap which negatively affects the mark of their overall dissertation paper .
Concise and to-the-point information will help you effectively convey your point to the readers.
Although you must demonstrate how your findings relate to previous research, it is equally important to ensure you are not simply rewriting what has already been said in the introduction and literature review chapters.
The best strategy is to use examples from previous sections to postulate an argument.
Hyperlinks are recommended to take the reader from one section to another. This is especially important for submitting electronic documents as .word or .pdf files. Hyperlinking is tedious and time-consuming, so you should allow for this in your dissertation timeline to avoid rushing in the closing stages.
Also read: How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation.
Using Subsections and Subheadings
You might want to reflect on the structure of the discussion in your organizstion of the dissertation discussion chapter, and for that, you will need to create sub-sections.
It is essential to keep subsections to the point and as short as possible. Use a layer of subheadings if possible.
For example
Subsection 4.1 of Chapter 4- Discussion can be further divided into sections 4.1.1 and 4.2.2. After three numerical layers (4.1.1, 4.2.2, and 4.2.3), any subheadings need not appear in the contents table.
The titles of all subsections will appear on your table of contents so choose the wordings carefully. A title too long or too short might confuse the reader. A one or two-word subheading will not give the reader enough information to understand the section.
Likewise, using a research question or long sentences in the subheading is not recommended. It might help to examine how other researchers and writers create these subheadings.
Critical Thinking
Your critical thinking skills are the crux of your dissertation discussion chapter. You will do yourself a great disservice if you fail to put the critical thinking element into the equation.
After all, this exercise aims to showcase clarity in your thoughts and arguments. Markers of the dissertation give more importance to the analysis and discussion chapter. But you could be marked negatively if this particular chapter lacks critical thinking.
Many students struggle to distinguish between fundamental descriptive analysis and critical thinking with their opinions on the research topic.
Critical thinking is a skill developed over time, and it might be daunting for you to come to terms with the idea of critical thinking and its use in your analysis. But even if you are no expert, you must try your best.

“Still unsure about how to write a dissertation discussion chapter ? Why not take advantage of our UK-based dissertation writing service ? Your dissertation is essential to your degree, so you cannot risk failing it.
With our custom writing service , you are guaranteed to have all your dissertation paper elements put into the right place. Our expert academics can help you with your full dissertation paper or a part of it. Click here to learn more about our dissertation services.
Duplication of Content
Another critical error students make reaffirming the point the graph/chart was supposed to make. Writing out the same information as presented in the graph defeats the whole purpose of having them in the first place.
You will be expected to form your opinions and arguments based on the findings (as presented by the graphs), so keep an eye on this mistake. Finally, avoid simply inserting a graph without any explanation whatsoever.
It should be noted that there is no correct or incorrect number of charts/figures one can use in the dissertation findings and discussion chapter. A balance must be struck.
Avoid Over Interpretation
This is a major no-no when writing a dissertation discussion. Do not make an argument that isn’t backed by your collected data.
The results and interpretations that cannot be supported should not be mentioned. Your research will be deemed unauthentic and will also be questioned by your supervisor if you do so. Results should be interpreted without any bias.
How to Write the Findings of a Dissertation.
Do not Speculate
Speculation in the discussion chapter of your dissertation is discouraged. Your dissertation’s discussion is based on your collected data and how it relates to your research questions. Thus, speculating here will undoubtedly undermine your research’s credibility.
Also, try not to generalise your findings. If your research is based on a specific population, do not state that the same findings might apply in every case. As indicated previously, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of your research.
On the other hand, if you think your discussion needs to address other populations as well, start your sentence like this ‘We speculate that..’ or ‘It is speculated that..’ This will keep you from getting into any trouble.
What are the elements of the Dissertation Discussion?
The list of the main elements of the discussion chapter are:
- Implications : Why are your findings important to academic and scientific communities, and what purpose would they serve?
- Future Recommendations: Advice for other researchers and scientists who explore the topic further in future.
What are the steps of writing a Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
- Write a summary of the findings
- Provide a summary of your findings
- Interpretations of Results
- Recognise the Limitations of your research
- Provide Recommendations for Future Research.
Can we use graphs and charts in the Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
Yes, using graphs to aid your statistical results and enhance presentation is essential, but do not overwhelm it with a lot of graphs in multiple colours.
You May Also Like
Do dissertations scare you? Struggling with writing a flawless dissertation? Well, congratulations, you have landed in the perfect place. In this blog, we will take you through the detailed process of writing a dissertation. Sounds fun? We thought so!
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
Not sure how to write dissertation title page? All dissertations must have a dissertation title page where necessary information should be clearly presented
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Writing the Dissertation - Guides for Success: Results and Discussion
- Writing the Dissertation Homepage
- Overview and Planning
- Research Question
- Literature Review
- Methodology
- Results and Discussion
- The Difference
- What to Avoid
Overview of writing the results and discussion
The results and discussion follow on from the methods or methodology chapter of the dissertation. This creates a natural transition from how you designed your study, to what your study reveals, highlighting your own contribution to the research area.
Disciplinary differences
Please note: this guide is not specific to any one discipline. The results and discussion can vary depending on the nature of the research and the expectations of the school or department, so please adapt the following advice to meet the demands of your project and department. Consult your supervisor for further guidance; you can also peruse our Writing Across Subjects guide .
Guide contents
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common conventions of the results and discussion chapters, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows:
- The Difference - Breaks down the distinctions between the results and discussion chapters.
- Results - Provides a walk-through of common characteristics of the results chapter.
- Discussion - Provides a walk-through of how to approach writing your discussion chapter, including structure.
- What to Avoid - Covers a few frequent mistakes you'll want to...avoid!
- FAQs - Guidance on first- vs. third-person, limitations and more.
- Checklist - Includes a summary of key points and a self-evaluation checklist.
Training and tools
- The Academic Skills team has recorded a Writing the Dissertation workshop series to help you with each section of a standard dissertation, including a video on writing the results and discussion (embedded below).
- The dissertation planner tool can help you think through the timeline for planning, research, drafting and editing.
- iSolutions offers training and a Word template to help you digitally format and structure your dissertation.
Introduction
The results of your study are often followed by a separate chapter of discussion. This is certainly the case with scientific writing. Some dissertations, however, might incorporate both the results and discussion in one chapter. This depends on the nature of your dissertation and the conventions within your school or department. Always follow the guidelines given to you and ask your supervisor for further guidance.
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the essentials of writing your results and discussion, giving you the necesary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to leave a positive impression on your markers! This guide covers the results and discussion as separate – although interrelated – chapters, as you'll see in the next two tabs. However, you can easily adapt the guidance to suit one single chapter – keep an eye out for some hints on how to do this throughout the guide.
Results or discussion - what's the difference?
To understand what the results and discussion sections are about, we need to clearly define the difference between the two.
The results should provide a clear account of the findings . This is written in a dry and direct manner, simply highlighting the findings as they appear once processed. It’s expected to have tables and graphics, where relevant, to contextualise and illustrate the data.
Rather than simply stating the findings of the study, the discussion interprets the findings to offer a more nuanced understanding of the research. The discussion is similar to the second half of the conclusion because it’s where you consider and formulate a response to the question, ‘what do we now know that we didn’t before?’ (see our Writing the Conclusion guide for more). The discussion achieves this by answering the research questions and responding to any hypotheses proposed. With this in mind, the discussion should be the most insightful chapter or section of your dissertation because it provides the most original insight.
Across the next two tabs of this guide, we will look at the results and discussion chapters separately in more detail.
Writing the results
The results chapter should provide a direct and factual account of the data collected without any interpretation or interrogation of the findings. As this might suggest, the results chapter can be slightly monotonous, particularly for quantitative data. Nevertheless, it’s crucial that you present your results in a clear and direct manner as it provides the necessary detail for your subsequent discussion.
Note: If you’re writing your results and discussion as one chapter, then you can either:
1) write them as distinctly separate sections in the same chapter, with the discussion following on from the results, or...
2) integrate the two throughout by presenting a subset of the results and then discussing that subset in further detail.
Next, we'll explore some of the most important factors to consider when writing your results chapter.
How you structure your results chapter depends on the design and purpose of your study. Here are some possible options for structuring your results chapter (adapted from Glatthorn and Joyner, 2005):
- Chronological – depending on the nature of the study, it might be important to present your results in order of how you collected the data, such as a pretest-posttest design.
- Research method – if you’ve used a mixed-methods approach, you could isolate each research method and instrument employed in the study.
- Research question and/or hypotheses – you could structure your results around your research questions and/or hypotheses, providing you have more than one. However, keep in mind that the results on their own don’t necessarily answer the questions or respond to the hypotheses in a definitive manner. You need to interpret the findings in the discussion chapter to gain a more rounded understanding.
- Variable – you could isolate each variable in your study (where relevant) and specify how and whether the results changed.
Tables and figures
For your results, you are expected to convert your data into tables and figures, particularly when dealing with quantitative data. Making use of tables and figures is a way of contextualising your results within the study. It also helps to visually reinforce your written account of the data. However, make sure you’re only using tables and figures to supplement , rather than replace, your written account of the results (see the 'What to avoid' tab for more on this).
Figures and tables need to be numbered in order of when they appear in the dissertation, and they should be capitalised. You also need to make direct reference to them in the text, which you can do (with some variation) in one of the following ways:
Figure 1 shows…
The results of the test (see Figure 1) demonstrate…
The actual figures and tables themselves also need to be accompanied by a caption that briefly outlines what is displayed. For example:
Table 1. Variables of the regression model
Table captions normally appear above the table, whilst figures or other such graphical forms appear below, although it’s worth confirming this with your supervisor as the formatting can change depending on the school or discipline. The style guide used for writing in your subject area (e.g., Harvard, MLA, APA, OSCOLA) often dictates correct formatting of tables, graphs and figures, so have a look at your style guide for additional support.
Using quotations
If your qualitative data comes from interviews and focus groups, your data will largely consist of quotations from participants. When presenting this data, you should identify and group the most common and interesting responses and then quote two or three relevant examples to illustrate this point. Here’s a brief example from a qualitative study on the habits of online food shoppers:
Regardless of whether or not participants regularly engage in online food shopping, all but two respondents commented, in some form, on the convenience of online food shopping:
"It’s about convenience for me. I’m at work all week and the weekend doesn’t allow much time for food shopping, so knowing it can be ordered and then delivered in 24 hours is great for me” (Participant A).
"It fits around my schedule, which is important for me and my family” (Participant D).
"In the past, I’ve always gone food shopping after work, which has always been a hassle. Online food shopping, however, frees up some of my time” (Participant E).
As shown in this example, each quotation is attributed to a particular participant, although their anonymity is protected. The details used to identify participants can depend on the relevance of certain factors to the research. For instance, age or gender could be included.
Writing the discussion
The discussion chapter is where “you critically examine your own results in the light of the previous state of the subject as outlined in the background, and make judgments as to what has been learnt in your work” (Evans et al., 2014: 12). Whilst the results chapter is strictly factual, reporting on the data on a surface level, the discussion is rooted in analysis and interpretation , allowing you and your reader to delve beneath the surface.
Next, we will review some of the most important factors to consider when writing your discussion chapter.
Like the results, there is no single way to structure your discussion chapter. As always, it depends on the nature of your dissertation and whether you’re dealing with qualitative, quantitative or mixed-methods research. It’s good to be consistent with the results chapter, so you could structure your discussion chapter, where possible, in the same way as your results.
When it comes to structure, it’s particularly important that you guide your reader through the various points, subtopics or themes of your discussion. You should do this by structuring sections of your discussion, which might incorporate three or four paragraphs around the same theme or issue, in a three-part way that mirrors the typical three-part essay structure of introduction, main body and conclusion.

