Guide to Essay Writing: 5 Steps to Write an Outstanding Essay
Feel passionately about something and want to share it? Write an essay! Disagree with a popular opinion and wish to convince others to join you? Write an essay! Need to write something because the college you dream of attending is making you? Write an essay!
“Essay” is a loose term for writing that asserts the author’s opinion on a topic, whether academic, editorial, or even humorous. There are a thousand different approaches to essay writing and a million different topics to choose from, but what we’ve found is that good essay writing tends to follow the same framework.
Give your essays extra polish Grammarly helps you write with confidence Write with Grammarly
Below we discuss that framework and how you can apply it to your essays, whatever types they may be. But first, let’s start with a basic overview of how to write an essay.

Table of contents
How to write an essay.
Your essay needs a thesis statement
The essay-writing process
Essay structure, know your essay’s audience, 6 types of essays, essay writing tips.
The basic steps for how to write an essay are:
- Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write.
- Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph.
- Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar.
- Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details.
- Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
Want to know more? We cover the specifics below, but for now let’s talk about the nucleus of any good essay: the topic.
Your essay needs a thesis statement
Three things to consider before writing your essay:
Of these, the most important by far is your thesis, or the crux of what your essay is about.
Your thesis, encapsulated in your thesis statement , is the central point you’re trying to make. The thesis of Bertrand Russell’s essay “ In Praise of Idleness ,” for example, is that people focus too much on work and don’t value time spent idly. Essays can occasionally stray and go into related tangents, but they always come back to that one core idea in the thesis.
You should always pinpoint your thesis before writing. If you’re having trouble nailing it down, ask yourself, “What’s the one thing I want my reader to remember when they’re done reading my essay?”
The best practice is to include your thesis as soon as possible, even in your topic sentence if it’s appropriate. You’ll want to reiterate it throughout the essay as well, especially when wrapping up everything in the conclusion.
The rest of your essay, then, supports your thesis. You can include empirical evidence, testimonials, logical deductions, or even persuasive rhetoric —whatever gets the job done. The point is that you’re building upon your initial thesis, not switching to completely different topics.
If you’re writing an essay, research paper , term paper, novel, short story, poem , screenplay, blog article about essay writing—when writing just about anything , really—it’s crucial to follow an efficient writing process. Even if you prefer the stream-of-consciousness style for writing your rough draft, you still need to have an orderly system that allows you to revise and hone.
For essay writing, we recommend this five-step writing process :
1 Brainstorming
It always helps to collect your thoughts before you begin writing by brainstorming . Based on your prompt or thesis, try to generate as many ideas as possible to include in your essay. Think of as many as time allows, knowing that you’ll be able to set aside the ideas that don’t work later.
2 Preparing
The preparation phase consists of both outlining your essay and collecting resources for evidence. Take a look at the results of your brainstorming session. First, isolate the ideas that are essential to support your thesis and then organize them in a logical and progressive order. In this stage you’ll incorporate your essay structure, which we explain below.
If you want empirical evidence or complementary citations, track them down now. The way you write citations depends on the style guide you’re using. The three most common style guides for academics are MLA , APA , and Chicago , and each has its own particular rules and requirements for citing just about any kind of source, including newspaper articles , websites , speeches , and YouTube videos .
This is the main stage of essay writing where you roll up your sleeves and actually write your first draft . Remember that everything doesn’t have to be perfect; this is your first draft, not your final draft, so give yourself the freedom to make errors. If you’re focusing on getting every single word right, you’ll miss the big picture.
The revisions stage involves your second draft, your third draft, or even your twelfth draft if necessary. Address all the nuances and subtleties you glossed over in the first draft.
Pay attention to both word choice and clarity , as well as sophisticated writing techniques like avoiding the passive voice . If you’re not confident in your writing skills yet, the Grammarly Editor ensures your writing is readable, clear, and concise by offering sentence structure and word choice suggestions, plus clarity revisions as you write. Grammarly helps catch common mistakes with sentence structure—like run-on sentences, sentence fragments, passive voice, and more.