Figure 1: The three-part cycle that embodies a typical essay structure and reflects how you structure themes or subtopics in your discussion.
This is your topic sentence where you clearly state the focus of this paragraph/section. It’s often a fairly short, declarative statement in order to grab the reader’s attention, and it should be clearly related to your research purpose, such as responding to a research question.
This constitutes your analysis where you explore the theme or focus, outlined in the topic sentence, in further detail by interrogating why this particular theme or finding emerged and the significance of this data. This is also where you bring in the relevant secondary literature.
This is the evaluative stage of the cycle where you explicitly return back to the topic sentence and tell the reader what this means in terms of answering the relevant research question and establishing new knowledge. It could be a single sentence, or a short paragraph, and it doesn’t strictly need to appear at the end of every section or theme. Instead, some prefer to bring the main themes together towards the end of the discussion in a single paragraph or two. Either way, it’s imperative that you evaluate the significance of your discussion and tell the reader what this means.
A note on the three-part structure
This is often how you’re taught to construct a paragraph, but the themes and ideas you engage with at dissertation level are going to extend beyond the confines of a short paragraph. Therefore, this is a structure to guide how you write about particular themes or patterns in your discussion. Think of this structure like a cycle that you can engage in its smallest form to shape a paragraph; in a slightly larger form to shape a subsection of a chapter; and in its largest form to shape the entire chapter. You can 'level up' the same basic structure to accommodate a deeper breadth of thinking and critical engagement.
Using secondary literature
Your discussion chapter should return to the relevant literature (previously identified in your literature review ) in order to contextualise and deepen your reader’s understanding of the findings. This might help to strengthen your findings, or you might find contradictory evidence that serves to counter your results. In the case of the latter, it’s important that you consider why this might be and the implications for this. It’s through your incorporation of secondary literature that you can consider the question, ‘What do we now know that we didn’t before?’
Limitations
You may have included a limitations section in your methodology chapter (see our Writing the Methodology guide ), but it’s also common to have one in your discussion chapter. The difference here is that your limitations are directly associated with your results and the capacity to interpret and analyse those results.
Think of it this way: the limitations in your methodology refer to the issues identified before conducting the research, whilst the limitations in your discussion refer to the issues that emerged after conducting the research. For example, you might only be able to identify a limitation about the external validity or generalisability of your research once you have processed and analysed the data. Try not to overstress the limitations of your work – doing so can undermine the work you’ve done – and try to contextualise them, perhaps by relating them to certain limitations of other studies.
Recommendations
It’s often good to follow your limitations with some recommendations for future research. This creates a neat linearity from what didn’t work, or what could be improved, to how other researchers could address these issues in the future. This helps to reposition your limitations in a positive way by offering an action-oriented response. Try to limit the amount of recommendations you discuss – too many can bring the end of your discussion to a rather negative end as you’re ultimately focusing on what should be done, rather than what you have done. You also don’t need to repeat the recommendations in your conclusion if you’ve included them here.
What to avoid
This portion of the guide will cover some common missteps you should try to avoid in writing your results and discussion.
Over-reliance on tables and figures
It’s very common to produce visual representations of data, such as graphs and tables, and to use these representations in your results chapter. However, the use of these figures should not entirely replace your written account of the data. You don’t need to specify every detail in the data set, but you should provide some written account of what the data shows, drawing your reader’s attention to the most important elements of the data. The figures should support your account and help to contextualise your results. Simply stating, ‘look at Table 1’, without any further detail is not sufficient. Writers often try to do this as a way of saving words, but your markers will know!
Ignoring unexpected or contradictory data
Research can be a complex process with ups and downs, surprises and anomalies. Don’t be tempted to ignore any data that doesn’t meet your expectations, or that perhaps you’re struggling to explain. Failing to report on data for these, and other such reasons, is a problem because it undermines your credibility as a researcher, which inevitably undermines your research in the process. You have to do your best to provide some reason to such data. For instance, there might be some methodological reason behind a particular trend in the data.
Including raw data
You don’t need to include any raw data in your results chapter – raw data meaning unprocessed data that hasn’t undergone any calculations or other such refinement. This can overwhelm your reader and obscure the clarity of the research. You can include raw data in an appendix, providing you feel it’s necessary.
Presenting new results in the discussion
You shouldn’t be stating original findings for the first time in the discussion chapter. The findings of your study should first appear in your results before elaborating on them in the discussion.
Overstressing the significance of your research
It’s important that you clarify what your research demonstrates so you can highlight your own contribution to the research field. However, don’t overstress or inflate the significance of your results. It’s always difficult to provide definitive answers in academic research, especially with qualitative data. You should be confident and authoritative where possible, but don’t claim to reach the absolute truth when perhaps other conclusions could be reached. Where necessary, you should use hedging (see definition) to slightly soften the tone and register of your language.
Definition: Hedging refers to 'the act of expressing your attitude or ideas in tentative or cautious ways' (Singh and Lukkarila, 2017: 101). It’s mostly achieved through a number of verbs or adverbs, such as ‘suggest’ or ‘seemingly.’
Q: What’s the difference between the results and discussion?
A: The results chapter is a factual account of the data collected, whilst the discussion considers the implications of these findings by relating them to relevant literature and answering your research question(s). See the tab 'The Differences' in this guide for more detail.
Q: Should the discussion include recommendations for future research?
A: Your dissertation should include some recommendations for future research, but it can vary where it appears. Recommendations are often featured towards the end of the discussion chapter, but they also regularly appear in the conclusion chapter (see our Writing the Conclusion guide for more). It simply depends on your dissertation and the conventions of your school or department. It’s worth consulting any specific guidance that you’ve been given, or asking your supervisor directly.
Q: Should the discussion include the limitations of the study?
A: Like the answer above, you should engage with the limitations of your study, but it might appear in the discussion of some dissertations, or the conclusion of others. Consider the narrative flow and whether it makes sense to include the limitations in your discussion chapter, or your conclusion. You should also consult any discipline-specific guidance you’ve been given, or ask your supervisor for more. Be mindful that this is slightly different to the limitations outlined in the methodology or methods chapter (see our Writing the Methodology guide vs. the 'Discussion' tab of this guide).
Q: Should the results and discussion be in the first-person or third?
A: It’s important to be consistent , so you should use whatever you’ve been using throughout your dissertation. Third-person is more commonly accepted, but certain disciplines are happy with the use of first-person. Just remember that the first-person pronoun can be a distracting, but powerful device, so use it sparingly. Consult your lecturer for discipline-specific guidance.
Q: Is there a difference between the discussion and the conclusion of a dissertation?
A: Yes, there is a difference. The discussion chapter is a detailed consideration of how your findings answer your research questions. This includes the use of secondary literature to help contextualise your discussion. Rather than considering the findings in detail, the conclusion briefly summarises and synthesises the main findings of your study before bringing the dissertation to a close. Both are similar, particularly in the way they ‘broaden out’ to consider the wider implications of the research. They are, however, their own distinct chapters, unless otherwise stated by your supervisor.
The results and discussion chapters (or chapter) constitute a large part of your dissertation as it’s here where your original contribution is foregrounded and discussed in detail. Remember, the results chapter simply reports on the data collected, whilst the discussion is where you consider your research questions and/or hypothesis in more detail by interpreting and interrogating the data. You can integrate both into a single chapter and weave the interpretation of your findings throughout the chapter, although it’s common for both the results and discussion to appear as separate chapters. Consult your supervisor for further guidance.
Here’s a final checklist for writing your results and discussion. Remember that not all of these points will be relevant for you, so make sure you cover whatever’s appropriate for your dissertation. The asterisk (*) indicates any content that might not be relevant for your dissertation. To download a copy of the checklist to save and edit, please use the Word document, below.
- Results and discussion self-evaluation checklist
| Aspect of Results or Discussion Chapters | Yes/Unsure/No |
|---|---|
| I have my results and discussion in a that suits the nature of my research. | |
| I have used (where relevant) my written account of the results. | |
| I have to discuss and interpret my findings. | |
| I have that might not adhere to my expectations or that might not correspond with other findings in the data. | |
| I have of my research and for future research. | |
| I have used my discussion to answer the question, , conveying to the reader the of my findings. |

- << Previous: Methodology
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2024 11:54 AM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/writing_the_dissertation
How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?
Reflecting on and Comparing Your Data, Recognising the Strengths and Limitations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
661 Accesses
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with subsections and paragraphs. We also present a list of points to do and avoid when writing the discussion together with a Discussion chapter checklist.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Braun V, Clarke V (2013) Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. SAGE Publications, London
Google Scholar
McGregor SLT (2018) Understanding and evaluating research: a critical guide. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles, CA
Book Google Scholar
PLOS (2023) Author resources. How to write discussions and conclusions. Accessed Mar 3, 2023, from https://plos.org/resource/how-to-write-conclusions/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Cottrell S (2017) Critical thinking skills: effective analysis, argument and reflection, 3rd edn. Palgrave, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
The discussion section of a research paper analyzes and interprets the findings, provides context, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future research directions.
Updated on September 15, 2023

Structure your discussion section right, and you’ll be cited more often while doing a greater service to the scientific community. So, what actually goes into the discussion section? And how do you write it?
The discussion section of your research paper is where you let the reader know how your study is positioned in the literature, what to take away from your paper, and how your work helps them. It can also include your conclusions and suggestions for future studies.
First, we’ll define all the parts of your discussion paper, and then look into how to write a strong, effective discussion section for your paper or manuscript.
Discussion section: what is it, what it does
The discussion section comes later in your paper, following the introduction, methods, and results. The discussion sets up your study’s conclusions. Its main goals are to present, interpret, and provide a context for your results.
What is it?
The discussion section provides an analysis and interpretation of the findings, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future directions for research.
This section combines information from the preceding parts of your paper into a coherent story. By this point, the reader already knows why you did your study (introduction), how you did it (methods), and what happened (results). In the discussion, you’ll help the reader connect the ideas from these sections.
Why is it necessary?
The discussion provides context and interpretations for the results. It also answers the questions posed in the introduction. While the results section describes your findings, the discussion explains what they say. This is also where you can describe the impact or implications of your research.
Adds context for your results
Most research studies aim to answer a question, replicate a finding, or address limitations in the literature. These goals are first described in the introduction. However, in the discussion section, the author can refer back to them to explain how the study's objective was achieved.
Shows what your results actually mean and real-world implications
The discussion can also describe the effect of your findings on research or practice. How are your results significant for readers, other researchers, or policymakers?
What to include in your discussion (in the correct order)
A complete and effective discussion section should at least touch on the points described below.
Summary of key findings
The discussion should begin with a brief factual summary of the results. Concisely overview the main results you obtained.
Begin with key findings with supporting evidence
Your results section described a list of findings, but what message do they send when you look at them all together?
Your findings were detailed in the results section, so there’s no need to repeat them here, but do provide at least a few highlights. This will help refresh the reader’s memory and help them focus on the big picture.
Read the first paragraph of the discussion section in this article (PDF) for an example of how to start this part of your paper. Notice how the authors break down their results and follow each description sentence with an explanation of why each finding is relevant.
State clearly and concisely
Following a clear and direct writing style is especially important in the discussion section. After all, this is where you will make some of the most impactful points in your paper. While the results section often contains technical vocabulary, such as statistical terms, the discussion section lets you describe your findings more clearly.
Interpretation of results
Once you’ve given your reader an overview of your results, you need to interpret those results. In other words, what do your results mean? Discuss the findings’ implications and significance in relation to your research question or hypothesis.
Analyze and interpret your findings
Look into your findings and explore what’s behind them or what may have caused them. If your introduction cited theories or studies that could explain your findings, use these sources as a basis to discuss your results.
For example, look at the second paragraph in the discussion section of this article on waggling honey bees. Here, the authors explore their results based on information from the literature.
Unexpected or contradictory results
Sometimes, your findings are not what you expect. Here’s where you describe this and try to find a reason for it. Could it be because of the method you used? Does it have something to do with the variables analyzed? Comparing your methods with those of other similar studies can help with this task.
Context and comparison with previous work
Refer to related studies to place your research in a larger context and the literature. Compare and contrast your findings with existing literature, highlighting similarities, differences, and/or contradictions.
How your work compares or contrasts with previous work
Studies with similar findings to yours can be cited to show the strength of your findings. Information from these studies can also be used to help explain your results. Differences between your findings and others in the literature can also be discussed here.
How to divide this section into subsections
If you have more than one objective in your study or many key findings, you can dedicate a separate section to each of these. Here’s an example of this approach. You can see that the discussion section is divided into topics and even has a separate heading for each of them.
Limitations
Many journals require you to include the limitations of your study in the discussion. Even if they don’t, there are good reasons to mention these in your paper.
Why limitations don’t have a negative connotation
A study’s limitations are points to be improved upon in future research. While some of these may be flaws in your method, many may be due to factors you couldn’t predict.
Examples include time constraints or small sample sizes. Pointing this out will help future researchers avoid or address these issues. This part of the discussion can also include any attempts you have made to reduce the impact of these limitations, as in this study .
How limitations add to a researcher's credibility
Pointing out the limitations of your study demonstrates transparency. It also shows that you know your methods well and can conduct a critical assessment of them.
Implications and significance
The final paragraph of the discussion section should contain the take-home messages for your study. It can also cite the “strong points” of your study, to contrast with the limitations section.
Restate your hypothesis
Remind the reader what your hypothesis was before you conducted the study.
How was it proven or disproven?
Identify your main findings and describe how they relate to your hypothesis.
How your results contribute to the literature
Were you able to answer your research question? Or address a gap in the literature?
Future implications of your research
Describe the impact that your results may have on the topic of study. Your results may show, for instance, that there are still limitations in the literature for future studies to address. There may be a need for studies that extend your findings in a specific way. You also may need additional research to corroborate your findings.
Sample discussion section
This fictitious example covers all the aspects discussed above. Your actual discussion section will probably be much longer, but you can read this to get an idea of everything your discussion should cover.
Our results showed that the presence of cats in a household is associated with higher levels of perceived happiness by its human occupants. These findings support our hypothesis and demonstrate the association between pet ownership and well-being.
The present findings align with those of Bao and Schreer (2016) and Hardie et al. (2023), who observed greater life satisfaction in pet owners relative to non-owners. Although the present study did not directly evaluate life satisfaction, this factor may explain the association between happiness and cat ownership observed in our sample.
Our findings must be interpreted in light of some limitations, such as the focus on cat ownership only rather than pets as a whole. This may limit the generalizability of our results.
Nevertheless, this study had several strengths. These include its strict exclusion criteria and use of a standardized assessment instrument to investigate the relationships between pets and owners. These attributes bolster the accuracy of our results and reduce the influence of confounding factors, increasing the strength of our conclusions. Future studies may examine the factors that mediate the association between pet ownership and happiness to better comprehend this phenomenon.
This brief discussion begins with a quick summary of the results and hypothesis. The next paragraph cites previous research and compares its findings to those of this study. Information from previous studies is also used to help interpret the findings. After discussing the results of the study, some limitations are pointed out. The paper also explains why these limitations may influence the interpretation of results. Then, final conclusions are drawn based on the study, and directions for future research are suggested.