5 Proofreading
When all the heavy-duty revisions are finished, it’s time for the final polish. Go through your essay and correct misspellings , formatting issues, or grammatical errors. This is also where you can turn to Grammarly’s AI-powered writing assistant, which helps catch these common mistakes for you. Or copy and paste your writing to check your grammar and get instant feedback on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and other mistakes you might have missed.
Essay structure almost always follows a simple beginning-middle-end format, or in this case, an introduction-body-conclusion format. However, it’s what’s contained within those sections that makes all the difference.
Introduction
Essays follow the same guidelines for introductions as any other piece of writing, with an extra emphasis on presenting the thesis prominently, ideally in the topic sentence. By the end of your introduction paragraph, your reader should know without a doubt what your essay is about. From there, follow the conventional best practices on how to write an introduction .
Body paragraphs
The majority of your essay is body paragraphs , all of which support your thesis and present evidence.
Pay close attention to how you organize your body paragraphs. Some arguments benefit from a logical progression, where one point leads to a second, and that second point leads to a third. Remember that the reader doesn’t understand the topic like you do (that’s why you’re writing the essay), so structure your paragraphs in the way that’s best for their comprehension.
What if you’re writing an argumentative essay where you compare and contrast two or more points of view? Do you present your argument first and then share opposing points of view, or do you open with your opposition’s argument and then refute it?
Serious writers can get pretty technical about how to organize an argumentative essay. There are three approaches in particular used often: Aristotlian (classical), Rogerian , and Toulmin . However, these can get exceedingly complicated, so for a simple essay, a basic structure will do just fine:
- Counterpoint
- Evidence supporting your point and/or disproving counterpoint
Essay conclusions wrap up or summarize your thesis in a way that’s easy for the reader to digest. If you get the chance, you can add a new perspective or context for understanding your thesis, but in general the conclusion should not present any new evidence or supporting data. Rather, it’s more of a recap. For more specific tips, read about how to write a conclusion for an essay here .
Five-paragraph essay
For quick and simple essays, you don’t need to get too technical with your essay structure. The five-paragraph essay structure works well in a pinch. This contains:
- One introduction paragraph
- Three body paragraphs
- One conclusion paragraph
While this essay structure might not be flexible enough for more advanced topics, it comes in handy when speed is a factor, like during timed tests.
Your final consideration is who will read your essay—a teacher, an admissions counselor, your peers, the internet at large, etc.
No matter what you’re writing, your audience should influence your language. For one thing, your readers determine whether the essay is formal or casual , which has an enormous impact on language, word choice, and style . Take emojis for example: In a casual essay they might be welcome, but for formal writing they’re not the most appropriate choice. 😓
Your audience also affects the essay’s tone, or how you sound on an emotional level (enthusiastic, cautious, confident, etc.). If you’d like to know more, you can read about the 10 common types of tone here .
Like any form of writing, essays come in many different types . Sometimes the assignment dictates the type, as with admissions essays, and other times the thesis will determine it. Regardless, it helps to know what your options are, so here are some of the most common essay types:
1 Argumentative essay
Argumentative essays assert or defend a position. This is the most common type of school paper, so keep that in mind when writing your first college essay .
2 Admissions essay
Most colleges request an admissions essay in applications, which typically revolve around why you’re interested in their school.
3 Persuasive essay
A persuasive essay is just as it sounds: an essay to persuade or convince the reader of a certain point. It’s similar to an argumentative essay— they both strongly favor a particular point of view, but the difference is the end goal: Argumentative essays just have to present their case, while persuasive essays have to present their case and win over the reader.
4 Compare-and-contrast essay
When you want to devote equal attention to two opposing things, a compare-and-contrast essay works better than argumentative or persuasive essays, which lean to one side over the other.
5 Personal essay
Personal essays are often anecdotal or real-life stories of the authors, like the works of David Sedaris . Because they tend to follow narrative structures, the thesis can be flexible or interpretive.
6 Expository essay
An expository essay thoroughly explains a certain topic to expand the reader’s knowledge. It is similar to an argumentative and persuasive essay in format, but with one key difference: expository essays don’t have a bias.
Master the five fundamentals
Especially for school essays, your reader will scrutinize how well you handle the fundamentals. Knowing about essay structure and the writing process is one thing, but can you demonstrate an understanding of language style? Can you develop your thesis logically and coherently? Are your references and citations trustworthy?