How to make your discussion flow naturally
If you find writing in scientific English challenging, the discussion and conclusions are often the hardest parts of the paper to write. That’s because you’re not just listing up studies, methods, and outcomes. You’re actually expressing your thoughts and interpretations in words.
- How formal should it be?
- What words should you use, or not use?
- How do you meet strict word limits, or make it longer and more informative?
Always give it your best, but sometimes a helping hand can, well, help. Getting a professional edit can help clarify your work’s importance while improving the English used to explain it. When readers know the value of your work, they’ll cite it. We’ll assign your study to an expert editor knowledgeable in your area of research. Their work will clarify your discussion, helping it to tell your story. Find out more about AJE Editing.

Adam Goulston, PsyD, MS, MBA, MISD, ELS
Science Marketing Consultant
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 8. The Discussion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The purpose of the discussion section is to interpret and describe the significance of your findings in relation to what was already known about the research problem being investigated and to explain any new understanding or insights that emerged as a result of your research. The discussion will always connect to the introduction by way of the research questions or hypotheses you posed and the literature you reviewed, but the discussion does not simply repeat or rearrange the first parts of your paper; the discussion clearly explains how your study advanced the reader's understanding of the research problem from where you left them at the end of your review of prior research.
Annesley, Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Peacock, Matthew. “Communicative Moves in the Discussion Section of Research Articles.” System 30 (December 2002): 479-497.
Importance of a Good Discussion
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it:
- Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
- Presents the underlying meaning of your research, notes possible implications in other areas of study, and explores possible improvements that can be made in order to further develop the concerns of your research;
- Highlights the importance of your study and how it can contribute to understanding the research problem within the field of study;
- Presents how the findings from your study revealed and helped fill gaps in the literature that had not been previously exposed or adequately described; and,
- Engages the reader in thinking critically about issues based on an evidence-based interpretation of findings; it is not governed strictly by objective reporting of information.
Annesley Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Bitchener, John and Helen Basturkmen. “Perceptions of the Difficulties of Postgraduate L2 Thesis Students Writing the Discussion Section.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 5 (January 2006): 4-18; Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
These are the general rules you should adopt when composing your discussion of the results :
- Do not be verbose or repetitive; be concise and make your points clearly
- Avoid the use of jargon or undefined technical language
- Follow a logical stream of thought; in general, interpret and discuss the significance of your findings in the same sequence you described them in your results section [a notable exception is to begin by highlighting an unexpected result or a finding that can grab the reader's attention]
- Use the present verb tense, especially for established facts; however, refer to specific works or prior studies in the past tense
- If needed, use subheadings to help organize your discussion or to categorize your interpretations into themes
II. The Content
The content of the discussion section of your paper most often includes :
- Explanation of results : Comment on whether or not the results were expected for each set of findings; go into greater depth to explain findings that were unexpected or especially profound. If appropriate, note any unusual or unanticipated patterns or trends that emerged from your results and explain their meaning in relation to the research problem.
- References to previous research : Either compare your results with the findings from other studies or use the studies to support a claim. This can include re-visiting key sources already cited in your literature review section, or, save them to cite later in the discussion section if they are more important to compare with your results instead of being a part of the general literature review of prior research used to provide context and background information. Note that you can make this decision to highlight specific studies after you have begun writing the discussion section.
- Deduction : A claim for how the results can be applied more generally. For example, describing lessons learned, proposing recommendations that can help improve a situation, or highlighting best practices.
- Hypothesis : A more general claim or possible conclusion arising from the results [which may be proved or disproved in subsequent research]. This can be framed as new research questions that emerged as a consequence of your analysis.
III. Organization and Structure
Keep the following sequential points in mind as you organize and write the discussion section of your paper:
- Think of your discussion as an inverted pyramid. Organize the discussion from the general to the specific, linking your findings to the literature, then to theory, then to practice [if appropriate].
- Use the same key terms, narrative style, and verb tense [present] that you used when describing the research problem in your introduction.
- Begin by briefly re-stating the research problem you were investigating and answer all of the research questions underpinning the problem that you posed in the introduction.
- Describe the patterns, principles, and relationships shown by each major findings and place them in proper perspective. The sequence of this information is important; first state the answer, then the relevant results, then cite the work of others. If appropriate, refer the reader to a figure or table to help enhance the interpretation of the data [either within the text or as an appendix].
- Regardless of where it's mentioned, a good discussion section includes analysis of any unexpected findings. This part of the discussion should begin with a description of the unanticipated finding, followed by a brief interpretation as to why you believe it appeared and, if necessary, its possible significance in relation to the overall study. If more than one unexpected finding emerged during the study, describe each of them in the order they appeared as you gathered or analyzed the data. As noted, the exception to discussing findings in the same order you described them in the results section would be to begin by highlighting the implications of a particularly unexpected or significant finding that emerged from the study, followed by a discussion of the remaining findings.
- Before concluding the discussion, identify potential limitations and weaknesses if you do not plan to do so in the conclusion of the paper. Comment on their relative importance in relation to your overall interpretation of the results and, if necessary, note how they may affect the validity of your findings. Avoid using an apologetic tone; however, be honest and self-critical [e.g., in retrospect, had you included a particular question in a survey instrument, additional data could have been revealed].
- The discussion section should end with a concise summary of the principal implications of the findings regardless of their significance. Give a brief explanation about why you believe the findings and conclusions of your study are important and how they support broader knowledge or understanding of the research problem. This can be followed by any recommendations for further research. However, do not offer recommendations which could have been easily addressed within the study. This would demonstrate to the reader that you have inadequately examined and interpreted the data.
IV. Overall Objectives
The objectives of your discussion section should include the following: I. Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings
Briefly reiterate the research problem or problems you are investigating and the methods you used to investigate them, then move quickly to describe the major findings of the study. You should write a direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results, usually in one paragraph.
II. Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important
No one has thought as long and hard about your study as you have. Systematically explain the underlying meaning of your findings and state why you believe they are significant. After reading the discussion section, you want the reader to think critically about the results and why they are important. You don’t want to force the reader to go through the paper multiple times to figure out what it all means. If applicable, begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most significant or unanticipated finding first, then systematically review each finding. Otherwise, follow the general order you reported the findings presented in the results section.
III. Relate the Findings to Similar Studies
No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for your research. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your study differs from other research about the topic. Note that any significant or unanticipated finding is often because there was no prior research to indicate the finding could occur. If there is prior research to indicate this, you need to explain why it was significant or unanticipated. IV. Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings
It is important to remember that the purpose of research in the social sciences is to discover and not to prove . When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. This is especially important when describing the discovery of significant or unanticipated findings.
V. Acknowledge the Study’s Limitations
It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor! Note any unanswered questions or issues your study could not address and describe the generalizability of your results to other situations. If a limitation is applicable to the method chosen to gather information, then describe in detail the problems you encountered and why. VI. Make Suggestions for Further Research
You may choose to conclude the discussion section by making suggestions for further research [as opposed to offering suggestions in the conclusion of your paper]. Although your study can offer important insights about the research problem, this is where you can address other questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or highlight hidden issues that were revealed as a result of conducting your research. You should frame your suggestions by linking the need for further research to the limitations of your study [e.g., in future studies, the survey instrument should include more questions that ask..."] or linking to critical issues revealed from the data that were not considered initially in your research.
NOTE: Besides the literature review section, the preponderance of references to sources is usually found in the discussion section . A few historical references may be helpful for perspective, but most of the references should be relatively recent and included to aid in the interpretation of your results, to support the significance of a finding, and/or to place a finding within a particular context. If a study that you cited does not support your findings, don't ignore it--clearly explain why your research findings differ from theirs.
V. Problems to Avoid
- Do not waste time restating your results . Should you need to remind the reader of a finding to be discussed, use "bridge sentences" that relate the result to the interpretation. An example would be: “In the case of determining available housing to single women with children in rural areas of Texas, the findings suggest that access to good schools is important...," then move on to further explaining this finding and its implications.
- As noted, recommendations for further research can be included in either the discussion or conclusion of your paper, but do not repeat your recommendations in the both sections. Think about the overall narrative flow of your paper to determine where best to locate this information. However, if your findings raise a lot of new questions or issues, consider including suggestions for further research in the discussion section.
- Do not introduce new results in the discussion section. Be wary of mistaking the reiteration of a specific finding for an interpretation because it may confuse the reader. The description of findings [results section] and the interpretation of their significance [discussion section] should be distinct parts of your paper. If you choose to combine the results section and the discussion section into a single narrative, you must be clear in how you report the information discovered and your own interpretation of each finding. This approach is not recommended if you lack experience writing college-level research papers.
- Use of the first person pronoun is generally acceptable. Using first person singular pronouns can help emphasize a point or illustrate a contrasting finding. However, keep in mind that too much use of the first person can actually distract the reader from the main points [i.e., I know you're telling me this--just tell me!].
Analyzing vs. Summarizing. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Discussion. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Hess, Dean R. "How to Write an Effective Discussion." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004); Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sauaia, A. et al. "The Anatomy of an Article: The Discussion Section: "How Does the Article I Read Today Change What I Will Recommend to my Patients Tomorrow?” The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 74 (June 2013): 1599-1602; Research Limitations & Future Research . Lund Research Ltd., 2012; Summary: Using it Wisely. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Discussion. Writing in Psychology course syllabus. University of Florida; Yellin, Linda L. A Sociology Writer's Guide . Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2009.
Writing Tip
Don’t Over-Interpret the Results!
Interpretation is a subjective exercise. As such, you should always approach the selection and interpretation of your findings introspectively and to think critically about the possibility of judgmental biases unintentionally entering into discussions about the significance of your work. With this in mind, be careful that you do not read more into the findings than can be supported by the evidence you have gathered. Remember that the data are the data: nothing more, nothing less.
MacCoun, Robert J. "Biases in the Interpretation and Use of Research Results." Annual Review of Psychology 49 (February 1998): 259-287; Ward, Paulet al, editors. The Oxford Handbook of Expertise . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Write Two Results Sections!
One of the most common mistakes that you can make when discussing the results of your study is to present a superficial interpretation of the findings that more or less re-states the results section of your paper. Obviously, you must refer to your results when discussing them, but focus on the interpretation of those results and their significance in relation to the research problem, not the data itself.
Azar, Beth. "Discussing Your Findings." American Psychological Association gradPSYCH Magazine (January 2006).
Yet Another Writing Tip
Avoid Unwarranted Speculation!
The discussion section should remain focused on the findings of your study. For example, if the purpose of your research was to measure the impact of foreign aid on increasing access to education among disadvantaged children in Bangladesh, it would not be appropriate to speculate about how your findings might apply to populations in other countries without drawing from existing studies to support your claim or if analysis of other countries was not a part of your original research design. If you feel compelled to speculate, do so in the form of describing possible implications or explaining possible impacts. Be certain that you clearly identify your comments as speculation or as a suggestion for where further research is needed. Sometimes your professor will encourage you to expand your discussion of the results in this way, while others don’t care what your opinion is beyond your effort to interpret the data in relation to the research problem.
- << Previous: Using Non-Textual Elements
- Next: Limitations of the Study >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2024 10:20 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

How to Write an Impressive Thesis Results Section

After collecting and analyzing your research data, it’s time to write the results section. This article explains how to write and organize the thesis results section, the differences in reporting qualitative and quantitative data, the differences in the thesis results section across different fields, and the best practices for tables and figures.
What is the thesis results section?
The thesis results section factually and concisely describes what was observed and measured during the study but does not interpret the findings. It presents the findings in a logical order.
What should the thesis results section include?
- Include all relevant results as text, tables, or figures
- Report the results of subject recruitment and data collection
- For qualitative research, present the data from all statistical analyses, whether or not the results are significant
- For quantitative research, present the data by coding or categorizing themes and topics
- Present all secondary findings (e.g., subgroup analyses)
- Include all results, even if they do not fit in with your assumptions or support your hypothesis
What should the thesis results section not include?
- If the study involves the thematic analysis of an interview, don’t include complete transcripts of all interviews. Instead, add these as appendices
- Don’t present raw data. These may be included in appendices
- Don’t include background information (this should be in the introduction section )
- Don’t speculate on the meaning of results that do not support your hypothesis. This will be addressed later in the discussion and conclusion sections.
- Don’t repeat results that have been presented in tables and figures. Only highlight the pertinent points or elaborate on specific aspects
How should the thesis results section be organized?
The opening paragraph of the thesis results section should briefly restate the thesis question. Then, present the results objectively as text, figures, or tables.
Quantitative research presents the results from experiments and statistical tests , usually in the form of tables and figures (graphs, diagrams, and images), with any pertinent findings emphasized in the text. The results are structured around the thesis question. Demographic data are usually presented first in this section.
For each statistical test used, the following information must be mentioned:
- The type of analysis used (e.g., Mann–Whitney U test or multiple regression analysis)
- A concise summary of each result, including descriptive statistics (e.g., means, medians, and modes) and inferential statistics (e.g., correlation, regression, and p values) and whether the results are significant
- Any trends or differences identified through comparisons
- How the findings relate to your research and if they support or contradict your hypothesis
Qualitative research presents results around key themes or topics identified from your data analysis and explains how these themes evolved. The data are usually presented as text because it is hard to present the findings as figures.
For each theme presented, describe:
- General trends or patterns observed
- Significant or representative responses
- Relevant quotations from your study subjects
Relevant characteristics about your study subjects
Differences among the results section in different fields of research
Nevertheless, results should be presented logically across all disciplines and reflect the thesis question and any hypotheses that were tested.
The presentation of results varies considerably across disciplines. For example, a thesis documenting how a particular population interprets a specific event and a thesis investigating customer service may both have collected data using interviews and analyzed it using similar methods. Still, the presentation of the results will vastly differ because they are answering different thesis questions. A science thesis may have used experiments to generate data, and these would be presented differently again, probably involving statistics. Nevertheless, results should be presented logically across all disciplines and reflect the thesis question and any hypotheses that were tested.
Differences between reporting thesis results in the Sciences and the Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) domains
In the Sciences domain (qualitative and experimental research), the results and discussion sections are considered separate entities, and the results from experiments and statistical tests are presented. In the HSS domain (qualitative research), the results and discussion sections may be combined.
There are two approaches to presenting results in the HSS field:
- If you want to highlight important findings, first present a synopsis of the results and then explain the key findings.
- If you have multiple results of equal significance, present one result and explain it. Then present another result and explain that, and so on. Conclude with an overall synopsis.
Best practices for using tables and figures
The use of figures and tables is highly encouraged because they provide a standalone overview of the research findings that are much easier to understand than wading through dry text mentioning one result after another. The text in the results section should not repeat the information presented in figures and tables. Instead, it should focus on the pertinent findings or elaborate on specific points.
Some popular software programs that can be used for the analysis and presentation of statistical data include Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS ) , R software , MATLAB , Microsoft Excel, Statistical Analysis Software (SAS) , GraphPad Prism , and Minitab .
The easiest way to construct tables is to use the Table function in Microsoft Word . Microsoft Excel can also be used; however, Word is the easier option.
General guidelines for figures and tables
- Figures and tables must be interpretable independent from the text
- Number tables and figures consecutively (in separate lists) in the order in which they are mentioned in the text
- All tables and figures must be cited in the text
- Provide clear, descriptive titles for all figures and tables
- Include a legend to concisely describe what is presented in the figure or table
Figure guidelines
- Label figures so that the reader can easily understand what is being shown
- Use a consistent font type and font size for all labels in figure panels
- All abbreviations used in the figure artwork should be defined in the figure legend
Table guidelines
- All table columns should have a heading abbreviation used in tables should be defined in the table footnotes
- All numbers and text presented in tables must correlate with the data presented in the manuscript body
Quantitative results example : Figure 3 presents the characteristics of unemployed subjects and their rate of criminal convictions. A statistically significant association was observed between unemployed people <20 years old, the male sex, and no household income.

Qualitative results example: Table 5 shows the themes identified during the face-to-face interviews about the application that we developed to anonymously report corruption in the workplace. There was positive feedback on the app layout and ease of use. Concerns that emerged from the interviews included breaches of confidentiality and the inability to report incidents because of unstable cellphone network coverage.
|
|
| Ease of use of the app | The app was easy to use, and I did not have to contact the helpdesk |
| I wish all apps were so user-friendly! | |
| App layout | The screen was not cluttered. The text was easy to read |
| The icons on the screen were easy to understand | |
| Confidentiality | I am scared that the app developers will disclose my name to my employer |
| Unstable network coverage | I was unable to report an incident that occurred at one of our building sites because there was no cellphone reception |
| I wanted to report the incident immediately , but I had to wait until I was home, where the cellphone network signal was strong |
Table 5. Themes and selected quotes from the evaluation of our app designed to anonymously report workplace corruption.
Tips for writing the thesis results section
- Do not state that a difference was present between the two groups unless this can be supported by a significant p-value .
- Present the findings only . Do not comment or speculate on their interpretation.
- Every result included must have a corresponding method in the methods section. Conversely, all methods must have associated results presented in the results section.
- Do not explain commonly used methods. Instead, cite a reference.
- Be consistent with the units of measurement used in your thesis study. If you start with kg, then use the same unit all throughout your thesis. Also, be consistent with the capitalization of units of measurement. For example, use either “ml” or “mL” for milliliters, but not both.
- Never manipulate measurement outcomes, even if the result is unexpected. Remain objective.
Results vs. discussion vs. conclusion
Results are presented in three sections of your thesis: the results, discussion, and conclusion.
- In the results section, the data are presented simply and objectively. No speculation or interpretation is given.
- In the discussion section, the meaning of the results is interpreted and put into context (e.g., compared with other findings in the literature ), and its importance is assigned.
- In the conclusion section, the results and the main conclusions are summarized.
A thesis is the most crucial document that you will write during your academic studies. For professional thesis editing and thesis proofreading services , visit Enago Thesis Editing for more information.
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Review Checklist
Have you completed all data collection procedures and analyzed all results ?
Have you included all results relevant to your thesis question, even if they do not support your hypothesis?
Have you reported the results objectively , with no interpretation or speculation?
For quantitative research, have you included both descriptive and inferential statistical results and stated whether they support or contradict your hypothesis?
Have you used tables and figures to present all results?
In your thesis body, have you presented only the pertinent results and elaborated on specific aspects that were presented in the tables and figures?
Are all tables and figures correctly labeled and cited in numerical order in the text?
Frequently Asked Questions
What file formats do you accept for plagiarism check service +.
We accept all file formats, including Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, PDF, Latex, etc.
What information do i need to provide with my Plagiarism Check order? +
Please upload your research manuscript when you order Plagiarism Check Service . If you want to include the tables, charts, and figure legends in the plagiarism check, please ensure that all content is in editable formats and in one single document.
Is repetition percentage of 25-30% considered acceptable by the journal editors? +
Acceptable repetition rate varies by journal but aim for low percentages (usually <5%). Avoid plagiarism (including self-plagiarism), cite sources, and use detection tools. Plagiarism can lead to rejection, reputation damage, and serious consequences. Consult your institution for guidance on addressing plagiarism concerns.
Do you offer help to rewrite and paraphrase text that has plagiarism concern in my manuscript? +
We can help you rewrite and paraphrase text in your manuscript to ensure it is not plagiarized under our Developmental Content Rewriting Service. You can provide specific passages or sentences that you are concerned about, and we can assist you in rephrasing them or citing the source materials in a proper format.
Which languages does iThenticate support in its database? +
iThenticate searches for content matches in the following 30 languages: Chinese (Simplified and Traditional), Japanese, Thai, Korean, Catalan, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Hungarian, Italian, Norwegian (Bokmal, Nynorsk), Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Serbian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Arabic, Greek, Hebrew, Farsi, Russian, and Turkish. Please note that iThenticate will match your text with text of the same language.
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter: Guide & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter: Guide & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Dissertation discussion section is a chapter that interprets the results obtained from research and offers an in-depth analysis of findings. In this section, students need to analyze the outcomes, evaluate their significance, and compare them to previous research. The discussion section may also explore the limitations of the study and suggest further research perspectives.
If you are stuck with your thesis or dissertation discussion chapter, you are in the right place to complete this section successfully. This article will outline our best solutions and methods on how to write the discussion of a dissertation or thesis. We also will share advanced dissertation discussion examples to help you finalize your PhD work. Feel like academic writing gives you hassles? Remember that you can always rely on academic experts qualified in your field to get professional dissertation help online .
What Is a Dissertation Discussion?
First and foremost, students need to have a clear understanding of what dissertation discussion is. This is not the same as your results section , where you share data from your research. You are going deeper into the explanation of the existing data in your thesis or dissertation discussion section. In other words, you illustrate practical implications of your research and how the data can be used, researched further, or limited. What will make your discussion section of a dissertation excellent:
- clear structure
- practical implication
- elaboration on future work on this topic.
This section should go after research methodology and before the dissertation conclusion . It should be directly relevant to questions posed in your introduction. The biggest mistake you can make is to rewrite your result chapter with other words and add some limitations and recommendation paragraphs. However, this is an entirely different type of writing you need to complete.
Purpose of a Dissertation Discussion Chapter
A dissertation discussion section is critical to explaining students’ findings and the application of data to real-life cases. As we mentioned before, this section will often be read right after the dissertation methods . It evaluates and elaborates on findings and helps to understand the importance of your performed thesis research. A dissertation discussion opens a new perspective on further research on the same field or topic. It also outlines critical data to consider in subsequent studies. In a nutshell, this is the section where you explain your work to a broad audience.
Structure of a Dissertation Discussion Section
Let’s start your writing journey of this research part with a clear delineation of what it should include and then briefly discuss each component. Here are some basic things you need to consider for an excellent discussion chapter of dissertation :
- Brief summary It does not mean copying an introduction section. However, the first few paragraphs will make an overview of your findings and topic.
- Interpretations This is a critical component of your work — elaborate on your results and explain possible ways of using them.
- Implication Research work is not just 100+ pages of text. Students should explain and illustrate how it could be used for solving practical problems.
- Constraints This is where you outline your limitations. For instance, your research was done only on students, and it may have different results with elderly people.
- Recommendations You can also define possible ways of future research on the exact topic when writing a discussion for your thesis or dissertation. Tell readers, for example, that it would be helpful to run similar research in other specific circumstances.
How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
One of the most commonly asked questions for our experts is how to write the discussion section of a dissertation or thesis. We understand why it can be complicated to get a clear answer. Students often think that this section is similar to the result chapter and just retells it in other words. But it is not so. Let’s go through all steps to writing a discussion in a dissertation, and share our best examples from academic papers.
1. Remind Your Research Questions & Objectives
Writing the discussion chapter of a dissertation is not a big deal if you understand its aim and each component in a text structure. First of all, you need to evaluate how your results help to answer research questions you defined in the beginning. It is not about repeating the result, you did it in previous paragraphs. However, dissertation or thesis discussion should underline how your findings help to answer the research problem. Start writing from a brief intro by recalling research questions or hypotheses . Then, show how your results answer them or support a hypothesis in your work.
2. Sum Up Key Findings
Next part of your discussion for dissertation is to provide a short summary of previous data. But do not respite the same summary paragraphs from results or introduction of a dissertation . Here researchers should be more thoughtful and go deeper into the work’s aims. Try to explain in a few sentences what you get from running research. For instance, starters usually write the statement that “our data proves that…” or “survey results illustrate a clear correlation between a and b that is critical for proving our working hypothesis…”. A discussion chapter of your dissertation is not just a fixation on results but a more profound summary connected to research goals and purpose. Here is an example: Summary of Findings Example
According to the data, implementing the co-orientation theory was successful and can be used for the same circumstances in the future. As we found, most participants agreed with the importance of those theses on the five fundamental reforms. It means that the results identified a successful government work in choosing the messages to communicate about examined reforms. At the same time, the situation is not so favorable with implementing the principles of two-way symmetrical communications. According to the results, people did not feel that the government had a mutual, open, and equal dialogue with the public about the reforms.
3. Interpret the Results
The most critical part of a discussion section is to explain and enact the results you’ve got. It is the most significant part of any text. Students should be clear about what to include in these paragraphs. Here is some advice to make this elaboration structured:
- Identify correlations or patterns in the data for dissertation discussion.
- Underline how results can answer research questions or prove your hypothesis.
- Emphasize how your findings are connected to the previous topic studies.
- Point out essential statements you can use in future research.
- Evaluate the significance of your results and any unexpected data you have.
- What others can learn from your research and how this work contributes to the field.
- Consider any possible additional or unique explanation of your findings.
- Go deeper with options of how results can be applied in practice.
Writing a dissertation discussion chapter can be tough, but here is a great sample to learn from. Example of Interpretations in Disssertation Discussion
Our study underlines the importance of future research on using TikTok for political communication. As discussed above, TikTok is the most commonly used social media platform for many young voters. This means that political discussion will also move to this platform. Our research and typology of political communication content can be used in the future planning of effective political campaigns. For example, we can assume that “play videos” have enormous potential to facilitate complicated topics and provide specific agenda settings. We also identified additional affordances of TikTok used for political communication, such as built-in video editors, playlists for specific topics, a green screen for news explainers, and duets for reflection on news and discussion. It means that these features make TikTok suitable for efficient political communications.
4. Discuss How Your Findings Relate to the Literature
Here we came to the implications of your findings for the dissertation discussion. In other words, this is a few sentences on how your work is connected to other studies on the same research topic or what literature gap you are going to fill with the data and research you launched. Remember to mention how your study address the limitations you have discovered while writing a literature review . First, outline how your hypothesis relates to theories or previous works in the field. Maybe, you challenged some theories or tried to define your own. Be specific in this section. Second, define a practical implementation of your work. Maybe, it can support recommendations or change legislation. Discussion chapter of a thesis is a place where you explain your work, make it valuable, and incorporate additional meaning for some specific data. Example of Implications in Disssertation Discussion
As we pointed out in the literature review, there are few works on using TikTok affordances for political communications, and this topic can be expanded in the future. Government institutions have already understood the importance of this platform for efficient communication with younger audiences, and we will see more political projects on TikTok. That is why expanding research on using TikTok for political communication will be enormous in the following years. Our work is one of the first research on the role of emerging media in war communication and can be used as a practical guide for government's strategic planning in times of emergencies.
5. Mention Possible Limitations
It is pretty tricky to conduct research without limitations. You will always have some, which does not mean that your work is not good. When you write a discussion chapter in a thesis or dissertation, focus on what may influence your results and how changing independent variables can affect your data collection methods and final outcomes. Here are some points to consider when you structure your dissertation discussion limitation part:
- If results can change in case you change the reference group?
- What will happen with data if it changes circumstances?
- What could influence results?
Critical thinking and analysis can help you to outline possible limitations. It can be the age of the reference group, change of questionnaire in a survey, or specific use of data extraction equipment. Be transparent about what could affect your results. Example of Complications
Although this study has provided critical first insights into the effects of multimodal disinformation and rebuttals, there are some limitations. First and most importantly, the effects of multimodal disinformation and rebuttals partially depend on the topic of the message. Although fact-checkers reduce credibility of disinformation in both settings, and attitudinal congruence plays a consistent role in conditioning responses to multimodal disinformation, visuals do not have the same impact on affecting the credibility of news on school shootings and refugees.
6. Provide Recommendations for Further Research
Writing a dissertation discussion also makes a connection to possible future research. So, other scientists may complete that. While elaborating on possible implementations of your study, you may also estimate future approaches in topic research. Here are some points to consider while your discussion in thesis writing:
- Outline questions related to your topic that you did not answer in defined study or did not outline as research questions. There are other possible gaps to research.
- Suggest future research based on limitations. For example, if you define surveyed people’s age as a limitation, recommend running another survey for older or younger recipients.
Example of Recommendations
As we mentioned before, our study has some limitations, as the research was conducted based on data from United State citizens. However, for a better understanding of government communication practices, it would be productive to implement the same research in other countries. Some cultural differences can influence the communication strategies the government uses in times of emergency. Another possible way to examine this topic is to conduct research using a specific period of time. For future studies, it will be beneficial to expand the number of survey recipients.
7. Conclude Your Thesis/ Dissertation Discussion
You are almost done, the last step is to provide a brief summary of a section. It is not the same as a conclusion for whole research. However, you need to briefly outline key points from the dissertation discussion. To finalize writing the discussion section of a dissertation, go through the text and check if there is no unimportant information. Do not overload the text with relevant data you did not present in the result section. Be specific in your summary paragraphs. It is a holistic view of everything you pointed out. Provide a few sentences to systemize all you outlined in the text. Example of a Concluding Summary in a Dissertation Discussion Section
To summarize, Airbnb has expertise in communicating CSR and CSA campaigns. We defined their communication strategy about the program for Ukrainian refugees as quite successful. They applied all the principles of CSR communication best practices, used dialogic theory to engage with the public on social media, and created clear messaging on applying for the program. Airbnb examples of CSR communication can be used by other businesses to create a communication strategy for unplanned CSR campaigns. Moreover, it can be further researched how Airbnb's CSR campaign influenced the organizational reputation in the future.
Dissertation Discussion Example
If we need to share one piece of practical advice, it would be to use thesis or dissertation discussion examples when writing your own copy. StudyCrumb provides the best samples from real students' work to help you understand the stylistic and possible structure of this part. It does not mean you need to copy and paste them into your work. However, you can use a dissertation discussion example for inspiration and brainstorming ideas for breaking writing blocks. Here’s a doctoral thesis discussion chapter example.
Dissertation Discussion Writing Tips
Before reading this blog, you should already know how to write a thesis discussion. However, we would share some essential tips you need to have in mind while working on the document.
- Be consistent Your dissertation discussion chapter is a part of bigger research, and it should be in line with your whole work.
- Understand your reader You are writing an academic text that will be analyzed by professionals and experts in the same field. Be sure that you are not trying to simplify your discussion.
- Be logical Do not jump into a new line of discussion if you did not delineate it as a research question at the beginning.
- Be clear Do not include any data that was not presented in the result section.
- Consider word choice Use such terms as “our data indicate…” or “our data suggests…” instead of “the data proves.”
- Use proper format Follow the formatting rules specified by a specific paper style (e.g., APA style format , MLA format , or Chicago format ) or provided by your instructor.
Bottom Line on Writing a Dissertation Discussion Chapter
At this stage, it should not be a question for you on how to write a discussion chapter in a PhD thesis or dissertation. Let’s make it clear. It is not a result section but still a place to elaborate on data and go deeper with explanations. Dissertation discussion section includes some intro, result interpretations, limitations, and recommendations for future research. Our team encourages you to use examples before starting your own piece of writing. It will help you to realize the purpose and structure of this chapter and inspire better texts! If you have other questions regarding the PhD writing process, check our blog for more insights. From detailed instruction on how to write a dissertation or guide on formatting a dissertation appendix , we’ve got you covered.
Order dissertation discussion from our proficient writers. They will take a significant burden off of you. Instead, they will carry out high-level academic work in a short time.
FAQ About Dissertation Discussion Chapter
1. where does a discussion section go in a dissertation.
Dissertation discussion section is used to go right after the result chapter. The logic is simple — you share your data and then go to the elaboration and explanation of it. Check the sample thesis we provide to students for details on structure.
2. How long should a dissertation discussion chapter be?
It is not a surprise that dissertation discussion chapter is extremely significant for the research. Here you will go into the details of your study and interpret results to prove or not your hypothesis. It should take almost 25% of your work.
3. What tense should I use in a dissertation discussion?
Thesis or dissertation discussion used to have some rules on using tenses. You need to use the present tense when referring to established facts and use the past tense when referring to previous studies. And check your text before submission to ensure that you did not miss something.
4. What not to include in a dissertation discussion section?
The answer is easy. Discussion section of a dissertation should not include any new findings or describe some unsupported claims. Also, do not try to feel all possible gaps with one research. It may be better to outline your ideas for future studies in recommendations.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