When you’re ready for the next step of essay writing, take a look at the five concepts you must master to write better essays . The tips there pick up where this guide leaves off.

Seek out another pair of eyes
This tip is not just for essays; it’s always advisable to have someone else read over your writing before finalizing it. All too often we miss the forest for the trees, and thinking long and hard on the same topic can give you tunnel vision. The solution is to get a fresh take from someone who’s seeing it for the first time.
Typically you can swap with a friend and edit each others’ works. If that’s not an option, however, you can also use a writing center or join a writing group online. At the very least, you should sleep on it and take another look when you’re refreshed.
Remember: Grammar and form are essential
It’s not always about what you say, but how you say it. You could have the most obvious, objectively agreeable thesis in the world, but if your writing is incoherent, confusing, and full of mistakes, it’s tough to engage with your reader.
For when your writing needs to make the right impact, Grammarly Premium offers full-sentence rewrites for confusing sentences—from splitting long sentences, cutting extra words, or rearranging key phrases—in addition to catching common grammar mistakes. It also gives you readability-focused formatting suggestions, so you know your writing is clear. It also helps those who are looking to improve their writing skill level in English, with suggestions for commonly misused words and phrases.
Honing your writing with these elements in mind is key to relaying your point to your reader—and asserting your thesis as effectively as possible.

How to Make Your Essay Better: 7 Tips for Stronger Essays

By Krystal N. Craiker

Essay writing doesn’t have to be intimidating. With a few tips, you can improve your writing skills for any type of academic essay.
How to Write Better Essays
7 tips on how to make your essay better, how to become a better essay writer.
The best way to sum up how to write better essays is, “Make sure you’re answering the question.”
This sounds obvious, but you would be surprised how many students struggle with this.
From not understanding the prompt to poor research skills to off-topic body paragraphs, it’s easy for an essay to derail.
We’ve got seven tips for writing better essays that will help you avoid common mistakes and craft the best essays possible.

Here are our top tips for improving your essay writing skills.
Understand the Prompt or Research Question
The first step in your writing process is to fully understand the essay topic. If your professor gave you a prompt for your academic essay, spend some time analyzing it.
First, take note of whether you’re writing an expository or persuasive essay. The tone, structure, and word choice will differ between essay types.
Pay close attention to the wording of the prompt.
If your teacher wants you to “analyze” the effects of new technology in World War I, but you turn in a descriptive overview of the technology, you are not answering the question.
If they have given you a topic but no prompt, you’ll need to create a guiding question for your research.
Be specific in what you are trying to research, or you’ll end up overwhelmed with a topic that is too big in scope.
“Symbolism in modern literature” is too broad for a term paper, but “How does F. Scott Fitzgerald use symbolism in The Great Gatsby ?” is an achievable topic.

Take Excellent Notes
Once you understand exactly what your essay is about, you can begin the research phase. Create a strong note-taking system.
Write down any idea or quote you might want to use. Cite every note properly to save time on your citations and to avoid accidental plagiarism.
Once you have gathered your research, organize your notes into categories. This will help you plan the structure of your essay.
You’ll likely find that some of your research doesn’t fit into your essay once you start writing. That’s okay—it’s better to have too much information to support your argument than too little.
Write a Strong Thesis Statement
Possibly the most important step in essay writing is to craft a strong thesis statement. A thesis statement is a brief—usually single-sentence—explanation of what your essay is about.
The thesis statement guides the entire essay: every point you make should support your thesis.
A strong thesis is specific and long enough to address the major points of your essay.
In a persuasive or argumentative essay, your thesis should clearly establish the argument you are making.
Make an Outline
Once you have all your research, it’s easy to get overwhelmed. How do you turn the information into a cohesive essay?
Rather than writing an essay with no roadmap, an outline will keep you on track. An outline helps you organize your thoughts, plan your arguments, and sort your research.
A good outline saves you time, too! You can compile the relevant evidence in your notes before writing, so you don’t have to find that specific quote in the middle of essay writing.