- Translation
Writing a compelling results and discussion section
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 12 March, 2021
- Academic Writing Skills
In the results section of your academic paper, you present what you found when you conducted your analyses, whereas in your discussion section you explain what your results mean and connect them to prior research studies. In other words, the results section is where you describe what you did, and the discussion sections is where you describe what this means for the field.
The results section should include the findings of your study without any interpretations or implications that you can draw from those results. Here, you present the findings using text supported by tables, charts, graphs and other figures. For example, in the following excerpt from article by Tolksdorf, Crawshaw, & Rohlfing, (2021), you can see how directly they report the results of their study.
Contrary to our hypothesis, there was no main effect of time, F(3, ∞) = 0.638, p = 0.166, and no significant interaction between experimental condition and time, F(3, ∞) = 0.427, p = 0.133, indicating that no significant changes in children's social referencing behavior were found in either group over the entire course of the sessions, including all learning and test situations. However, there was a highly significant main effect of condition F(1, 16.99) = 49.08, p < 0.001, demonstrating that children in the human condition displayed social referencing significantly more often than their peers interacting with the robotic partner. (p. 6)
Further in the results section the authors use a table to illustrate their results.
Table 1 presents an overview of the different interactional contexts in which children’s social referencing was situated during the long-term interaction. (p. 6)
As you can see, the results section is very direct and reports the outcome from the statistical analyses conducted. Tables and figures can help break up this section, as it can be very technical. In addition, using visuals in this way makes the results more accessible to readers.
The discussion section, which follows the results section, will include an explanation of the results. In this section, you should connect your results to previous research studies, make explicit connections back to your research question(s) and include an explanation about how the results might be generalized. This is where you make an argument that supports your main conclusions. Unlike the results section, the discussion section is where you interpret your results and explain what they mean, draw implications from your results and articulate why they matter, discuss any limitations of your results, and provide recommendations that can be made from these results. The following excerpts from the Tolksdorf, Crawshaw, & Rohlfing, (2021), help to further illustrate the difference between the results and discussions sections.
Contrary to our prior assumption, we could not observe a significant decrease in children’s social referencing in both groups despite the repetition of the interaction and increasing familiarity with the situation. Whereas, there appeared to be a slight decreasing tendency from the second to the third learning situation in each group, this trend may have been slowed down by the subsequent novel situation of the retention task, which again increased children’s reliance on the caregiver despite increasing familiarity with the interaction partner. (p. 8)
The large difference in children’s social referencing behavior between an interaction with the human vs. robotic partner is striking. One explanation for our findings is that a human partner naturally responds to various social cues (Kahle and Argyle, 2014) from the child in ways that social robots are not yet capable of, given their present technological limitations. (p. 8)
Notice how the authors provide a critical analysis of their results and offer explanations for what they found. In the second excerpt, observe how they tie an explanation for their result to prior research conducted in the field. Focusing on the results and discussion sections of different articles, and highlighting language that differentiates these sections from each other, can really help you to write your academic papers effectively.
Although the length and structure of the discussion section across research papers varies, there are some commonalities in the structure and content of these sections. Below is a suggested outline for a discussion section.
Paragraph 1.
In this paragraph provide a broad overview of the importance of your study. This is where you should restate your research topic. Avoid just repeating what you included in the results section. Include the main research findings that answer your primary research question(s).
Paragraph 2–3.
This section should be a critical analysis of your major findings. Here, you should articulate your interpretations of those findings. You should include whether these were the findings you expected and also whether they support any hypothesis you had. Provide explanations for the significance of the results and for any unexpected findings. Link your primary findings back to prior research studies. This section would also include any implications of your results.
Paragraph 4.
Here you would include a discussion of any secondary findings that are of note. Additionally, you would also include any limitations of your study and how future studies might mitigate these limitations. The excerpt below, from the Tolksdorf, Crawshaw, & Rohlfing, (2021) study, provides an example of this.
We would also like to point to the possibility that the study design and procedure could have impacted our results. Adapting the design of the interaction from the robot experimental setting to be suitably comparable when taking place with a human interaction partner required us to make certain decisions. (p. 9)
Paragraph 5.
This should include the conclusion of the discussion section, and future directions. In this section you could include any new research questions that arose as a result of your study. Implications from your findings for the field should also be discussed in this paragraph.
There are a number of common errors researchers make when writing the results and discussion sections. The following checklist can help you avoid these common mistakes.
Do not include interpretations or explanations of the findings in your results section. Remember that in the results section you are telling the reader what you found and in the discussion section you are telling them what it means and why it matters.
Do not exclude negative findings from your results section. Although the temptation is to report only positive findings, negative findings are important to other researchers.
You should not introduce any findings in your discussion section that were not included in the results section. These two sections should align, and you should discuss and explain only what you have already reported.
Don’t restate results in the discussion paper without an explanation or critical analysis of what they mean and why they matter.
Don’t forget to go back and check that these two sections align, and the flow from the results section to the discussion section is smooth and clear.
Tolksdorf NF, Crawshaw CE and Rohlfing KJ (2021) Comparing the Effects of a Different Social Partner (Social Robot vs. Human) on Children's Social Referencing in Interaction. Front. Educ. 5:569615. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.569615
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928. We only work with native English-speaking editors with advanced or postdoctoral degrees in their disciplines.
To know more about our services: Link(https://www.cwauthors.com/EditingServices)
Our academic writing and publishing training courses, online materials, and blog articles contain numerous tips and tricks to help you navigate academic writing and publishing, and maximise your potential as a researcher.
Join us on our FREE series of webinars designed to help the researchers in achieving their publication success.
Register: (https://www.cwauthors.com/article/webinar-schedule-2020)
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 21 August 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 25 October 2022.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion . It should not be a second results section .
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary: A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarise your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasise weaknesses or failures.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarising your major findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported – aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that …
- The study demonstrates a correlation between …
- This analysis supports the theory that …
- The data suggest that …
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualising your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organise your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis …
- Contrary to the hypothesised association …
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2007) that …
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is x .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of …
- The results do not fit with the theory that …
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between …
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to …
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of …
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalisability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analysing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalisability of the results is limited by …
- The reliability of these data is impacted by …
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm …
- The methodological choices were constrained by …
- It is beyond the scope of this study to …
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done – give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish …
- Future studies should take into account …
- Avenues for future research include …