An outline will also stop you from reading your finished essay and realizing you went completely off track.
With an outline, you can avoid finding paragraphs that don’t support your thesis right before you submit the essay.

Craft a Great Introduction
An academic essay needs a strong introductory paragraph.
The introduction is the first impression of your essay. It prepares the reader for what’s coming and gets them excited to read your paper.
A good introduction has three things:
- A hook (e.g. insightful statement, quote, interesting fact)
- Brief background information about the topic
- A thesis statement
Using this formula will help you write a strong introduction for your essay.
Have Original Ideas and Interpretations
The best academic writing advice a professor ever gave me was, “You’ve shown me what other people have said about the topic. I want to know what you think about the topic.”
Even a fact-heavy or data-heavy essay needs original ideas and interpretations. For every piece of information you cite, whether you quote or paraphrase it , offer original commentary.
Focus on insights, new interpretations, or even questions that you have. These are all ways to provide original ideas in your essay.
Proofread for Readability
A good essay is a proofread essay.
Readability, or how easy something is to read, has many factors. Spelling and grammar are important, but so is sentence structure, word choice , and other stylistic features.
Academic essays should be readable without being too simple. In general, aim for a readability score that is close to your grade level in school.
There are several ways to check readability scores, including using ProWritingAid’s Readability Report.
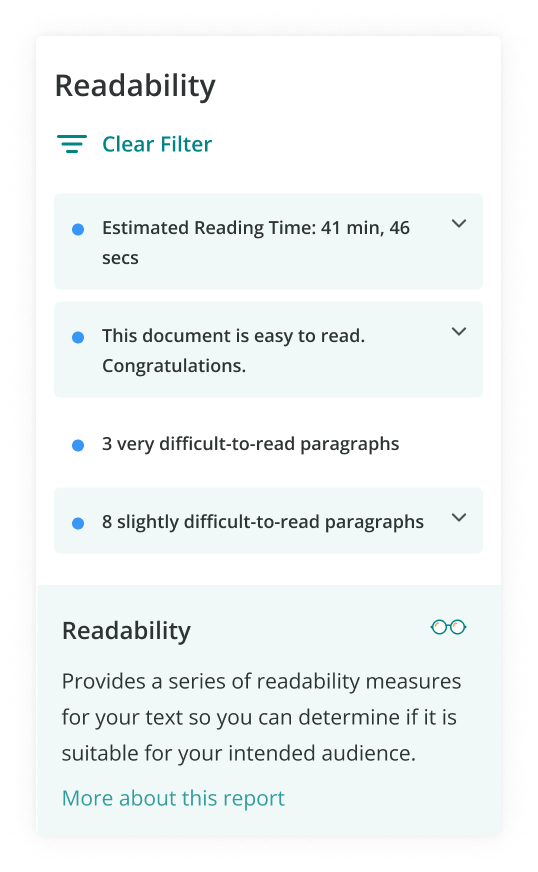
The quickest way to increase readability is to fix grammar and spelling mistakes . You can also raise the readability score by using more complex and compound-complex sentences.
ProWritingAid can offer suggestions on how to improve your essay and take it to the next level.
Our free essay checker will check for spelling and grammar errors, plus several other types of writing mistakes.
The essay checker will offer you suggestions on sentence length and passive voice.
It will help you trim the excess words that bog down your writing by analyzing your sticky sentences and overused words.
The essay checker is here to help you turn in an error-free essay.
Want to improve your essay writing skills?
Use prowritingaid.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Krystal N. Craiker
Krystal N. Craiker is the Writing Pirate, an indie romance author and blog manager at ProWritingAid. She sails the seven internet seas, breaking tropes and bending genres. She has a background in anthropology and education, which brings fresh perspectives to her romance novels. When she’s not daydreaming about her next book or article, you can find her cooking gourmet gluten-free cuisine, laughing at memes, and playing board games. Krystal lives in Dallas, Texas with her husband, child, and basset hound.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:
A clear, arguable thesis will tell your readers where you are going to end up, but it can also help you figure out how to get them there. Put your thesis at the top of a blank page and then make a list of the points you will need to make to argue that thesis effectively.