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 5 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a results section | tips & examples, research paper appendix | example & templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
Training videos | Faqs

Academic Phrases for Writing Results & Discussion Sections of a Research Paper
Overview | Abstract | Introduction | Literature Review | Materials & Methods | Results & Discussion | Conclusion & Future Work | Acknowledgements & Appendix
The results and discussion sections are one of the challenging sections to write. It is important to plan this section carefully as it may contain a large amount of scientific data that needs to be presented in a clear and concise fashion. The purpose of a Results section is to present the key results of your research. Results and discussions can either be combined into one section or organized as separate sections depending on the requirements of the journal to which you are submitting your research paper. Use subsections and subheadings to improve readability and clarity. Number all tables and figures with descriptive titles. Present your results as figures and tables and point the reader to relevant items while discussing the results. This section should highlight significant or interesting findings along with P values for statistical tests. Be sure to include negative results and highlight potential limitations of the paper. You will be criticised by the reviewers if you don’t discuss the shortcomings of your research. This often makes up for a great discussion section, so do not be afraid to highlight them.
The results and discussion section of your research paper should include the following:
- Comparison with prior studies
- Limitations of your work
- Casual arguments
- Speculations
- Deductive arguments
1. Findings
From the short review above, key findings emerge: __ We describe the results of __, which show __ This suggests that __ We showed that __ Our findings on __ at least hint that __ This is an important finding in the understanding of the __ The present study confirmed the findings about __ Another promising finding was that __ Our results demonstrated that __ This result highlights that little is known about the __ A further novel finding is that __ Together, the present findings confirm __ The implications of these findings are discussed in __ The results demonstrate two things. First, __. Second, __ The results of the experiment found clear support for the __ This analysis found evidence for __ Planned comparisons revealed that __ Our results casts a new light on __ This section summarises the findings and contributions made. It performs well, giving good results. This gives clearly better results than __ The results confirm that this a good choice for __ From the results, it is clear that __ In this section, we will illustrate some experimental results. This delivers significantly better results due to __ The result now provides evidence to __ It leads to good results, even if the improvement is negligible. This yields increasingly good results on data. The result of this analysis is then compared with the __ The applicability of these new results are then tested on __ This is important to correctly interpret the results. The results are substantially better than __ The results lead to similar conclusion where __ Superior results are seen for __ From these results it is clear that __ Extensive results carried out show that this method improves __ We obtain good results with this simple method. However, even better results are achieved when using our algorithm. It is worth discussing these interesting facts revealed by the results of __ Overall, our method was the one that obtained the most robust results. Slightly superior results are achieved with our algorithm. The result is equal to or better than a result that is currently accepted.
2. Comparison with prior studies
The results demonstrated in this chapter match state of the art methods. Here we compare the results of the proposed method with those of the traditional methods. These results go beyond previous reports, showing that __ In line with previous studies __ This result ties well with previous studies wherein __ Contrary to the findings of __ we did not find __ They have demonstrated that __ Others have shown that __ improves __ By comparing the results from __, we hope to determine __ However, in line with the ideas of __, it can be concluded that __ When comparing our results to those of older studies, it must be pointed out that __ We have verified that using __ produces similar results Overall these findings are in accordance with findings reported by __ Even though we did not replicate the previously reported __, our results suggest that __ A similar conclusion was reached by __ However, when comparing our results to those of older studies, it must be pointed out __ This is consistent with what has been found in previous __ A similar pattern of results was obtained in __ The findings are directly in line with previous findings These basic findings are consistent with research showing that __ Other results were broadly in line with __
3. Limitations of your work
Because of the lack of __ we decided to not investigate __ One concern about the findings of __ was that __ Because of this potential limitation, we treat __ The limitations of the present studies naturally include __ Regarding the limitations of __, it could be argued that __ Another limitation of this __ This limitation is apparent in many __ Another limitation in __ involves the issue of __ The main limitation is the lack of __ One limitation is found in this case. One limitation of these methods however is that they __ It presents some limitations such as __ Although widely accepted, it suffers from some limitations due to __ An apparent limitation of the method is __ There are several limitations to this approach. One limitation of our implementation is that it is __ A major source of limitation is due to __ The approach utilised suffers from the limitation that __ The limitations are becoming clear __ It suffers from the same limitations associated with a __
4. Casual arguments
A popular explanation of __ is that __ It is by now generally accepted that __ A popular explanation is that __ As it is not generally agreed that __ These are very small and difficult to observe. It is important to highlight the fact that __ It is notable that __ An important question associated with __ is __ This did not impair the __ This is important because there is __ This implies that __ is associated with __ This is indicative for lack of __ This will not be biased by __ There were also some important differences in __ It is interesting to note that, __ It is unlikely that __ This may alter or improve aspects of __ In contrast, this makes it possible to __ This is particularly important when investigating __ This has been used to successfully account for __ This introduces a possible confound in __ This was included to verify that __
5. Speculations
However, we acknowledge that there are considerable discussions among researchers as to __ We speculate that this might be due to __ There are reasons to doubt this explanation of __ It remains unclear to which degree __ are attributed to __ However, __ does seem to improve __ This does seem to depend on __ It is important to note, that the present evidence relies on __ The results show that __ does not seem to impact the __ However, the extent to which it is possible to __ is unknown Alternatively, it could simply mean that __ It is difficult to explain such results within the context of __ It is unclear whether this is a suitable for __ This appears to be a case of __ From this standpoint, __ can be considered as __ To date, __remain unknown Under certain assumptions, this can be construed as __ Because of this potential limitation, we treat __ In addition, several questions remain unanswered. At this stage of understanding, we believe__ Therefore, it remains unclear whether __ This may explain why __
6. Deductive arguments
A difference between these __ can only be attributable to __ Nonetheless, we believe that it is well justified to __ This may raise concerns about __ which can be addressed by __ As discussed, this is due to the fact that __ Results demonstrate that this is not necessarily true. These findings support the notion that __ is not influenced by __ This may be the reason why we did not find __ In order to test whether this is equivalent across __, we __ Therefore, __ can be considered to be equivalent for __
Similar Posts

Academic Phrases for Writing Conclusion Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to conclusion section such as summary of results and future work.

How to Write a Research Paper? A Beginners Guide with Useful Academic Phrases
This blog explains how to write a research paper and provides writing ideas in the form of academic phrases.

Academic Phrases for Writing Literature Review Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to literature review such as summary of previous literature, research gap and research questions.

Academic Phrases for Writing Acknowledgements & Appendix Sections of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to thanking colleagues, acknowledging funders and writing the appendix section.

Academic Phrases for Writing Abstract Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to the abstract section. An abstract is a self-contained and short synopsis that describes a larger work.

Academic Writing Resources – Academic PhraseBank | Academic Vocabulary & Word Lists
In this blog, we review various academic writing resources such as academic phrasebank, academic wordlists, academic vocabulary training sites.
32 Comments
Awesome vocab given, I am really thankful. keep it up!
Why didn’t I find this earlier? Thank you very much! Bless your soul!
thank you!! very useful!!!
Thank you, thank you thank you!!
I’m currently writing up my PhD thesis and as a non-native English speaker, I find this site extremely useful. Thanks for making it!
Very ve4y resourceful..well done Sam
Plesse add me to your mailing list Email: [email protected]
Hi, would like to clarify if that is “casual” or “causal”? Thanks!
Hi there, it should read “causal.”
Thanx for this. so helpful!
Very helpful. Thanks
thank you so much
- Pingback: Scholarly Paraphrasing Tool and Essay Rewriter for Rewording Academic Papers - Ref-N-Write: Scientific Research Paper Writing Software Tool - Improve Academic English Writing Skills
thankyouuuuuu
thank you very much
wow thanks for the help!!
Quite interesting! Thanks a lot!
This is ammmaazzinggg, too bad im in my last year of university this is very handy!!!
Extremely Useful. Thank-you so much.
This is an excellent collection of phrases for effective writing
Thank you so much, it has been helpful.
I found it extremely important!!!
It is a precise, brief and important guides;
It is a very important which gives a guide;
It is a very important guiding explanation for writing result and discussion;
It is a very important guiding academic phrases for writing;
thank you so much.I was in need of this.
- Pingback: Research Paper Structure – Main Sections and Parts of a Research Paper
Thank you so much!!! They are so helpful!
thank its very important.
This is timely, I needed it. Thanks
This is very helpful. Thanks.
You saved my Bachoelor thesis! Huge thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 91 Share Facebook
- 68 Share Twitter
- 53 Share LinkedIn
- 0.1K Share Email
US gets DQ in men's 4x100m relay final as medal drought continues
Team usa had a collision on the first exchange of the baton., by eric mullin • published august 9, 2024 • updated on august 9, 2024 at 4:24 pm.
Even down Noah Lyles , the United States looked primed to finally snap its Olympic medal drought in the men's 4x100m relay final on Friday .
But disaster struck early for Team USA at Stade de France .
Free 24/7 Connecticut news stream: Watch NBC CT wherever you are
American Christian Coleman collided with teammate Kenny Bednarek on the first exchange of the baton, causing the U.S. to fall behind the pack.
The bad exchange left the Americans with simply too much ground to make up, as the quartet of Coleman, Bednarek, Kyree King and Fred Kerley combined to cross the finish line seventh.
Get top local stories in Connecticut delivered to you every morning. Sign up for NBC Connecticut's News Headlines newsletter.

Sha'Carri Richardson and Gabby Thomas lead Team USA to track gold, women's basketball advances to finals

When was the last Olympics where Team USA didn't win the most golds, total medals?
Shortly after the race, the Americans were then disqualified for an illegal pass on the first exchange.
“It just didn’t happen,” Coleman said. “Maybe we could have put in some more work. I just think in the moment it didn’t happen.”
Canada won gold with a time of 37.50 seconds , with South Africa (37.57) and Great Britain (37.61) rounding out the Olympic podium.
Team USA was looking for its first medal in the event since a second-place finish at the 2004 Athens Games . The U.S. hasn't won gold since the 2000 Sydney Games .
“At the end of the day, we knew what we could do,” King said. “We came out here and we had the mindset of no risk, no reward, so we went out there and went big. It didn’t happen.”
Earlier Friday, the women's 4x100m relay team of Sha'Carri Richardson , Gabby Thomas , Melissa Jefferson and Twanisha "Teetee" Terry sprinted to United States' first gold since 2016 .
The Associated Press contributed to this story.
This article tagged under:

Free Download
Discussion Chapter Template
The fastest (and smartest) way to craft a strong discussion section for your dissertation, thesis or research project.
Available in Google Doc, Word & PDF format 4.9 star rating, 5000 + downloads

Step-by-step instructions
Tried & tested academic format
Fill-in-the-blanks simplicity
Pro tips, tricks and resources

What It Covers
This template covers all the core components required in the discussion chapter (or section) of a typical dissertation or thesis, including:
- The opening/ overview section
- Overview of key findings
- Interpretation of the findings
- Concluding summary
The purpose of each section is explained in plain language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. The template also includes practical examples to help you understand exactly what’s required, along with links to additional free resources (articles, videos, etc.) to help you along your research journey.
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
download your copy
100% Free to use. Instant access.
I agree to receive the free template and other useful resources.
Download Now (Instant Access)

FAQs: Thesis Discussion Template
Faq: thesis discussion template, what types of dissertations/theses can this template be used for.
The discussion chapter template follows the standard format for academic research projects, which means it will be suitable for the majority of dissertations, theses and research projects (especially those within the sciences).
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the discussion chapter/section will vary between universities and degree programs. For example, your university may require that the discussion chapter and conclusion chapter are merged into one, or that the results and discussion are covered together (this is often the case with qualitative research). So, be sure to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalise your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a dissertation, thesis or research project at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the discussion chapter to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same. Again, be sure to check your university’s requirements and norms in terms of document structure.
How long should the discussion chapter be?
This can vary a fair deal, depending on the level of study (undergrad, Master or Doctoral), the field of research, as well as your university’s specific requirements. Therefore, it’s best to check with your university or review past dissertations from your program to get an accurate estimate.
Can I share this template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, please reference this page as your source.
What format is the template (DOC, PDF, PPT, etc.)?
The dissertation discussion chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
Do you have templates for the other chapters?
Yes, we do. We are constantly developing our collection of free resources to help students complete their dissertations and theses. You can view all of our template resources here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my discussion/analysis?
Yes, we can provide coaching-based assistance with your discussion chapter (or any other chapter). If you’re interested, get in touch to discuss our private coaching services .
Additional Resources
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis, you’ll also want to check these out…
1-On-1 Private Coaching
Research Bootcamps
The Grad Coach YouTube Channel
The Grad Coach Podcast