For example, consider this example from the thesis handout : While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake”(54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well”(51) is less convincing.
To argue this thesis, the author needs to do the following:
- Show what is persuasive about Sandel’s claims about the problems with striving for perfection.
- Show what is not convincing about Sandel’s claim that we can clearly distinguish between medically necessary enhancements and other enhancements.
Once you have broken down your thesis into main claims, you can then think about what sub-claims you will need to make in order to support each of those main claims. That step might look like this:
- Evidence that Sandel provides to support this claim
- Discussion of why this evidence is convincing even in light of potential counterarguments
- Discussion of cases when medically necessary enhancement and non-medical enhancement cannot be easily distinguished
- Analysis of what those cases mean for Sandel’s argument
- Consideration of counterarguments (what Sandel might say in response to this section of your argument)
Each argument you will make in an essay will be different, but this strategy will often be a useful first step in figuring out the path of your argument.
Strategy #2: Use subheadings, even if you remove them later
Scientific papers generally include standard subheadings to delineate different sections of the paper, including “introduction,” “methods,” and “discussion.” Even when you are not required to use subheadings, it can be helpful to put them into an early draft to help you see what you’ve written and to begin to think about how your ideas fit together. You can do this by typing subheadings above the sections of your draft.
If you’re having trouble figuring out how your ideas fit together, try beginning with informal subheadings like these:
- Introduction
- Explain the author’s main point
- Show why this main point doesn’t hold up when we consider this other example
- Explain the implications of what I’ve shown for our understanding of the author
- Show how that changes our understanding of the topic
For longer papers, you may decide to include subheadings to guide your reader through your argument. In those cases, you would need to revise your informal subheadings to be more useful for your readers. For example, if you have initially written in something like “explain the author’s main point,” your final subheading might be something like “Sandel’s main argument” or “Sandel’s opposition to genetic enhancement.” In other cases, once you have the key pieces of your argument in place, you will be able to remove the subheadings.
Strategy #3: Create a reverse outline from your draft
While you may have learned to outline a paper before writing a draft, this step is often difficult because our ideas develop as we write. In some cases, it can be more helpful to write a draft in which you get all of your ideas out and then do a “reverse outline” of what you’ve already written. This doesn’t have to be formal; you can just make a list of the point in each paragraph of your draft and then ask these questions:
- Are those points in an order that makes sense to you?
- Are there gaps in your argument?
- Do the topic sentences of the paragraphs clearly state these main points?
- Do you have more than one paragraph that focuses on the same point? If so, do you need both paragraphs?
- Do you have some paragraphs that include too many points? If so, would it make more sense to split them up?
- Do you make points near the end of the draft that would be more effective earlier in your paper?
- Are there points missing from this draft?
- picture_as_pdf Tips for Organizing Your Essay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you want to write better essays, you will need to understand the criteria teachers use to score them. Find out what they are and how to improve.
How to write an essay. The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details.
From not understanding the prompt to poor research skills to off-topic body paragraphs, it’s easy for an essay to derail. We’ve got seven tips for writing better essays that will help you avoid common mistakes and craft the best essays possible.
A sure way to improve your paper is to strengthen the way you present your argument. Whether you only have a thesis statement or already have a fully-written essay, these tips can help your paper flow logically from start to finish.
This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and organize your text logically.
To write a strong essay, you need an introduction, a main body organized into paragraphs, and a conclusion. See how it's done with examples.
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction , focused paragraphs , clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion . Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence , and each point is directly related to the thesis statement .
Verbs like analyze, compare, discuss, explain, make an argument, propose a solution, trace, or research can help you understand what you’re being asked to do with an assignment. Unless the instructor has specified otherwise, most of your paper assignments at Harvard will ask you to make an argument.
Strategy #1: Decompose your thesis into paragraphs. A clear, arguable thesis will tell your readers where you are going to end up, but it can also help you figure out how to get them there. Put your thesis at the top of a blank page and then make a list of the points you will need to make to argue that thesis effectively.
In this journey through the art of essay writing in English, you’ve learned how to craft an essay that captivates, informs, and persuades. From selecting a topic to preparing a compelling conclusion, every step contributes to the overall quality of your essay.