Informing Educator Preparation Programs_Daniela Vilarinho Rezende Pereira
until file(s) become available
Informing Educator Preparation Programs: Insights into Technology Integration
The overarching purpose of this three-paper dissertation was to investigate the affordances of technology in educational settings and gain insight into how preservice and inservice teachers integrate technology as they design, develop, implement, and manage learning experiences. To meet this goal, three studies were conducted. In study 1 the purpose was to describe how preservice teachers identify educational problems and suggest solutions in which educational technology can be meaningfully implemented by using a problem-solving lens. Participated in this study 100 preservice teachers enrolled in an introductory educational technology course. Students’ technology integration activity was analyzed for this study. This activity, divided into three parts, required that students (1) shared and reflected on their best academic learning experience, (2) described how they could integrate technology into that learning experience, and (3) revisited their suggestions for technology integration, evaluated their ideas, and suggested revisions. Data were analyzed using an ill-structured problem-solving model synthesized from previous literature: identifying problems, generating solutions, making justifications, and monitoring. Results of this study indicated that preservice teachers had a simplistic understanding of technology integration, likely resulting from underdeveloped problem-solving skills. In study 2 the purpose was to identify the instructional strategies and technology affordances used while integrating technology that facilitated the development of student creativity by completing a systematic literature review about how technology (i.e., social media) is being used by educators to foster creativity. After the process of identification and screening, a total of 27 articles met the inclusion criteria and were selected for further analysis. The results indicated that, in most studies in which the use of technology was associated with promoting student creativity, a student-centered approach was used. Students had autonomy and flexibility to produce content, express their opinions, and share their experiences using social media. Also, participants used social media to create their own products, communicate with others, and collaborate virtually. In the studies, we identified that the social media affordances of ownership, association, and visibility lead to fostering student creativity. In conclusion, social media, when integrated with appropriate instructional strategies, can be successfully used as an educational tool to build an environment that promotes student creativity. In study 3 the purpose was to analyze the forms in which special education teachers design learning experiences that provide an environment for creativity development for students from special education and how their proposed technology integration plays a role in it across different settings (i.e., face-to-face, blended, and online learning). Three practicing teachers enrolled in an online graduate program in special education participated in this study. For the purpose of this study, the primary data source consisted of assignments (i.e., artifacts and reflections) submitted by students to the Technology Integration - Blended and Online Teaching (Ti-BOT) program, a licensure required as part of their Special Education program. Artifacts were analyzed through the lens of the existing literature on learning environments for creativity. Reflections were analyzed using a thematic analysis approach, applying a combination of inductive and deductive coding. The artifacts presented by the participants included elements of a creative environment and technology often facilitated the development of such an environment. However, the participants did not appear to explicitly and intentionally design activities to foster creativity, but to make modifications to learning activities and assessments that reflected the level of individualization and adaptations that are typically expected from special education teachers, described in individualized education plans (IEPs), and guided by Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles. With the findings from this three-paper dissertation, the goal is to provide recommendations for how educator preparation programs can improve how they are approaching technology integration, gain deeper understanding of technology integration across diverse contexts and tools, and offer strategies for supporting the deeper consideration of how technologies can be meaningfully used.
Degree Type
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Curriculum and Instruction
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, additional committee member 5, usage metrics.
- Curriculum and pedagogy not elsewhere classified
Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 30, Number 9—September 2024
Role of Direct Sexual Contact in Human Transmission of Monkeypox Virus, Italy
Suggested citation for this article
The 2022 global mpox outbreak was driven by human-to-human transmission, but modes of transmission by sexual relationship versus sexual contact remain unclear. We evaluated sexual transmission of mpox by using monkeypox virus (MPXV) G2R-mRNA as a marker of ongoing viral replication through in vitro experiments. We analyzed clinical samples of 15 MPXV-positive patients in Italy from different biological regions by using the setup method. The presence of MPXV DNA, MPXV G2R-mRNA, or both in all analyzed lesion swab samples, independent of viral load, confirmed a higher infectivity risk from skin lesions. Positivity for MPXV G2R-mRNA in nasopharyngeal swabs was associated with high MPXV load, whereas positive results for MPXV G2R-mRNA were obtained only in the 2 semen samples with the lowest MPXV loads. Our results suggest that close or skin-to-skin contact during sexual intercourse is the main route of sexual transmission and that semen is a minor driver of infection, regardless of MPXV load.
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) is the etiologic agent of zoonotic mpox disease. Although the virus was first discovered in colonies of monkeys kept for research in 1958, MPXV is mainly transmitted to humans through physical contact with wild infected animals (i.e., squirrels, rats, and mice), with contaminated materials, or with an infectious person ( 1 ). The first human case of mpox was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo; the virus is endemic in central and west Africa, where outbreaks are regularly reported ( 1 ).
Before 2022, sporadic mpox cases had been described outside Africa, mainly linked to travel. However, during May–June 2022, the emergence and rapid spread of mpox in >50 countries where the disease was not endemic, led the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare the mpox outbreak a public health emergency of international concern ( 2 ). The outbreak, caused mostly by the clade IIb variant of the virus, was driven by human-to-human transmission via close contact with infected persons; most cases were described among men who had sex with men. In several studies, viral DNA has been identified and isolated in the semen of infected persons for weeks after they acquired the infection, supporting the hypothesis of sexual transmission ( 2 – 4 ). Viral DNA was also detected in biologic samples such as saliva, nasopharyngeal swabs (NPS), blood, and urine, thus not always implying the infectivity of the biologic sample ( 5 ). Now, new in vivo and in vitro models able to mimic aspects of viral biology, such as infectivity, can be developed ( 6 ).
Cell culture is considered the standard for virus isolation. Nevertheless, several factors, such as suboptimal sensitivity, eventual long storage of the samples, or the presence of antibodies against the virus in the clinical samples, can contribute to the failure of this procedure, resulting in the inability to establish real viability and infectivity. To improve knowledge about the route of transmission of this infection, finding an alternative method able to overcome problems associated with viral isolation and verify the infective capacity of MPXV in different biological regions is essential.
Considering that MPXV replication strategy is based on a cascade of 3 gene classes (early, intermediate, and late) ( 7 , 8 ), in this study, we explored the possibility of using an early transcript as a marker of ongoing viral replication. G2R is a crucial gene transcribed during the early phase of infection and can interact with the viral RNA polymerase during the intermediate and late phases of viral replication, thus affecting the fidelity of the transcription process ( 8 ). Therefore, we selected G2R as a surrogate marker of ongoing replication, because the presence of the G2R-mRNA transcript discriminates between actively replicating and nonreplicating samples, providing an indirect indication of the possible transmission mode.
We conducted a preliminary experiment using Vero E6 cells infected in vitro with MPXV to assess the effectiveness of the developed method for detecting and measuring G2R-mRNA levels. We then analyzed clinical specimens that tested positive for MPXV DNA.
Ethics Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and with protocol code no. 40z, Register of Non-Covid Trials 2022. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Lazzaro Spallanzani Institute MpoxCohort protocol “Studio di coorte osservazionale monocentrica su soggetti che afferiscono per sospetto clinico o epidemiologico di malattia del vaiolo delle scimmie (mpox).”
In Vitro Experiments
We maintained Vero E6 cells in modified eagle medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO 2 and exposed to MPXV isolate hMpxv/Italy/un-INMI-Pt2/2022, clade/lineage IIb B.1 (GISAID accession no. EPI_ISL_13251120 [ https://www.gisaid.org ]; GenBank accession no. ON745215.1) for 1 hour and 30 minutes at 37°C at a multiplicity of infection of 0.01. At the end of the adsorption period, we washed and incubated cells at 37°C; at 30 minutes and 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 24, and 48 hours postinfection (hpi), we harvested, inactivated, and tested cells and supernatants for MPXV DNA and G2R-mRNA presence by digital droplet PCR (ddPCR).
Clinical Samples
During May–September 2022, a total of 29 samples (7 nasopharyngeal swab, 10 skin lesion swab, 8 semen, and 4 urine samples) were collected for diagnostic purposes from 15 patients admitted to the National Institute for Infectious Diseases (INMI) Lazzaro Spallanzani in Rome, Italy. Patients had a positive diagnosis of mpox within 7 days of symptom onset. We retrospectively analyzed those samples.
MPXV DNA and G2R-mRNA Quantification
To establish the presence of viral DNA, we first analyzed samples from different anatomic sites of patients with an mpox diagnosis by a commercial MPXV real-time PCR kit (Jiangsu BioPerfectus Technologies Co., Ltd., http://www.bioperfectus.com ) on the ELITe InGenius instrument (ELITechGroup SAS, https://www.elitechgroup.com ), obtaining a semiquantitative measure by cycle threshold (Ct) value. We further analyzed biological samples that tested positive for MPXV DNA by real-time PCR and cell supernatants from the in vitro experiments by using ddPCR to obtain quantitative results expressed as copies per milliliter. In brief, we extracted 140 μL of supernatant from infected cells and biologic samples by using the QIAamp Viral DNA Mini Kit (QIAGEN, https://www.qiagen.com ) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. We quantified MPXV DNA by using the QX200 AutoDG Digital Droplet PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, https://www.bio-rad.com ), as previously described ( 9 ).
To perform G2R-mRNA quantification, we extracted total RNA by using the RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. To selectively degrade any traces of DNA, we treated RNA extracted with DNase (TURBO DNase Kit; Thermo Fisher Scientific, https://www.thermofisher.com ). We then reverse transcribed 10 μL of RNA per sample according to the instructions of the SuperScript IV First-Strand cDNA Synthesis reaction kit (Thermo Fisher) by using 50 μmol OLigo d(T)20 as primers to select mRNA. We performed quantification by using the Bio-Rad QX200 AutoDG ddPCR system, targeting the early gene, G2R-mRNA ( 10 ). To confirm the absence of MPXV DNA fragments, all RNA-extracted samples underwent MPXV DNA PCR after treatment with DNase.
Statistical Analysis
We performed linear regression analysis by using GraphPad Prism version 9 ( https://www.graphpad.com ). We expressed results as correlation coefficients (r).
In Vitro Cell Culture Experiments
Figure 1 . In vitro kinetics of MPXV infection in Vero E6 cell line in study of role of direct sexual contact in human transmission of MPXV, Italy. Cell-associated G2R-mRNA, a surrogate marker...
To establish if G2R-mRNA could be considered a surrogate marker of ongoing MPXV replication, we tested for its presence in vitro in infected Vero E6 cells. Cell-associated G2R-mRNA was detected at low levels until 30 minutes postinfection, when it started to increase, showing a peak at 1 hpi ( Figure 1 ). This result was expected because the G2R gene is early transcribed during viral infection. After 1 hpi, we observed a slight increase in cell-associated G2R-mRNAs throughout the infection until 24 hpi; levels remained stable thereafter. All RNA samples treated with DNase were negative for MPXV DNA, confirming the absence of MPXV DNA fragments and the strength of the setup method (data not shown).
MPXV DNA levels released in the supernatant steadily increased at each timepoint, peaking at 24 hpi. We observed substantially lower levels of DNA released in the supernatants for mRNA cell-associated DNA, starting at 30 minutes postinfection and continuing throughout the observation period.
MPXV DNA and G2R-mRNA in Clinical Specimens
Figure 2 . Linear regression analysis of Ct values and MPXV DNA levels in clinical specimens from study of role of direct sexual contact in human transmission of MPXV, Italy. Results show highly...
MPXV DNA and G2R-mRNA were present in NPS, skin lesion swabs, urine, and semen samples ( Table ). All samples were positive for MPXV DNA by diagnostic real-time PCR (mean Ct 27.3, range 13.3–37.7), except for all urine and 2 semen samples that showed negative results (Ct >45.0). We performed absolute quantification of positive MPXV DNA samples by ddPCR, and linear regression analysis found a highly negative correlation (r = −0.99) between the Ct values and the amount of MPXV DNA ( Figure 2 ).
G2R-mRNA was detectable in all skin lesions (r = 0.71) and 4 out of 7 NPS samples (r = 0.64), showing a good correlation with MPXV DNA in both matrices. Of note, we observed low positivity for G2R-mRNA presence in only 2 of 8 semen samples; therefore, we could not correlate those results with DNA levels. Nevertheless, we emphasize that semen samples with the highest DNA copy numbers tested negative for G2R-mRNA, which is different from what we observed in other matrices ( Table ).
During January 1, 2022–February 2024, more than 94,000 laboratory-confirmed cases of mpox, including 181 deaths, were reported to WHO from 117 member states across all 6 WHO regions ( 11 ). Cases and sustained chains of transmission have been reported concurrently in nonendemic and endemic countries in widely disparate geographic areas and have involved mainly, but not exclusively, men who have sex with men. Although close physical contact with lesions on the skin or mucosal surfaces of mpox-symptomatic persons represents the main factor for human-to-human transmission in this outbreak ( 12 ), recent studies suggest that sexual activity could represent an important route of disease transmission ( 2 , 13 ). Lesions on the genitalia, perianal, and inguinal areas of infected persons that tested positive for MPXV DNA ( 4 , 14 ), as well as the high prevalence of positivity in semen samples from mpox cases ( 9 , 15 ), have been considered further evidence supporting the sexual transmission route. A correlation between the amount of viral load and infectious virus titer has already been described for lesion and NPS swab samples ( 16 ); on the contrary, difficulties in viral isolation were found for semen samples, even when the viral load was high ( 17 ). That evidence opens the issue concerning the difference between sexual and sexual contact transmissions. To overcome problems associated with viral isolation and to verify the real infectious capacity of MPXV in different biological regions, we first evaluated the possibility of using MPXV G2R-mRNA as a marker of ongoing viral replication through in vitro experiments. The presence of high levels of G2R-mRNA during the early phase of infection (within 1 hour), associated with low levels of MPXV DNA, confirms that this method reflects the replication strategy of MPXV, because G2R is an early gene. Therefore, we applied the same method in vivo to analyze clinical samples from different biological regions of MPXV-positive patients.
Our results showed the presence of either MPXV DNA or MPXV G2R-mRNA in all analyzed lesion swab samples, independent of MPXV DNA load, thus confirming a higher infectivity risk from skin lesions. As far as NPS samples are concerned, the presence of MPXV G2R-mRNA was associated with a high MPXV DNA load, indicating higher infectivity in NPS samples with low Ct values ( 16 ). When analyzing semen samples, we obtained positive results for MPXV G2R-mRNA in only the 2 samples with the lowest MPXV DNA level, suggesting that this biologic fluid could represent a minor route in the context of sexual transmission, regardless of viral load. A possible explanation for the other 6 semen samples showing high MPXV DNA levels in the absence of viral replication (i.e., negative MPXV G2R-mRNA) could be a passive diffusion from skin lesions on the genitals or hands ( 18 ). In fact, when analyzing data coming from patient 1, we observed a lesion on the penis with a high viral load (Ct 22.2) and a clear positivity for the presence of G2R-mRNA, indicating active replication in that site. Nevertheless, semen from the same patient showed a high viral load (Ct 24.5), in the absence of active replication (negative G2R-mRNA), with negative urine samples, suggesting possible contamination of semen from a lesion on the penis.
In conclusion, the use of MPXV G2R-mRNA as a marker of replication enables discrimination between infected and contaminated samples, overcoming the problems related to viral isolation and providing an explanation for the difficulty encountered in isolating the virus from semen samples even with a high viral load ( 17 ). Despite the limited number of tested samples, our data support the evidence that sexual contact is the main route of sexual transmission, whereas semen samples can represent a minor driver of infection, independent of MPXV DNA load. This evidence is crucial to enable development of proper interventions and to provide valuable support for decision-making regarding protective measures for mpox patients and their close contacts.
Dr. Sberna is a research scientist at the National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani, Rome, Italy. His primary research interests are HIV, viral infections, respiratory viruses, and chronic and emerging acute infections.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Ministero della Salute: Ricerca Corrente—Linea 1.
Author contributions: G.S., molecular testing, analysis of results, writing; G.R., C.M., molecular testing; V.M., A.A., A.D.A., enrolling patients and editing; F.M., E.G., review and editing; E.L., L.B., conceptualization, writing, review, and editing. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
- World Health Organization . Mpox (monkeypox). 2023 April 18 [ cited 2023 Nov 20 ]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/monkeypox
- Thornhill JP , Barkati S , Walmsley S , Rockstroh J , Antinori A , Harrison LB , et al. ; SHARE-net Clinical Group . Monkeypox virus infection in humans across 16 countries—April–June 2022. N Engl J Med . 2022 ; 387 : 679 – 91 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- World Health Organization . Mpox (monkeypox) outbreak 2022—global. 2022 [ cited 2023 Nov 20 ]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/situations/monkeypox-oubreak-2022
- Antinori A , Mazzotta V , Vita S , Carletti F , Tacconi D , Lapini LE , et al. ; INMI Monkeypox Group . Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of four cases of monkeypox support transmission through sexual contact, Italy, May 2022. Euro Surveill . 2022 ; 27 : 2200421 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Lapa D , Carletti F , Mazzotta V , Matusali G , Pinnetti C , Meschi S , et al. ; INMI Monkeypox Study Group . Monkeypox virus isolation from a semen sample collected in the early phase of infection in a patient with prolonged seminal viral shedding. Lancet Infect Dis . 2022 ; 22 : 1267 – 9 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Rosa RB , Ferreira de Castro E , Vieira da Silva M , Paiva Ferreira DC , Jardim ACG , Santos IA , et al. In vitro and in vivo models for monkeypox. iScience . 2023 ; 26 : 105702 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Arndt WD , White SD , Johnson BP , Huynh T , Liao J , Harrington H , et al. Monkeypox virus induces the synthesis of less dsRNA than vaccinia virus, and is more resistant to the anti-poxvirus drug, IBT, than vaccinia virus. Virology . 2016 ; 497 : 125 – 35 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Condit RC , Xiang Y , Lewis JI . Mutation of vaccinia virus gene G2R causes suppression of gene A18R ts mutants: implications for control of transcription. Virology . 1996 ; 220 : 10 – 9 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Colavita F , Mazzotta V , Rozera G , Abbate I , Carletti F , Pinnetti C , et al. Kinetics of viral DNA in body fluids and antibody response in patients with acute Monkeypox virus infection. iScience . 2023 ; 26 : 106102 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Meis RJ , Condit RC . Genetic and molecular biological characterization of a vaccinia virus gene which renders the virus dependent on isatin-beta-thiosemicarbazone (IBT). Virology . 1991 ; 182 : 442 – 54 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- World Health Organization . 2022–23 mpox (monkeypox) outbreak: global trends 2022 . 2024 February [ cited 2024 Apr 24 ]. https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/mpx_global
- Tiecco G , Degli Antoni M , Storti S , Tomasoni LR , Castelli F , Quiros-Roldan E . Monkeypox, a literature review: what is new and where does this concerning virus come from? Viruses . 2022 ; 14 : 1894 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Sah R , Abdelaal A , Reda A , Katamesh BE , Manirambona E , Abdelmonem H , et al. Monkeypox and its possible sexual transmission: where are we now with its evidence? Pathogens . 2022 ; 11 : 924 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Mahase E . Monkeypox: Gay and bisexual men with high exposure risk will be offered vaccine in England. BMJ . 2022 ; 377 : o1542 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Reda A , Abdelaal A , Brakat AM , Lashin BI , Abouelkheir M , Abdelazeem B , et al. Monkeypox viral detection in semen specimens of confirmed cases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virol . 2023 ; 95 : e28250 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Paran N , Yahalom-Ronen Y , Shifman O , Lazar S , Ben-Ami R , Yakubovsky M , et al. Monkeypox DNA levels correlate with virus infectivity in clinical samples, Israel, 2022. Euro Surveill . 2022 ; 27 : 2200636 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Noe S , Zange S , Seilmaier M , Antwerpen MH , Fenzl T , Schneider J , et al. Clinical and virological features of first human monkeypox cases in Germany. Infection . 2023 ; 51 : 265 – 70 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Reda A , Sah R , Rodriguez-Morales AJ , Shah J . Viral replication and infectivity of monkeypox through semen. Lancet Infect Dis . 2022 ; 22 : 1531 – 2 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Figure 1 . In vitro kinetics of MPXV infection in Vero E6 cell line in study of role of direct sexual contact in human transmission of MPXV, Italy. Cell-associated G2R-mRNA, a surrogate...
- Figure 2 . Linear regression analysis of Ct values and MPXV DNA levels in clinical specimens from study of role of direct sexual contact in human transmission of MPXV, Italy. Results show...
- Table . Molecular results of analyzed samples in study of role of direct sexual contact in human transmission of MPXV, Italy
Suggested citation for this article : Sberna G, Rozera G, Minosse C, Bordi L, Mazzotta V, D’Abramo A, et al. Role of direct sexual contact in human transmission of monkeypox virus, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Sep [ date cited ]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid3009.240075
DOI: 10.3201/eid3009.240075
Original Publication Date: August 09, 2024
Table of Contents – Volume 30, Number 9—September 2024
| EID Search Options |
|---|
| – Search articles by author and/or keyword. |
| – Search articles by the topic country. |
| – Search articles by article type and issue. |
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Licia Bordi, Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Via Portuense 292, Rome 00149, Italy
Comment submitted successfully, thank you for your feedback.
There was an unexpected error. Message not sent.
Metric Details
Article views: 37.
Data is collected weekly and does not include downloads and attachments. View data is from .
What is the Altmetric Attention Score?
The Altmetric Attention Score for a research output provides an indicator of the amount of attention that it has received. The score is derived from an automated algorithm, and represents a weighted count of the amount of attention Altmetric picked up for a research output.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results.. It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review and paper or dissertation topic, and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion.It should not be a second results section.. There are different ways to write this ...
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context. The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively. In quantitative research, for each question or hypothesis, state: The type of analysis used; ... In qualitative research, results and discussion are sometimes combined.
Tips to Write the Results Section. Direct the reader to the research data and explain the meaning of the data. Avoid using a repetitive sentence structure to explain a new set of data. Write and highlight important findings in your results. Use the same order as the subheadings of the methods section.
When writing a dissertation or thesis, the results and discussion sections can be both the most interesting as well as the most challenging sections to write. You may choose to write these sections separately, or combine them into a single chapter, depending on your university's guidelines and your own preferences.
The discussion chapter is where you interpret and explain your results within your thesis or dissertation. This contrasts with the results chapter, where you merely present and describe the analysis findings (whether qualitative or quantitative). In the discussion chapter, you elaborate on and evaluate your research findings, and discuss the ...
Dissertation discussion is the chapter where you explore the relevance, significance, and meanings of your findings - allowing you to showcase your talents in describing and analyzing the results of your study.. Here, you will be expected to demonstrate how your research findings answer the research questions established or test the hypothesis.
Guide contents. As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common conventions of the results and discussion chapters, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows: The Difference - Breaks down the distinctions between the results and discussion chapters.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you've found in terms of the quantitative data you've collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts.
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with ...
The discussion provides context and interpretations for the results. It also answers the questions posed in the introduction. While the results section describes your findings, the discussion explains what they say. This is also where you can describe the impact or implications of your research. Adds context for your results
The discussion section should relate your results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for your research. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in ...
What exactly is the results chapter? The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods).This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and discuss its ...
Tips for Writing the Discussion Section. Start with the big picture - WHY is your study important? o Think of yourself as telling the story of how your findings answer the question you posed and why your findings matter, how your field's status quo or understanding is changed by your results. o Clearly signal that you are answering the ...
The content in the thesis discussion section overlaps with the results section—the results section presents the data, and the discussion section interprets it. The structure of the discussion section differs according to the type of research (quantitative vs. qualitative).In qualitative research, such as in the Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) domain, the discussion and results from ...
Include all relevant results as text, tables, or figures. Report the results of subject recruitment and data collection. For qualitative research, present the data from all statistical analyses, whether or not the results are significant. For quantitative research, present the data by coding or categorizing themes and topics.
Dissertation discussion section is a chapter that interprets the results obtained from research and offers an in-depth analysis of findings. In this section, students need to analyze the outcomes, evaluate their significance, and compare them to previous research.
Paragraph 1. In this paragraph provide a broad overview of the importance of your study. This is where you should restate your research topic. Avoid just repeating what you included in the results section. Include the main research findings that answer your primary research question (s).
Infographic: 5 Differences between the results and discussion sections. Most journals expect you to follow the IMRaD (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) format while writing your research paper. It is possible that you might be slightly confused about what to include in the Results and Discussions sections.
The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results.. It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review, and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion.It should not be a second results section.. There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your ...
The results and discussion sections are one of the challenging sections to write. It is important to plan this section carefully as it may contain a large amount of scientific data that needs to be presented in a clear and concise fashion. The purpose of a Results section is to present the key results of your research.
American Christian Coleman collided with teammate Kenny Bednarek on the first exchange of the baton, causing the U.S. to fall behind the pack. The bad exchange left the Americans with simply too ...
This template covers all the core components required in the discussion chapter (or section) of a typical dissertation or thesis, including: The purpose of each section is explained in plain language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. The template also includes practical examples to help you understand exactly ...
The overarching purpose of this three-paper dissertation was to investigate the affordances of technology in educational settings and gain insight into how preservice and inservice teachers integrate technology as they design, develop, implement, and manage learning experiences. To meet this goal, three studies were conducted. In study 1 the purpose was to describe how preservice teachers ...
Positivity for MPXV G2R-mRNA in nasopharyngeal swabs was associated with high MPXV load, whereas positive results for MPXV G2R-mRNA were obtained only in the 2 semen samples with the lowest MPXV loads. Our results suggest that close or skin-to-skin contact during sexual intercourse is the main route of sexual transmission and that semen is a ...